|
Surface Ionization
Thermal ionization, also known as surface ionization or contact ionization, is a physical process whereby the atoms are desorbed from a hot surface, and in the process are ionized. Thermal ionization is used to make simple ion sources, for mass spectrometry and for generating ion beams. Thermal ionization has seen extensive use in determining atomic weights, in addition to being used in many geological/nuclear applications. Physics The likelihood of ionization is a function of the filament temperature, the work function of the filament substrate and the ionization energy of the element. This is summarised in the Saha–Langmuir equation: : \frac = \frac \exp \Bigg(\frac\Bigg) where :: \frac = ratio of ion number density to neutral number density :: \frac = ratio of statistical weights (degeneracy) of ionic (''g''+) and neutral (''g''0) states :: W = work function of surface :: \Delta E_\text = ionization energy of desorbed element :: k = Boltzmann constant :: T = surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desorption
Desorption is the physical process where Adsorption, adsorbed atoms or molecules are released from a surface into the surrounding vacuum or fluid. This occurs when a molecule gains enough energy to overcome the activation barrier and the binding energy that keep it attached to the surface. Desorption is the reverse of the process of adsorption, which differs from absorption in that adsorption refers to substances bound to the surface, rather than being absorption (chemistry), absorbed into the bulk. Desorption can occur from any of several processes, or a combination of them: it may result from heat (thermal energy); incident light such as infrared, visible, or ultraviolet photons; or an incident beam of energetic particles such as electrons. It may also occur following chemical reactions such as oxidation or reduction in an electrochemical cell or after a chemical reaction of a adsorbed compounds in which the surface may act as a catalyst. Mechanisms Depending on the nature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
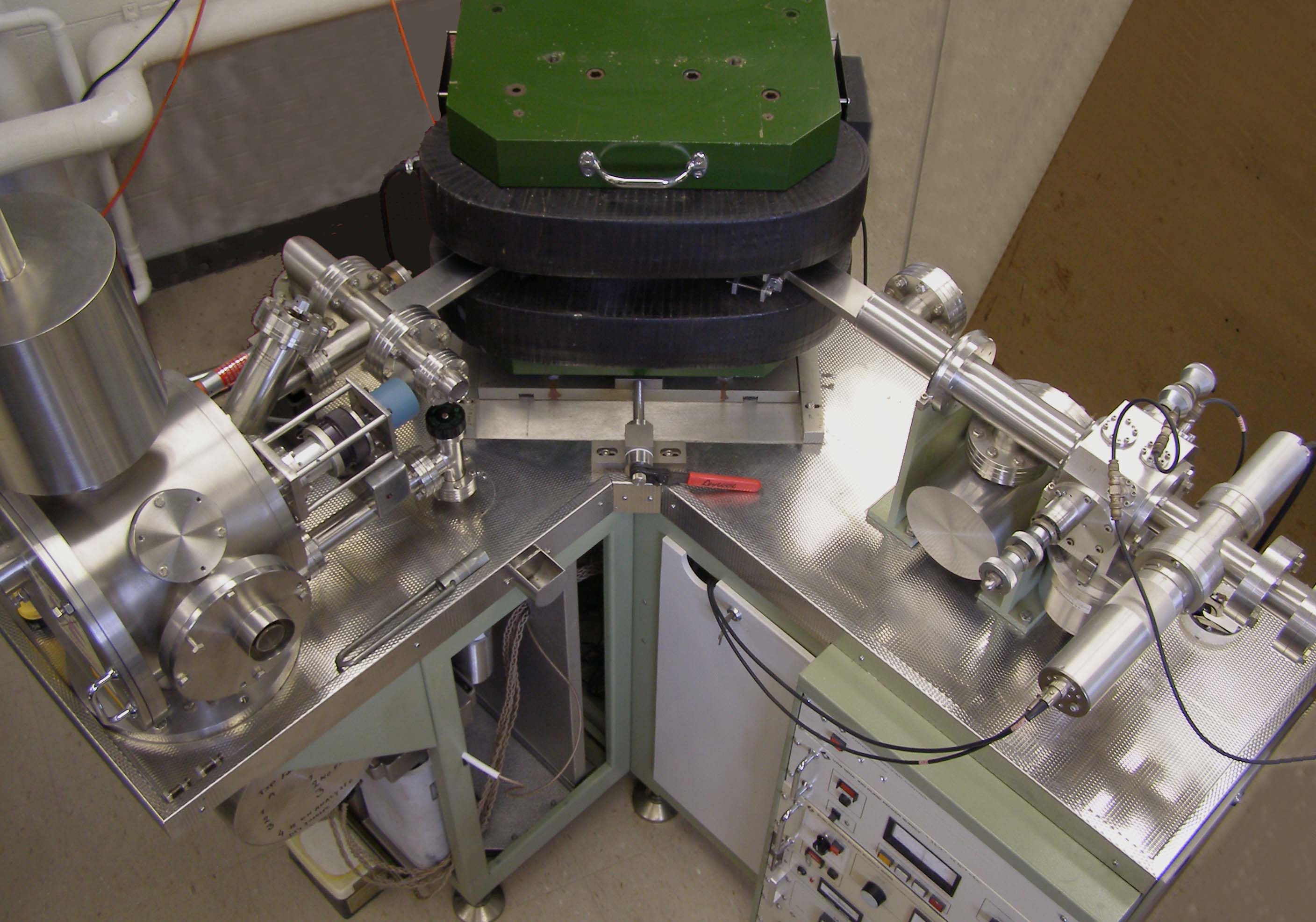
Thermal Ionization Mass Spectrometry
Thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS), also known as surface ionization, is a highly sensitive isotope mass spectrometry characterization technique. The isotopic ratios of radionuclides are used to get an accurate measurement for the elemental analysis of a sample. Singly charged ions of the sample are formed by the thermal ionization effect. A chemically purified liquid sample is placed on a metal filament which is then heated to evaporate the solvent. The removal of an electron from the purified sample is consequently achieved by heating the filament enough to release an electron, which then ionizes the atoms of the sample. TIMS utilizes a magnetic sector mass analyzer to separate the ions based on their mass to charge ratio. The ions gain velocity by an electrical potential gradient and are focused into a beam by electrostatic lenses. The ion beam then passes through the magnetic field of the electromagnet where it is partitioned into separate ion beams based on the ion's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meghnad Saha
Meghnad Saha (6 October 1893 – 16 February 1956) was an Indian astrophysicist and politician who helped devise the theory of Thermal ionization, thermal ionisation. His Saha ionization equation, Saha ionisation equation allowed astronomers to accurately relate the Stellar classification, spectral classes of stars to their actual temperatures. Biography Meghnad Saha was born on 6 October 1893 to a lower-caste Bengali Hindu family in the village of Kaliakair Upazila, Sheoratali in Gazipur District, Gazipur, then part of the Dhaka Division, Dacca district of the Bengal Presidency (now Bangladesh). He was the fifth of eight children born to Jagannath Saha, a poor shopkeeper, and his wife, Bhubaneshwari Devi. Due to the superstitious religious ideologies of the orthodox haughty Brahmins of the time and his childhood and career experiences of casteism, Saha developed a hatred for Hinduism from a young age. During his youth, he was forced to leave Dhaka Collegiate School because h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irving Langmuir
Irving Langmuir (; January 31, 1881 – August 16, 1957) was an American chemist, physicist, and metallurgical engineer. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1932 for his work in surface chemistry. Langmuir's most famous publication is the 1919 article "The Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms and Molecules" in which, building on Gilbert N. Lewis's cubical atom theory and Walther Kossel's chemical bonding theory, he outlined his "concentric theory of atomic structure". Langmuir became embroiled in a priority dispute with Lewis over this work; Langmuir's presentation skills were largely responsible for the popularization of the theory, although the credit for the theory itself belongs mostly to Lewis. While at General Electric from 1909 to 1950, Langmuir advanced several fields of physics and chemistry, inventing the gas-filled incandescent lamp and the hydrogen welding technique. The Langmuir Laboratory for Atmospheric Research near Socorro, New Mexico, was named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langmuir–Taylor Detector
A Langmuir–Taylor detector, also called surface ionization detector or hot wire detector, is a kind of ionization detector used in mass spectrometry, developed by John Taylor based on the work of Irving Langmuir and K. H. Kingdon. Construction This detector usually consists of a heated thin filament or ribbon of a metal with a high work function (typically tungsten or rhenium). Neutral atoms or molecules that strike the filament can boil off as positive ions in a process known as surface ionization, and these may be either measured as a current or detected, individually, using an electron multiplier and particle counting electronics. Applications This detector is mostly used with alkali atoms, having a low ionization potential, with applications in mass spectrometry and atomic clock An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first isolated as a metal in 1783. Its important ores include scheelite and wolframite, the latter lending the element its alternative name. The free element is remarkable for its robustness, especially the fact that it has the highest melting point of all known elements, melting at . It also has the highest boiling point, at . Its density is 19.254 g/cm3, comparable with that of uranium and gold, and much higher (about 1.7 times) than that of lead. Polycrystalline tungsten is an intrinsically brittle and hard material (under standard conditions, when uncombined), making it difficult to work into metal. However, pure single-crystalline tungsten is more ductile and can be cut with a hard-steel hacksaw. Tungsten occurs in many alloys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmium
Osmium () is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Os and atomic number 76. It is a hard, brittle, bluish-white transition metal in the platinum group that is found as a Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, trace element in alloys, mostly in platinum ores. Osmium is the densest naturally occurring element. When experimentally measured using X-ray crystallography, it has a density of . Manufacturers use its alloys with platinum, iridium, and other platinum-group metals to make fountain pen Nib (pen)#Nib tipping, nib tipping, electrical contacts, and in other applications that require extreme durability and hardness. Osmium is among the Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, rarest elements in the Earth's crust, making up only 50 parts per trillion (Parts-per notation#Parts-per expressions, ppt). Characteristics Physical properties Osmium is a hard, brittle, blue-gray metal, and the densest stable element—about twice as dense as lead. The density of os ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable nuclide, stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its Amphoterism, amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and base (chemistry), bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Lead compounds, Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strontium
Strontium is a chemical element; it has symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, it is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is exposed to air. Strontium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of its two vertical neighbors in the periodic table, calcium and barium. It occurs naturally mainly in the minerals celestine and strontianite, and is mostly mined from these. Both strontium and strontianite are named after Strontian, a village in Scotland near which the mineral was discovered in 1790 by Adair Crawford and William Cruickshank; it was identified as a new element the next year from its crimson-red flame test color. Strontium was first isolated as a metal in 1808 by Humphry Davy using the then newly discovered process of electrolysis. During the 19th century, strontium was mostly used in the production of sugar from sugar beets (see strontian proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiometric Dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to Chronological dating, date materials such as Rock (geology), rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurity, impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares the abundance of a naturally occurring Radionuclide, radioactive isotope within the material to the abundance of its Radioactive decay, decay products, which form at a known constant rate of decay. Radiometric dating of minerals and rocks was pioneered by Ernest Rutherford (1906) and Bertram Boltwood (1907). Radiometric dating is now the principal source of information about the Absolute dating, absolute age of rocks and other Geology, geological features, including the age of Paleontology, fossilized life forms or the age of Earth itself, and can also be used to date a wide range of natural and Artifact (archaeology), man-made materials. Together with stratigraphy, stratigraphic principles, ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Filament
An incandescent light bulb, also known as an incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe, is an electric light that produces illumination by Joule heating a filament until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb that is either evacuated or filled with inert gas to protect the filament from oxidation. Electric current is supplied to the filament by terminals or wires embedded in the glass. A bulb socket provides mechanical support and electrical connections. Incandescent bulbs are manufactured in a wide range of sizes, light output, and voltage ratings, from 1.5 volts to about 300 volts. They require no external regulating equipment, have low manufacturing costs, and work equally well on either alternating current or direct current. As a result, the incandescent bulb became widely used in household and commercial lighting, for portable lighting such as table lamps, car headlamps, and flashlights, and for decorative and advertising lighting. Incandescent bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |