|
Unified S-band
The Unified S-band (USB) system is a tracking and communication system developed for the Apollo program by NASA and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). It operated in the S band portion of the microwave spectrum, unifying voice communications, television, telemetry, command, tracking and ranging into a single system to save size and weight and simplify operations. The USB ground network was managed by the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC). Commercial contractors included Collins Radio, Blaw-Knox, Motorola and Energy Systems. Basis The previous programs, Mercury and Gemini, had separate radio systems for voice, telemetry, and tracking. Uplink voice and command, and downlink voice and telemetry data were sent via ultra high frequency (UHF) and very high frequency (VHF) systems. The tracking capability was a C band beacon interrogated by a ground-based radar. With the much greater distance of Apollo, passive ranging was not feasible, so a new active ranging system was req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra High Frequency
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequency, radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (one decimeter). Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the super-high frequency (SHF) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF (very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by Line-of-sight propagation, line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for UHF television broadcasting, television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, satellite phones, and numerous other applications. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Space Bands
Deep space bands and near space bands are frequency bands that have been allocated to space research services by the International Telecommunication Union for use in deep space and near space The mesosphere (; ) is the third layer of the atmosphere, directly above the stratosphere and directly below the thermosphere. In the mesosphere, temperature decreases as altitude increases. This characteristic is used to define its limits: i ... research. * = No assignment or not supported by the DSN References {{reflist * Microwave bands Telemetry Radio astronomy Jet Propulsion Laboratory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
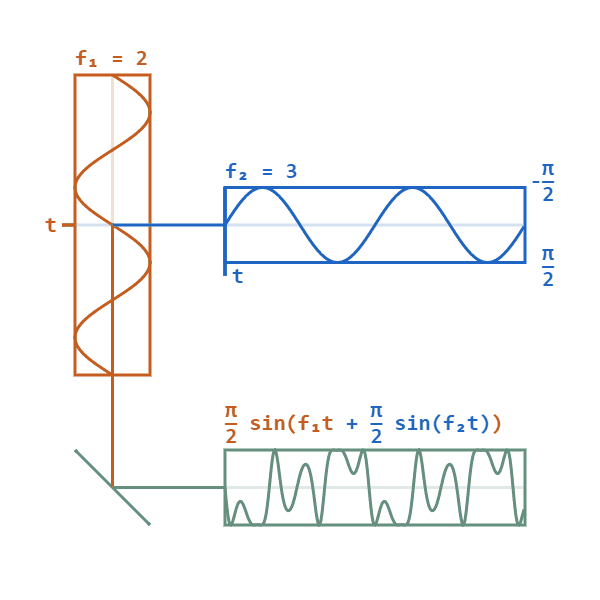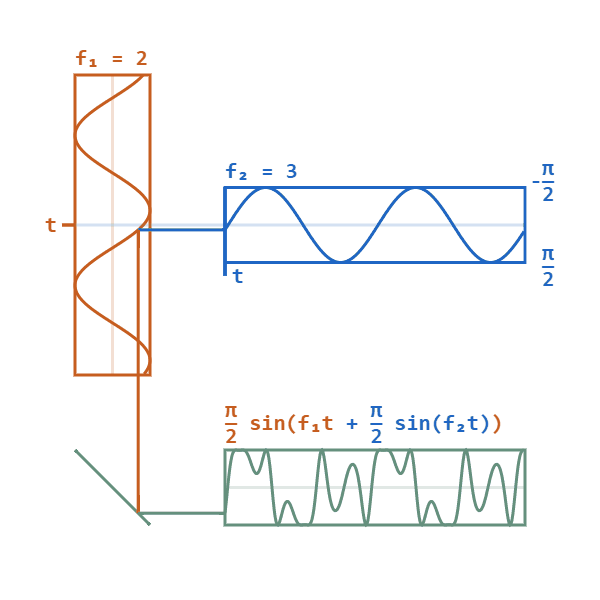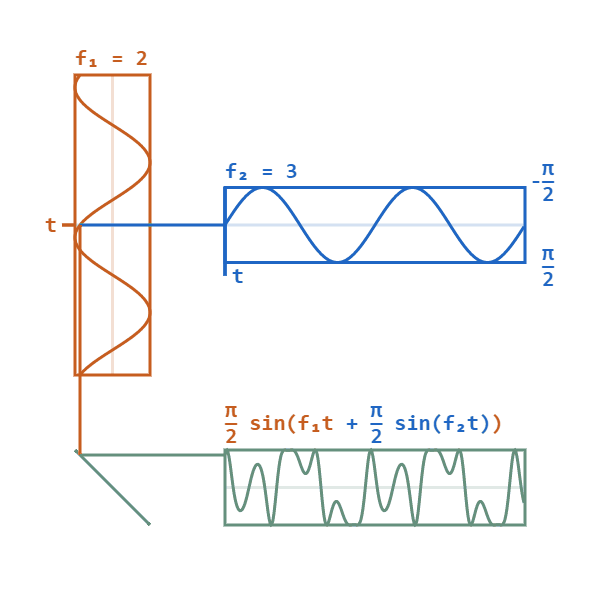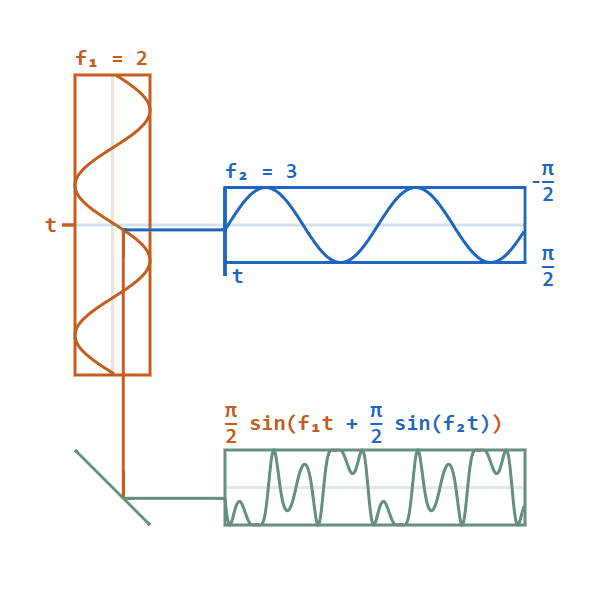
Phase Modulation
Phase modulation (PM) is a modulation pattern for conditioning communication signals for transmission. It encodes a message signal as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave. Phase modulation is one of the two principal forms of angle modulation, together with frequency modulation. In phase modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the baseband signal modifies the phase of the carrier signal keeping its amplitude and frequency constant. The phase of a carrier signal is modulated to follow the changing signal level (amplitude) of the message signal. The peak amplitude and the frequency of the carrier signal are maintained constant, but as the amplitude of the message signal changes, the phase of the carrier changes correspondingly. Phase modulation is widely used for transmitting radio waves and is an integral part of many digital transmission coding schemes that underlie a wide range of technologies like Wi-Fi, GSM and satellite television. It is also used fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier Frequency
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a much higher frequency than the input signal does. The purpose of the carrier is usually either to transmit the information through space as an electromagnetic wave (as in radio communication), or to allow several carriers at different frequencies to share a common physical transmission medium by frequency division multiplexing (as in a cable television system). The term originated in radio communication, where the carrier wave creates the waves which carry the information (modulation) through the air from the transmitter to the receiver. The term is also used for an unmodulated emission in the absence of any modulating signal. In music production, carrier signals can be controlled by a modulating signal to change the sound property of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronous Demodulation
Synchronization is the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. For example, the conductor of an orchestra keeps the orchestra synchronized or ''in time''. Systems that operate with all parts in synchrony are said to be synchronous or ''in sync''—and those that are not are ''asynchronous''. Today, time synchronization can occur between systems around the world through satellite navigation signals and other time and frequency transfer techniques. Navigation and railways Time-keeping and synchronization of clocks is a critical problem in long-distance ocean navigation. Before radio navigation and satellite-based navigation, navigators required accurate time in conjunction with astronomical observations to determine how far east or west their vessel traveled. The invention of an accurate marine chronometer revolutionized marine navigation. By the end of the 19th century, important ports provided time signals in the form of a signal gun, flag, or dropping time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |