|
Triliteral
The roots of verbs and most nouns in the Semitic languages are characterized as a sequence of consonants or " radicals" (hence the term consonantal root). Such abstract consonantal roots are used in the formation of actual words by adding the vowels and non-root consonants (or "transfixes"), which go with a particular morphological category around the root consonants, in an appropriate way, generally following specific patterns. It is a peculiarity of Semitic linguistics that many of these consonantal roots are triliterals, meaning that they consist of three letters (although there are a number of quadriliterals, and in some languages also biliterals). Such roots are also common in other Afroasiatic languages. While Berber mostly has triconsonantal roots, Chadic, Omotic, and Cushitic have mostly biconsonantal roots; and Egyptian shows a mix of biconsonantal and triconsonantal roots. Triconsonantal roots A triliteral or triconsonantal root (; , ';, '; , ') is a root containing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitic Languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic, Amharic, Tigrinya language, Tigrinya, Aramaic, Hebrew language, Hebrew, Maltese language, Maltese, Modern South Arabian languages and numerous other ancient and modern languages. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of Western Asia, West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Malta, and in large Immigration, immigrant and Expatriate, expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three Generations of Noah, sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis. Semitic languages List of languages by first written account, occur in written form from a very early historical date in West Asia, with East Semitic languages, East Semitic Akkadian language, Akkadian (also known as Ancient Assyrian language, Assyrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
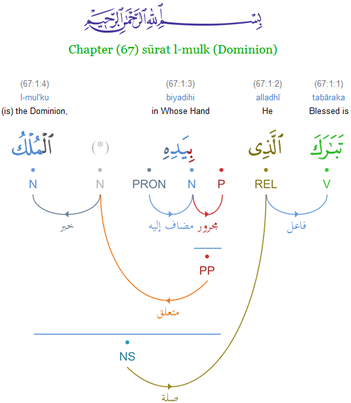
Arabic Grammar
Arabic grammar () is the grammar of the Arabic language. Arabic is a Semitic languages, Semitic language and its grammar has many similarities with the Semitic languages#Grammar, grammar of other Semitic languages. Classical Arabic and Modern Standard Arabic have largely the same grammar; colloquial spoken varieties of Arabic can vary in different ways. The largest differences between classical and colloquial Arabic are the loss of morpheme, morphological markings of grammatical case; changes in word order, an overall shift towards a more analytic language, analytic morphosyntax, the loss of the previous system of grammatical mood, along with the evolution of a new system; the loss of the inflected passive voice, except in a few relict varieties; restriction in the use of the Dual (grammatical number), dual number and (for most varieties) the loss of the feminine plural. Many Arabic dialects, Maghrebi Arabic in particular, also have significant vowel shifts and unusual consonant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afroasiatic Languages
The Afroasiatic languages (also known as Afro-Asiatic, Afrasian, Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic) are a language family (or "phylum") of about 400 languages spoken predominantly in West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of the Sahara and Sahel. Over 500 million people are native speakers of an Afroasiatic language, constituting the fourth-largest language family after Indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, and Niger–Congo. Most linguists divide the family into six branches: Berber (Amazigh), Chadic, Cushitic, Egyptian, Omotic, and Semitic. The vast majority of Afroasiatic languages are considered indigenous to the African continent, including all those not belonging to the Semitic branch (which originated in West Asia). The five most spoken languages are; Arabic (of all varieties) which is by far the most widely spoken within the family, with around 411 million native speakers concentrated primarily in West Asia and North Africa, the Chadic Hausa language w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Grammar
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' Lashon H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Hebrew Grammar
The grammar of Modern Hebrew shares similarities with that of its Biblical Hebrew counterpart, but it has evolved significantly over time. Modern Hebrew grammar incorporates analytic constructions, expressing such forms as dative, allative, and accusative using prepositional particles rather than morphological cases. Modern Hebrew grammar is also fusional synthetic: Zuckermann, Ghil'ad (2006)Complement Clause Types in Israeli ''Complementation: A Cross-Linguistic Typology'' (RMW Dixon & AY Aikhenvald, eds), Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 72–92. inflection plays a role in the formation of verbs and nouns (using non-concatenative discontinuous morphemes realised by vowel transfixation) and the declension of prepositions (i.e. with pronominal suffixes). Representation of Hebrew examples Examples of Hebrew here are represented using the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) as well as native script. Although most speakers collapse the phonemes into ,Zuckermann, Ghil� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Language
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akkadian Language
Akkadian ( ; )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the World's Ancient Languages''. Ed. Roger D. Woodard (2004, Cambridge) Pages 218–280 was an East Semitic language that is attested in ancient Mesopotamia ( Akkad, Assyria, Isin, Larsa, Babylonia and perhaps Dilmun) from the mid- third millennium BC until its gradual replacement in common use by Old Aramaic among Assyrians and Babylonians from the 8th century BC. Akkadian, which is the earliest documented Semitic language, is named after the city of Akkad, a major centre of Mesopotamian civilization during the Akkadian Empire (–2154 BC). It was written using the cuneiform script, originally used for Sumerian, but also used to write multiple languages in the region including Eblaite, Hurrian, Elamite, Old Persian and Hittite. The influence of Sumerian on Akkadian went beyond just the cuneiform script; owing to their close proximity, a lengthy span of con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemination
In phonetics and phonology, gemination (; from Latin 'doubling', itself from '' gemini'' 'twins'), or consonant lengthening, is an articulation of a consonant for a longer period of time than that of a singleton consonant. It is distinct from stress. Gemination is represented in many writing systems by a doubled letter and is often perceived as a doubling of the consonant.William Ham, ''Phonetic and Phonological Aspects of Geminate Timing'', p. 1–18 Some phonological theories use 'doubling' as a synonym for gemination, while others describe two distinct phenomena. Consonant length is a distinctive feature in certain languages, such as Japanese. Other languages, such as Greek, do not have word-internal phonemic consonant geminates. Consonant gemination and vowel length are independent in languages like Arabic, Japanese, Hungarian, Malayalam, and Finnish; however, in languages like Italian, Norwegian, and Swedish, vowel length and consonant length are interdependent. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causative
In linguistics, a causative (abbreviated ) is a valency-increasing operationPayne, Thomas E. (1997). Describing morphosyntax: A guide for field linguists'' Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 173–186. that indicates that a subject either causes someone or something else to do or be something or causes a change in state of a non- volitional event. Normally, it brings in a new argument (the causer), A, into a transitive clause, with the original subject S becoming the object O. All languages have ways to express causation but differ in the means. Most, if not all, languages have specific or ''lexical'' causative forms (such as English ''rise'' → ''raise'', ''lie'' → ''lay'', ''sit'' → ''set''). Some languages also have morphological devices (such as inflection) that change verbs into their causative forms or change adjectives into verbs of ''becoming''. Other languages employ periphrasis, with control verbs, idiomatic expressions or auxiliary verbs. There tends to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Afroasiatic
Proto-Afroasiatic (PAA), also known as Proto-Hamito-Semitic, Proto-Semito-Hamitic, and Proto-Afrasian, is the reconstructed proto-language from which all modern Afroasiatic languages are descended. Though estimations vary widely, it is believed by scholars to have been spoken as a single language around 12,000 to 18,000 years ago (12 to 18 kya), that is, between 16,000 and 10,000 BC. Although no consensus exists as to the location of the Afroasiatic homeland, the putative homeland of Proto-Afroasiatic speakers, the majority of scholars agree that it was located within a region of West Asia or Northeast Africa. The reconstruction of Proto-Afroasiatic is problematic and has not progressed to the degree found in Indo-European linguistics. The immense amount of time over which the branches have been separated, coupled with the wide gap between the attestations of the original branches (3rd millennium BC for Egyptian language in Northeast Africa and Semitic languages in Western As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Semitic Language
Proto-Semitic is the Linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed common ancestor of the Semitic languages. There is no consensus regarding the location of the linguistic homeland for Proto-Semitic: scholars hypothesize that it may have originated in the Levant, the Sahara, the Horn of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, or northern Africa. The Semitic language family is considered part of the broader macro-family of Afroasiatic languages. Dating The earliest attestations of any Semitic language are in Akkadian language, Akkadian, dating to around the 24th to 23rd centuries BC (see Sargon of Akkad) and the Eblaite language, but earlier evidence of Akkadian comes from personal names in Sumerian language, Sumerian texts from the first half of the third millennium BC. One of the earliest known Akkadian inscriptions was found on a bowl at Ur, addressed to the very early pre-Sargonic king Meskiagnunna of Ur (–2450 BC) by his queen Gan-saman, who is thought to have been from Akkad. The earli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palgrave Macmillan
Palgrave Macmillan is a British academic and trade publishing company headquartered in the London Borough of Camden. Its programme includes textbooks, journals, monographs, professional and reference works in print and online. It maintains offices in London, New York City, New York, Shanghai, Melbourne, Sydney, Hong Kong, Delhi and Johannesburg. Palgrave Macmillan was created in 2000 when St. Martin's Press in the US united with Macmillan Publishers in the UK to combine their worldwide academic publishing operations. The company was known simply as Palgrave until 2002, but has since been known as Palgrave Macmillan. It is a subsidiary of Springer Nature. Until 2015, it was part of the Macmillan Publishers, Macmillan Group and therefore wholly owned by the German publishing company Holtzbrinck Publishing Group (which still owns a controlling interest in Springer Nature). As part of Macmillan, it was headquartered at the Macmillan campus in Kings Cross, London with other Macmilla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |