|
Neural Network
A neural network is a group of interconnected units called neurons that send signals to one another. Neurons can be either biological cells or signal pathways. While individual neurons are simple, many of them together in a network can perform complex tasks. There are two main types of neural networks. *In neuroscience, a '' biological neural network'' is a physical structure found in brains and complex nervous systems – a population of nerve cells connected by synapses. *In machine learning, an '' artificial neural network'' is a mathematical model used to approximate nonlinear functions. Artificial neural networks are used to solve artificial intelligence problems. In biology In the context of biology, a neural network is a population of biological neurons chemically connected to each other by synapses. A given neuron can be connected to hundreds of thousands of synapses. Each neuron sends and receives electrochemical signals called action potentials to its conne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task (computing), tasks without explicit Machine code, instructions. Within a subdiscipline in machine learning, advances in the field of deep learning have allowed Neural network (machine learning), neural networks, a class of statistical algorithms, to surpass many previous machine learning approaches in performance. ML finds application in many fields, including natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, email filtering, agriculture, and medicine. The application of ML to business problems is known as predictive analytics. Statistics and mathematical optimisation (mathematical programming) methods comprise the foundations of machine learning. Data mining is a related field of study, focusing on exploratory data analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation Function
The activation function of a node in an artificial neural network is a function that calculates the output of the node based on its individual inputs and their weights. Nontrivial problems can be solved using only a few nodes if the activation function is ''nonlinear''. Modern activation functions include the logistic ( sigmoid) function used in the 2012 speech recognition model developed by Hinton et al; the ReLU used in the 2012 AlexNet computer vision model and in the 2015 ResNet model; and the smooth version of the ReLU, the GELU, which was used in the 2018 BERT model. Comparison of activation functions Aside from their empirical performance, activation functions also have different mathematical properties: ; Nonlinear: When the activation function is non-linear, then a two-layer neural network can be proven to be a universal function approximator. This is known as the Universal Approximation Theorem. The identity activation function does not satisfy this property. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Network (machine Learning)
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of connected units or nodes called ''artificial neurons'', which loosely model the neurons in the brain. Artificial neuron models that mimic biological neurons more closely have also been recently investigated and shown to significantly improve performance. These are connected by ''edges'', which model the synapses in the brain. Each artificial neuron receives signals from connected neurons, then processes them and sends a signal to other connected neurons. The "signal" is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs, called the ''activation function''. The strength of the signal at each connection is determined by a ''weight'', which adjusts during the learning process. Typically, neuron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
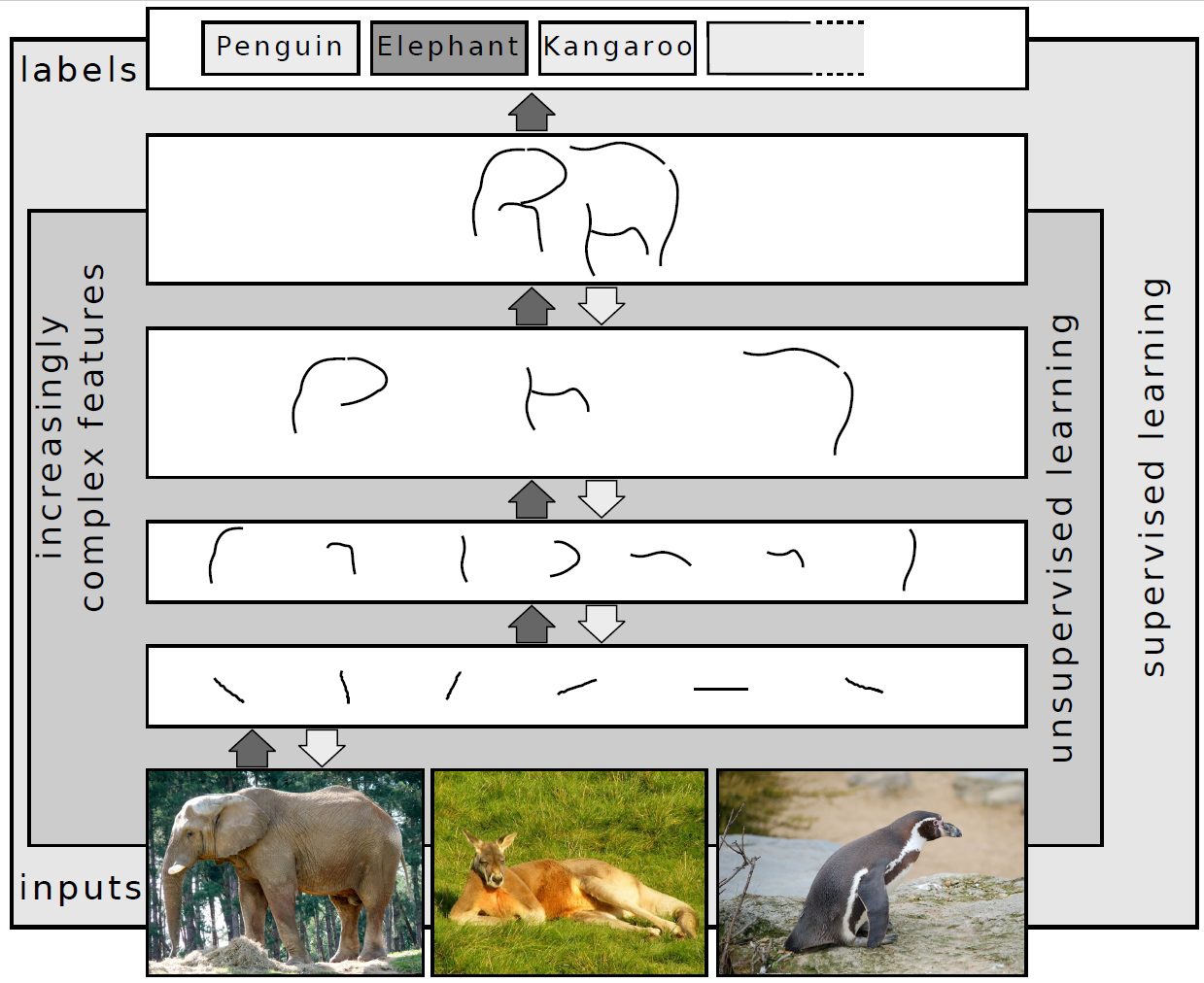
Deep Neural Network
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural network (machine learning), neural networks to perform tasks such as Statistical classification, classification, Regression analysis, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from Neuroscience, biological neuroscience and is centered around stacking Artificial neuron, artificial neurons into layers and "training" them to process data. The adjective "deep" refers to the use of multiple layers (ranging from three to several hundred or thousands) in the network. Methods used can be either Supervised learning, supervised, Semi-supervised learning, semi-supervised or Unsupervised learning, unsupervised. Some common deep learning network architectures include Fully connected network, fully connected networks, deep belief networks, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks, Generative adversarial network, generative adversarial networks, Transformer (ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to machine perception, perceive their environment and use machine learning, learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. High-profile applications of AI include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search); recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon (company), Amazon, and Netflix); virtual assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, and Amazon Alexa, Alexa); autonomous vehicles (e.g., Waymo); Generative artificial intelligence, generative and Computational creativity, creative tools (e.g., ChatGPT and AI art); and Superintelligence, superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
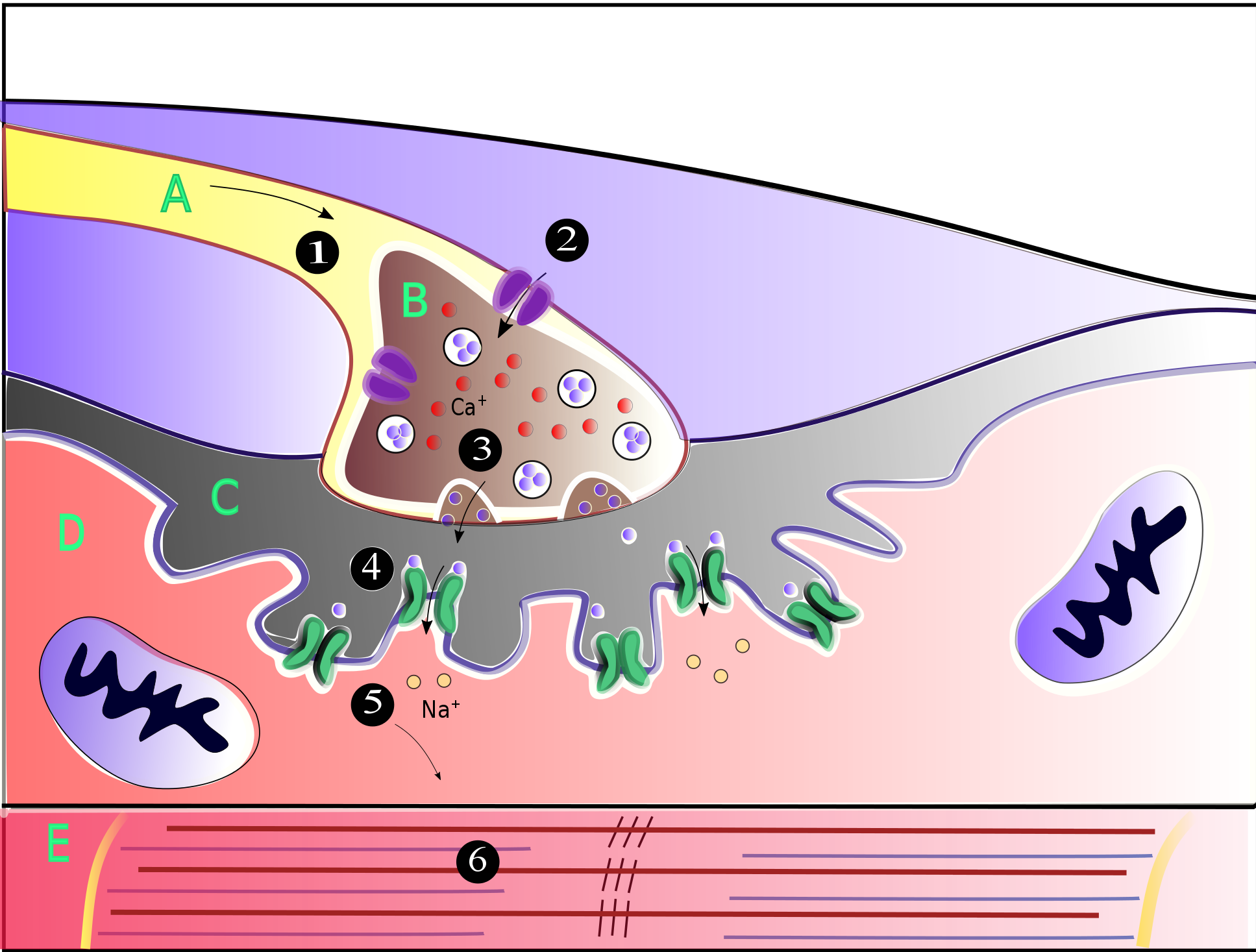
Neuromuscular Junctions
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction. Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. In the neuromuscular system, nerves from the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system are linked and work together with muscles. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-gated calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmins) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Cell
A muscle cell, also known as a myocyte, is a mature contractile Cell (biology), cell in the muscle of an animal. In humans and other vertebrates there are three types: skeletal muscle, skeletal, smooth muscle, smooth, and Cardiac muscle, cardiac (cardiomyocytes). A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with multinucleated, many nuclei and is called a ''muscle fiber''. Muscle cells develop from embryonic precursor cells called myoblasts. Skeletal muscle cells form by cell fusion, fusion of myoblasts to produce multinucleated cells (syncytium, syncytia) in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells both contain myofibrils and sarcomeres and form a striated muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle cells form the cardiac muscle in the walls of the heart chambers, and have a single central Cell nucleus, nucleus. Cardiac muscle cells are joined to neighboring cells by intercalated discs, and when joined in a visible unit they are described as a ''cardiac m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Network Example
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue first arose in wormlike organisms about 550 to 600 million years ago. In vertebrates, it consists of two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are enclosed bundles of the long fibers, or axons, that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. Nerves that transmit signals from the brain are called motor nerves (efferent), while those nerves that transmit information from the body to the CNS are called sensory nerves (afferent). The PNS is divided into two separate subsystems, the somatic and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Network Software
Neural network software is used to simulate, research, develop, and apply artificial neural networks, software concepts adapted from biological neural networks, and in some cases, a wider array of adaptive systems such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. Simulators Neural network simulators are software applications that are used to simulate the behavior of artificial or biological neural networks. They focus on one or a limited number of specific types of neural networks. They are typically stand-alone and not intended to produce general neural networks that can be integrated in other software. Simulators usually have some form of built-in visualization to monitor the training process. Some simulators also visualize the physical structure of the neural network. Research simulators Historically, the most common type of neural network software was intended for researching neural network structures and algorithms. The primary purpose of this type of software is, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurons
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Neuron
An artificial neuron is a mathematical function conceived as a model of a biological neuron in a neural network. The artificial neuron is the elementary unit of an ''artificial neural network''. The design of the artificial neuron was inspired by biological neural circuitry. Its inputs are analogous to excitatory postsynaptic potentials and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials at neural dendrites, or . Its weights are analogous to synaptic weights, and its output is analogous to a neuron's action potential which is transmitted along its axon. Usually, each input is separately weighted, and the sum is often added to a term known as a ''bias'' (loosely corresponding to the threshold potential), before being passed through a nonlinear function known as an activation function. Depending on the task, these functions could have a sigmoid shape (e.g. for binary classification), but they may also take the form of other nonlinear functions, piecewise linear functions, or step fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |