|
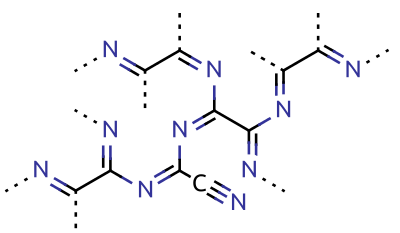
Pseudohalogen
Pseudohalogens are polyatomic analogues of halogens, whose chemistry, resembling that of the true halogens, allows them to substitute for halogens in several classes of chemical compounds. Pseudohalogens occur in pseudohalogen molecules, inorganic molecules of the general forms ''Ps''–''Ps'' or ''Ps''–X (where ''Ps'' is a pseudohalogen group), such as cyanogen; pseudohalide anions, such as cyanide ion; inorganic acids, such as hydrogen cyanide; as ligands in coordination complexes, such as ferricyanide; and as functional groups in organic molecules, such as the nitrile group. Well-known pseudohalogen functional groups include cyanide, cyanate, thiocyanate, and azide. Common pseudohalogens and their nomenclature Many pseudohalogens are known by specialized common names according to where they occur in a compound. Well-known ones include (the true halogen chlorine is listed for comparison): is considered to be a pseudohalogen ion due to its disproportionation reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanogen
Cyanogen is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula . Its structure is . The simplest stable carbon nitride, it is a Transparency and translucency, colorless and highly toxic gas with a pungency, pungent odor. The molecule is a pseudohalogen. Cyanogen molecules are linear molecular geometry, linear, and consist of two CN groups ‒ analogous to diatomic halogen molecules, such as chlorine, Cl, but far less oxidizing. The two cyanide, cyano groups are bonded together at their carbon atoms, though other isomers have been detected. The name is also used for the CN radical, and hence is used for compounds such as cyanogen bromide () (but see also ''Cyano radical''). When burned at increased pressure with oxygen, it is possible to get a blue tinted flame, the temperature of which is about 4800°C (a higher temperature is possible with ozone). It is as such regarded as the gas with the second highest temperature of burning (after dicyanoacetylene). Cyanogen is the anhy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidizing agent, oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Electronegativity#Pauling electronegativity, Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval Alchemy, alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride Salt (chemistry), salts like ammonium chloride (sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride (common salt), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and . However, the nature of fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiocyanate
Thiocyanates are salts containing the thiocyanate anion (also known as rhodanide or rhodanate). is the conjugate base of thiocyanic acid. Common salts include the colourless salts potassium thiocyanate and sodium thiocyanate. Mercury(II) thiocyanate was formerly used in pyrotechnics. Thiocyanate is analogous to the cyanate ion, , wherein oxygen is replaced by sulfur. is one of the pseudohalides, due to the similarity of its reactions to that of halide ions. Thiocyanate used to be known as rhodanide (from a Greek word for rose) because of the red colour of its complexes with iron. Thiocyanate is produced by the reaction of elemental sulfur or thiosulfate with cyanide: : : The second reaction is catalyzed by thiosulfate sulfurtransferase, a hepatic mitochondrial enzyme, and by other sulfur transferases, which together are responsible for around 80% of cyanide metabolism in the body. Oxidation of thiocyanate inevitably produces hydrogen sulfate. The other product depe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halogens
The halogens () are a group (periodic table), group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related chemical element, elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would exclude tennessine as its chemistry is unknown and is theoretically expected to be more like that of gallium. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is known as group 17. The word "halogen" means "salt former" or "salt maker". When halogens react with metals, they produce a wide range of Salt (chemistry), salts, including calcium fluoride, sodium chloride (common table salt), silver bromide and potassium iodide. The group of halogens is the only Group (periodic table), periodic table group that contains elements in three of the main State of matter, states of matter at standard temperature and pressure, though not far above room temperature the same becomes true of groups alkali metals, 1 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen (H−), a hydrogen ion with two electrons. In modern usage, this is typically only used for ionic bonds, but it is sometimes (and has been more frequently in the past) applied to all chemical compound, compounds containing covalent bond, covalently bound H atoms. In this broad and potentially archaic sense, water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of nitrogen, etc. In covalent compounds, it implies hydrogen is attached to a less electronegative chemical element, element. In such cases, the H centre has nucleophilic character, which contrasts with the protic character of acids. The hydride anion is very rarely observed. Almost all of the elements form Binary compounds of hydrogen, binary compounds with hydrogen, the exceptions being helium, He, neon, Ne, argon, Ar, krypton, Kr, promethium, Pm, osmium, Os, iridium, Ir, radon, Rn, francium, Fr, and radium, Ra. exotic atom#exotic molecules, Exotic molecules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organochloride
Organochlorine chemistry is concerned with the properties of organochlorine compounds, or organochlorides, organic compounds that contain one or more carbon–chlorine bonds. The chloroalkane class (alkanes with one or more hydrogens substituted by chlorine) includes common examples. The wide structural variety and divergent chemical properties of organochlorides lead to a broad range of names, applications, and properties. Organochlorine compounds have wide use in many applications, though some are of profound environmental concern, with TCDD being one of the most notorious. Organochlorides such as trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, dichloromethane and chloroform are commonly used as solvents and are referred to as "chlorinated solvents". Physical and chemical properties Chlorination modifies the physical properties of hydrocarbons in several ways. These compounds are typically denser than water due to the higher atomic weight of chlorine versus hydrogen. They have hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) Preferred IUPAC name, recommends using the name "alkene" only for Open-chain compound, acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for Cyclic compound, cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with ''n'' being a >1 natural number (which is two hydrogens less than the corresponding alkane). When ''n'' is four or more, isomers are possible, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Chloride
The Chemical compound, compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry. Hydrochloric acid, the aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride, is also commonly given the formula HCl. Reactions Hydrogen chloride is a diatomic molecule, consisting of a hydrogen atom H and a chlorine atom Cl connected by a Polar-covalent bond, polar covalent bond. The chlorine atom is much more Electronegativity, electronegative than the hydrogen atom, which makes this bond polar. Consequently, the molecule has a large Molecular dipole moment, dipole moment with a negative partial charge (δ−) at the chlorine atom and a positive partial charge (δ+) at the hydrogen atom. In part because of its high polarity, HCl is very soluble in water (and in other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 118 picometers (for C2H2) is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (132 pm, for C2H4) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |