|
Phenanthrene
Phenanthrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) with formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a colorless, crystal-like solid, but can also appear yellow. Phenanthrene is used to make dyes, plastics, pesticides, explosives, and drugs. It has also been used to make bile acids, cholesterol and steroids. Phenanthrene occurs naturally and also is a man-made chemical. Commonly, humans are exposed to phenanthrene through inhalation of cigarette smoke, but there are many routes of exposure. Animal studies have shown that phenanthrene is a potential carcinogen. However, according to IARC, it is not identified as a probable, possible or confirmed human carcinogen. Phenanthrene's three fused rings are angled as in the phenacenes, rather than straight as in the acenes. The compounds with a phenanthrene skeleton but with nitrogen atoms in place of CH sites are known as phenanthrolines. History and etymology Phenanthrene was discovered in coal tar in 1872 inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenanthrenequinone
Phenanthrenedione is a quinone derivative of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. It is an orange, water-insoluble solid. Laboratory synthesis and use It has been prepared by oxidation of phenanthrene with chromic acid. It is used as an artificial mediator for electron acceptor/donor in Mo/W containing formate dehydrogenase reduction of carbon dioxide to formate and vice versa. It is a better electron acceptor than the natural nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). Safety It is cytotoxic and potentially mutagenic. Phenanthrenequinone is one of many contributors to harmful particulate emissions from diesel motor vehicles. Related compounds * 1,10-Phenanthroline-5,6-dione 1,10-Phenanthroline-5,6-dione is an organic compound with the formula . It is the quinone derivative of 1,10-phenanthroline. The compound exhibits many reactions, including condensations with diamines to give quinoxalines and decarbonylation to ... References Quinones Phenanthrenes {{organic-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon
A Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is any member of a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple fused aromatic rings. Most are produced by the incomplete combustion of organic matter— by engine exhaust fumes, tobacco, incinerators, in roasted meats and cereals, or when biomass burns at lower temperatures as in forest fires. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings, and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. PAHs are uncharged, non-polar and planar. Many are colorless. Many of them are also found in fossil fuel deposits such as coal and in petroleum. Exposure to PAHs can lead to different types of cancer, to fetal development complications, and to cardiovascular issues. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are discussed as possible starting materials for abiotic syntheses of materials required by the earliest forms of life. Nomenclature and structure The terms polyaromatic hydrocarbon, or polynuclear aromatic hydro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenic Acid
Diphenic acid, also known as Dibenzoic acid, is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4CO2H)2. It is the most studied of several isomeric dicarboxylic acids of biphenyl. It is a white solid that can be prepared in the laboratory from anthranilic acid via the diazonium salt. It is the product of the microbial action on phenanthrene. The compound forms a variety of coordination polymers. It also exhibits atropisomerism. It can form an internal Organic acid anhydride, anhydride featuring a seven-membered ring fused to the two benzene rings. : Preparation Diphenic acid is prepared from anthranilic acid by diazotization, followed by reduction with copper(I). : It can also be synthesized from the oxidation of phenanthrene by peracetic acid, which is first prepared from acetic acid and 90% hydrogen peroxide: :CH3COOH + H2O2 ⇌ CH3COOOH + H2O :4 CH3COOOH + C14H10 → 4 CH3COOH + C14H10O4 Phenanthrene can also be treated with other oxidizing agents (such as hydrogen peroxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracene
Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) of formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes, as a scintillator to detect high energy particles, as production of pharmaceutical drugs. Anthracene is colorless but exhibits a blue (400–500 nm peak) fluorescence under ultraviolet radiation. History and etymology Crude anthracene (with a melting point of only 180°) was discovered in 1832 by Jean-Baptiste Dumas and Auguste Laurent who crystalized it from a fraction of coal tar later known as "anthracene oil". Since their (inaccurate) measurements showed the proportions of carbon and hydrogen of it to be the same as in naphthalene, Laurent called it ''paranaphtaline'' in his 1835 publication of the discovery, which is translated to English as paranaphthalene. Two years later, however, he decided to rename the compound to its modern name d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scintillator
A scintillator ( ) is a material that exhibits scintillation, the property of luminescence, when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate (i.e. re-emit the absorbed energy in the form of light). Sometimes, the excited state is metastable, so the relaxation back down from the excited state to lower states is delayed (necessitating anywhere from a few nanoseconds to hours depending on the material). The process then corresponds to one of two phenomena: delayed fluorescence or phosphorescence. The correspondence depends on the type of transition and hence the wavelength of the emitted optical photon. Principle of operation A scintillation detector or scintillation counter is obtained when a scintillator is coupled to an electronic light sensor such as a photomultiplier tube (PMT), photodiode, or silicon photomultiplier. PMTs absorb the light emitted by the scintillator and re-emit it in the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Oxidation
Organic reductions or organic oxidations or organic redox reactions are redox reactions that take place with organic compounds. In organic chemistry oxidations and reductions are different from ordinary redox reactions, because many reactions carry the name but do not actually involve electron transfer.March Jerry; (1985). Advanced Organic Chemistry reactions, mechanisms and structure (3rd ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, inc. Instead the relevant criterion for organic oxidation is gain of oxygen and/or loss of hydrogen.''Organic Redox Systems: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications'', Tohru Nishinaga 2016 Simple functional groups can be arranged in order of increasing oxidation state. The oxidation numbers are only an approximation: When methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide its oxidation number changes from −4 to +4. Classical reductions include alkene reduction to alkanes and classical oxidations include alcohol oxidation, oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes. In oxidation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
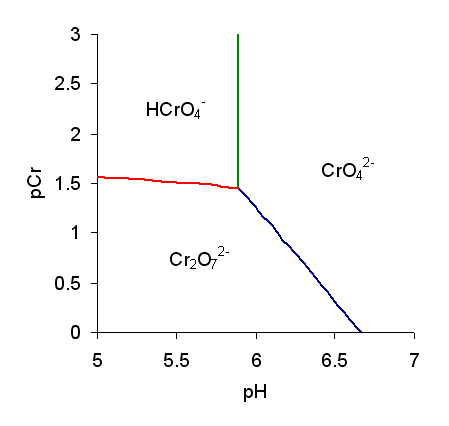
Chromic Acid
Chromic acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is also a jargon for a solution formed by the addition of sulfuric acid to aqueous solutions of dichromate. It consists at least in part of chromium trioxide. The term "chromic acid" is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixture for glass. Chromic acid may also refer to the molecular species, of which the trioxide is the anhydride. Chromic acid features chromium in an oxidation state of +6 (and a valence of VI or 6). It is a strong and corrosive oxidizing agent and a moderate carcinogen. Molecular chromic acid Molecular chromic acid, , in principle, resembles sulfuric acid, . It would ionize accordingly: : The p''K''a for the equilibrium is not well characterized. Reported values vary between about −0.8 to 1.6. The structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debye
The debye ( , ; symbol: D) is a CGS unit (a non- SI metric unit) of electric dipole momentTwo equal and opposite charges separated by some distance constitute an electric dipole. This dipole possesses an electric dipole moment whose value is given as charge times length of separation. The dipole itself is a vector whose direction coincides with the position vector of the positive charge with respect to the negative charge: : p = ''q''r. named in honour of the physicist Peter J. W. Debye. It is defined as statcoulomb-centimetres.The statcoulomb is also known as the franklin or electrostatic unit of charge. : 1 statC = 1 Fr = 1 esu = 1 cm3/2⋅g1/2⋅s−1. Historically the debye was defined as the dipole moment resulting from two charges of opposite sign but an equal magnitude of 10−10 statcoulomb10−10 statcoulomb corresponds to approximately 0.2083 units of elementary charge. (generally called e.s.u. (electrostatic unit) in ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Reduction
Organic reductions or organic oxidations or organic redox reactions are redox reactions that take place with organic compounds. In organic chemistry oxidations and reductions are different from ordinary redox reactions, because many reactions carry the name but do not actually involve electron transfer.March Jerry; (1985). Advanced Organic Chemistry reactions, mechanisms and structure (3rd ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, inc. Instead the relevant criterion for organic oxidation is gain of oxygen and/or loss of hydrogen.''Organic Redox Systems: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications'', Tohru Nishinaga 2016 Simple functional groups can be arranged in order of increasing oxidation state. The oxidation numbers are only an approximation: When methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide its oxidation number changes from −4 to +4. Classical reductions include alkene reduction to alkanes and classical oxidations include oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes. In oxidations electrons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |