|
Excavator
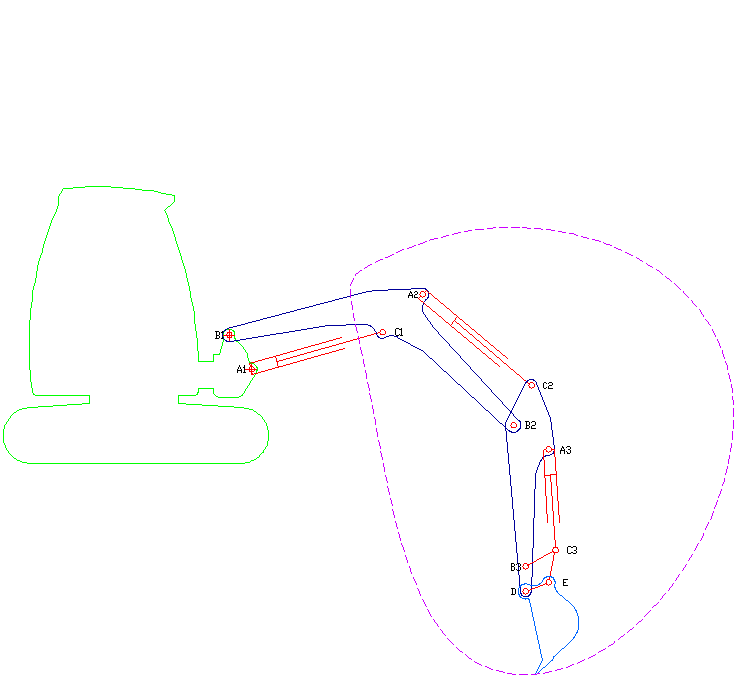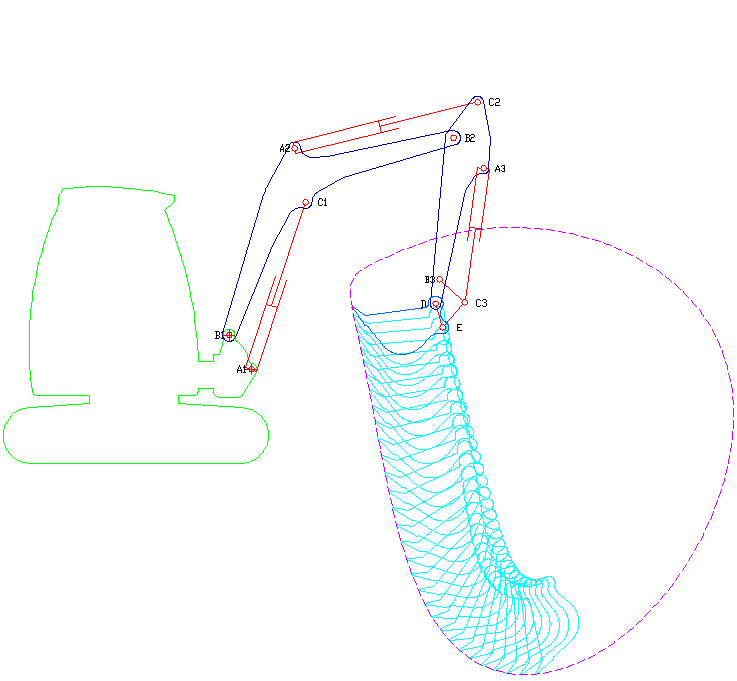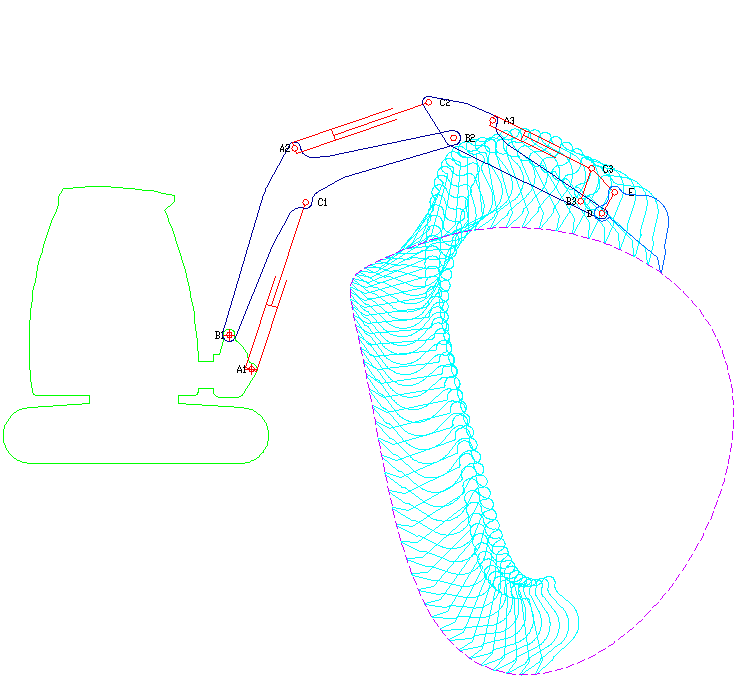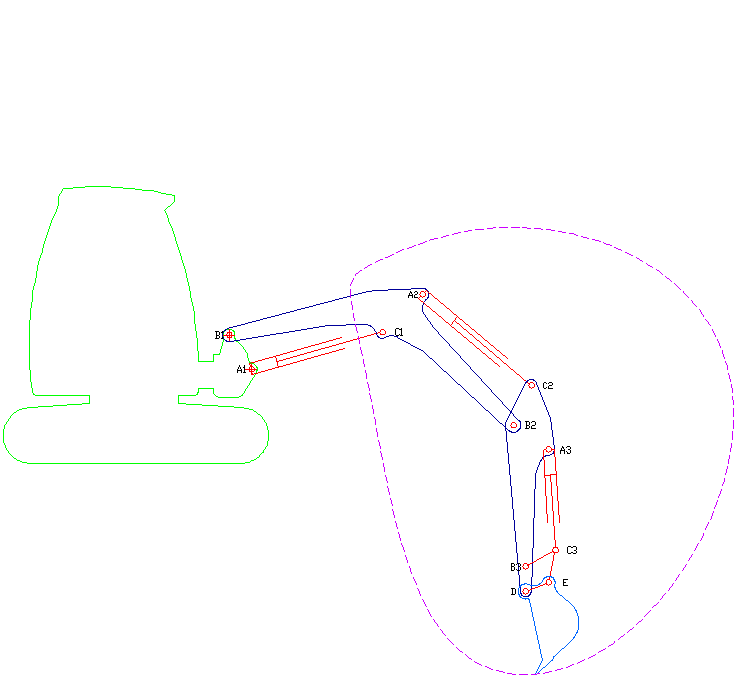
Excavators are heavy equipment (construction), heavy construction equipment primarily consisting of a backhoe, boom, dipper (or stick), Bucket (machine part), bucket, and cab on a rotating platform known as the "house". The modern excavator's house sits atop an undercarriage with Caterpillar track, tracks or wheels, being an evolution of the steam shovel (which itself evolved into the power shovel when steam was replaced by diesel and electric power). All excavation-related movement and functions of a hydraulic excavator are accomplished through the use of hydraulic fluid, with hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic motors, which replaced winches, chains, and steel ropes. Another principle change was the direction of the digging action, with modern excavators pulling their buckets toward them like a dragline rather than pushing them away to fill them the way the first powered shovels did. Terminology Excavators are also called diggers, scoopers, mechanical shovels, or 360-degree ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Shovel
A steam shovel is a large steam engine, steam-powered excavating machine designed for lifting and moving material such as Rock (geology), rock and soil. It is the earliest type of power shovel or excavator. Steam shovels played a major role in public works in the 19th and early 20th century, being key to the construction of railroads and the Panama Canal. The development of simpler, cheaper Diesel fuel, diesel, gasoline and Electricity, electric Power shovel, shovels caused steam shovels to fall out of favor in the 1930s. History Origins and development Grimshaw of Boulton & Watt devised the first steam-powered excavator in 1796. In 1833 William Brunton patented another steam-powered excavator which he provided further details on in 1836. The steam shovel was invented by William Otis, who received a patent for his design in 1839. The first machines were known as 'partial-swing', since the boom could not rotate through 360 degrees. They were built on a railway chassis, on whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydro Excavation
A suction excavator, or vacuum excavator, is a construction vehicle that removes heavy debris or other materials from a hole on land using vacuuming. Suction excavators are meant to be less destructive than regular excavators. The suction excavator uses suction fans for the airflow to suck up the material that is then transported into the holding tank. Hydro excavation, a type of suction excavator using high-pressure water jets, is sometimes referred to as ''daylighting'', as the underground utilities are exposed to daylight during the process. Some suction excavators also use an air filter. History Since 1993, RSP UK Suction Excavators Ltd. has produced suction structures mounted onto two, three, and four-axle vehicles, stationary suction units, and custom-made machines. Pacific Tek, also founded in 1993, has created the Angled Vacuum Excavator Tank (1997) and the 180° Swivel Mount Valve Operator (1999). In 1998, the Mobile Tiefbau Saugsysteme produced another type of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backhoe
A backhoe is a type of excavating equipment, or excavator, consisting of a digging bucket on the end of a two-part articulated arm. It is typically mounted on the back of a tractor or loader (equipment), front loader, the latter forming a "backhoe loader" (a US term, but known as a "JCB (heavy equipment manufacturer), JCB" in Ireland and the UK). The section of the arm closest to the vehicle is known as the wikt:boom#Noun 2, boom, while the section that carries the bucket is known as the :wikt:dipper#Noun, dipper (or dipper-stick), both terms derived from steam shovels. The boom, which is the long piece of the backhoe arm attached to the tractor through a pivot called the king-post, is located closest to the cab. It allows the arm to pivot left and right, typically through a range of 180 to 200 degrees, and also enables lifting and lowering movements. Description The term "backhoe" refers to the action of the bucket, not its location on the vehicle. That is, a backhoe digs by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Breaker
A breaker is a powerful percussion hammer fitted to an excavator for demolishing hard (rock or concrete) structures. It is powered by an auxiliary hydraulic system from the excavator, which is fitted with a foot-operated valve for this purpose. Additionally, demolition crews employ the hoe ram for jobs too large for jackhammering or areas where blasting is not possible due to safety or environmental issues. Breakers are often referred to as "hammers", "peckers", "hoe rams" or "hoe rammers". These terms are popular and commonly used amongst construction/demolition workers. The first hydraulic breaker, Hydraulikhammer HM 400, was invented in 1967 by German company Krupp (today German company Atlas Copco) in Essen. Notable manufacturers See also * Excavator * Particulates Particulate matter (PM) or particulates are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspension (chemistry), suspended in the atmosphere of Earth, air. An ''aerosol'' is a mixture of particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Equipment (construction)
Heavy equipment, heavy machinery, earthmovers, construction vehicles, or construction equipment, refers to heavy-duty vehicles specially designed to execute construction tasks, most frequently involving earthwork operations or other large construction tasks. ''Heavy equipment'' usually comprises five equipment systems: the implement, traction, structure, power train, and control/information. Heavy equipment has been used since at least the 1st century BC, when the ancient Roman engineer Vitruvius described a crane powered by human or animal labor in ''De architectura''. Heavy equipment functions through the mechanical advantage of a simple machine that multiplies the ratio between input force applied and force exerted, easing and speeding tasks which often could otherwise take hundreds of people and many weeks' labor. Some such equipment uses hydraulic drives as a primary source of motion. The word plant, in this context, has come to mean any type of industrial equipm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dredging
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing dams, dikes, and other controls for streams and shorelines; and recovering valuable mineral deposits or marine life having commercial value. In all but a few situations the excavation is undertaken by a specialist floating plant, known as a dredger. Usually the main objectives of dredging is to recover material of value, or to create a greater depth of water. Dredging systems can either be shore-based, brought to a location based on barges, or built into purpose-built vessels. Dredging can have environmental impacts: it can disturb marine sediments, creating dredge plumes which can lead to both short- and long-term water pollution, damage or destroy seabed ecosystems, and release legacy human-sourced toxins captured in the sediment. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bucket (machine Part)
A bucket (also called a scoop to qualify shallower designs of tools) is a specialized container attached to a machine, as compared to a bucket adapted for manual use by a human being. It is a bulk material handling component. The bucket has an inner volume as compared to other types of machine attachments like blades or shovels. The bucket could be attached to the lifting hook of a crane, at the end of the arm of an excavating machine, to the wires of a dragline excavator, to the arms of a power shovel or a tractor equipped with a backhoe loader or to a loader, or to a dredge. The name "bucket" may have been coined from buckets used in water wheels, or used in water turbines or in similar-looking devices. Purposes Buckets in mechanical engineering can have a distinct quality from the traditional bucket (pail) whose purpose is to contain things. Larger versions of this type of bucket equip bucket trucks to contain human beings, buckets in water-hauling systems in mines or, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Shovel
A power shovel, also known as a motor shovel, stripping shovel, front shovel, mining shovel or rope shovel, is a bucket-equipped machine usually powered by steam, diesel fuel, gasoline or electricity and used for digging and loading earth or fragmented rock and for mineral extraction. Power shovels are a type of rope/cable excavator, where the digging arm is controlled and powered by winches and steel ropes, rather than hydraulics like in the modern hydraulic excavators. Basic parts of a power shovel include the track system, cabin, cables, rack, stick, boom foot-pin, saddle block, boom, boom point sheaves and bucket. The size of bucket varies from 0.73 to 53 cubic meters. Design Power shovels normally consist of a revolving deck with a power plant, drive and control mechanisms, usually a counterweight, and a front attachment, such as a crane ("boom") which supports a handle ("dipper" or "dipper stick") with a digger (" bucket") at the end. The term "dipper" is also sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demolition
Demolition (also known as razing and wrecking) is the science and engineering in safely and efficiently tearing down buildings and other artificial structures. Demolition contrasts with deconstruction (building), deconstruction, which involves taking a building apart while carefully preserving valuable elements for reuse purposes. For small buildings, such as houses, that are only two or three stories high, demolition is a rather simple process. The building is pulled down either manually or mechanically using large hydraulic equipment: elevated work platforms, cranes, excavators or bulldozers. Larger buildings may require the use of a wrecking ball, a heavy weight on a cable that is swung by a Crane (machine), crane into the side of the buildings. Wrecking balls are especially effective against masonry, but are less easily controlled and often less efficient than other methods. Newer methods may use rotational hydraulic shears and silenced rockbreakers attached to excavat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow Blower
A snow blower or snowblower or snow thrower is a machine for removing snow from an area where it is problematic, such as a driveway, sidewalk, roadway, railroad track, ice rink, or runway. The commonly used term "snow blower" is a misnomer, as the snow is moved using an auger or impeller instead of being blown (by air). It can use either electric power (line power or battery) or a gasoline or diesel engine to throw snow to another location or into a truck to be hauled away. This is in contrast with the action of snow plows, which push snow to the front or side. Typically, the snow is discharged to one side, but most snow throwers have a movable chute that can direct snow across the full 180 degrees of motion in front of the appliance. Snow blowers range from the very small, capable of removing only a few inches (a few more cm) of light snow in an path, to the very large, mounted onto heavy-duty winter service vehicles and capable of moving wide, or wider, swaths of heavy s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caterpillar Track
Continuous track or tracked treads are a system of vehicle propulsion used in tracked vehicles, running on a continuous band of treads or track plates driven by two or more wheels. The large surface area of the tracks distributes the weight of the vehicle better than steel or rubber tyres on an equivalent vehicle, enabling continuous tracked vehicles to traverse soft ground with less likelihood of becoming stuck due to sinking. Modern continuous tracks can be made with soft belts of synthetic rubber, reinforced with steel wires, in the case of lighter agricultural machinery. The more common classical type is a solid chain track made of steel plates (with or without rubber pads), also called caterpillar tread or tank tread, which is preferred for robust and heavy construction vehicles and military vehicles. The prominent treads of the metal plates are both hard-wearing and damage resistant, especially in comparison to rubber tyres. The aggressive treads of the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |