|
Puddling (civil Engineering)
Puddling is a traditional civil engineering technique used to create watertight barriers in canals, reservoirs, and earthworks by compacting clay to prevent water leakage. The process involves kneading, mixing, and compacting clay—often with water—to form an impermeable layer known as puddle clay. This method has historically been essential in the construction of canals, dams, and embankments, particularly before the development of modern waterproofing materials."puddle, n. 4" also called puddling. ''Oxford English Dictionary''. 2nd. ed. 2009. Puddling was widely used during the 18th and 19th centuries, notably in the construction of Britain’s canal network, where engineers such as James Brindley and Thomas Telford employed it to line waterways and prevent seepage. Although largely replaced by modern materials like concrete and synthetic liners, puddling remains relevant in the restoration of historic structures and some environmentally sensitive projects where natural m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montgomery Canal At Redwith Bridge Puddled
Montgomery refers to: People For people with the name Montgomery, see Montgomery (name) Places Belgium * Montgomery Square, Brussels * Montgomery metro station, Brussels Pakistan * Montgomery (town), British India, former name of Sahiwal, Punjab * Montgomery District, an administrative district in the Lahore division of former Punjab Province of British India ** Montgomery Tahsil, an administrative subdivision of Montgomery District in Punjab province of British India United Kingdom Wales * Montgomery, Powys ** Montgomery Canal ** Montgomery Castle * Montgomeryshire (other) United States * Montgomery, Alabama, state capital * Montgomery, Georgia * Montgomery, Illinois * Montgomery, Indiana * Montgomery, Iowa * Montgomery, Kentucky * Montgomery, Louisiana * Montgomery, Massachusetts * Montgomery, Michigan * Montgomery, Minnesota * Montgomery, Mississippi * Montgomery, New York (other) * Montgomery, Ohio * Montgomery, Pennsylvania * Montgomery, Ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loam
Loam (in geology and soil science) is soil composed mostly of sand (particle size > ), silt (particle size > ), and a smaller amount of clay (particle size < ). By weight, its mineral composition is about 40–40–20% concentration of sand–silt–clay, respectively. These proportions can vary to a degree, however, and result in different types of loam soils: sandy loam, silty loam, clay loam, sandy clay loam, silty clay loam, and loam. In the USDA, United States Department of Agriculture, soil texture, textural classification triangle, the only soil that is not predominantly sand, silt, or clay is called "loam". Loam soils generally contain more nutrients, moisture, and humus than sandy soils, have better drainage and infiltration of water and air than silt- and clay-rich soils, and are easier to tillage, till than clay soils. In fact, the primary definition of loam in most dictionaries is soils containing hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Society Of London
The Geological Society of London, known commonly as the Geological Society, is a learned society based in the United Kingdom. It is the oldest national geological society in the world and the largest in Europe, with more than 12,000 Fellows. Fellows are entitled to the postnominal FGS (Fellow of the Geological Society), over 2,000 of whom are Chartered Geologists (CGeol). The Society is a registered charity, no. 210161. It is also a member of the Science Council, and is licensed to award Chartered Scientist to qualifying members. The mission of the society is: "Making geologists acquainted with each other, stimulating their zeal, inducing them to adopt one nomenclature, facilitating the communication of new facts and ascertaining what is known in their science and what remains to be discovered". History The Society was founded on 13 November 1807 at the Freemasons' Tavern, Great Queen Street, in the Covent Garden district of London. It was partly the outcome of a previou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The British Canal System
The canal network of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom played a vital role in the Industrial Revolution. The UK was the first country to develop a nationwide canal network which, at its peak, expanded to nearly in length. The canals allowed raw materials to be transported to a place of manufacture, and finished goods to be transported to consumers, more quickly and cheaply than by a land based route. The canal network was extensive and included feats of civil engineering such as the Anderton Boat Lift, the Manchester Ship Canal, the Worsley Navigable Levels and the Pontcysyllte Aqueduct. In the post-medieval period, some rivers were canalised for boat traffic. The Exeter Ship Canal was completed in 1567. The Sankey Canal was the first British canal of the Industrial Revolution, opening in 1757. The Bridgewater Canal followed in 1761 and proved to be highly profitable. The majority of the network was built in the "Golden Age" of canals, between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canals Of The United Kingdom
The canals of the United Kingdom are a major part of the network of inland waterways in the United Kingdom. They have a History of the British canal system, varied history, from use for irrigation and transport, through becoming the focus of the Industrial Revolution, to today's role of recreational boating. Despite a period of abandonment, today the canal system in the United Kingdom is again increasing in use, with abandoned and derelict canals being reopened, and the construction of some new routes. Canals in England and Wales are maintained by List of navigation authorities in the United Kingdom, navigation authorities. The biggest navigation authorities are the Canal & River Trust and the Environment Agency, but other canals are managed by companies, local authorities or charitable trusts. The majority of List of canals of the United Kingdom, canals in the United Kingdom can accommodate boats with a length of between and are now used primarily for leisure. There are a number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cob (material)
Cob, cobb, or clom (in Wales) is a natural building material made from subsoil, water, fibrous organic material (typically straw), and sometimes lime. The contents of subsoil vary, and if it does not contain the right mixture, it can be modified with sand or clay. Cob is fireproof, termite proof, resistant to seismic activity, and uses low-cost materials, although it is very labour intensive. It can be used to create artistic and sculptural forms, and its use has been revived in recent years by the natural building and sustainability movements. In technical building and engineering documents, such as the Uniform Building Code of the western USA, cob may be referred to as "unburned clay masonry," when used in a structural context. It may also be referred to as "aggregate" in non-structural contexts, such as "clay and sand aggregate," or more simply "organic aggregate," such as where cob is a filler between post and beam construction. History and usage ''Cob'' is an English t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adobe
Adobe (from arabic: الطوب Attub ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for mudbrick. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used to refer to any kind of earthen construction, or various architectural styles like Pueblo Revival or Territorial Revival. Most adobe buildings are similar in appearance to cob and rammed earth buildings. Adobe is among the earliest building materials, and is used throughout the world. Adobe architecture has been dated to before 5,100 BP. Description Adobe bricks are rectangular prisms small enough that they can quickly air dry individually without cracking. They can be subsequently assembled, with the application of adobe mud to bond the individual bricks into a structure. There is no standard size, with substantial variations over the years and in different regions. In some areas a popular size measured weighing about ; in other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
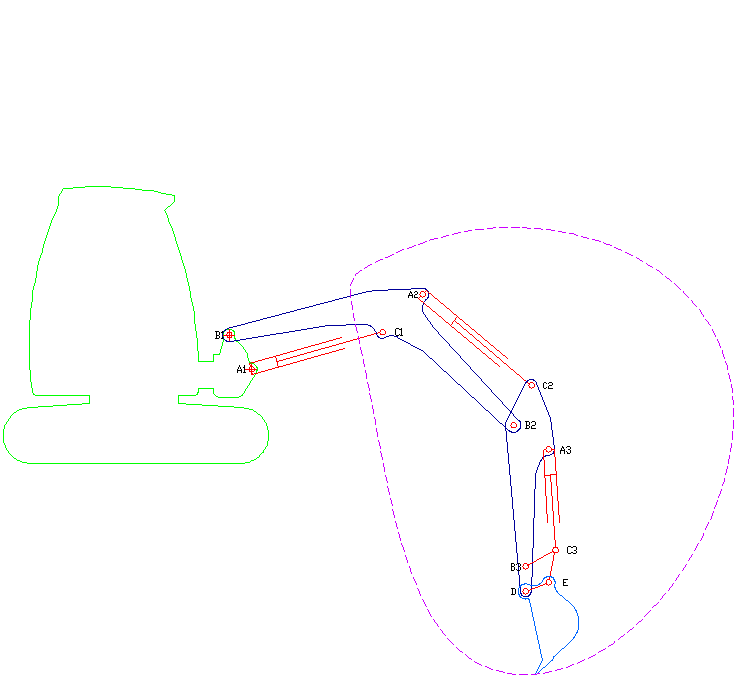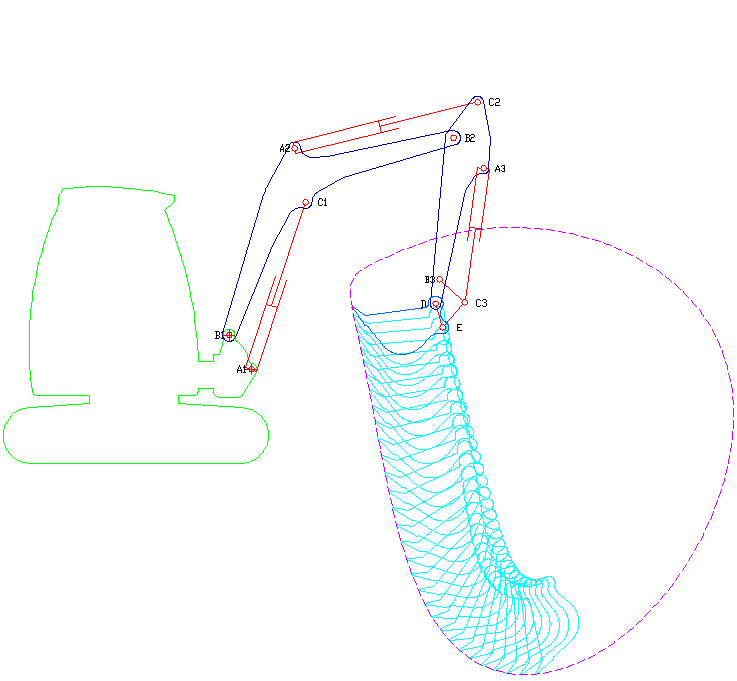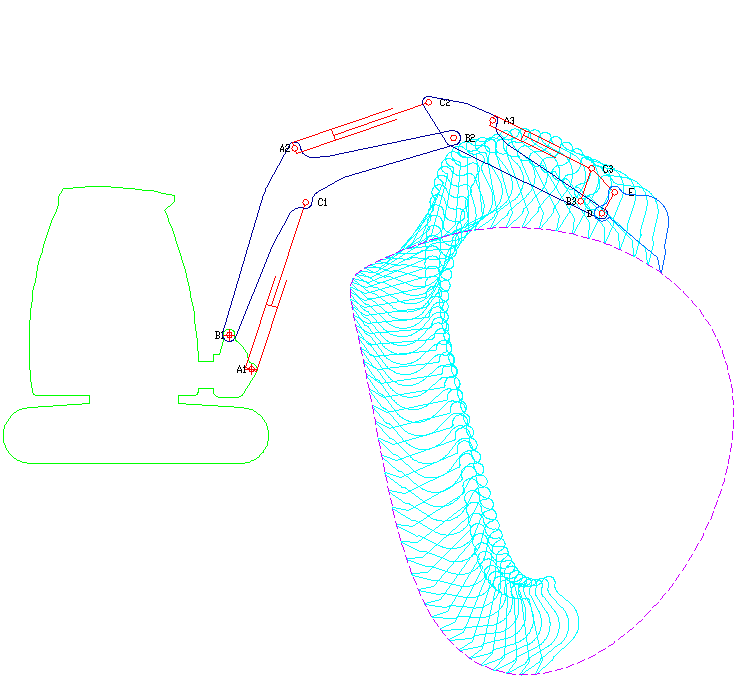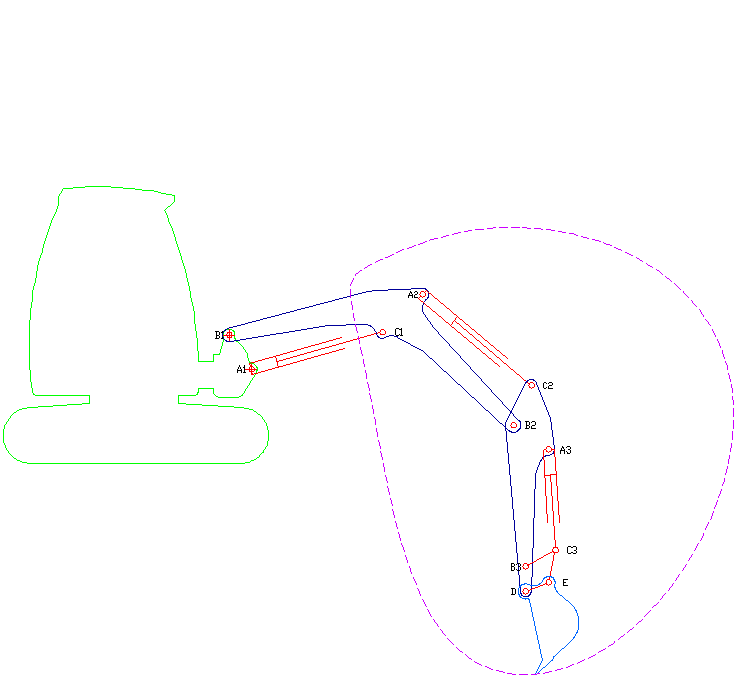
Excavator
Excavators are heavy equipment (construction), heavy construction equipment primarily consisting of a backhoe, boom, dipper (or stick), Bucket (machine part), bucket, and cab on a rotating platform known as the "house". The modern excavator's house sits atop an undercarriage with Caterpillar track, tracks or wheels, being an evolution of the steam shovel (which itself evolved into the power shovel when steam was replaced by diesel and electric power). All excavation-related movement and functions of a hydraulic excavator are accomplished through the use of hydraulic fluid, with hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic motors, which replaced winches, chains, and steel ropes. Another principle change was the direction of the digging action, with modern excavators pulling their buckets toward them like a dragline rather than pushing them away to fill them the way the first powered shovels did. Terminology Excavators are also called diggers, scoopers, mechanical shovels, or 360-degree ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Water Vole
The European water vole (''Arvicola amphibius'') or northern water vole is a semi-aquatic rodent. It is often informally called the water rat, though it only superficially resembles a true rat. Water voles have rounder noses than rats, deep brown fur, chubby faces and short fuzzy ears; unlike rats their tails, paws and ears are covered with hair. In the wild, on average, water voles only live about five months. Maximum longevity in captivity is two and a half years. Appearance Water voles reach in length, plus a tail which is about half the length of the body. Weights reported for adults are variable. It is possible for large, optimal adults to weigh as much as However, these are peak weights. Elsewhere, the mean body mass has been reported as , although this figure includes immature water voles. The minimum weight to successfully breed as well as to survive winter is reportedly in females and in males.Yavuz, Güliz, Ercüment Çolak, and Teoman Kankılıç. ''Investiga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole (animal)
Moles are small, fossorial, subterranean mammals. They have cylindrical bodies, velvety fur, very small, inconspicuous eyes and ears, reduced hindlimbs, and short, powerful forelimbs with large paws adapted for digging. The word "mole" most commonly refers to many species in the family Talpidae (which are named after the Latin word for mole, ''talpa''). True moles are found in most parts of North America, Europe (except for Ireland) and Asia. Other mammals referred to as moles include the African Golden mole, golden moles and the Australian Marsupial mole, marsupial moles, which have a similar ecology and lifestyle to true moles but are unrelated. Moles may be viewed as pests to gardeners, but they provide positive contributions to soil, gardens, and ecosystems, including soil aeration, feeding on slugs and small creatures that eat plant roots, and providing prey for other wildlife. They eat earthworms and other small invertebrates in the soil. Terminology In Middle English, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees (also known as dikes) are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. The word ''dam'' can be traced back to Middle English, and before that, from Middle Dutch, as seen in the names of many old cities, such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam. Ancient dams were built in Mesopotamia and the Middle East for water control. The earliest known dam is the Jawa Dam in Jordan, dating to 3,000 BC. Egyptians also bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puddle (other)
A puddle is a small accumulation of liquid on a surface. Puddle or Puddles may also refer to: * Puddle, Cornwall, hamlet in England * ''Puddle'' (video game) * Puddle (M. C. Escher), a woodcut by M. C. Escher * Weld puddle, a crucial part of the welding process * In rowing, an oval patch of disturbed water indicative of rowing skill * Puddle clay, a type of waterproof cement * Puddle of Mudd, an American post-grunge band * The Puddle, the New Zealand music group * Puddles the Clown, the stage name of Mike Geier, and the associated band Puddles Pity Party * Puddling (agriculture), wet tillage of rice paddies to prepare them for rice planting * Puddling (biology), the process by which butterflies extract nutrients from damp surfaces * Puddling (civil engineering), a method for producing waterproof puddle or lining an existing area with puddle clay * Puddling (metallurgy), an obsolete method for purifying pig iron * Puddling furnace Puddling is the process of converting pig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |