|
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)''P''2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)''P''2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of important signaling proteins. PIP2 also forms lipid clusters that sort proteins. PIP2 is formed primarily by the type I phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinases from PI(4)P. In metazoans, PIP2 can also be formed by type II phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate 4-kinases from PI(5)P. The fatty acids of PIP2 are variable in different species and tissues, but the most common fatty acids are stearic in position 1 and arachidonic in 2. Signaling pathways PIP2 is a part of many cellular signaling pathways, including PIP2 cycle, PI3K signalling, and PI5P metabolism. Recently, it has been found in the nucleus with unknown function. Functions Cytoskeleton dynamics near membranes PIP2 regulates the organization, polymerization, and bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipid
Phospholipids are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typically have omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA integrated as part of the phospholipid molecule. The phosphate group can be modified with simple organic molecules such as choline, ethanolamine or serine. Phospholipids are a key component of all cell membranes. They can form lipid bilayers because of their amphiphilic characteristic. In eukaryotes, cell membranes also contain another class of lipid, sterol, interspersed among the phospholipids. The combination provides fluidity in two dimensions combined with mechanical strength against rupture. Purified phospholipids are produced commercially and have found applications in nanotechnology and materials science. The first phospholipid identified in 1847 as such in biological tissues w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
α1 Adrenergic Receptor
alpha-1 (α1) adrenergic are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) associated with the Gq heterotrimeric G protein. α1-adrenergic receptors are subdivided into three highly homologous subtypes, i.e., α1A-, α1B-, and α1D-adrenergic receptor subtypes. There is no α1C receptor. At one time, there was a subtype known as α1C, but it was found to be identical to the previously discovered α1A receptor subtype. To avoid confusion, naming was continued with the letter D. Catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) signal through the α1-adrenergic receptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems. The crystal structure of the α1B-adrenergic receptor subtype has been determined in complex with the inverse agonist (+)-cyclazosin. Effects The α1-adrenergic receptor has several general functions in common with the α2-adrenergic receptor, but also has specific effects of its own. α1-receptors primarily mediate smooth muscle contraction, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone-releasing Hormone
Growth may refer to: Biology * Auxology, the study of all aspects of human physical growth * Bacterial growth *Cell growth *Growth hormone, a peptide hormone that stimulates growth *Human development (biology) *Plant growth *Secondary growth, growth that thickens woody plants *A tumor or other such neoplasm Economics * Economic growth, the increase in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services * Growth investing, a style of investment strategy focused on capital appreciation Mathematics * Exponential growth, also called geometric growth * Hyperbolic growth * Linear growth, refers to two distinct but related notions * Logistic growth, characterized as an S curve Social science * Developmental psychology * Erikson's stages of psychosocial development * Human development (humanity) * Personal development * Population growth Other uses * ''Growth'' (film), a 2010 American horror film * Izaugsme (''Growth''), a Latvian political party * ''Grown'' (album), by 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Channel
Sodium channels are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na+) through a cell (biology), cell's cell membrane, membrane. They belong to the Cation channel superfamily, superfamily of cation channels. Classification They are classified into 2 types: Function In excitable cells such as neurons, muscle, myocytes, and certain types of glia, sodium channels are responsible for the Action potential#Stimulation and rising phase, rising phase of action potentials. These channels go through three different states called resting, active and inactive states. Even though the resting and inactive states would not allow the ions to flow through the channels the difference exists with respect to their structural conformation. Selectivity Sodium channels are highly selective for the transport of ions across cell membranes. The high selectivity with respect to the sodium ion is achieved in many different ways. All involve encapsulation of the sodium ion in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (abbreviated Btk or BTK), also known as tyrosine-protein kinase BTK, is a tyrosine kinase that is encoded by the ''BTK'' gene in humans. BTK plays a crucial role in B cell development. Structure BTK contains five different protein interaction domains. These domains include an amino terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, a proline-rich TEC homology (TH) domain, SRC homology (SH) domains SH2 and SH3, as well as a protein kinase domain with tyrosine phosphorylation activity. Part of the TH domain is folded against the PH domain while the rest is intrinsically disordered. Function BTK plays a crucial role in B cell development as it is required for transmitting signals from the pre-B cell receptor that forms after successful immunoglobulin heavy chain rearrangement. It also has a role in mast cell activation through the high-affinity IgE receptor. BTK contains a PH domain that binds phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3). PIP3 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDPK1
In the field of biochemistry, PDPK1 refers to the protein 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1, an enzyme which is encoded by the ''PDPK1'' gene in humans. It is implicated in the development and progression of melanomas. Function PDPK1 is a master kinase, which is crucial for the activation of AKT/PKB and many other AGC kinases including PKC, S6K, SGK. An important role for PDPK1 is in the signaling pathways activated by several growth factors and hormones including insulin signaling. Mice lacking PDPK1 die during early embryonic development, indicating that this enzyme is critical for transmitting the growth-promoting signals necessary for normal mammalian development. Mice that are deficient in PDPK1 have a ≈40% decrease in body mass, mild glucose intolerance, and are resistant to cancer brought about by hyperactivation of the PI3K pathway (PTEN+/-). Plant PDK1 plays an important role in regulating PIN-mediated auxin transport, and is thus involved in v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase B
Protein kinase B (PKB), also known as Akt, is the collective name of a set of three serine/threonine-specific protein kinases that play key roles in multiple cellular processes such as glucose metabolism, apoptosis, cell proliferation, transcription (biology), transcription, and cell migration. Family members - Isoforms There are three different genes that encode isoforms of protein kinase B. These three genes are referred to as ''AKT1'', ''AKT2'', and ''AKT3'' and encode the RAC alpha, beta, and gamma serine/threonine protein kinases respectively. The terms PKB and Akt may refer to the products of all three genes collectively, but sometimes are used to refer to PKB alpha and Akt1 alone. Akt1 is involved in cellular survival pathways, by inhibiting Apoptosis, apoptotic processes. Akt1 is also able to induce protein synthesis pathways, and is therefore a key signaling protein in the cellular pathways that lead to skeletal muscle hypertrophy and general tissue growth. A mouse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)''P''3), abbreviated PIP3, is the product of the class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases' (PI 3-kinases) phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2). It is a phospholipid that resides on the plasma membrane. Discovery In 1988, Lewis C. Cantley published a paper describing the discovery of a novel type of phosphoinositide kinase with the unprecedented ability to phosphorylate the 3' position of the inositol ring resulting in the formation of phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P). Working independently, Alexis Traynor-Kaplan and coworkers published a paper demonstrating that a novel lipid, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5 trisphosphate (PIP3) occurs naturally in human neutrophils with levels that increased rapidly following physiologic stimulation with chemotactic peptide. Subsequent studies demonstrated that ''in vivo'' the enzyme originally identified by Cantley's group prefers PtdIns(4,5)P2 as a substrate, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class I PI 3-kinases
Class I PI 3-kinases are a subgroup of the enzyme family, phosphoinositide 3-kinase that possess a common protein domain structure, substrate specificity, and method of activation. Class I PI 3-kinases are further divided into two subclasses, class IA PI 3-kinases and class IB PI 3-kinases. Class IA PI 3-kinases Class IA PI 3-kinases are activated by receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). There are three catalytic subunits that are classified as class IA PI 3-kinases: *p110α The phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase, catalytic subunit alpha (the HUGO-approved official symbol = PIK3CA; HGNC ID, HGNC:8975), also called p110α protein, is a class I PI 3-kinase catalytic subunit. The human p110α protein is en ... * p110β * p110δ There are currently five regulatory subunits that are known to associate with class IA PI 3-kinases catalytic subunits: * p85α and p85β * p55α and p55γ * p50α Class IB PI 3-kinases Class IB PI 3-kinases are activated by G-protein-coup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for "little net". It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. There are two types of ER that share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of Cell (biology), cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER dependin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase C
In cell biology, protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine amino acid residues on these proteins, or a member of this family. PKC enzymes in turn are activated by signals such as increases in the concentration of diacylglycerol (DAG) or calcium ions (Ca2+). Hence PKC enzymes play important roles in several signal transduction cascades. In biochemistry, the PKC family consists of fifteen isozymes in humans. They are divided into three subfamilies, based on their second messenger requirements: conventional (or classical), novel, and atypical. Conventional (c)PKCs contain the isoforms α, βI, βII, and γ. These require Ca2+, DAG, and a phospholipid such as phosphatidylserine for activation. Novel (n)PKCs include the δ, ε, η, and θ isoforms, and require DAG, but do not require Ca2+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
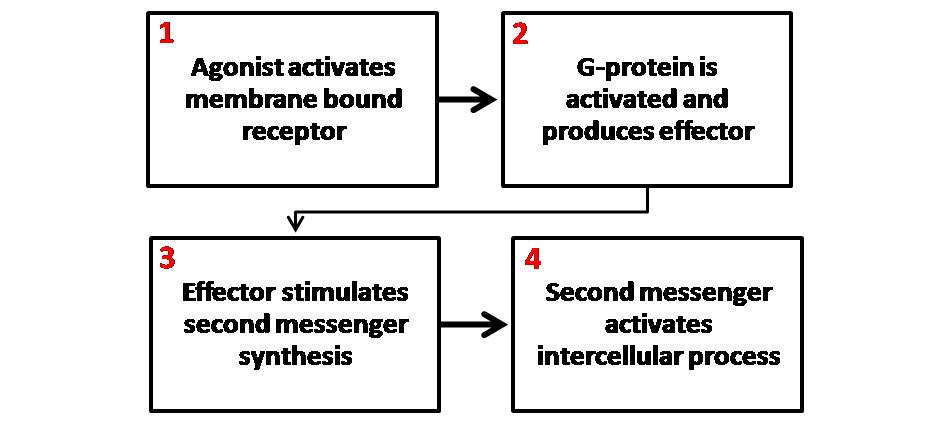
Second Messenger System
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form of cell signaling, encompassing both first messengers and second messengers, are classified as autocrine signaling, autocrine, juxtacrine signalling, juxtacrine, paracrine signaling, paracrine, and endocrine system, endocrine depending on the range of the signal.) Second messengers trigger physiological changes at cellular level such as Cell proliferation, proliferation, cellular differentiation, differentiation, migration, survival, apoptosis and depolarization. They are one of the triggers of intracellular signal transduction cascades. Examples of second messenger molecules include cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cyclic GMP, inositol triphosphate, diacylglycerol, and calcium. First messengers are extracellular factors, often hormones or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |