|
Transfer-matrix Method (optics)
The transfer-matrix method is a method used in optics and acoustics to analyze the propagation of electromagnetic wave, electromagnetic or acoustic waves through a stratified medium; a stack of thin films. This is, for example, relevant for the design of anti-reflective coatings and dielectric mirrors. The Reflection (physics), reflection of light from a single interface between two medium (optics), media is described by the Fresnel equations. However, when there are multiple Wiktionary:interface, interfaces, such as in the figure, the reflections themselves are also partially transmitted and then partially reflected. Depending on the exact path length, these reflections can Interference (wave propagation), interfere destructively or constructively. The overall reflection of a layer structure is the sum of an infinite number of reflections. The transfer-matrix method is based on the fact that, according to Maxwell's equations, there are simple continuity conditions for the elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) describes their capacity to exert attractive or repulsive forces on another charged object. Charged particles exert attractive forces on each other when the sign of their charges are opposite, one being positive while the other is negative, and repel each other when the signs of the charges are the same. Because these forces are exerted mutually, two charges must be present for the forces to take place. These forces are described by Coulomb's law, which says that the greater the magnitude of the charges, the greater the force, and the greater the distance between them, the weaker the force. Informally, the greater the charge of an object, the stronger its electric field. Similarly, an electric field is stronger nearer charged objects and weaker f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabry–Pérot Interferometer
In optics, a Fabry–Pérot interferometer (FPI) or etalon is an optical cavity made from two parallel reflecting surfaces (i.e.: thin mirrors). Optical waves can pass through the optical cavity only when they are in resonance with it. It is named after Charles Fabry and Alfred Perot, who developed the instrument in 1899. ''Etalon'' is from the French ''étalon'', meaning "measuring gauge" or "standard". Etalons are widely used in telecommunications, lasers and spectroscopy to control and measure the wavelengths of light. Recent advances in fabrication technique allow the creation of very precise tunable Fabry–Pérot interferometers. The device is technically an interferometer when the distance between the two surfaces (and with it the resonance length) can be changed, and an etalon when the distance is fixed (however, the two terms are often used interchangeably). Basic description The heart of the Fabry–Pérot interferometer is a pair of partially reflective glass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmittance
Electromagnetic radiation can be affected in several ways by the medium in which it propagates. It can be Scattering, scattered, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbed, and Fresnel equations, reflected and refracted at discontinuities in the medium. This page is an overview of the last 3. The transmittance of a material and any surfaces is its effectiveness in transmitting radiant energy; the fraction of the initial (incident) radiation which propagates to a location of interest (often an observation location). This may be described by the transmission coefficient. Surface Transmittance Hemispherical transmittance Hemispherical transmittance of a surface, denoted ''T'', is defined as :T = \frac, where *Φet is the radiant flux ''transmitted'' by that surface into the hemisphere on the opposite side from the incident radiation; *Φei is the radiant flux received by that surface. Hemispheric transmittance may be calculated as an integral over the directional trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
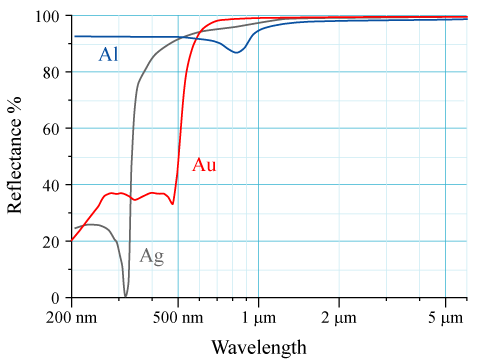
Reflectance
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic structure of the material to the electromagnetic field of light, and is in general a function of the frequency, or wavelength, of the light, its polarization, and the angle of incidence. The dependence of reflectance on the wavelength is called a ''reflectance spectrum'' or ''spectral reflectance curve''. Mathematical definitions Hemispherical reflectance The ''hemispherical reflectance'' of a surface, denoted , is defined as R = \frac, where is the radiant flux ''reflected'' by that surface and is the radiant flux ''received'' by that surface. Spectral hemispherical reflectance The ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in frequency'' and ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in wavelength'' of a surface, denoted and respectively, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Linear Group
In mathematics, the special linear group \operatorname(n,R) of degree n over a commutative ring R is the set of n\times n Matrix (mathematics), matrices with determinant 1, with the group operations of ordinary matrix multiplication and matrix inversion. This is the normal subgroup of the general linear group given by the kernel (algebra), kernel of the determinant :\det\colon \operatorname(n, R) \to R^\times. where R^\times is the multiplicative group of R (that is, R excluding 0 when R is a field). These elements are "special" in that they form an Algebraic variety, algebraic subvariety of the general linear group – they satisfy a polynomial equation (since the determinant is polynomial in the entries). When R is the finite field of order q, the notation \operatorname(n,q) is sometimes used. Geometric interpretation The special linear group \operatorname(n,\R) can be characterized as the group of ''volume and orientation (mathematics), orientation preserving'' linear tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell's Equation
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, electric and magnetic circuits. The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, wireless communication, lenses, radar, etc. They describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated by charges, currents, and changes of the fields.''Electric'' and ''magnetic'' fields, according to the theory of relativity, are the components of a single electromagnetic field. The equations are named after the physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell, who, in 1861 and 1862, published an early form of the equations that included the Lorentz force law. Maxwell first used the equations to propose that light is an electromagnetic phenomenon. The modern form of the equations in their most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Number
In the physical sciences, the wavenumber (or wave number), also known as repetency, is the spatial frequency of a wave. Ordinary wavenumber is defined as the number of wave cycles divided by length; it is a physical quantity with dimension of reciprocal length, expressed in SI units of cycles per metre or reciprocal metre (m−1). Angular wavenumber, defined as the wave phase divided by time, is a quantity with dimension of angle per length and SI units of radians per metre. They are analogous to temporal frequency, respectively the '' ordinary frequency'', defined as the number of wave cycles divided by time (in cycles per second or reciprocal seconds), and the ''angular frequency'', defined as the phase angle divided by time (in radians per second). In multidimensional systems, the wavenumber is the magnitude of the ''wave vector''. The space of wave vectors is called ''reciprocal space''. Wave numbers and wave vectors play an essential role in optics and the physics of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permeability (electromagnetism)
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of magnetization produced in a material in response to an applied magnetic field. Permeability is typically represented by the (italicized) Greek letter Mu (letter), ''μ''. It is the ratio of the Magnetic field, magnetic induction B to the magnetizing field H in a material. The term was coined by William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin in 1872, and used alongside permittivity by Oliver Heaviside in 1885. The reciprocal of permeability is magnetic reluctivity. In SI units, permeability is measured in Henry (unit), henries per Metre, meter (H/m), or equivalently in newton (unit), newtons per ampere squared (N/A2). The permeability constant ''μ''0, also known as the magnetic constant or the permeability of free space, is the proportionality between magnetic induction and magnetizing force when forming a magnetic field in a classical vacuum. A closely related property of materials is magnetic susceptibility, which is a Dimensionless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption (electromagnetic Radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is how matter (typically electrons bound in atoms) takes up a photon's energy—and so transforms electromagnetic energy into internal energy of the absorber (for example, thermal energy). A notable effect of the absorption of electromagnetic radiation is attenuation of the radiation; attenuation is the gradual reduction of the intensity of light waves as they propagate through a medium. Although the absorption of waves does not usually depend on their intensity (linear absorption), in certain conditions (optics) the medium's transparency changes by a factor that varies as a function of wave intensity, and saturable absorption (or nonlinear absorption) occurs. Quantifying absorption Many approaches can potentially quantify radiation absorption, with key examples following. * The absorption coefficient along with some closely related derived quantities * The attenuation coefficient (NB used infrequently with meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Normal
In geometry, a normal is an object (e.g. a line, ray, or vector) that is perpendicular to a given object. For example, the normal line to a plane curve at a given point is the infinite straight line perpendicular to the tangent line to the curve at the point. A normal vector is a vector perpendicular to a given object at a particular point. A normal vector of length one is called a unit normal vector or normal direction. A curvature vector is a normal vector whose length is the curvature of the object. Multiplying a normal vector by results in the opposite vector, which may be used for indicating sides (e.g., interior or exterior). In three-dimensional space, a surface normal, or simply normal, to a surface at point is a vector perpendicular to the tangent plane of the surface at . The vector field of normal directions to a surface is known as '' Gauss map''. The word "normal" is also used as an adjective: a line ''normal'' to a plane, the ''normal'' component of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. The interval of time between events is called the period. It is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times per minute (2 hertz), its period is one half of a second. Special definitions of frequency are used in certain contexts, such as the angular frequency in rotational or cyclical properties, when the rate of angular progress is measured. Spatial frequency is defined for properties that vary or cccur repeatedly in geometry or space. The unit of measurement of frequency in the International System of Units (SI) is the hertz, having the symbol Hz. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |