|
Thermopile
A thermopile is an electronic device that converts thermal energy into electrical energy. It is composed of several thermocouples connected usually in series or, less commonly, in parallel. Such a device works on the principle of the thermoelectric effect, i.e., generating a voltage when its dissimilar metals (thermocouples) are exposed to a temperature difference. Operation Thermocouples operate by measuring the temperature differential from their junction point to the point in which the thermocouple output voltage is measured. Once a closed circuit is made up of more than one metal and there is a difference in temperature between junctions and points of transition from one metal to another, a current is produced as if generated by a difference of potential between the hot and cold junction. Thermocouples can be connected in series as thermocouple pairs with a junction located on either side of a thermal resistance layer. The output from the thermocouple pair will be a vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
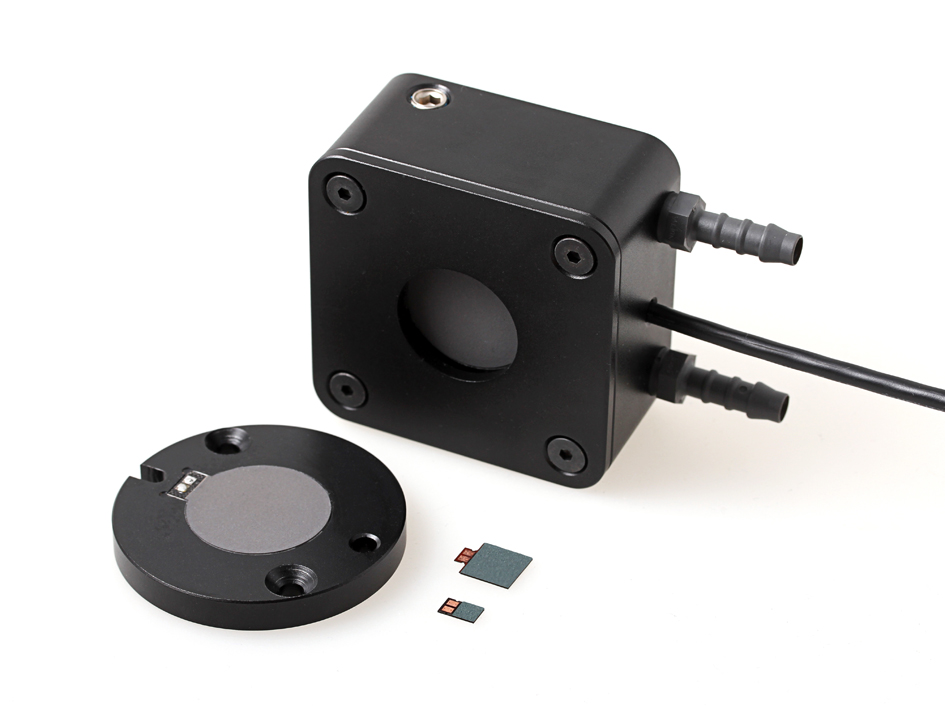
Thermopile Laser Sensors
Thermopile laser sensors (Fig 1) are used for measuring laser power from a few μW to several W (see section 2.4). The incoming radiation of the laser is converted into heat energy at the surface. This heat input produces a temperature gradient across the sensor. Making use of the thermoelectric effect a voltage is generated by this temperature gradient. Since the voltage is directly proportional to the incoming radiation, it can be directly related to the irradiation power (see section 2.1). Unlike photodiodes, thermopile sensors can be used for a broad spectrum of wavelengths ranging from UV to MIR (depending on the characteristics of the absorption coating at different wavelengths). Further, photodiodes are reverse biased and saturate for optical powers above a certain value (typically in mW), making thermopile sensors suitable for high power measurements. Pyroelectric sensor and calorimeter are commonly used for measuring the energy of laser pulses. Pyroelectric sensor can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermopile2
A thermopile is an electronic device that converts thermal energy into electrical energy. It is composed of several thermocouples connected usually in series or, less commonly, in parallel. Such a device works on the principle of the thermoelectric effect, i.e., generating a voltage when its dissimilar metals (thermocouples) are exposed to a temperature difference. Operation Thermocouples operate by measuring the temperature differential from their junction point to the point in which the thermocouple output voltage is measured. Once a closed circuit is made up of more than one metal and there is a difference in temperature between junctions and points of transition from one metal to another, a current is produced as if generated by a difference of potential between the hot and cold junction. Thermocouples can be connected in series as thermocouple pairs with a junction located on either side of a thermal resistance layer. The output from the thermocouple pair will be a voltag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Flux Sensor
] A heat flux sensor is a transducer that generates an electrical signal proportional to the total heat transfer, heat rate applied to the surface of the sensor. The measured heat rate is divided by the surface area of the sensor to determine the heat flux. The heat flux can have different origins; in principle convective, Thermal radiation, radiative as well as Thermal conduction, conductive heat can be measured. Heat flux sensors are known under different names, such as heat flux transducers, heat flux gauges, or heat flux plates. Some instruments are actually single-purpose heat flux sensors, like pyranometers for solar radiation measurement. Other heat flux sensors include Gardon gauges (also known as a circular-foil gauge), thin-film thermopiles, and Schmidt-Boelter gauges. Usage Heat flux sensors are used for a variety of applications. Common applications are studies of building envelope thermal resistance, studies of the effect of fire and flames or laser power measurem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermocouple
A thermocouple, also known as a "thermoelectrical thermometer", is an electrical device consisting of two dissimilar electrical conductors forming an electrical junction. A thermocouple produces a temperature-dependent voltage as a result of the Seebeck effect, and this voltage can be interpreted to measure temperature. Thermocouples are widely used as list of temperature sensors, temperature sensors. Commercial thermocouples are inexpensive, interchangeable, are supplied with standard Electrical connector, connectors, and can measure a wide range of temperatures. In contrast to most other methods of temperature measurement, thermocouples are self-powered and require no external form of excitation. The main limitation with thermocouples is accuracy; system errors of less than one degree Celsius (°C) can be difficult to achieve. Thermocouples are widely used in science and industry. Applications include temperature measurement for kilns, gas turbine exhaust, diesel engines, and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seebeck Effect
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa via a thermocouple. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, heat is transferred from one side to the other, creating a temperature difference. This effect can be used to generate electricity, measure temperature or change the temperature of objects. Because the direction of heating and cooling is affected by the applied voltage, thermoelectric devices can be used as temperature controllers. The term "thermoelectric effect" encompasses three separately identified effects: the Seebeck effect (temperature differences cause electromotive forces), the Peltier effect (thermocouples create temperature differences), and the Thomson effect (the Seebeck coefficient varies with temperature). The Seebeck and Peltier effects are different manifestations of the same physical proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Temperature Thermopile
Differential may refer to: Mathematics * Differential (mathematics) comprises multiple related meanings of the word, both in calculus and differential geometry, such as an infinitesimal change in the value of a function * Differential algebra * Differential calculus ** Differential of a function, represents a change in the linearization of a function *** Total differential is its generalization for functions of multiple variables ** Differential (infinitesimal) (e.g. ''dx'', ''dy'', ''dt'' etc.) are interpreted as infinitesimals ** Differential topology * Differential (pushforward) The total derivative of a map between manifolds. * Differential exponent, an exponent in the factorisation of the different ideal * Differential geometry, exterior differential, or exterior derivative, is a generalization to differential forms of the notion of differential of a function on a differentiable manifold * Differential (coboundary), in homological algebra and algebraic topology, one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoelectric Materials
Thermoelectric materials show the thermoelectric effect in a strong or convenient form. The ''thermoelectric effect'' refers to phenomena by which either a temperature difference creates an electric potential or an electric current creates a temperature difference. These phenomena are known more specifically as the Seebeck effect (creating a voltage from temperature difference), Peltier effect (driving heat flow with an electric current), and Thomson effect (reversible heating or cooling within a conductor when there is both an electric current and a temperature gradient). While all materials have a nonzero thermoelectric effect, in most materials it is too small to be useful. However, low-cost materials that have a sufficiently strong thermoelectric effect (and other required properties) are also considered for applications including power generation and refrigeration. The most commonly used thermoelectric material is based on bismuth telluride (). Thermoelectric materials are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrheliometer
A pyrheliometer is an instrument that can measure direct beam solar irradiance. Sunlight enters the instrument through a window and is directed onto a thermopile which converts heat to an electrical signal that can be recorded. The signal voltage is converted via a formula to measure watts per square metre. Standards Pyrheliometer measurement specifications are subject to International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and World Meteorological Organization (WMO) standards. Comparisons between pyrheliometers for intercalibration are carried out regularly to measure the amount of solar energy received. The aim of the International Pyrheliometer Comparisons, which take place every 5 years at the World Radiation Centre in Davos, is to ensure the world-wide transfer of the World Radiometric Reference. During this event, all participants bring their instruments, solar-tracking and data acquisition systems to Davos to conduct simultaneous solar radiation measurements with the Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
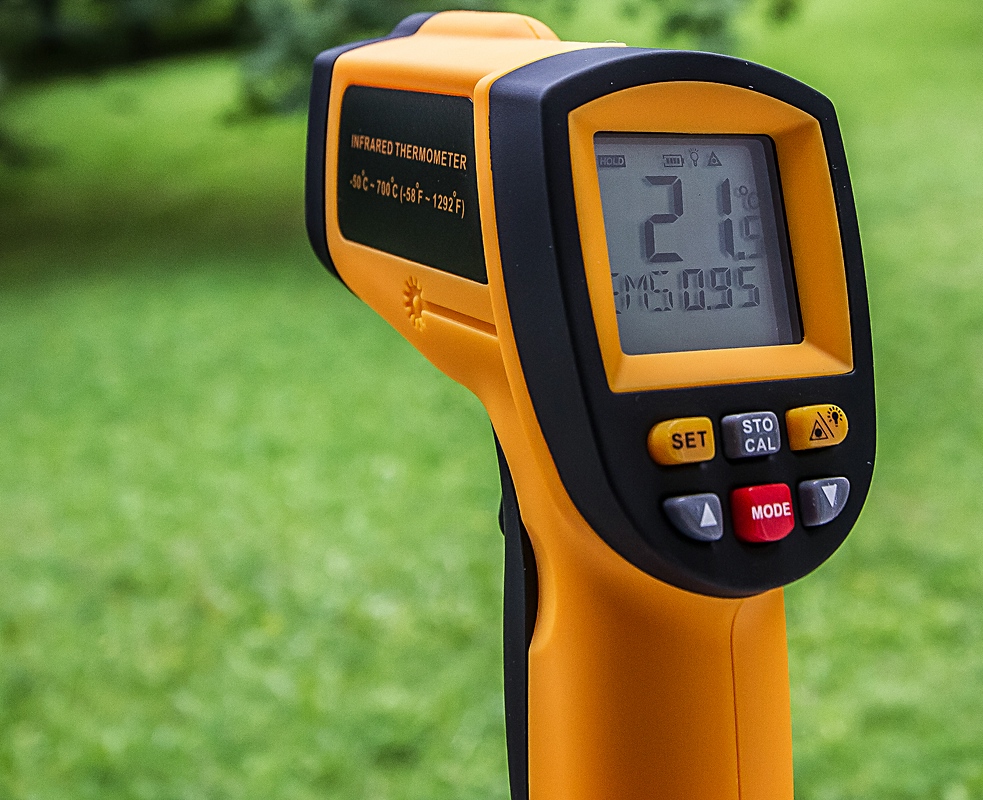
Infrared Thermometer
An infrared thermometer is a thermometer which infers temperature from a portion of the thermal radiation sometimes called black-body radiation emitted by the object being measured. They are sometimes called laser thermometers as a laser is used to help aim the thermometer, or non-contact thermometers or temperature guns, to describe the device's ability to measure temperature from a distance. By knowing the amount of infrared energy emitted by the object and its emissivity, the object's temperature can often be determined within a certain range of its actual temperature. Infrared thermometers are a subset of devices known as "thermal radiation thermometers". Sometimes, especially near ambient temperatures, readings may be subject to error due to the reflection of radiation from a hotter body, or due to an incorrectly assumed emissivity. The design essentially consists of a lens to focus the infrared thermal radiation on to a detector, which converts the radiant power to an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a device that measures the proper acceleration of an object. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change (mathematics), rate of change of velocity) of the object relative to an observer who is in free fall (that is, relative to an inertial frame of reference). Proper acceleration is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration with respect to a given coordinate system, which may or may not be accelerating. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an Gravitational acceleration, acceleration due to Earth's gravity straight upwards of about Standard gravity, ''g'' ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, an accelerometer that is in free fall will measure zero acceleration. Accelerometers have many uses in industry, consumer products, and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |