|
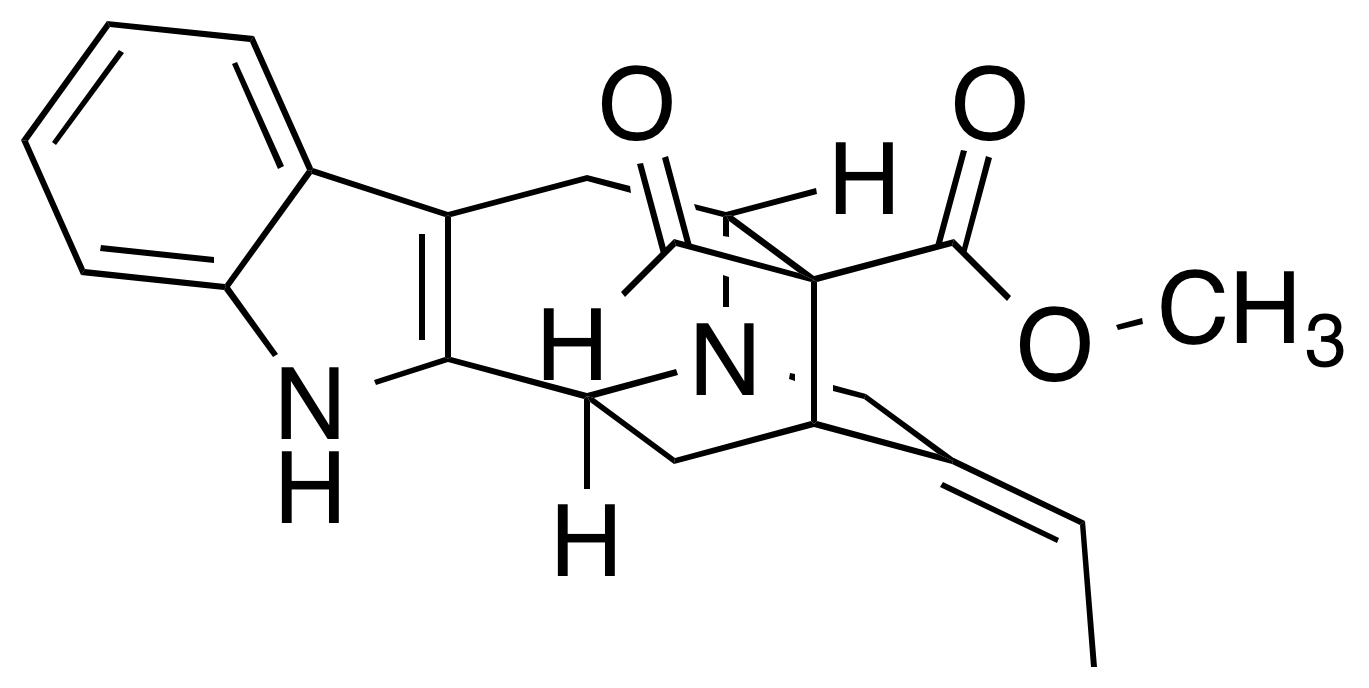
Polyneuridine-aldehyde Esterase
The enzyme polyneuridine-aldehyde esterase (EC 3.1.1.78) catalysis, catalyzes the following reaction: :polyneuridine aldehyde + H2O \rightleftharpoons 16-epivellosimine + CO2 + methanol This enzyme participates in indole alkaloid biosynthesis. Nomenclature This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on carboxylic ester bonds. The List of enzymes, systematic name is polyneuridine aldehyde hydrolase (decarboxylating). Other names in common use include: * polyneuridine aldehyde esterase * PNAE Homologues This enzyme is found in various forms in plant species such as ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', ''Glycine max'' (soybean), ''Vitis vinifera'' (wine grape), and ''Solanum lycopersicum'' (tomato) among others. Polyneuridine-aldehyde esterase also appears in select bacteria including ''Enterobacter cloacae''. Structure The secondary structure of this enzyme consists mainly of alpha helices, α helices. In its native form, this enzyme has a tertiary st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysis
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indole Alkaloid
Indole alkaloids are a class of alkaloids containing a structural moiety of indole; many indole alkaloids also include isoprene groups and are thus called terpene indole or secologanin tryptamine alkaloids. Containing more than 4100 known different compounds, it is one of the largest classes of alkaloids. Many of them possess significant physiological activity and some of them are used in medicine. The amino acid tryptophan is the biochemical precursor of indole alkaloids. History The action of some indole alkaloids has been known for ages. Aztecs used the psilocybin mushrooms which contain alkaloids psilocybin and psilocin. The flowering plant ''Rauvolfia serpentina'' which contains reserpine was a common medicine in India around 1000 BC. Africans used the roots of the perennial rainforest shrub Iboga, which contain ibogaine, as a stimulant. An infusion of Calabar bean seeds was given to people accused of crime in Nigeria: its rejection by stomach was regarded as a sign of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha/beta Hydrolase Fold
The alpha/beta hydrolase superfamily is a superfamily of hydrolytic enzymes of widely differing phylogenetic origin and catalytic function that share a common fold. The core of each enzyme is an alpha/beta-sheet (rather than a barrel), containing 8 beta strands connected by 6 alpha helices. The enzymes are believed to have diverged from a common ancestor, retaining little obvious sequence similarity, but preserving the arrangement of the catalytic residues. All have a catalytic triad, the elements of which are borne on loops, which are the best-conserved structural features of the fold. The alpha/beta hydrolase fold includes proteases, lipases, peroxidases, esterases, epoxide hydrolases and dehalogenases. Database The ESTHER database provides a large collection of information about this superfamily of proteins. Subfamilies * 3-oxoadipate enol-lactonase Human proteins containing this domain ABHD10; ABHD11; ABHD12; ABHD12B; ABHD13; ABHD2; ABHD3; ABHD4; A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Triad
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acid residues that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, aminoacylase, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An acid-base (chemistry), base-nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the Substrate (chemistry), substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to release the Product (chemistry), product and regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine, but occasionally threonine or even selenocysteine. The Protein tertiary structure, 3D structure of the enzyme brings together the triad residues in a precise orientation, even though they may be far apart in the sequence (Protein primary structure, primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carboxylation, the addition of CO2 to a compound. Enzymes that catalyze decarboxylations are called decarboxylases or, the more formal term, carboxy-lyases (Enzyme Commission number, EC number 4.1.1). In organic chemistry The term "decarboxylation" usually means replacement of a carboxyl group () with a hydrogen atom: : Decarboxylation is one of the oldest known organic reactions. It is one of the processes assumed to accompany pyrolysis and destructive distillation. Overall, decarboxylation depends upon stability of the carbanion synthon , although the anion may not be a true chemical intermediate. Typically, carboxylic acids decarboxylate slowly, but carboxylic acids with an α el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g., alkyl, alkenyl, aryl), or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They often have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid () is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources of the cation, and this simplification is used pervasively in organic chemistry. For exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of Biomolecule, biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolase
In biochemistry, hydrolases constitute a class of enzymes that commonly function as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond: :\ce \quad \xrightarrowtext\quad \ce This typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases. Esterases cleave ester bonds in lipids and phosphatases cleave phosphate groups off molecules. An example of crucial esterase is acetylcholine esterase, which assists in transforming the neuron impulse into the acetate group after the hydrolase breaks the acetylcholine into choline and acetic acid. Acetic acid is an important metabolite in the body and a critical intermediate for other reactions such as glycolysis. Lipases hydrolyze glycerides. Glycosidases cleave sugar molecules off carbohydrates and peptidases hydrolyze peptide bonds. Nucleosidases hydrolyze the bonds of nucleo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |