|
Room And Power Mill
A room and power mill was a type of textile mill found in Lancashire, England, in the 19th century. Small businesses paid the owner rent for space for their machines and power from the mill engine or waterwheel. The system In, for example Nelson, many mills were operated by The Nelson Room and Power Company and the Walverden Room and Power Company. This allowed specialised companies to start up. Such a company may have had 20 dobby looms and just do "fancies". Examples * Beehive Mill, Jersey Street, Great Ancoats *Brownsfield Mill, Great Ancoats *Vale Mill, Todmorden See also * :Lists of textile mills in the United Kingdom *List of mills owned by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation Limited *List of mills in Rochdale *List of mills in Oldham This list of mills in Oldham, lists textile factories that have existed in the town of Oldham, within Metropolitan Borough of Oldham in Greater Manchester, England. From the Industrial Revolution until the 20th century, Oldham was a major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
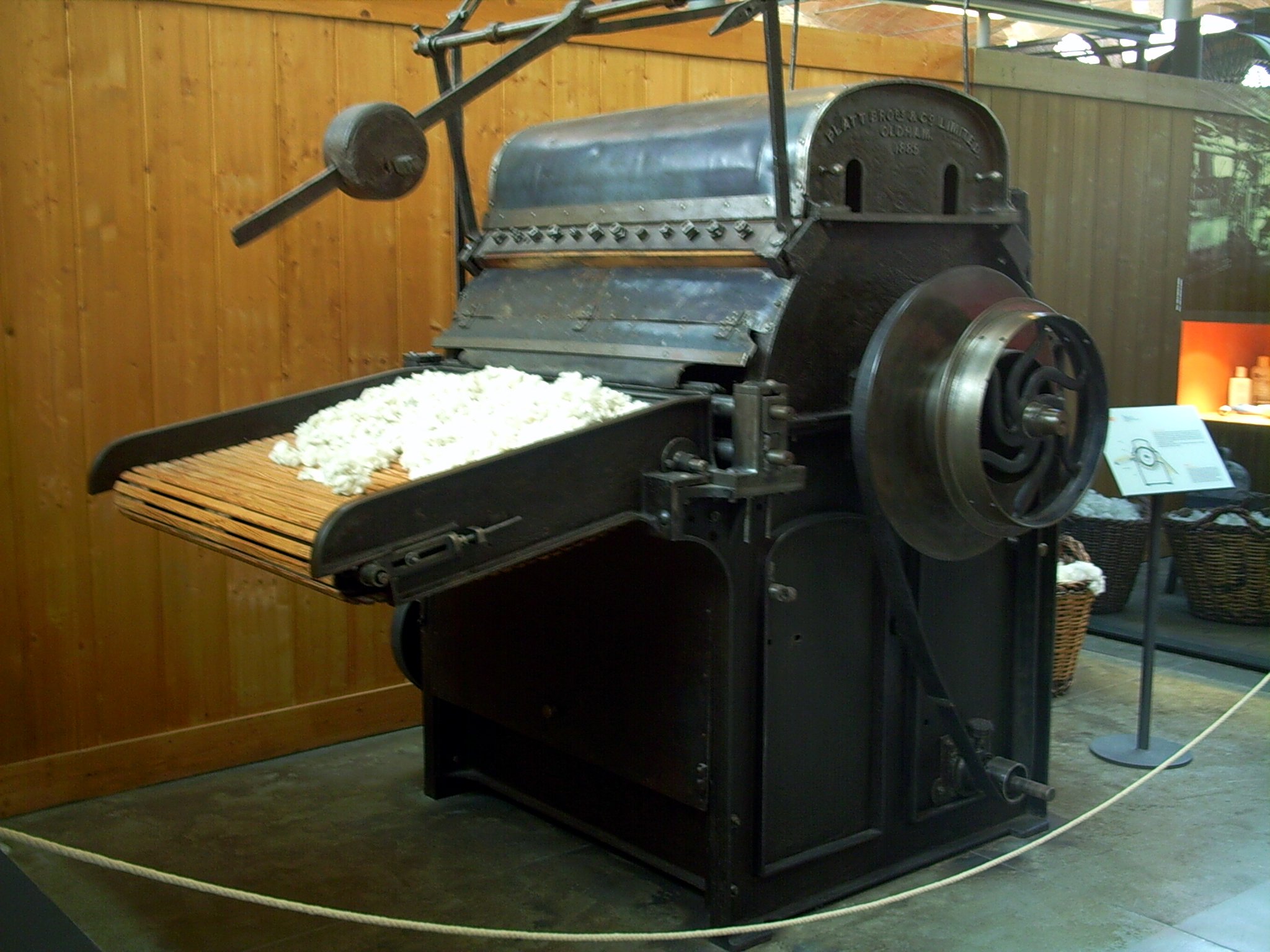
Textile Mill
Textile Manufacturing or Textile Engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods such as clothing, household items, upholstery and various industrial products. Different types of fibres are used to produce yarn. Cotton remains the most widely used and common natural fiber making up 90% of all-natural fibers used in the textile industry. People often use cotton clothing and accessories because of comfort, not limited to different weathers. There are many variable processes available at the spinning and fabric-forming stages coupled with the complexities of the finishing and colouration processes to the production of a wide range of products. History Textile manufacturing in the modern era is an evolved form of the art and craft industries. Until the 18th and 19th centuries, the textile industry was a household work. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly. The non-metropolitan county of Lancashire was created by the Local Government Act 1972. It is administered by Lancashire County Council, based in Preston, and twelve district councils. Although Lancaster is still considered the county town, Preston is the administrative centre of the non-metropolitan county. The ceremonial county has the same boundaries except that it also includes Blackpool and Blackburn with Darwen, which are unitary authorities. The historic county of Lancashire is larger and includes the cities of Manchester and Liverpool as well as the Furness and Cartmel peninsulas, but excludes Bowland area of the West Riding of Yorkshire transferred to the non-metropolitan county in 1974 History Before the county During Roman times the area was part of the Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
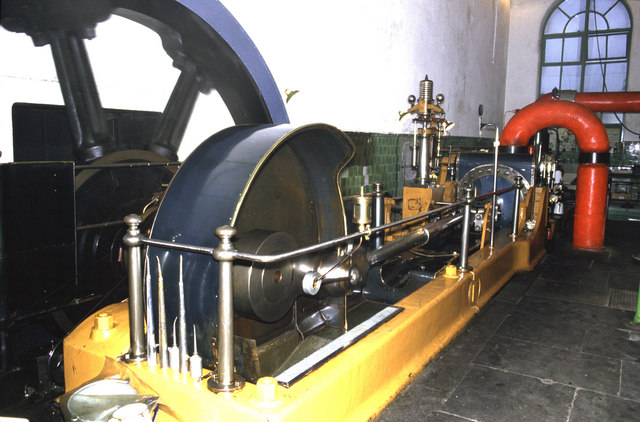
Stationary Steam Engine
Stationary steam engines are fixed steam engines used for pumping or driving mills and factories, and for power generation. They are distinct from locomotive engines used on railways, traction engines for heavy steam haulage on roads, steam cars (and other motor vehicles), agricultural engines used for ploughing or threshing, marine engines, and the steam turbines used as the mechanism of power generation for most nuclear power plants. They were introduced during the 18th century and widely made for the whole of the 19th century and most of the first half of the 20th century, only declining as electricity supply and the internal combustion engine became more widespread. Types of stationary steam engine There are different patterns of stationary steam engines, distinguished by the layout of the cylinders and crankshaft: * Beam engines have a rocking beam providing the connection between the vertical cylinder and crankshaft. *Table engines have the crosshead above the vert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterwheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with a number of blades or buckets arranged on the outside rim forming the driving car. Water wheels were still in commercial use well into the 20th century but they are no longer in common use. Uses included milling flour in gristmills, grinding wood into pulp for papermaking, hammering wrought iron, machining, ore crushing and pounding fibre for use in the manufacture of cloth. Some water wheels are fed by water from a mill pond, which is formed when a flowing stream is dammed. A channel for the water flowing to or from a water wheel is called a mill race. The race bringing water from the mill pond to the water wheel is a headrace; the one carrying water after it has left the wheel is commonly referred to as a tailrace. Waterwheels were used for various purposes from ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nelson, Lancashire
Nelson is a town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in the Borough of Pendle in Lancashire, England, with a population of 29,135 in 2011. It is 4 miles (6.4 km) north of Burnley and 2.5 miles southwest of Colne. It developed as a mill town during the Industrial Revolution, but has today lost much of its industry and is characterised by some of the lowest house prices in the whole of the United Kingdom. History An Iron Age hillfort called Castercliff is on a hill to the east of the town. The modern town spans the two parts of the Township (England), township of Marsden in the ancient parish of Whalley.An Early History of Burnley, Pendle and West Craven Clayton 2006, p.118 Little Marsden was on the southwest of Walverden Water, its lands considered part of the Manorialism, manor of Ightenhill and Great Marsden to the northeast, part of the manor of Colne. Great Marsden included the southern parts of Colne, and Little Marsden included all of modern-day Brierfield, La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
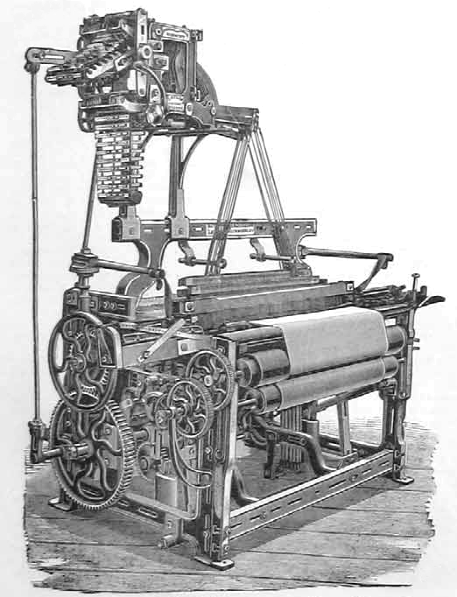
Dobby Loom
A dobby loom, or dobbie loom, is a type of floor loom that controls all the warp threads using a device called a dobby. Dobbies can produce more complex fabric designs than tappet looms but are limited in comparison to Jacquard looms. Dobby looms first appeared around 1843, roughly 40 years after Joseph Marie Jacquard invented the Jacquard device that can be mounted atop a loom to lift the individual heddles and warp threads. The word ''dobby'' is a corruption of "draw boy," which refers to the weaver's helpers who used to control the warp thread by pulling on draw threads. A dobby loom is an alternative to a treadle loom. Both are floor looms in which every warp thread on the loom is attached to a single shaft using a device called a heddle. A shaft is sometimes known as a harness. Each shaft controls a set of threads. Raising or lowering several shafts at the same time gives a huge variety of possible sheds (gaps) through which the shuttle containing the weft thread can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beehive Mill
Beehive Mill is a Grade II* listed former cotton mill in the district of Ancoats, Greater Manchester, England. It is located at (grid reference ) on a site surrounded by Radium Street, Jersey Street, Bengal Street and Naval Street. The building was constructed in three phases, the first two being in the early 1820s with the third phase being added in 1847. The second phase, built in 1824 and used as warehousing, is an important example of early fireproof construction. The roof of the 1824 warehouse belonging to Beehive Mill is the only known surviving example in Manchester of an advanced form of mill roof using cast and wrought iron, and which was prefabricated. The third phase was five storeys high and built along Bengal Street; this block was damaged by fire and partially rebuilt in 1861. The estimated value of the damage caused was £25,000. The adjacent Bengal Street block was destroyed by fire in July 2005. The fire threatened to destroy the rest of the complex, which house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Lists Of Textile Mills In The United Kingdom ...
{{Portal, United Kingdom, Lists Textile mills Textile mills in the United Kingdom Industrial history of the United Kingdom United Kingdom The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mills Owned By The Lancashire Cotton Corporation Limited
The Lancashire Cotton Corporation, Lancashire Cotton Corporation Limited was incorporated 23 January 1929, and became the world's largest spinner of cotton. It acquired 104 mills and closed about half to reduce capacity. In 1950, it operated 53 cotton mills.The Mills and organisation of the Lancashire Cotton Corporation- a descriptive book, pub LCC, Blackfriars House Manchester, January 1951 The 1950 mills (A–D) The 1950 mills (E–J) The 1950 mills (K–N) The 1950 mills (O–T) The 1950 mills (U–Z) Other Mills that were owned before 1951 See also References ;Notes ;Bibliography * * * * * External links Cottontown.org websiteSpinningtheweb.org.uk websiteInterview with Jim Shelmerdine, General manager, Manor Mill, Chadderton {{DEFAULTSORT:Mills Owned by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation Limited Textile mills owned by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mills In Rochdale
This is a list of mills known to have existed within Rochdale Borough, in Greater Manchester, England. The Mills and organisation of the Lancashire Cotton Corporation, a descriptive book, pub. LCC, Blackfriars House Manchester, January 1951 A-B C to D E to G H to L M to N O to P R to S T U to V W to Z See also * List of mills in Shaw and Crompton References External links Mills in Heywood (1922) {{DEFAULTSORT:Mills in Rochdale *Rochdale Buildings and structures in the Metropolitan Borough of Rochdale Rochdale Rochdale Rochdale Rochdale ( ) is a large town in Greater Manchester, England, at the foothills of the South Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mills In Oldham
This list of mills in Oldham, lists textile factories that have existed in the town of Oldham, within Metropolitan Borough of Oldham in Greater Manchester Greater Manchester is a metropolitan county and combined authority, combined authority area in North West England, with a population of 2.8 million; comprising ten metropolitan boroughs: City of Manchester, Manchester, City of Salford, Salford ..., England. From the Industrial Revolution until the 20th century, Oldham was a major centre of textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution, textile manufacture, particularly Spinning (textiles), cotton spinning. During this period, the valleys of the River Beal, River Irk, River Medlock and their tributaries were dominated by large rectangular brick-built factories, many of which still remain today as warehouses or converted for residential or retail use. A–E F–J K–O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |