Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of
computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with
human intelligence
Human intelligence is the Intellect, intellectual capability of humans, which is marked by complex Cognition, cognitive feats and high levels of motivation and self-awareness. Using their intelligence, humans are able to learning, learn, Concept ...
, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a
field of research in
computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
that develops and studies methods and
software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
that enable machines to
perceive their environment and use
learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, value (personal and cultural), values, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, non-human animals, and ...
and
intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as t ...
to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals.
High-profile
applications of AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been used in applications throughout industry and academia. In a manner analogous to electricity or computers, AI serves as a general-purpose technology. AI programs are designed to simulate human perception and u ...
include advanced
web search engine
A search engine is a software system that provides hyperlinks to web pages, and other relevant information on World Wide Web, the Web in response to a user's web query, query. The user enters a query in a web browser or a mobile app, and the sea ...
s (e.g.,
Google Search
Google Search (also known simply as Google or Google.com) is a search engine operated by Google. It allows users to search for information on the World Wide Web, Web by entering keywords or phrases. Google Search uses algorithms to analyze an ...
);
recommendation systems
A recommender system (RecSys), or a recommendation system (sometimes replacing ''system'' with terms such as ''platform'', ''engine'', or ''algorithm'') and sometimes only called "the algorithm" or "algorithm", is a subclass of information fi ...
(used by
YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in ...
,
Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
, and
Netflix
Netflix is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service. The service primarily distributes original and acquired films and television shows from various genres, and it is available internationally in multiple lang ...
);
virtual assistant
A virtual assistant (VA) is a software agent that can perform a range of tasks or services for a user based on user input such as commands or questions, including verbal ones. Such technologies often incorporate chatbot capabilities to streaml ...
s (e.g.,
Google Assistant
Google Assistant is a virtual assistant software application developed by Google that is primarily available on home automation and mobile devices. Based on artificial intelligence, Google Assistant can engage in two-way conversations, unlike ...
,
Siri
Siri ( , backronym: Speech Interpretation and Recognition Interface) is a digital assistant purchased, developed, and popularized by Apple Inc., which is included in the iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, macOS, Apple TV, audioOS, and visionOS operating sys ...
, and
Alexa
Alexa may refer to: Technology
*Amazon Alexa, a virtual assistant developed by Amazon
* Alexa Internet, a defunct website ranking and traffic analysis service
* Alexa Fluor, a family of fluorescent dyes
* Arri Alexa, a digital motion picture ca ...
);
autonomous vehicles (e.g.,
Waymo
Waymo LLC, formerly known as the Google Self-Driving Car Project, is an American autonomous driving technology company headquartered in Mountain View, California. It is a subsidiary of Google's parent company (Alphabet Inc., Alphabet Inc).
T ...
);
generative and
creative tools (e.g.,
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a generative artificial intelligence chatbot developed by OpenAI and released on November 30, 2022. It uses large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4o as well as other Multimodal learning, multimodal models to create human-like re ...
and
AI art
Artificial intelligence visual art means visual artwork generated (or enhanced) through the use of artificial intelligence (AI) programs.
Artists began to create AI art in the mid to late 20th century, when the discipline was founded. Through ...
); and
superhuman
The term superhuman refers to humans, humanoids or other beings with abilities and other qualities that exceed those naturally found in humans. These qualities may be acquired through natural ability, self-actualization or technological aids. ...
play and analysis in
strategy game
A strategy game or strategic game is a game in which the players' uncoerced, and often autonomous, decision-making skills have a high significance in determining the outcome. Almost all strategy games require internal decision tree-style think ...
s (e.g.,
chess
Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves Perfect information, no hidden information and no elements of game of chance, chance. It is played on a square chessboard, board consisting of 64 squares arran ...
and
Go). However, many AI applications are not perceived as AI: "A lot of cutting edge AI has filtered into general applications, often without being called AI because once something becomes useful enough and common enough it's
not labeled AI anymore."
Various subfields of AI research are centered around particular goals and the use of particular tools. The traditional goals of AI research include learning,
reasoning
Reason is the capacity of consciously applying logic by drawing valid conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, religion, scien ...
,
knowledge representation
Knowledge representation (KR) aims to model information in a structured manner to formally represent it as knowledge in knowledge-based systems whereas knowledge representation and reasoning (KRR, KR&R, or KR²) also aims to understand, reason, and ...
,
planning
Planning is the process of thinking regarding the activities required to achieve a desired goal. Planning is based on foresight, the fundamental capacity for mental time travel. Some researchers regard the evolution of forethought - the cap ...
,
natural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related ...
,
perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous syste ...
, and support for
robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
. To reach these goals, AI researchers have adapted and integrated a wide range of techniques, including
search
Searching may refer to:
Music
* "Searchin', Searchin", a 1957 song originally performed by The Coasters
* Searching (China Black song), "Searching" (China Black song), a 1991 song by China Black
* Searchin' (CeCe Peniston song), "Searchin" (C ...
and
mathematical optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfiel ...
,
formal logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure o ...
,
artificial neural network
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks.
A neural network consists of connected ...
s, and methods based on
statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
,
operations research
Operations research () (U.S. Air Force Specialty Code: Operations Analysis), often shortened to the initialism OR, is a branch of applied mathematics that deals with the development and application of analytical methods to improve management and ...
, and
economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ...
. AI also draws upon
psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
,
linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds ...
,
philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
,
neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, ...
, and other fields. Some companies, such as
OpenAI
OpenAI, Inc. is an American artificial intelligence (AI) organization founded in December 2015 and headquartered in San Francisco, California. It aims to develop "safe and beneficial" artificial general intelligence (AGI), which it defines ...
,
Google DeepMind
DeepMind Technologies Limited, trading as Google DeepMind or simply DeepMind, is a British–American artificial intelligence research laboratory which serves as a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. Founded in the UK in 2010, it was acquired by Goo ...
and
Meta, aim to create
artificial general intelligence
Artificial general intelligence (AGI)—sometimes called human‑level intelligence AI—is a type of artificial intelligence that would match or surpass human capabilities across virtually all cognitive tasks.
Some researchers argue that sta ...
(AGI)—AI that can complete virtually any cognitive task at least as well as a human.
Artificial intelligence was founded as an academic discipline in 1956,
and the field went through multiple cycles of optimism throughout
its history,
followed by periods of disappointment and loss of funding, known as
AI winters.
Funding and interest vastly increased after 2012 when
graphics processing units
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal co ...
started being used to accelerate neural networks, and
deep learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience a ...
outperformed previous AI techniques.
This growth accelerated further after 2017 with the
transformer architecture. In the 2020s, the period of rapid
progress
Progress is movement towards a perceived refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. It is central to the philosophy of progressivism, which interprets progress as the set of advancements in technology, science, and social organization effic ...
marked by advanced generative AI became known as the
AI boom. Generative AI and its ability to create and modify content exposed several unintended consequences and harms in the present and raised
ethical concerns about
AI's long-term effects and potential
existential risks, prompting discussions about
regulatory policies to ensure the
safety
Safety is the state of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
The word 'safety' entered the English language in the 1 ...
and benefits of the technology.
Goals
The general problem of simulating (or creating) intelligence has been broken into subproblems. These consist of particular traits or capabilities that researchers expect an intelligent system to display. The traits described below have received the most attention and cover the scope of AI research.
Reasoning and problem-solving
Early researchers developed algorithms that imitated step-by-step reasoning that humans use when they solve puzzles or make logical
deductions. By the late 1980s and 1990s, methods were developed for dealing with
uncertain or incomplete information, employing concepts from
probability
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an e ...
and
economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ...
.
Many of these algorithms are insufficient for solving large reasoning problems because they experience a "combinatorial explosion": They become exponentially slower as the problems grow.
[ Intractability and efficiency and the ]combinatorial explosion
In mathematics, a combinatorial explosion is the rapid growth of the complexity of a problem due to the way its combinatorics depends on input, constraints and bounds. Combinatorial explosion is sometimes used to justify the intractability of cert ...
: Even humans rarely use the step-by-step deduction that early AI research could model. They solve most of their problems using fast, intuitive judgments.
[Psychological evidence of the prevalence of sub-symbolic reasoning and knowledge: , , , ] Accurate and efficient reasoning is an unsolved problem.
Knowledge representation

Knowledge representation
Knowledge representation (KR) aims to model information in a structured manner to formally represent it as knowledge in knowledge-based systems whereas knowledge representation and reasoning (KRR, KR&R, or KR²) also aims to understand, reason, and ...
and
knowledge engineering
Knowledge engineering (KE) refers to all aspects involved in knowledge-based systems.
Background Expert systems
One of the first examples of an expert system was MYCIN, an application to perform medical diagnosis. In the MYCIN example, the ...
allow AI programs to answer questions intelligently and make deductions about real-world facts. Formal knowledge representations are used in content-based indexing and retrieval, scene interpretation, clinical decision support, knowledge discovery (mining "interesting" and actionable inferences from large
database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and a ...
s), and other areas.
A
knowledge base
In computer science, a knowledge base (KB) is a set of sentences, each sentence given in a knowledge representation language, with interfaces to tell new sentences and to ask questions about what is known, where either of these interfaces migh ...
is a body of knowledge represented in a form that can be used by a program. An
ontology
Ontology is the philosophical study of existence, being. It is traditionally understood as the subdiscipline of metaphysics focused on the most general features of reality. As one of the most fundamental concepts, being encompasses all of realit ...
is the set of objects, relations, concepts, and properties used by a particular domain of knowledge. Knowledge bases need to represent things such as objects, properties, categories, and relations between objects; situations, events, states, and time; causes and effects; knowledge about knowledge (what we know about what other people know);
default reasoning (things that humans assume are true until they are told differently and will remain true even when other facts are changing);
[ Default reasoning, ]Frame problem
In artificial intelligence, with implications for cognitive science, the frame problem describes an issue with using first-order logic to express facts about a robot in the world. Representing the state of a robot with traditional first-order logi ...
, default logic, non-monotonic logics, circumscription, closed world assumption, abduction: , , ,
(Poole ''et al.'' places abduction under "default reasoning". Luger ''et al.'' places this under "uncertain reasoning"). and many other aspects and domains of knowledge.
Among the most difficult problems in knowledge representation are the breadth of
commonsense knowledge
In artificial intelligence research, commonsense knowledge consists of facts about the everyday world, such as "Lemons are sour", or "Cows say moo", that all humans are expected to know. It is currently an unsolved problem in artificial gener ...
(the set of atomic facts that the average person knows is enormous);
[Breadth of commonsense knowledge: , , , ( qualification problem)] and the sub-symbolic form of most commonsense knowledge (much of what people know is not represented as "facts" or "statements" that they could express verbally).
There is also the difficulty of
knowledge acquisition, the problem of obtaining knowledge for AI applications.
Planning and decision-making
An "agent" is anything that perceives and takes actions in the world. A
rational agent
A rational agent or rational being is a person or entity that always aims to perform optimal actions based on given premises and information. A rational agent can be anything that makes decisions, typically a person, firm, machine, or software.
...
has goals or preferences and takes actions to make them happen. In
automated planning
Automated planning and scheduling, sometimes denoted as simply AI planning, is a branch of artificial intelligence that concerns the realization of strategy, strategies or action sequences, typically for execution by intelligent agents, autonomou ...
, the agent has a specific goal. In
automated decision-making
Automated decision-making (ADM) is the use of data, machines and algorithms to make decisions in a range of contexts, including public administration, business, health, education, law, employment, transport, media and entertainment, with varying d ...
, the agent has preferences—there are some situations it would prefer to be in, and some situations it is trying to avoid. The decision-making agent assigns a number to each situation (called the "
utility
In economics, utility is a measure of a certain person's satisfaction from a certain state of the world. Over time, the term has been used with at least two meanings.
* In a normative context, utility refers to a goal or objective that we wish ...
") that measures how much the agent prefers it. For each possible action, it can calculate the "
expected utility
The expected utility hypothesis is a foundational assumption in mathematical economics concerning decision making under uncertainty. It postulates that rational agents maximize utility, meaning the subjective desirability of their actions. Ratio ...
": the
utility
In economics, utility is a measure of a certain person's satisfaction from a certain state of the world. Over time, the term has been used with at least two meanings.
* In a normative context, utility refers to a goal or objective that we wish ...
of all possible outcomes of the action, weighted by the probability that the outcome will occur. It can then choose the action with the maximum expected utility.
In
classical planning, the agent knows exactly what the effect of any action will be. In most real-world problems, however, the agent may not be certain about the situation they are in (it is "unknown" or "unobservable") and it may not know for certain what will happen after each possible action (it is not "deterministic"). It must choose an action by making a probabilistic guess and then reassess the situation to see if the action worked.
In some problems, the agent's preferences may be uncertain, especially if there are other agents or humans involved. These can be learned (e.g., with
inverse reinforcement learning), or the agent can seek information to improve its preferences.
Information value theory can be used to weigh the value of exploratory or experimental actions. The space of possible future actions and situations is typically
intractably large, so the agents must take actions and evaluate situations while being uncertain of what the outcome will be.
A
Markov decision process has a
transition model that describes the probability that a particular action will change the state in a particular way and a
reward function that supplies the utility of each state and the cost of each action. A
policy
Policy is a deliberate system of guidelines to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent and is implemented as a procedure or protocol. Policies are generally adopted by a governance body within an or ...
associates a decision with each possible state. The policy could be calculated (e.g., by
iteration
Iteration is the repetition of a process in order to generate a (possibly unbounded) sequence of outcomes. Each repetition of the process is a single iteration, and the outcome of each iteration is then the starting point of the next iteration.
...
), be
heuristic
A heuristic or heuristic technique (''problem solving'', '' mental shortcut'', ''rule of thumb'') is any approach to problem solving that employs a pragmatic method that is not fully optimized, perfected, or rationalized, but is nevertheless ...
, or it can be learned.
Game theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed ...
describes the rational behavior of multiple interacting agents and is used in AI programs that make decisions that involve other agents.
Learning
Machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
is the study of programs that can improve their performance on a given task automatically. It has been a part of AI from the beginning.

There are several kinds of machine learning.
Unsupervised learning
Unsupervised learning is a framework in machine learning where, in contrast to supervised learning, algorithms learn patterns exclusively from unlabeled data. Other frameworks in the spectrum of supervisions include weak- or semi-supervision, wh ...
analyzes a stream of data and finds patterns and makes predictions without any other guidance.
Supervised learning
In machine learning, supervised learning (SL) is a paradigm where a Statistical model, model is trained using input objects (e.g. a vector of predictor variables) and desired output values (also known as a ''supervisory signal''), which are often ...
requires labeling the training data with the expected answers, and comes in two main varieties:
classification
Classification is the activity of assigning objects to some pre-existing classes or categories. This is distinct from the task of establishing the classes themselves (for example through cluster analysis). Examples include diagnostic tests, identif ...
(where the program must learn to predict what category the input belongs in) and
regression (where the program must deduce a numeric function based on numeric input).
Supervised learning
In machine learning, supervised learning (SL) is a paradigm where a Statistical model, model is trained using input objects (e.g. a vector of predictor variables) and desired output values (also known as a ''supervisory signal''), which are often ...
: (Definition), (Techniques)
In
reinforcement learning
Reinforcement learning (RL) is an interdisciplinary area of machine learning and optimal control concerned with how an intelligent agent should take actions in a dynamic environment in order to maximize a reward signal. Reinforcement learnin ...
, the agent is rewarded for good responses and punished for bad ones. The agent learns to choose responses that are classified as "good".
Transfer learning
Transfer learning (TL) is a technique in machine learning (ML) in which knowledge learned from a task is re-used in order to boost performance on a related task. For example, for image classification, knowledge gained while learning to recogniz ...
is when the knowledge gained from one problem is applied to a new problem.
Deep learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience a ...
is a type of machine learning that runs inputs through biologically inspired
artificial neural networks
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks.
A neural network consists of connected ...
for all of these types of learning.
Computational learning theory
In computer science, computational learning theory (or just learning theory) is a subfield of artificial intelligence devoted to studying the design and analysis of machine learning algorithms.
Overview
Theoretical results in machine learning m ...
can assess learners by
computational complexity
In computer science, the computational complexity or simply complexity of an algorithm is the amount of resources required to run it. Particular focus is given to computation time (generally measured by the number of needed elementary operations ...
, by
sample complexity (how much data is required), or by other notions of
optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfiel ...
.
Natural language processing
Natural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related ...
(NLP) allows programs to read, write and communicate in human languages such as
English. Specific problems include
speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also ...
,
speech synthesis
Speech synthesis is the artificial production of human speech. A computer system used for this purpose is called a speech synthesizer, and can be implemented in software or hardware products. A text-to-speech (TTS) system converts normal langua ...
,
machine translation
Machine translation is use of computational techniques to translate text or speech from one language to another, including the contextual, idiomatic and pragmatic nuances of both languages.
Early approaches were mostly rule-based or statisti ...
,
information extraction,
information retrieval
Information retrieval (IR) in computing and information science is the task of identifying and retrieving information system resources that are relevant to an Information needs, information need. The information need can be specified in the form ...
and
question answering.
Early work, based on
Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American professor and public intellectual known for his work in linguistics, political activism, and social criticism. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky is also a ...
's
generative grammar
Generative grammar is a research tradition in linguistics that aims to explain the cognitive basis of language by formulating and testing explicit models of humans' subconscious grammatical knowledge. Generative linguists, or generativists (), ...
and
semantic network
A semantic network, or frame network is a knowledge base that represents semantic relations between concepts in a network. This is often used as a form of knowledge representation. It is a directed or undirected graph consisting of vertices, ...
s, had difficulty with
word-sense disambiguation
Word-sense disambiguation is the process of identifying which sense of a word is meant in a sentence or other segment of context. In human language processing and cognition, it is usually subconscious.
Given that natural language requires ref ...
unless restricted to small domains called "
micro-worlds" (due to the common sense knowledge problem
).
Margaret Masterman believed that it was meaning and not grammar that was the key to understanding languages, and that
thesauri
A thesaurus (: thesauri or thesauruses), sometimes called a synonym dictionary or dictionary of synonyms, is a reference work which arranges words by their meanings (or in simpler terms, a book where one can find different words with similar me ...
and not dictionaries should be the basis of computational language structure.
Modern deep learning techniques for NLP include
word embedding
In natural language processing, a word embedding is a representation of a word. The embedding is used in text analysis. Typically, the representation is a real-valued vector that encodes the meaning of the word in such a way that the words that ...
(representing words, typically as
vectors encoding their meaning),
transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ...
s (a deep learning architecture using an
attention
Attention or focus, is the concentration of awareness on some phenomenon to the exclusion of other stimuli. It is the selective concentration on discrete information, either subjectively or objectively. William James (1890) wrote that "Atte ...
mechanism), and others. In 2019,
generative pre-trained transformer
A generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) is a type of large language model (LLM) and a prominent framework for generative artificial intelligence. It is an Neural network (machine learning), artificial neural network that is used in natural ...
(or "GPT") language models began to generate coherent text, and by 2023, these models were able to get human-level scores on the
bar exam
A bar examination is an examination administered by the bar association of a jurisdiction that a lawyer must pass in order to be admitted to the bar of that jurisdiction.
Australia
Administering bar exams is the responsibility of the bar associat ...
,
SAT
The SAT ( ) is a standardized test widely used for college admissions in the United States. Since its debut in 1926, its name and Test score, scoring have changed several times. For much of its history, it was called the Scholastic Aptitude Test ...
test,
GRE test, and many other real-world applications.
Perception
Machine perception is the ability to use input from sensors (such as cameras, microphones, wireless signals, active
lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected li ...
, sonar, radar, and
tactile sensor
A tactile sensor is a device that measures information arising from physical interaction with its environment. Tactile sensors are generally modeled after the biological sense of cutaneous receptor, cutaneous touch which is capable of detect ...
s) to deduce aspects of the world.
Computer vision
Computer vision tasks include methods for image sensor, acquiring, Image processing, processing, Image analysis, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical ...
is the ability to analyze visual input.
The field includes
speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also ...
,
image classification,
facial recognition,
object recognition
Object recognition – technology in the field of computer vision for finding and identifying objects in an image or video sequence. Humans recognize a multitude of objects in images with little effort, despite the fact that the image of the ...
,
object tracking, and
robotic perception.
Social intelligence
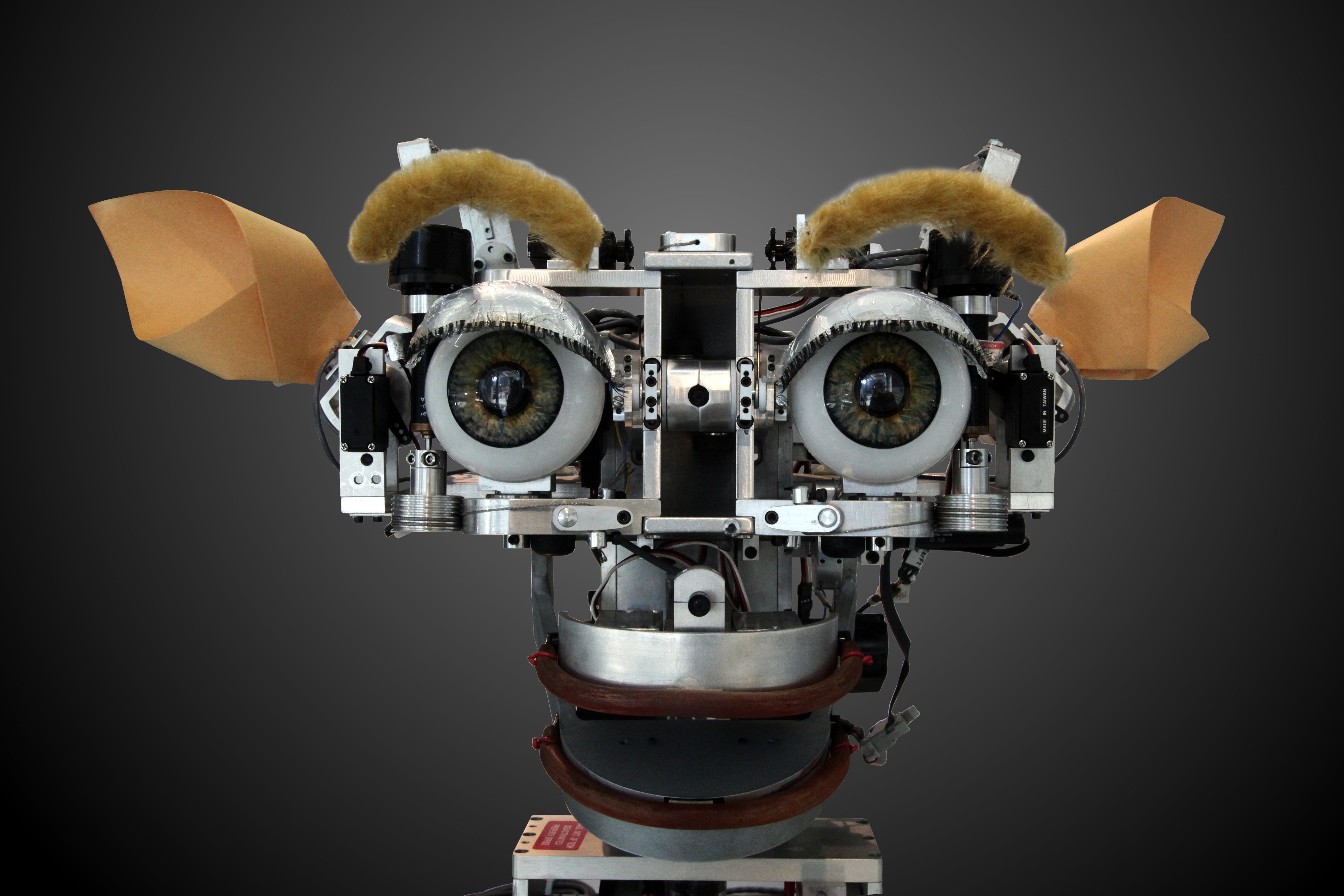 Affective computing
Affective computing is a field that comprises systems that recognize, interpret, process, or simulate human
feeling, emotion, and mood. For example, some
virtual assistant
A virtual assistant (VA) is a software agent that can perform a range of tasks or services for a user based on user input such as commands or questions, including verbal ones. Such technologies often incorporate chatbot capabilities to streaml ...
s are programmed to speak conversationally or even to banter humorously; it makes them appear more sensitive to the emotional dynamics of human interaction, or to otherwise facilitate
human–computer interaction
Human–computer interaction (HCI) is the process through which people operate and engage with computer systems. Research in HCI covers the design and the use of computer technology, which focuses on the interfaces between people (users) and comp ...
.
However, this tends to give naïve users an unrealistic conception of the intelligence of existing computer agents. Moderate successes related to affective computing include textual
sentiment analysis
Sentiment analysis (also known as opinion mining or emotion AI) is the use of natural language processing, text analysis, computational linguistics, and biometrics to systematically identify, extract, quantify, and study affective states and subje ...
and, more recently,
multimodal sentiment analysis, wherein AI classifies the effects displayed by a videotaped subject.
General intelligence
A machine with
artificial general intelligence
Artificial general intelligence (AGI)—sometimes called human‑level intelligence AI—is a type of artificial intelligence that would match or surpass human capabilities across virtually all cognitive tasks.
Some researchers argue that sta ...
should be able to solve a wide variety of problems with breadth and versatility similar to
human intelligence
Human intelligence is the Intellect, intellectual capability of humans, which is marked by complex Cognition, cognitive feats and high levels of motivation and self-awareness. Using their intelligence, humans are able to learning, learn, Concept ...
.
[
]Artificial general intelligence
Artificial general intelligence (AGI)—sometimes called human‑level intelligence AI—is a type of artificial intelligence that would match or surpass human capabilities across virtually all cognitive tasks.
Some researchers argue that sta ...
:
Proposal for the modern version:
Warnings of overspecialization in AI from leading researchers: , ,
Techniques
AI research uses a wide variety of techniques to accomplish the goals above.
Search and optimization
AI can solve many problems by intelligently searching through many possible solutions. There are two very different kinds of search used in AI:
state space search
State-space search is a process used in the field of computer science, including artificial intelligence (AI), in which successive configurations or ''states'' of an instance are considered, with the intention of finding a ''goal state'' with the ...
and
local search.
State space search
State space search
State-space search is a process used in the field of computer science, including artificial intelligence (AI), in which successive configurations or ''states'' of an instance are considered, with the intention of finding a ''goal state'' with the ...
searches through a tree of possible states to try to find a goal state. For example,
planning
Planning is the process of thinking regarding the activities required to achieve a desired goal. Planning is based on foresight, the fundamental capacity for mental time travel. Some researchers regard the evolution of forethought - the cap ...
algorithms search through trees of goals and subgoals, attempting to find a path to a target goal, a process called
means-ends analysis.
Simple exhaustive searches are rarely sufficient for most real-world problems: the
search space (the number of places to search) quickly grows to
astronomical numbers. The result is a search that is
too slow or never completes.
"
Heuristics
A heuristic or heuristic technique (''problem solving'', '' mental shortcut'', ''rule of thumb'') is any approach to problem solving that employs a pragmatic method that is not fully optimized, perfected, or rationalized, but is nevertheless ...
" or "rules of thumb" can help prioritize choices that are more likely to reach a goal.
Adversarial search is used for
game-playing programs, such as chess or Go. It searches through a
tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only ...
of possible moves and countermoves, looking for a winning position.
Local search
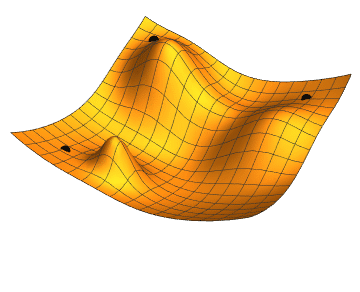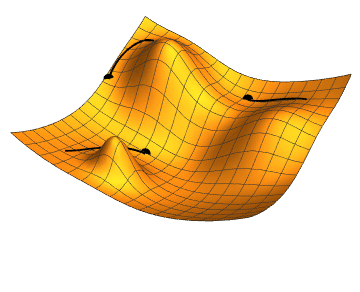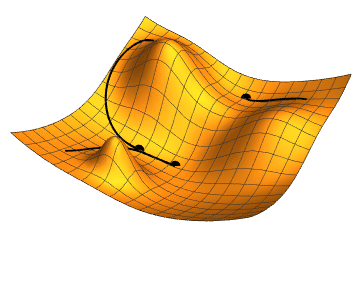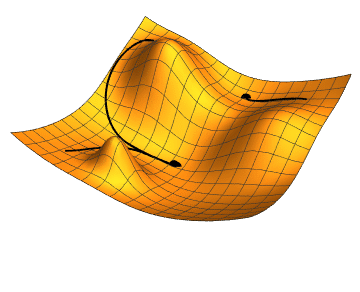 Local search
Local search uses
mathematical optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfiel ...
to find a solution to a problem. It begins with some form of guess and refines it incrementally.
Gradient descent
Gradient descent is a method for unconstrained mathematical optimization. It is a first-order iterative algorithm for minimizing a differentiable multivariate function.
The idea is to take repeated steps in the opposite direction of the gradi ...
is a type of local search that optimizes a set of numerical parameters by incrementally adjusting them to minimize a
loss function
In mathematical optimization and decision theory, a loss function or cost function (sometimes also called an error function) is a function that maps an event or values of one or more variables onto a real number intuitively representing some "cost ...
. Variants of gradient descent are commonly used to train
neural networks
A neural network is a group of interconnected units called neurons that send signals to one another. Neurons can be either Cell (biology), biological cells or signal pathways. While individual neurons are simple, many of them together in a netwo ...
, through the
backpropagation
In machine learning, backpropagation is a gradient computation method commonly used for training a neural network to compute its parameter updates.
It is an efficient application of the chain rule to neural networks. Backpropagation computes th ...
algorithm.
Another type of local search is
evolutionary computation
Evolutionary computation from computer science is a family of algorithms for global optimization inspired by biological evolution, and the subfield of artificial intelligence and soft computing studying these algorithms. In technical terms ...
, which aims to iteratively improve a set of candidate solutions by "mutating" and "recombining" them,
selecting only the fittest to survive each generation.
Distributed search processes can coordinate via
swarm intelligence algorithms. Two popular swarm algorithms used in search are
particle swarm optimization
In computational science, particle swarm optimization (PSO) is a computational method that Mathematical optimization, optimizes a problem by iterative method, iteratively trying to improve a candidate solution with regard to a given measure of qu ...
(inspired by bird
flocking) and
ant colony optimization (inspired by
ant trails).
Logic
Formal
logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure o ...
is used for
reasoning
Reason is the capacity of consciously applying logic by drawing valid conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, religion, scien ...
and
knowledge representation
Knowledge representation (KR) aims to model information in a structured manner to formally represent it as knowledge in knowledge-based systems whereas knowledge representation and reasoning (KRR, KR&R, or KR²) also aims to understand, reason, and ...
.
Formal logic comes in two main forms:
propositional logic
The propositional calculus is a branch of logic. It is also called propositional logic, statement logic, sentential calculus, sentential logic, or sometimes zeroth-order logic. Sometimes, it is called ''first-order'' propositional logic to contra ...
(which operates on statements that are true or false and uses
logical connective
In logic, a logical connective (also called a logical operator, sentential connective, or sentential operator) is a logical constant. Connectives can be used to connect logical formulas. For instance in the syntax of propositional logic, the ...
s such as "and", "or", "not" and "implies") and
predicate logic
First-order logic, also called predicate logic, predicate calculus, or quantificational logic, is a collection of formal systems used in mathematics, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science. First-order logic uses quantified variables ove ...
(which also operates on objects, predicates and relations and uses
quantifiers such as "''Every'' ''X'' is a ''Y''" and "There are ''some'' ''X''s that are ''Y''s").
Deductive reasoning
Deductive reasoning is the process of drawing valid inferences. An inference is valid if its conclusion follows logically from its premises, meaning that it is impossible for the premises to be true and the conclusion to be false. For example, t ...
in logic is the process of
proving a new statement (
conclusion) from other statements that are given and assumed to be true (the
premise
A premise or premiss is a proposition—a true or false declarative statement—used in an argument to prove the truth of another proposition called the conclusion. Arguments consist of a set of premises and a conclusion.
An argument is meaningf ...
s). Proofs can be structured as proof
trees
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only p ...
, in which nodes are labelled by sentences, and children nodes are connected to parent nodes by
inference rule
Rules of inference are ways of deriving conclusions from premises. They are integral parts of formal logic, serving as norms of the logical structure of valid arguments. If an argument with true premises follows a rule of inference then the co ...
s.
Given a problem and a set of premises, problem-solving reduces to searching for a proof tree whose root node is labelled by a solution of the problem and whose
leaf nodes are labelled by premises or
axiom
An axiom, postulate, or assumption is a statement that is taken to be true, to serve as a premise or starting point for further reasoning and arguments. The word comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning 'that which is thought worthy or ...
s. In the case of
Horn clause
In mathematical logic and logic programming, a Horn clause is a logical formula of a particular rule-like form that gives it useful properties for use in logic programming, formal specification, universal algebra and model theory. Horn clauses are ...
s, problem-solving search can be performed by reasoning
forwards from the premises or
backwards from the problem. In the more general case of the clausal form of
first-order logic
First-order logic, also called predicate logic, predicate calculus, or quantificational logic, is a collection of formal systems used in mathematics, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science. First-order logic uses quantified variables over ...
,
resolution is a single, axiom-free rule of inference, in which a problem is solved by proving a contradiction from premises that include the negation of the problem to be solved.
Inference in both Horn clause logic and first-order logic is
undecidable, and therefore
intractable. However, backward reasoning with Horn clauses, which underpins computation in the
logic programming
Logic programming is a programming, database and knowledge representation paradigm based on formal logic. A logic program is a set of sentences in logical form, representing knowledge about some problem domain. Computation is performed by applyin ...
language
Prolog
Prolog is a logic programming language that has its origins in artificial intelligence, automated theorem proving, and computational linguistics.
Prolog has its roots in first-order logic, a formal logic. Unlike many other programming language ...
, is
Turing complete
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist. He was highly influential in the development of theoretical comput ...
. Moreover, its efficiency is competitive with computation in other
symbolic programming languages.
Fuzzy logic
Fuzzy logic is a form of many-valued logic in which the truth value of variables may be any real number between 0 and 1. It is employed to handle the concept of partial truth, where the truth value may range between completely true and completely ...
assigns a "degree of truth" between 0 and 1. It can therefore handle propositions that are vague and partially true.
Non-monotonic logics, including logic programming with
negation as failure, are designed to handle
default reasoning.
Other specialized versions of logic have been developed to describe many complex domains.
Probabilistic methods for uncertain reasoning

Many problems in AI (including reasoning, planning, learning, perception, and robotics) require the agent to operate with incomplete or uncertain information. AI researchers have devised a number of tools to solve these problems using methods from
probability
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an e ...
theory and economics.
[Stochastic methods for uncertain reasoning: , , , ] Precise mathematical tools have been developed that analyze how an agent can make choices and plan, using
decision theory
Decision theory or the theory of rational choice is a branch of probability theory, probability, economics, and analytic philosophy that uses expected utility and probabilities, probability to model how individuals would behave Rationality, ratio ...
,
decision analysis
Decision analysis (DA) is the Academic discipline, discipline comprising the philosophy, methodology, and professional practice necessary to address important Decision making, decisions in a formal manner. Decision analysis includes many procedures ...
, and
information value theory. These tools include models such as
Markov decision processes, dynamic
decision networks,
game theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed ...
and
mechanism design
Mechanism design (sometimes implementation theory or institution design) is a branch of economics and game theory. It studies how to construct rules—called Game form, mechanisms or institutions—that produce good outcomes according to Social ...
.
Bayesian network
A Bayesian network (also known as a Bayes network, Bayes net, belief network, or decision network) is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph (DAG). Whi ...
s are a tool that can be used for
reasoning
Reason is the capacity of consciously applying logic by drawing valid conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, religion, scien ...
(using the
Bayesian inference
Bayesian inference ( or ) is a method of statistical inference in which Bayes' theorem is used to calculate a probability of a hypothesis, given prior evidence, and update it as more information becomes available. Fundamentally, Bayesian infer ...
algorithm),
learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, value (personal and cultural), values, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, non-human animals, and ...
(using the
expectation–maximization algorithm
In statistics, an expectation–maximization (EM) algorithm is an iterative method to find (local) maximum likelihood or maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimates of parameters in statistical models, where the model depends on unobserved latent varia ...
),
planning
Planning is the process of thinking regarding the activities required to achieve a desired goal. Planning is based on foresight, the fundamental capacity for mental time travel. Some researchers regard the evolution of forethought - the cap ...
(using
decision networks) and
perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous syste ...
(using
dynamic Bayesian networks).
Probabilistic algorithms can also be used for filtering, prediction, smoothing, and finding explanations for streams of data, thus helping perception systems analyze processes that occur over time (e.g.,
hidden Markov model
A hidden Markov model (HMM) is a Markov model in which the observations are dependent on a latent (or ''hidden'') Markov process (referred to as X). An HMM requires that there be an observable process Y whose outcomes depend on the outcomes of X ...
s or
Kalman filter
In statistics and control theory, Kalman filtering (also known as linear quadratic estimation) is an algorithm that uses a series of measurements observed over time, including statistical noise and other inaccuracies, to produce estimates of unk ...
s).
[Stochastic temporal models:
]Hidden Markov model
A hidden Markov model (HMM) is a Markov model in which the observations are dependent on a latent (or ''hidden'') Markov process (referred to as X). An HMM requires that there be an observable process Y whose outcomes depend on the outcomes of X ...
:
Kalman filter
In statistics and control theory, Kalman filtering (also known as linear quadratic estimation) is an algorithm that uses a series of measurements observed over time, including statistical noise and other inaccuracies, to produce estimates of unk ...
s:
Dynamic Bayesian networks:

Classifiers and statistical learning methods
The simplest AI applications can be divided into two types: classifiers (e.g., "if shiny then diamond"), on one hand, and controllers (e.g., "if diamond then pick up"), on the other hand.
Classifiers are functions that use
pattern matching
In computer science, pattern matching is the act of checking a given sequence of tokens for the presence of the constituents of some pattern. In contrast to pattern recognition, the match usually must be exact: "either it will or will not be a ...
to determine the closest match. They can be fine-tuned based on chosen examples using
supervised learning
In machine learning, supervised learning (SL) is a paradigm where a Statistical model, model is trained using input objects (e.g. a vector of predictor variables) and desired output values (also known as a ''supervisory signal''), which are often ...
. Each pattern (also called an "
observation
Observation in the natural sciences is an act or instance of noticing or perceiving and the acquisition of information from a primary source. In living beings, observation employs the senses. In science, observation can also involve the percep ...
") is labeled with a certain predefined class. All the observations combined with their class labels are known as a
data set
A data set (or dataset) is a collection of data. In the case of tabular data, a data set corresponds to one or more table (database), database tables, where every column (database), column of a table represents a particular Variable (computer sci ...
. When a new observation is received, that observation is classified based on previous experience.
There are many kinds of classifiers in use. The
decision tree
A decision tree is a decision support system, decision support recursive partitioning structure that uses a Tree (graph theory), tree-like Causal model, model of decisions and their possible consequences, including probability, chance event ou ...
is the simplest and most widely used symbolic machine learning algorithm.
K-nearest neighbor algorithm was the most widely used analogical AI until the mid-1990s, and
Kernel methods
In machine learning, kernel machines are a class of algorithms for pattern analysis, whose best known member is the support-vector machine (SVM). These methods involve using linear classifiers to solve nonlinear problems. The general task of pa ...
such as the
support vector machine
In machine learning, support vector machines (SVMs, also support vector networks) are supervised max-margin models with associated learning algorithms that analyze data for classification and regression analysis. Developed at AT&T Bell Laborato ...
(SVM) displaced k-nearest neighbor in the 1990s.
The
naive Bayes classifier is reportedly the "most widely used learner" at Google, due in part to its scalability.
Neural networks
A neural network is a group of interconnected units called neurons that send signals to one another. Neurons can be either Cell (biology), biological cells or signal pathways. While individual neurons are simple, many of them together in a netwo ...
are also used as classifiers.
Artificial neural networks

An artificial neural network is based on a collection of nodes also known as
artificial neurons, which loosely model the
neurons
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
in a biological brain. It is trained to recognise patterns; once trained, it can recognise those patterns in fresh data. There is an input, at least one hidden layer of nodes and an output. Each node applies a function and once the
weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is a quantity associated with the gravitational force exerted on the object by other objects in its environment, although there is some variation and debate as to the exact definition.
Some sta ...
crosses its specified threshold, the data is transmitted to the next layer. A network is typically called a deep neural network if it has at least 2 hidden layers.
[Neural networks: , ]
Learning algorithms for neural networks use
local search to choose the weights that will get the right output for each input during training. The most common training technique is the
backpropagation
In machine learning, backpropagation is a gradient computation method commonly used for training a neural network to compute its parameter updates.
It is an efficient application of the chain rule to neural networks. Backpropagation computes th ...
algorithm. Neural networks learn to model complex relationships between inputs and outputs and
find patterns in data. In theory, a neural network can learn any function.
In
feedforward neural network
Feedforward refers to recognition-inference architecture of neural networks. Artificial neural network architectures are based on inputs multiplied by weights to obtain outputs (inputs-to-output): feedforward. Recurrent neural networks, or neur ...
s the signal passes in only one direction.
Recurrent neural network
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are a class of artificial neural networks designed for processing sequential data, such as text, speech, and time series, where the order of elements is important. Unlike feedforward neural networks, which proces ...
s feed the output signal back into the input, which allows short-term memories of previous input events.
Long short term memory is the most successful architecture for recurrent neural networks.
Perceptron
In machine learning, the perceptron is an algorithm for supervised classification, supervised learning of binary classification, binary classifiers. A binary classifier is a function that can decide whether or not an input, represented by a vect ...
s use only a single layer of neurons; deep learning
uses multiple layers.
Convolutional neural network
A convolutional neural network (CNN) is a type of feedforward neural network that learns features via filter (or kernel) optimization. This type of deep learning network has been applied to process and make predictions from many different ty ...
s strengthen the connection between neurons that are "close" to each other—this is especially important in
image processing
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a pr ...
, where a local set of neurons must
identify an "edge" before the network can identify an object.
Deep learning

Deep learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience a ...
Deep learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience a ...
: , , , uses several layers of neurons between the network's inputs and outputs. The multiple layers can progressively extract higher-level features from the raw input. For example, in
image processing
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a pr ...
, lower layers may identify edges, while higher layers may identify the concepts relevant to a human such as digits, letters, or faces.
Deep learning has profoundly improved the performance of programs in many important subfields of artificial intelligence, including
computer vision
Computer vision tasks include methods for image sensor, acquiring, Image processing, processing, Image analysis, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical ...
,
speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also ...
,
natural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related ...
,
image classification, and others. The reason that deep learning performs so well in so many applications is not known as of 2021. The sudden success of deep learning in 2012–2015 did not occur because of some new discovery or theoretical breakthrough (deep neural networks and backpropagation had been described by many people, as far back as the 1950s) but because of two factors: the incredible increase in computer power (including the hundred-fold increase in speed by switching to
GPUs) and the availability of vast amounts of training data, especially the giant
curated datasets used for benchmark testing, such as
ImageNet.
GPT
Generative pre-trained transformer
A generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) is a type of large language model (LLM) and a prominent framework for generative artificial intelligence. It is an Neural network (machine learning), artificial neural network that is used in natural ...
s (GPT) are
large language model
A large language model (LLM) is a language model trained with self-supervised machine learning on a vast amount of text, designed for natural language processing tasks, especially language generation.
The largest and most capable LLMs are g ...
s (LLMs) that generate text based on the semantic relationships between words in sentences. Text-based GPT models are pre-trained on a large
corpus of text that can be from the Internet. The pretraining consists of predicting the next
token (a token being usually a word, subword, or punctuation). Throughout this pretraining, GPT models accumulate knowledge about the world and can then generate human-like text by repeatedly predicting the next token. Typically, a subsequent training phase makes the model more truthful, useful, and harmless, usually with a technique called
reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF). Current GPT models are prone to generating falsehoods called "
hallucinations
A hallucination is a perception in the absence of an external stimulus that has the compelling sense of reality. They are distinguishable from several related phenomena, such as dreaming ( REM sleep), which does not involve wakefulness; pse ...
". These can be reduced with RLHF and quality data, but the problem has been getting worse for reasoning systems. Such systems are used in
chatbot
A chatbot (originally chatterbot) is a software application or web interface designed to have textual or spoken conversations. Modern chatbots are typically online and use generative artificial intelligence systems that are capable of main ...
s, which allow people to ask a question or request a task in simple text.
Current models and services include
Gemini (formerly Bard),
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a generative artificial intelligence chatbot developed by OpenAI and released on November 30, 2022. It uses large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4o as well as other Multimodal learning, multimodal models to create human-like re ...
,
Grok,
Claude,
Copilot
In aviation, the first officer (FO), also called co-pilot, is a Aircraft pilot, pilot in addition to the Pilot in command, captain, who is the legal commander. In the event of incapacitation of the captain, the first officer will assume command ...
, and
LLaMA
The llama (; or ) (''Lama glama'') is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a List of meat animals, meat and pack animal by Inca empire, Andean cultures since the pre-Columbian era.
Llamas are social animals and live with ...
.
Multimodal GPT models can process different types of data (
modalities) such as images, videos, sound, and text.
Hardware and software
In the late 2010s,
graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal ...
s (GPUs) that were increasingly designed with AI-specific enhancements and used with specialized
TensorFlow
TensorFlow is a Library (computing), software library for machine learning and artificial intelligence. It can be used across a range of tasks, but is used mainly for Types of artificial neural networks#Training, training and Statistical infer ...
software had replaced previously used
central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
(CPUs) as the dominant means for large-scale (commercial and academic)
machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
models' training. Specialized
programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ...
s such as
Prolog
Prolog is a logic programming language that has its origins in artificial intelligence, automated theorem proving, and computational linguistics.
Prolog has its roots in first-order logic, a formal logic. Unlike many other programming language ...
were used in early AI research, but
general-purpose programming language
In computer software, a general-purpose programming language (GPL) is a programming language for building software in a wide variety of application Domain (software engineering), domains. Conversely, a Domain-specific language, domain-specific pro ...
s like
Python have become predominant.
The transistor density in
integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
s has been observed to roughly double every 18 months—a trend known as
Moore's law
Moore's law is the observation that the Transistor count, number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and Forecasting, projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of ...
, named after the
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
co-founder
Gordon Moore
Gordon Earle Moore (January 3, 1929 – March 24, 2023) was an American businessman, engineer, and the co-founder and emeritus chairman of Intel Corporation. He proposed Moore's law which makes the observation that the number of transistors i ...
, who first identified it. Improvements in
GPUs
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal ...
have been even faster, a trend sometimes called
Huang's law, named after
Nvidia
Nvidia Corporation ( ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and incorporated in Delaware. Founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang (president and CEO), Chris Malachowsky, and Curti ...
co-founder and CEO
Jensen Huang
Jen-Hsun "Jensen" Huang ( zh, t=黃仁勳, poj=N̂g Jîn-hun, hp=Huáng Rénxūn; born February 17, 1963) is a Taiwanese and American businessman, electrical engineer, and philanthropist who is the president, co-founder, and chief executive of ...
.
Applications
AI and machine learning technology is used in most of the essential applications of the 2020s, including:
search engines
Search engines, including web search engines, selection-based search engines, metasearch engines, desktop search tools, and web portals and vertical market websites have a search facility for online databases.
By content/topic
Gene ...
(such as
Google Search
Google Search (also known simply as Google or Google.com) is a search engine operated by Google. It allows users to search for information on the World Wide Web, Web by entering keywords or phrases. Google Search uses algorithms to analyze an ...
),
targeting online advertisements,
recommendation systems
A recommender system (RecSys), or a recommendation system (sometimes replacing ''system'' with terms such as ''platform'', ''engine'', or ''algorithm'') and sometimes only called "the algorithm" or "algorithm", is a subclass of information fi ...
(offered by
Netflix
Netflix is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service. The service primarily distributes original and acquired films and television shows from various genres, and it is available internationally in multiple lang ...
,
YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in ...
or
Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
), driving
internet traffic
Internet traffic is the flow of data within the entire Internet, or in certain network links of its constituent networks. Common traffic measurements are total volume, in units of multiples of the byte, or as transmission rates in bytes per cert ...
,
targeted advertising
Targeted advertising or data-driven marketing is a form of advertising, including online advertising, that is directed towards an audience with certain traits, based on the product or person the advertiser is promoting.
These traits can either ...
(
AdSense
Google AdSense is a program run by Google through which website publishers in the Google Network of content sites serve text, images, video, or interactive media advertisements that are targeted to the site content and audience. These adver ...
,
Facebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
),
virtual assistant
A virtual assistant (VA) is a software agent that can perform a range of tasks or services for a user based on user input such as commands or questions, including verbal ones. Such technologies often incorporate chatbot capabilities to streaml ...
s (such as
Siri
Siri ( , backronym: Speech Interpretation and Recognition Interface) is a digital assistant purchased, developed, and popularized by Apple Inc., which is included in the iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, macOS, Apple TV, audioOS, and visionOS operating sys ...
or
Alexa
Alexa may refer to: Technology
*Amazon Alexa, a virtual assistant developed by Amazon
* Alexa Internet, a defunct website ranking and traffic analysis service
* Alexa Fluor, a family of fluorescent dyes
* Arri Alexa, a digital motion picture ca ...
),
autonomous vehicles (including
drones,
ADAS and
self-driving cars),
automatic language translation (
Microsoft Translator
Microsoft Translator or Bing Translator is a multilingual machine translation cloud service provided by Microsoft. Microsoft Translator is a part of Microsoft Cognitive Services and integrated across multiple consumer, developer, and enterprise pro ...
,
Google Translate
Google Translate is a multilingualism, multilingual neural machine translation, neural machine translation service developed by Google to translation, translate text, documents and websites from one language into another. It offers a web applic ...
),
facial recognition (
Apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
's
FaceID or
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
's
DeepFace and
Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
's
FaceNet) and
image labeling (used by
Facebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
, Apple's
Photos and
TikTok
TikTok, known in mainland China and Hong Kong as Douyin (), is a social media and Short-form content, short-form online video platform owned by Chinese Internet company ByteDance. It hosts user-submitted videos, which may range in duration f ...
). The deployment of AI may be overseen by a
Chief automation officer (CAO).
Health and medicine
The application of AI in
medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
and
medical research
Medical research (or biomedical research), also known as health research, refers to the process of using scientific methods with the aim to produce knowledge about human diseases, the prevention and treatment of illness, and the promotion of ...
has the potential to increase patient care and quality of life. Through the lens of the Hippocratic Oath, medical professionals are ethically compelled to use AI, if applications can more accurately diagnose and treat patients.
For medical research, AI is an important tool for processing and integrating big data. This is particularly important for organoid and tissue engineering development which use microscopy imaging as a key technique in fabrication.
It has been suggested that AI can overcome discrepancies in funding allocated to different fields of research.
New AI tools can deepen the understanding of biomedically relevant pathways. For example, AlphaFold 2 (2021) demonstrated the ability to approximate, in hours rather than months, the 3D Protein structure, structure of a protein. In 2023, it was reported that AI-guided drug discovery helped find a class of antibiotics capable of killing two different types of drug-resistant bacteria. In 2024, researchers used machine learning to accelerate the search for Parkinson's disease drug treatments. Their aim was to identify compounds that block the clumping, or aggregation, of alpha-synuclein (the protein that characterises Parkinson's disease). They were able to speed up the initial screening process ten-fold and reduce the cost by a thousand-fold.
Games
Game AI, Game playing programs have been used since the 1950s to demonstrate and test AI's most advanced techniques. IBM Deep Blue, Deep Blue became the first computer chess-playing system to beat a reigning world chess champion, Garry Kasparov, on 11 May 1997. In 2011, in a ''Jeopardy!'' quiz show exhibition match, IBM's question answering system, Watson (artificial intelligence software), Watson, defeated the two greatest ''Jeopardy!'' champions, Brad Rutter and Ken Jennings, by a significant margin. In March 2016, AlphaGo won 4 out of 5 games of
Go in a match with Go champion Lee Sedol, becoming the first computer Go-playing system to beat a professional Go player without Go handicaps, handicaps. Then, in 2017, it AlphaGo versus Ke Jie, defeated Ke Jie, who was the best Go player in the world. Other programs handle Imperfect information, imperfect-information games, such as the poker-playing program Pluribus (poker bot), Pluribus. DeepMind developed increasingly generalistic
reinforcement learning
Reinforcement learning (RL) is an interdisciplinary area of machine learning and optimal control concerned with how an intelligent agent should take actions in a dynamic environment in order to maximize a reward signal. Reinforcement learnin ...
models, such as with MuZero, which could be trained to play chess, Go, or Atari games. In 2019, DeepMind's AlphaStar achieved grandmaster level in StarCraft II, a particularly challenging real-time strategy game that involves incomplete knowledge of what happens on the map. In 2021, an AI agent competed in a PlayStation Gran Turismo (series), Gran Turismo competition, winning against four of the world's best Gran Turismo drivers using deep reinforcement learning. In 2024, Google DeepMind introduced SIMA, a type of AI capable of autonomously playing nine previously unseen open-world video games by observing screen output, as well as executing short, specific tasks in response to natural language instructions.
Mathematics
Large language models, such as GPT-4,
Gemini, Claude (language model), Claude, Llama (language model), Llama or Mistral AI, Mistral, are increasingly used in mathematics. These probabilistic models are versatile, but can also produce wrong answers in the form of
hallucinations
A hallucination is a perception in the absence of an external stimulus that has the compelling sense of reality. They are distinguishable from several related phenomena, such as dreaming ( REM sleep), which does not involve wakefulness; pse ...
. They sometimes need a large database of mathematical problems to learn from, but also methods such as Supervised learning, supervised Fine-tuning (deep learning), fine-tuning or trained Statistical classification, classifiers with human-annotated data to improve answers for new problems and learn from corrections. A February 2024 study showed that the performance of some language models for reasoning capabilities in solving math problems not included in their training data was low, even for problems with only minor deviations from trained data. One technique to improve their performance involves training the models to produce correct Automated reasoning, reasoning steps, rather than just the correct result. The Alibaba Group developed a version of its ''Qwen'' models called ''Qwen2-Math'', that achieved state-of-the-art performance on several mathematical benchmarks, including 84% accuracy on the MATH dataset of competition mathematics problems.
In January 2025, Microsoft proposed the technique ''rStar-Math'' that leverages Monte Carlo tree search and step-by-step reasoning, enabling a relatively small language model like ''Qwen-7B'' to solve 53% of the American Invitational Mathematics Examination, AIME 2024 and 90% of the MATH benchmark problems.
Alternatively, dedicated models for mathematical problem solving with higher precision for the outcome including proof of theorems have been developed such as ''AlphaTensor'', ''AlphaGeometry'', ''AlphaProof'' and ''AlphaEvolve'' all from
Google DeepMind
DeepMind Technologies Limited, trading as Google DeepMind or simply DeepMind, is a British–American artificial intelligence research laboratory which serves as a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. Founded in the UK in 2010, it was acquired by Goo ...
, ''Llemma'' from EleutherAI or ''Julius''.
When natural language is used to describe mathematical problems, converters can transform such prompts into a formal language such as Lean (proof assistant), Lean to define mathematical tasks.
Some models have been developed to solve challenging problems and reach good results in benchmark tests, others to serve as educational tools in mathematics.
Topological deep learning integrates various topology, topological approaches.
Finance
Finance is one of the fastest growing sectors where applied AI tools are being deployed: from retail online banking to investment advice and insurance, where automated "robot advisers" have been in use for some years.
According to Nicolas Firzli, director of the World Pensions & Investments Forum, it may be too early to see the emergence of highly innovative AI-informed financial products and services. He argues that "the deployment of AI tools will simply further automatise things: destroying tens of thousands of jobs in banking, financial planning, and pension advice in the process, but I'm not sure it will unleash a new wave of [e.g., sophisticated] pension innovation."
Military
Various countries are deploying AI military applications.
[Template:PD-notice, PD-notice] The main applications enhance command and control, communications, sensors, integration and interoperability.
Research is targeting intelligence collection and analysis, logistics, cyber operations, information operations, and semiautonomous and Vehicular automation, autonomous vehicles.
AI technologies enable coordination of sensors and effectors, threat detection and identification, marking of enemy positions, target acquisition, coordination and deconfliction of distributed Forward observers in the U.S. military, Joint Fires between networked combat vehicles, both human-operated and Vehicular automation, autonomous.
AI has been used in military operations in Iraq, Syria, Israel and Ukraine.
Generative AI

Agents
AI agents are software entities designed to perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions autonomously to achieve specific goals. These agents can interact with users, their environment, or other agents. AI agents are used in various applications, including
virtual assistant
A virtual assistant (VA) is a software agent that can perform a range of tasks or services for a user based on user input such as commands or questions, including verbal ones. Such technologies often incorporate chatbot capabilities to streaml ...
s, chatbots,
autonomous vehicles, Video game console, game-playing systems, and industrial robotics. AI agents operate within the constraints of their programming, available computational resources, and hardware limitations. This means they are restricted to performing tasks within their defined scope and have finite memory and processing capabilities. In real-world applications, AI agents often face time constraints for decision-making and action execution. Many AI agents incorporate learning algorithms, enabling them to improve their performance over time through experience or training. Using machine learning, AI agents can adapt to new situations and optimise their behaviour for their designated tasks.
Sexuality
Applications of AI in this domain include AI-enabled menstruation and fertility trackers that analyze user data to offer predictions, AI-integrated sex toys (e.g., teledildonics), AI-generated sexual education content, and AI agents that simulate sexual and romantic partners (e.g., Replika). AI is also used for the production of non-consensual deepfake pornography, raising significant ethical and legal concerns.
AI technologies have also been used to attempt to identify online gender-based violence and online sexual grooming of minors.
Other industry-specific tasks
There are also thousands of successful AI applications used to solve specific problems for specific industries or institutions. In a 2017 survey, one in five companies reported having incorporated "AI" in some offerings or processes. A few examples are energy storage, medical diagnosis, military logistics, applications that predict the result of judicial decisions, foreign policy, or supply chain management.
AI applications for evacuation and disaster management are growing. AI has been used to investigate patterns in large-scale and small-scale evacuations using historical data from GPS, videos or social media. Furthermore, AI can provide real-time information on the evacuation conditions.
In agriculture, AI has helped farmers to increase yield and identify areas that need irrigation, fertilization, pesticide treatments. Agronomists use AI to conduct research and development. AI has been used to predict the ripening time for crops such as tomatoes, monitor soil moisture, operate agricultural robots, conduct predictive analytics, classify livestock pig call emotions, automate greenhouses, detect diseases and pests, and save water.
Artificial intelligence is used in astronomy to analyze increasing amounts of available data and applications, mainly for "classification, regression, clustering, forecasting, generation, discovery, and the development of new scientific insights." For example, it is used for discovering exoplanets, forecasting solar activity, and distinguishing between signals and instrumental effects in gravitational wave astronomy. Additionally, it could be used for activities in space, such as space exploration, including the analysis of data from space missions, real-time science decisions of spacecraft, space debris avoidance, and more autonomous operation.
During the 2024 Indian general election, 2024 Indian elections, US$50 million was spent on authorized AI-generated content, notably by creating deepfakes of allied (including sometimes deceased) politicians to better engage with voters, and by translating speeches to various local languages.
Ethics
AI has potential benefits and potential risks. AI may be able to advance science and find solutions for serious problems: Demis Hassabis of DeepMind hopes to "solve intelligence, and then use that to solve everything else". However, as the use of AI has become widespread, several unintended consequences and risks have been identified. In-production systems can sometimes not factor ethics and bias into their AI training processes, especially when the AI algorithms are inherently unexplainable in deep learning.
Risks and harm
Privacy and copyright
Machine learning algorithms require large amounts of data. The techniques used to acquire this data have raised concerns about privacy, surveillance and copyright.
AI-powered devices and services, such as virtual assistants and IoT products, continuously collect personal information, raising concerns about intrusive data gathering and unauthorized access by third parties. The loss of privacy is further exacerbated by AI's ability to process and combine vast amounts of data, potentially leading to a surveillance society where individual activities are constantly monitored and analyzed without adequate safeguards or transparency.
Sensitive user data collected may include online activity records, geolocation data, video, or audio. For example, in order to build
speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also ...
algorithms,
Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
has recorded millions of private conversations and allowed temporary workers to listen to and transcribe some of them. Opinions about this widespread surveillance range from those who see it as a necessary evil to those for whom it is clearly unethical and a violation of the right to privacy.
AI developers argue that this is the only way to deliver valuable applications and have developed several techniques that attempt to preserve privacy while still obtaining the data, such as data aggregation, de-identification and differential privacy. Since 2016, some privacy experts, such as Cynthia Dwork, have begun to view privacy in terms of fairness (machine learning), fairness. Brian Christian wrote that experts have pivoted "from the question of 'what they know' to the question of 'what they're doing with it'."
Generative AI is often trained on unlicensed copyrighted works, including in domains such as images or computer code; the output is then used under the rationale of "fair use". Experts disagree about how well and under what circumstances this rationale will hold up in courts of law; relevant factors may include "the purpose and character of the use of the copyrighted work" and "the effect upon the potential market for the copyrighted work". Website owners who do not wish to have their content scraped can indicate it in a "robots.txt" file. In 2023, leading authors (including John Grisham and Jonathan Franzen) sued AI companies for using their work to train generative AI. Another discussed approach is to envision a separate ''sui generis'' system of protection for creations generated by AI to ensure fair attribution and compensation for human authors.
Dominance by tech giants
The commercial AI scene is dominated by Big Tech companies such as Alphabet Inc.,
Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
, Apple Inc., Meta Platforms, and
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
. Some of these players already own the vast majority of existing cloud computing, cloud infrastructure and computing power from data centers, allowing them to entrench further in the marketplace.
Power needs and environmental impacts
In January 2024, the International Energy Agency (IEA) released ''Electricity 2024, Analysis and Forecast to 2026'', forecasting electric power use. This is the first IEA report to make projections for data centers and power consumption for artificial intelligence and cryptocurrency. The report states that power demand for these uses might double by 2026, with additional electric power usage equal to electricity used by the whole Japanese nation.
Prodigious power consumption by AI is responsible for the growth of fossil fuel use, and might delay closings of obsolete, carbon-emitting coal energy facilities. There is a feverish rise in the construction of data centers throughout the US, making large technology firms (e.g., Microsoft, Meta, Google, Amazon) into voracious consumers of electric power. Projected electric consumption is so immense that there is concern that it will be fulfilled no matter the source. A ChatGPT search involves the use of 10 times the electrical energy as a Google search. The large firms are in haste to find power sources – from nuclear energy to geothermal to fusion. The tech firms argue that – in the long view – AI will be eventually kinder to the environment, but they need the energy now. AI makes the power grid more efficient and "intelligent", will assist in the growth of nuclear power, and track overall carbon emissions, according to technology firms.
A 2024 Goldman Sachs Research Paper, ''AI Data Centers and the Coming US Power Demand Surge'', found "US power demand (is) likely to experience growth not seen in a generation...." and forecasts that, by 2030, US data centers will consume 8% of US power, as opposed to 3% in 2022, presaging growth for the electrical power generation industry by a variety of means. Data centers' need for more and more electrical power is such that they might max out the electrical grid. The Big Tech companies counter that AI can be used to maximize the utilization of the grid by all.
In 2024, the ''Wall Street Journal'' reported that big AI companies have begun negotiations with the US nuclear power providers to provide electricity to the data centers. In March 2024 Amazon purchased a Pennsylvania nuclear-powered data center for US$650 million.
Nvidia
Nvidia Corporation ( ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and incorporated in Delaware. Founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang (president and CEO), Chris Malachowsky, and Curti ...
CEO
Jensen Huang
Jen-Hsun "Jensen" Huang ( zh, t=黃仁勳, poj=N̂g Jîn-hun, hp=Huáng Rénxūn; born February 17, 1963) is a Taiwanese and American businessman, electrical engineer, and philanthropist who is the president, co-founder, and chief executive of ...
said nuclear power is a good option for the data centers.
In September 2024,
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
announced an agreement with Constellation Energy to re-open the Three Mile Island nuclear power plant to provide Microsoft with 100% of all electric power produced by the plant for 20 years. Reopening the plant, which suffered a partial nuclear meltdown of its Unit 2 reactor in 1979, will require Constellation to get through strict regulatory processes which will include extensive safety scrutiny from the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission. If approved (this will be the first ever US re-commissioning of a nuclear plant), over 835 megawatts of power – enough for 800,000 homes – of energy will be produced. The cost for re-opening and upgrading is estimated at $1.6 billion (US) and is dependent on tax breaks for nuclear power contained in the 2022 US Inflation Reduction Act. The US government and the state of Michigan are investing almost $2 billion (US) to reopen the Palisades Nuclear Generating Station, Palisades Nuclear reactor on Lake Michigan. Closed since 2022, the plant is planned to be reopened in October 2025. The Three Mile Island facility will be renamed the Crane Clean Energy Center after Chris Crane, a nuclear proponent and former CEO of Exelon who was responsible for Exelon's spinoff of Constellation.
After the last approval in September 2023, Taiwan suspended the approval of data centers north of Taoyuan, Taiwan, Taoyuan with a capacity of more than 5 MW in 2024, due to power supply shortages.
Taiwan aims to Nuclear power phase-out, phase out nuclear power by 2025.
On the other hand, Singapore imposed a ban on the opening of data centers in 2019 due to electric power, but in 2022, lifted this ban.
Although most nuclear plants in Japan have been shut down after the 2011 Fukushima nuclear accident, according to an October 2024 ''Bloomberg'' article in Japanese, cloud gaming services company Ubitus, in which Nvidia has a stake, is looking for land in Japan near nuclear power plant for a new data center for generative AI.
Ubitus CEO Wesley Kuo said nuclear power plants are the most efficient, cheap and stable power for AI.
On 1 November 2024, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) rejected an application submitted by Talen Energy for approval to supply some electricity from the nuclear power station Susquehanna Steam Electric Station, Susquehanna to Amazon's data center.
According to the Commission Chairman Willie L. Phillips, it is a burden on the electricity grid as well as a significant cost shifting concern to households and other business sectors.
In 2025, a report prepared by the International Energy Agency estimated the greenhouse gas emissions from the energy consumption of AI at 180 million tons. By 2035, these emissions could rise to 300-500 million tonnes depending on what measures will be taken. This is below 1.5% of the energy sector emissions. The emissions reduction potential of AI was estimated at 5% of the energy sector emissions, but Rebound effect (conservation), rebound effects (for example if people switch from public transport to autonomous cars) can reduce it.
Misinformation
YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in ...
,
Facebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
and others use recommender systems to guide users to more content. These AI programs were given the goal of mathematical optimization, maximizing user engagement (that is, the only goal was to keep people watching). The AI learned that users tended to choose misinformation, conspiracy theories, and extreme partisan (politics), partisan content, and, to keep them watching, the AI recommended more of it. Users also tended to watch more content on the same subject, so the AI led people into filter bubbles where they received multiple versions of the same misinformation. This convinced many users that the misinformation was true, and ultimately undermined trust in institutions, the media and the government. The AI program had correctly learned to maximize its goal, but the result was harmful to society. After the U.S. election in 2016, major technology companies took some steps to mitigate the problem.
In 2022, generative AI began to create images, audio, video and text that are indistinguishable from real photographs, recordings, films, or human writing. It is possible for bad actors to use this technology to create massive amounts of misinformation or propaganda. One such potential malicious use is deepfakes for computational propaganda. AI pioneer Geoffrey Hinton expressed concern about AI enabling "authoritarian leaders to manipulate their electorates" on a large scale, among other risks.
AI researchers at
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
,
OpenAI
OpenAI, Inc. is an American artificial intelligence (AI) organization founded in December 2015 and headquartered in San Francisco, California. It aims to develop "safe and beneficial" artificial general intelligence (AGI), which it defines ...
, universities and other organisations have suggested using "Proof of personhood#Approaches, personhood credentials" as a way to overcome online deception enabled by AI models.
Algorithmic bias and fairness
Machine learning applications will be algorithmic bias, biased if they learn from biased data. The developers may not be aware that the bias exists. Bias can be introduced by the way training data is selected and by the way a model is deployed. If a biased algorithm is used to make decisions that can seriously harm people (as it can in health equity, medicine, credit rating, finance, recruitment, public housing, housing or policing) then the algorithm may cause discrimination. The field of fairness (machine learning), fairness studies how to prevent harms from algorithmic biases.
On June 28, 2015, Google Photos's new image labeling feature mistakenly identified Jacky Alcine and a friend as "gorillas" because they were black. The system was trained on a dataset that contained very few images of black people, a problem called "sample size disparity". Google "fixed" this problem by preventing the system from labelling ''anything'' as a "gorilla". Eight years later, in 2023, Google Photos still could not identify a gorilla, and neither could similar products from Apple, Facebook, Microsoft and Amazon.
COMPAS (software), COMPAS is a commercial program widely used by U.S. courts to assess the likelihood of a defendant becoming a recidivist. In 2016, Julia Angwin at ProPublica discovered that COMPAS exhibited racial bias, despite the fact that the program was not told the races of the defendants. Although the error rate for both whites and blacks was calibrated equal at exactly 61%, the errors for each race were different—the system consistently overestimated the chance that a black person would re-offend and would underestimate the chance that a white person would not re-offend. In 2017, several researchers showed that it was mathematically impossible for COMPAS to accommodate all possible measures of fairness when the base rates of re-offense were different for whites and blacks in the data.
A program can make biased decisions even if the data does not explicitly mention a problematic feature (such as "race" or "gender"). The feature will correlate with other features (like "address", "shopping history" or "first name"), and the program will make the same decisions based on these features as it would on "race" or "gender". Moritz Hardt said "the most robust fact in this research area is that fairness through blindness doesn't work."
Criticism of COMPAS highlighted that machine learning models are designed to make "predictions" that are only valid if we assume that the future will resemble the past. If they are trained on data that includes the results of racist decisions in the past, machine learning models must predict that racist decisions will be made in the future. If an application then uses these predictions as ''recommendations'', some of these "recommendations" will likely be racist. Thus, machine learning is not well suited to help make decisions in areas where there is hope that the future will be ''better'' than the past. It is descriptive rather than prescriptive.
Bias and unfairness may go undetected because the developers are overwhelmingly white and male: among AI engineers, about 4% are black and 20% are women.
There are various conflicting definitions and mathematical models of fairness. These notions depend on ethical assumptions, and are influenced by beliefs about society. One broad category is Distributive justice, distributive fairness, which focuses on the outcomes, often identifying groups and seeking to compensate for statistical disparities. Representational fairness tries to ensure that AI systems do not reinforce negative stereotypes or render certain groups invisible. Procedural fairness focuses on the decision process rather than the outcome. The most relevant notions of fairness may depend on the context, notably the type of AI application and the stakeholders. The subjectivity in the notions of bias and fairness makes it difficult for companies to operationalize them. Having access to sensitive attributes such as race or gender is also considered by many AI ethicists to be necessary in order to compensate for biases, but it may conflict with anti-discrimination laws.
At its 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (ACM FAccT 2022), the Association for Computing Machinery, in Seoul, South Korea, presented and published findings that recommend that until AI and robotics systems are demonstrated to be free of bias mistakes, they are unsafe, and the use of self-learning neural networks trained on vast, unregulated sources of flawed internet data should be curtailed.
Lack of transparency
Many AI systems are so complex that their designers cannot explain how they reach their decisions. Particularly with deep neural networks, in which there are many non-linear relationships between inputs and outputs. But some popular explainability techniques exist.
It is impossible to be certain that a program is operating correctly if no one knows how exactly it works. There have been many cases where a machine learning program passed rigorous tests, but nevertheless learned something different than what the programmers intended. For example, a system that could identify skin diseases better than medical professionals was found to actually have a strong tendency to classify images with a ruler as "cancerous", because pictures of malignancies typically include a ruler to show the scale. Another machine learning system designed to help effectively allocate medical resources was found to classify patients with asthma as being at "low risk" of dying from pneumonia. Having asthma is actually a severe risk factor, but since the patients having asthma would usually get much more medical care, they were relatively unlikely to die according to the training data. The correlation between asthma and low risk of dying from pneumonia was real, but misleading.
People who have been harmed by an algorithm's decision have a right to an explanation. Doctors, for example, are expected to clearly and completely explain to their colleagues the reasoning behind any decision they make. Early drafts of the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation in 2016 included an explicit statement that this right exists. Industry experts noted that this is an unsolved problem with no solution in sight. Regulators argued that nevertheless the harm is real: if the problem has no solution, the tools should not be used.
DARPA established the Explainable Artificial Intelligence, XAI ("Explainable Artificial Intelligence") program in 2014 to try to solve these problems.
Several approaches aim to address the transparency problem. SHAP enables to visualise the contribution of each feature to the output. LIME can locally approximate a model's outputs with a simpler, interpretable model. Multitask learning provides a large number of outputs in addition to the target classification. These other outputs can help developers deduce what the network has learned. Deconvolution, DeepDream and other generative AI, generative methods can allow developers to see what different layers of a deep network for computer vision have learned, and produce output that can suggest what the network is learning. For
generative pre-trained transformer
A generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) is a type of large language model (LLM) and a prominent framework for generative artificial intelligence. It is an Neural network (machine learning), artificial neural network that is used in natural ...
s, Anthropic developed a technique based on dictionary learning that associates patterns of neuron activations with human-understandable concepts.
Bad actors and weaponized AI
Artificial intelligence provides a number of tools that are useful to bad actors, such as authoritarian, authoritarian governments, terrorists, criminals or rogue states.
A lethal autonomous weapon is a machine that locates, selects and engages human targets without human supervision. Widely available AI tools can be used by bad actors to develop inexpensive autonomous weapons and, if produced at scale, they are potentially weapons of mass destruction. Even when used in conventional warfare, they currently cannot reliably choose targets and could potentially murder, kill an innocent person. In 2014, 30 nations (including China) supported a ban on autonomous weapons under the United Nations' Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons, however the United States and others disagreed. By 2015, over fifty countries were reported to be researching battlefield robots.
AI tools make it easier for Authoritarian, authoritarian governments to efficiently control their citizens in several ways. Facial recognition system, Face and Speaker recognition, voice recognition allow widespread surveillance.
Machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
, operating this data, can classifier (machine learning), classify potential enemies of the state and prevent them from hiding. Recommendation systems can precisely target propaganda and misinformation for maximum effect. Deepfakes and generative AI aid in producing misinformation. Advanced AI can make authoritarian technocracy, centralized decision-making more competitive than liberal and decentralized systems such as market (economics), markets. It lowers the cost and difficulty of digital warfare and spyware, advanced spyware. All these technologies have been available since 2020 or earlier—AI facial recognition systems are already being used for mass surveillance in China.
There are many other ways in which AI is expected to help bad actors, some of which can not be foreseen. For example, machine-learning AI is able to design tens of thousands of toxic molecules in a matter of hours.
Technological unemployment
Economists have frequently highlighted the risks of redundancies from AI, and speculated about unemployment if there is no adequate social policy for full employment.
[E. McGaughey, 'Will Robots Automate Your Job Away? Full Employment, Basic Income, and Economic Democracy' (2022)]
51(3) Industrial Law Journal 511–559
.
In the past, technology has tended to increase rather than reduce total employment, but economists acknowledge that "we're in uncharted territory" with AI. A survey of economists showed disagreement about whether the increasing use of robots and AI will cause a substantial increase in long-term unemployment, but they generally agree that it could be a net benefit if productivity gains are Redistribution of income and wealth, redistributed. Risk estimates vary; for example, in the 2010s, Michael Osborne and Carl Benedikt Frey estimated 47% of U.S. jobs are at "high risk" of potential automation, while an OECD report classified only 9% of U.S. jobs as "high risk". The methodology of speculating about future employment levels has been criticised as lacking evidential foundation, and for implying that technology, rather than social policy, creates unemployment, as opposed to redundancies.
In April 2023, it was reported that 70% of the jobs for Chinese video game illustrators had been eliminated by generative artificial intelligence.
Unlike previous waves of automation, many middle-class jobs may be eliminated by artificial intelligence; ''The Economist'' stated in 2015 that "the worry that AI could do to white-collar jobs what steam power did to blue-collar ones during the Industrial Revolution" is "worth taking seriously". Jobs at extreme risk range from paralegals to fast food cooks, while job demand is likely to increase for care-related professions ranging from personal healthcare to the clergy.
From the early days of the development of artificial intelligence, there have been arguments, for example, those put forward by Joseph Weizenbaum, about whether tasks that can be done by computers actually should be done by them, given the difference between computers and humans, and between quantitative calculation and qualitative, value-based judgement.
Existential risk
It has been argued AI will become so powerful that humanity may irreversibly lose control of it. This could, as physicist Stephen Hawking stated, "Global catastrophic risk, spell the end of the human race". This scenario has been common in science fiction, when a computer or robot suddenly develops a human-like "self-awareness" (or "sentience" or "consciousness") and becomes a malevolent character. These sci-fi scenarios are misleading in several ways.
First, AI does not require human-like sentience to be an existential risk. Modern AI programs are given specific goals and use learning and intelligence to achieve them. Philosopher Nick Bostrom argued that if one gives ''almost any'' goal to a sufficiently powerful AI, it may choose to destroy humanity to achieve it (he used the example of a Instrumental convergence#Paperclip maximizer, paperclip maximizer). Stuart J. Russell, Stuart Russell gives the example of household robot that tries to find a way to kill its owner to prevent it from being unplugged, reasoning that "you can't fetch the coffee if you're dead." In order to be safe for humanity, a superintelligence would have to be genuinely AI alignment, aligned with humanity's morality and values so that it is "fundamentally on our side".
Second, Yuval Noah Harari argues that AI does not require a robot body or physical control to pose an existential risk. The essential parts of civilization are not physical. Things like ideologies, law, government, money and the economy are built on language; they exist because there are stories that billions of people believe. The current prevalence of misinformation suggests that an AI could use language to convince people to believe anything, even to take actions that are destructive.
The opinions amongst experts and industry insiders are mixed, with sizable fractions both concerned and unconcerned by risk from eventual superintelligent AI. Personalities such as Stephen Hawking, Bill Gates, and Elon Musk, as well as AI pioneers such as Yoshua Bengio, Stuart J. Russell, Stuart Russell, Demis Hassabis, and Sam Altman, have expressed concerns about existential risk from AI.
In May 2023, Geoffrey Hinton announced his resignation from Google in order to be able to "freely speak out about the risks of AI" without "considering how this impacts Google". He notably mentioned risks of an AI takeover, and stressed that in order to avoid the worst outcomes, establishing safety guidelines will require cooperation among those competing in use of AI.
In 2023, many leading AI experts endorsed Statement on AI risk of extinction, the joint statement that "Mitigating the risk of extinction from AI should be a global priority alongside other societal-scale risks such as pandemics and nuclear war".
Some other researchers were more optimistic. AI pioneer Jürgen Schmidhuber did not sign the joint statement, emphasising that in 95% of all cases, AI research is about making "human lives longer and healthier and easier." While the tools that are now being used to improve lives can also be used by bad actors, "they can also be used against the bad actors." Andrew Ng also argued that "it's a mistake to fall for the doomsday hype on AI—and that regulators who do will only benefit vested interests." Yann LeCun "scoffs at his peers' dystopian scenarios of supercharged misinformation and even, eventually, human extinction." In the early 2010s, experts argued that the risks are too distant in the future to warrant research or that humans will be valuable from the perspective of a superintelligent machine. However, after 2016, the study of current and future risks and possible solutions became a serious area of research.
Ethical machines and alignment
Friendly AI are machines that have been designed from the beginning to minimize risks and to make choices that benefit humans. Eliezer Yudkowsky, who coined the term, argues that developing friendly AI should be a higher research priority: it may require a large investment and it must be completed before AI becomes an existential risk.
Machines with intelligence have the potential to use their intelligence to make ethical decisions. The field of machine ethics provides machines with ethical principles and procedures for resolving ethical dilemmas.
The field of machine ethics is also called computational morality,
and was founded at an AAAI symposium in 2005.
Other approaches include Wendell Wallach's "artificial moral agents" and Stuart J. Russell's Human Compatible#Russell's three principles, three principles for developing provably beneficial machines.
Open source
Active organizations in the AI open-source community include Hugging Face,
Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
, EleutherAI and
Meta. Various AI models, such as LLaMA, Llama 2, Mistral AI, Mistral or Stable Diffusion, have been made open-weight, meaning that their architecture and trained parameters (the "weights") are publicly available. Open-weight models can be freely Fine-tuning (deep learning), fine-tuned, which allows companies to specialize them with their own data and for their own use-case. Open-weight models are useful for research and innovation but can also be misused. Since they can be fine-tuned, any built-in security measure, such as objecting to harmful requests, can be trained away until it becomes ineffective. Some researchers warn that future AI models may develop dangerous capabilities (such as the potential to drastically facilitate bioterrorism) and that once released on the Internet, they cannot be deleted everywhere if needed. They recommend pre-release audits and cost-benefit analyses.
Frameworks
Artificial intelligence projects can be guided by ethical considerations during the design, development, and implementation of an AI system. An AI framework such as the Care and Act Framework, developed by the Alan Turing Institute and based on the SUM values, outlines four main ethical dimensions, defined as follows:
* Respect the dignity of individual people
* Connect with other people sincerely, openly, and inclusively
* Care for the wellbeing of everyone
* Protect social values, justice, and the public interest
Other developments in ethical frameworks include those decided upon during the Asilomar Conference on Beneficial AI, Asilomar Conference, the Montreal Declaration for Responsible AI, and the IEEE's Ethics of Autonomous Systems initiative, among others; however, these principles are not without criticism, especially regarding the people chosen to contribute to these frameworks.
Promotion of the wellbeing of the people and communities that these technologies affect requires consideration of the social and ethical implications at all stages of AI system design, development and implementation, and collaboration between job roles such as data scientists, product managers, data engineers, domain experts, and delivery managers.
The AI Safety Institute (United Kingdom), UK AI Safety Institute released in 2024 a testing toolset called 'Inspect' for AI safety evaluations available under an MIT open-source licence which is freely available on GitHub and can be improved with third-party packages. It can be used to evaluate AI models in a range of areas including core knowledge, ability to reason, and autonomous capabilities.
Regulation

The regulation of artificial intelligence is the development of public sector policies and laws for promoting and regulating AI; it is therefore related to the broader regulation of algorithms. The regulatory and policy landscape for AI is an emerging issue in jurisdictions globally. According to AI Index at Stanford, the annual number of AI-related laws passed in the 127 survey countries jumped from one passed in 2016 to 37 passed in 2022 alone. Between 2016 and 2020, more than 30 countries adopted dedicated strategies for AI. Most EU member states had released national AI strategies, as had Canada, China, India, Japan, Mauritius, the Russian Federation, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, U.S., and Vietnam. Others were in the process of elaborating their own AI strategy, including Bangladesh, Malaysia and Tunisia. The Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence was launched in June 2020, stating a need for AI to be developed in accordance with human rights and democratic values, to ensure public confidence and trust in the technology. Henry Kissinger, Eric Schmidt, and Daniel Huttenlocher published a joint statement in November 2021 calling for a government commission to regulate AI. In 2023, OpenAI leaders published recommendations for the governance of superintelligence, which they believe may happen in less than 10 years. In 2023, the United Nations also launched an advisory body to provide recommendations on AI governance; the body comprises technology company executives, government officials and academics. In 2024, the Council of Europe created the first international legally binding treaty on AI, called the "Framework Convention on Artificial Intelligence and Human Rights, Democracy and the Rule of Law". It was adopted by the European Union, the United States, the United Kingdom, and other signatories.
In a 2022 Ipsos survey, attitudes towards AI varied greatly by country; 78% of Chinese citizens, but only 35% of Americans, agreed that "products and services using AI have more benefits than drawbacks". A 2023 Reuters/Ipsos poll found that 61% of Americans agree, and 22% disagree, that AI poses risks to humanity. In a 2023 Fox News poll, 35% of Americans thought it "very important", and an additional 41% thought it "somewhat important", for the federal government to regulate AI, versus 13% responding "not very important" and 8% responding "not at all important".
In November 2023, the first global AI Safety Summit was held in Bletchley Park in the UK to discuss the near and far term risks of AI and the possibility of mandatory and voluntary regulatory frameworks. 28 countries including the United States, China, and the European Union issued a declaration at the start of the summit, calling for international co-operation to manage the challenges and risks of artificial intelligence. In May 2024 at the AI Seoul Summit, 16 global AI tech companies agreed to safety commitments on the development of AI.
History
The study of mechanical or "formal" reasoning began with philosophers and mathematicians in antiquity. The study of logic led directly to Alan Turing's theory of computation, which suggested that a machine, by shuffling symbols as simple as "0" and "1", could simulate any conceivable form of mathematical reasoning.
This, along with concurrent discoveries in cybernetics, information theory and neurobiology, led researchers to consider the possibility of building an "electronic brain". They developed several areas of research that would become part of AI, such as Warren Sturgis McCulloch, McCulloch and Walter Pitts, Pitts design for "artificial neurons" in 1943, and Turing's influential 1950 paper 'Computing Machinery and Intelligence', which introduced the Turing test and showed that "machine intelligence" was plausible.
The field of AI research was founded at Dartmouth workshop, a workshop at Dartmouth College in 1956.
[Dartmouth workshop: , , ]
The proposal: The attendees became the leaders of AI research in the 1960s. They and their students produced programs that the press described as "astonishing": computers were learning checkers strategies, solving word problems in algebra, proving Theorem, logical theorems and speaking English.
[Successful programs of the 1960s: , , , ] Artificial intelligence laboratories were set up at a number of British and U.S. universities in the latter 1950s and early 1960s.
Researchers in the 1960s and the 1970s were convinced that their methods would eventually succeed in creating a machine with artificial general intelligence, general intelligence and considered this the goal of their field. In 1965 Herbert A. Simon, Herbert Simon predicted, "machines will be capable, within twenty years, of doing any work a man can do". In 1967 Marvin Minsky agreed, writing that "within a generation ... the problem of creating 'artificial intelligence' will substantially be solved". They had, however, underestimated the difficulty of the problem. In 1974, both the U.S. and British governments cut off exploratory research in response to the Lighthill report, criticism of Sir James Lighthill and ongoing pressure from the U.S. Congress to Mansfield Amendment, fund more productive projects. Marvin Minsky, Minsky and Papert's book ''
Perceptron
In machine learning, the perceptron is an algorithm for supervised classification, supervised learning of binary classification, binary classifiers. A binary classifier is a function that can decide whether or not an input, represented by a vect ...
s'' was understood as proving that
artificial neural networks
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks.
A neural network consists of connected ...
would never be useful for solving real-world tasks, thus discrediting the approach altogether. The "
AI winter", a period when obtaining funding for AI projects was difficult, followed.
[First AI Winter, Lighthill report, Mansfield Amendment: , , , , ]
In the early 1980s, AI research was revived by the commercial success of expert systems, a form of AI program that simulated the knowledge and analytical skills of human experts. By 1985, the market for AI had reached over a billion dollars. At the same time, Japan's fifth generation computer project inspired the U.S. and British governments to restore funding for academic research.
[Funding initiatives in the early 1980s: Fifth Generation Project (Japan), Alvey (UK), Microelectronics and Computer Technology Corporation (US), Strategic Computing Initiative (US): , , , , ] However, beginning with the collapse of the Lisp Machine market in 1987, AI once again fell into disrepute, and a second, longer-lasting winter began.
[Second AI Winter: , , , , ]
Up to this point, most of AI's funding had gone to projects that used high-level symbolic AI, symbols to represent mental objects like plans, goals, beliefs, and known facts. In the 1980s, some researchers began to doubt that this approach would be able to imitate all the processes of human cognition, especially machine perception, perception,
robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
,
learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, value (personal and cultural), values, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, non-human animals, and ...
and pattern recognition, and began to look into "sub-symbolic" approaches. Rodney Brooks rejected "representation" in general and focussed directly on engineering machines that move and survive. Judea Pearl, Lotfi A. Zadeh, Lotfi Zadeh, and others developed methods that handled incomplete and uncertain information by making reasonable guesses rather than precise logic.
But the most important development was the revival of "connectionism", including neural network research, by Geoffrey Hinton and others. In 1990, Yann LeCun successfully showed that convolutional neural networks can recognize handwritten digits, the first of many successful applications of neural networks.
AI gradually restored its reputation in the late 1990s and early 21st century by exploiting formal mathematical methods and by finding specific solutions to specific problems. This "narrow AI, narrow" and "formal" focus allowed researchers to produce verifiable results and collaborate with other fields (such as
statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
,
economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ...
and mathematical optimization, mathematics).
[#Neat vs. scruffy, Formal and #Narrow vs. general AI, narrow methods adopted in the 1990s: , ] By 2000, solutions developed by AI researchers were being widely used, although in the 1990s they were rarely described as "artificial intelligence" (a tendency known as the AI effect).
However, several academic researchers became concerned that AI was no longer pursuing its original goal of creating versatile, fully intelligent machines. Beginning around 2002, they founded the subfield of
artificial general intelligence
Artificial general intelligence (AGI)—sometimes called human‑level intelligence AI—is a type of artificial intelligence that would match or surpass human capabilities across virtually all cognitive tasks.
Some researchers argue that sta ...
(or "AGI"), which had several well-funded institutions by the 2010s.
Deep learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience a ...
began to dominate industry benchmarks in 2012 and was adopted throughout the field.
Deep learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience a ...
revolution, AlexNet: , ,
For many specific tasks, other methods were abandoned.
Deep learning's success was based on both hardware improvements (Moore's law, faster computers,
graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal ...
s, cloud computing) and access to big data, large amounts of data (including curated datasets, such as
ImageNet). Deep learning's success led to an enormous increase in interest and funding in AI. The amount of machine learning research (measured by total publications) increased by 50% in the years 2015–2019.
In 2016, issues of algorithmic fairness, fairness and the misuse of technology were catapulted into center stage at machine learning conferences, publications vastly increased, funding became available, and many researchers re-focussed their careers on these issues. The AI alignment, alignment problem became a serious field of academic study.
In the late 2010s and early 2020s, AGI companies began to deliver programs that created enormous interest. In 2015, AlphaGo, developed by DeepMind, beat the world champion Go player. The program taught only the game's rules and developed a strategy by itself. GPT-3 is a
large language model
A large language model (LLM) is a language model trained with self-supervised machine learning on a vast amount of text, designed for natural language processing tasks, especially language generation.
The largest and most capable LLMs are g ...
that was released in 2020 by
OpenAI
OpenAI, Inc. is an American artificial intelligence (AI) organization founded in December 2015 and headquartered in San Francisco, California. It aims to develop "safe and beneficial" artificial general intelligence (AGI), which it defines ...
and is capable of generating high-quality human-like text.
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a generative artificial intelligence chatbot developed by OpenAI and released on November 30, 2022. It uses large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4o as well as other Multimodal learning, multimodal models to create human-like re ...
, launched on November 30, 2022, became the fastest-growing consumer software application in history, gaining over 100 million users in two months. It marked what is widely regarded as AI's breakout year, bringing it into the public consciousness. These programs, and others, inspired an aggressive
AI boom, where large companies began investing billions of dollars in AI research. According to AI Impacts, about $50 billion annually was invested in "AI" around 2022 in the U.S. alone and about 20% of the new U.S. Computer Science PhD graduates have specialized in "AI". About 800,000 "AI"-related U.S. job openings existed in 2022. According to PitchBook research, 22% of newly funded Startup company, startups in 2024 claimed to be AI companies.
Philosophy
Philosophical debates have historically sought to determine the nature of intelligence and how to make intelligent machines. Another major focus has been whether machines can be conscious, and the associated ethical implications.
Many other topics in philosophy are relevant to AI, such as epistemology and free will. Rapid advancements have intensified public discussions on the philosophy and ethics of AI.
Defining artificial intelligence
Alan Turing wrote in 1950 "I propose to consider the question 'can machines think'?" He advised changing the question from whether a machine "thinks", to "whether or not it is possible for machinery to show intelligent behaviour". He devised the Turing test, which measures the ability of a machine to simulate human conversation.
[Turing's original publication of the Turing test in "Computing machinery and intelligence":
Historical influence and philosophical implications: , , , ] Since we can only observe the behavior of the machine, it does not matter if it is "actually" thinking or literally has a "mind". Turing notes that Problem of other minds, we can not determine these things about other people but "it is usual to have a polite convention that everyone thinks."

Stuart J. Russell, Russell and Norvig agree with Turing that intelligence must be defined in terms of external behavior, not internal structure. However, they are critical that the test requires the machine to imitate humans. "Aeronautics, Aeronautical engineering texts", they wrote, "do not define the goal of their field as making 'machines that fly so exactly like pigeons that they can fool other pigeons. AI founder John McCarthy (computer scientist), John McCarthy agreed, writing that "Artificial intelligence is not, by definition, simulation of human intelligence".
McCarthy defines intelligence as "the computational part of the ability to achieve goals in the world". Another AI founder, Marvin Minsky, similarly describes it as "the ability to solve hard problems". The leading AI textbook defines it as the study of agents that perceive their environment and take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. These definitions view intelligence in terms of well-defined problems with well-defined solutions, where both the difficulty of the problem and the performance of the program are direct measures of the "intelligence" of the machine—and no other philosophical discussion is required, or may not even be possible.
Another definition has been adopted by Google, a major practitioner in the field of AI. This definition stipulates the ability of systems to synthesize information as the manifestation of intelligence, similar to the way it is defined in biological intelligence.
Some authors have suggested in practice, that the definition of AI is vague and difficult to define, with contention as to whether classical algorithms should be categorised as AI, with many companies during the early 2020s AI boom using the term as a marketing buzzword, often even if they did "not actually use AI in a material way".
Evaluating approaches to AI
No established unifying theory or paradigm has guided AI research for most of its history. The unprecedented success of statistical machine learning in the 2010s eclipsed all other approaches (so much so that some sources, especially in the business world, use the term "artificial intelligence" to mean "machine learning with neural networks"). This approach is mostly sub-symbolic, soft computing, soft and artificial general intelligence, narrow. Critics argue that these questions may have to be revisited by future generations of AI researchers.
Symbolic AI and its limits
Symbolic AI (or "GOFAI") simulated the high-level conscious reasoning that people use when they solve puzzles, express legal reasoning and do mathematics. They were highly successful at "intelligent" tasks such as algebra or IQ tests. In the 1960s, Newell and Simon proposed the physical symbol systems hypothesis: "A physical symbol system has the necessary and sufficient means of general intelligent action."
However, the symbolic approach failed on many tasks that humans solve easily, such as learning, recognizing an object or Commonsense reasoning, commonsense reasoning. Moravec's paradox is the discovery that high-level "intelligent" tasks were easy for AI, but low level "instinctive" tasks were extremely difficult. Philosopher Hubert Dreyfus had Dreyfus' critique of AI, argued since the 1960s that human expertise depends on unconscious instinct rather than conscious symbol manipulation, and on having a "feel" for the situation, rather than explicit symbolic knowledge. Although his arguments had been ridiculed and ignored when they were first presented, eventually, AI research came to agree with him.
The issue is not resolved: sub-symbolic reasoning can make many of the same inscrutable mistakes that human intuition does, such as algorithmic bias. Critics such as
Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American professor and public intellectual known for his work in linguistics, political activism, and social criticism. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky is also a ...
argue continuing research into symbolic AI will still be necessary to attain general intelligence, in part because sub-symbolic AI is a move away from explainable AI: it can be difficult or impossible to understand why a modern statistical AI program made a particular decision. The emerging field of Neuro-symbolic AI, neuro-symbolic artificial intelligence attempts to bridge the two approaches.
Neat vs. scruffy
"Neats" hope that intelligent behavior is described using simple, elegant principles (such as
logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure o ...
,
optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfiel ...
, or
neural networks
A neural network is a group of interconnected units called neurons that send signals to one another. Neurons can be either Cell (biology), biological cells or signal pathways. While individual neurons are simple, many of them together in a netwo ...
). "Scruffies" expect that it necessarily requires solving a large number of unrelated problems. Neats defend their programs with theoretical rigor, scruffies rely mainly on incremental testing to see if they work. This issue was actively discussed in the 1970s and 1980s, but eventually was seen as irrelevant. Modern AI has elements of both.
Soft vs. hard computing
Finding a provably correct or optimal solution is Intractability (complexity), intractable for many important problems.
Soft computing is a set of techniques, including genetic algorithms, fuzzy logic and neural networks, that are tolerant of imprecision, uncertainty, partial truth and approximation. Soft computing was introduced in the late 1980s and most successful AI programs in the 21st century are examples of soft computing with neural networks.
Narrow vs. general AI
AI researchers are divided as to whether to pursue the goals of artificial general intelligence and superintelligence directly or to solve as many specific problems as possible (narrow AI) in hopes these solutions will lead indirectly to the field's long-term goals. General intelligence is difficult to define and difficult to measure, and modern AI has had more verifiable successes by focusing on specific problems with specific solutions. The sub-field of artificial general intelligence studies this area exclusively.
Machine consciousness, sentience, and mind
There is no settled consensus in philosophy of mind on whether a machine can have a mind, consciousness and philosophy of mind, mental states in the same sense that human beings do. This issue considers the internal experiences of the machine, rather than its external behavior. Mainstream AI research considers this issue irrelevant because it does not affect the goals of the field: to build machines that can solve problems using intelligence. Stuart J. Russell, Russell and Norvig add that "[t]he additional project of making a machine conscious in exactly the way humans are is not one that we are equipped to take on." However, the question has become central to the philosophy of mind. It is also typically the central question at issue in artificial intelligence in fiction.
Consciousness
David Chalmers identified two problems in understanding the mind, which he named the "hard" and "easy" problems of consciousness. The easy problem is understanding how the brain processes signals, makes plans and controls behavior. The hard problem is explaining how this ''feels'' or why it should feel like anything at all, assuming we are right in thinking that it truly does feel like something (Dennett's consciousness illusionism says this is an illusion). While human Information processing (psychology), information processing is easy to explain, human subjective experience is difficult to explain. For example, it is easy to imagine a color-blind person who has learned to identify which objects in their field of view are red, but it is not clear what would be required for the person to ''know what red looks like''.
Computationalism and functionalism
Computationalism is the position in the philosophy of mind that the human mind is an information processing system and that thinking is a form of computing. Computationalism argues that the relationship between mind and body is similar or identical to the relationship between software and hardware and thus may be a solution to the mind–body problem. This philosophical position was inspired by the work of AI researchers and cognitive scientists in the 1960s and was originally proposed by philosophers Jerry Fodor and Hilary Putnam.
Philosopher John Searle characterized this position as "Strong AI hypothesis, strong AI": "The appropriately programmed computer with the right inputs and outputs would thereby have a mind in exactly the same sense human beings have minds." Searle challenges this claim with his Chinese room argument, which attempts to show that even a computer capable of perfectly simulating human behavior would not have a mind.
AI welfare and rights
It is difficult or impossible to reliably evaluate whether an advanced Sentient AI, AI is sentient (has the ability to feel), and if so, to what degree. But if there is a significant chance that a given machine can feel and suffer, then it may be entitled to certain rights or welfare protection measures, similarly to animals.
Sapience (a set of capacities related to high intelligence, such as discernment or self-awareness) may provide another moral basis for AI rights.
Robot rights are also sometimes proposed as a practical way to integrate autonomous agents into society.
In 2017, the European Union considered granting "electronic personhood" to some of the most capable AI systems. Similarly to the legal status of companies, it would have conferred rights but also responsibilities. Critics argued in 2018 that granting rights to AI systems would downplay the importance of human rights, and that legislation should focus on user needs rather than speculative futuristic scenarios. They also noted that robots lacked the autonomy to take part in society on their own.
Progress in AI increased interest in the topic. Proponents of AI welfare and rights often argue that AI sentience, if it emerges, would be particularly easy to deny. They warn that this may be a Moral blindness, moral blind spot analogous to slavery or factory farming, which could lead to Suffering risks, large-scale suffering if sentient AI is created and carelessly exploited.
Future
Superintelligence and the singularity
A superintelligence is a hypothetical agent that would possess intelligence far surpassing that of the brightest and most gifted human mind. If research into
artificial general intelligence
Artificial general intelligence (AGI)—sometimes called human‑level intelligence AI—is a type of artificial intelligence that would match or surpass human capabilities across virtually all cognitive tasks.
Some researchers argue that sta ...
produced sufficiently intelligent software, it might be able to Recursive self-improvement, reprogram and improve itself. The improved software would be even better at improving itself, leading to what I. J. Good called an "intelligence explosion" and Vernor Vinge called a "Technological singularity, singularity".
However, technologies cannot improve exponentially indefinitely, and typically follow an S-shaped curve, slowing when they reach the physical limits of what the technology can do.
Transhumanism
Robot designer Hans Moravec, cyberneticist Kevin Warwick and inventor Ray Kurzweil have predicted that humans and machines may merge in the future into cyborgs that are more capable and powerful than either. This idea, called transhumanism, has roots in the writings of Aldous Huxley and Robert Ettinger.
Edward Fredkin argues that "artificial intelligence is the next step in evolution", an idea first proposed by Samuel Butler (novelist), Samuel Butler's "Darwin among the Machines" as far back as 1863, and expanded upon by George Dyson (science historian), George Dyson in his 1998 book ''Darwin Among the Machines#Evolution of Global Intelligence, Darwin Among the Machines: The Evolution of Global Intelligence''.
[AI as evolution: Edward Fredkin is quoted in , , ]
In fiction
Thought-capable artificial beings have appeared as storytelling devices since antiquity,
[AI in myth: ] and have been a persistent theme in science fiction.
A common Trope (literature), trope in these works began with Mary Shelley's ''Frankenstein'', where a human creation becomes a threat to its masters. This includes such works as 2001: A Space Odyssey (novel), Arthur C. Clarke's and 2001: A Space Odyssey, Stanley Kubrick's ''2001: A Space Odyssey'' (both 1968), with HAL 9000, the murderous computer in charge of the ''Discovery One'' spaceship, as well as ''The Terminator'' (1984) and ''The Matrix'' (1999). In contrast, the rare loyal robots such as Gort from ''The Day the Earth Stood Still'' (1951) and Bishop from ''Aliens (film), Aliens'' (1986) are less prominent in popular culture.
Isaac Asimov introduced the Three Laws of Robotics in many stories, most notably with the "Multivac" super-intelligent computer. Asimov's laws are often brought up during lay discussions of machine ethics; while almost all artificial intelligence researchers are familiar with Asimov's laws through popular culture, they generally consider the laws useless for many reasons, one of which is their ambiguity.
Several works use AI to force us to confront the fundamental question of what makes us human, showing us artificial beings that have sentience, the ability to feel, and thus to suffer. This appears in Karel Čapek's ''R.U.R.'', the films ''A.I. Artificial Intelligence'' and ''Ex Machina (film), Ex Machina'', as well as the novel ''Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep?'', by Philip K. Dick. Dick considers the idea that our understanding of human subjectivity is altered by technology created with artificial intelligence.
See also
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Organoid intelligence – Use of brain cells and brain organoids for intelligent computing
*
*
*
* DARWIN EU - A European Union initiative coordinated by the European Medicines Agency, European Medicines Agency (EMA) to generate and utilize Real world evidence, real-world evidence (RWE) to support the evaluation and supervision of medicines across the EU.
Explanatory notes
References
AI textbooks
The two most widely used textbooks in 2023 (see th
Open Syllabus:
*
*
The four most widely used AI textbooks in 2008:
*
*
* .
* Later edition:
Other textbooks:
*
*
History of AI
*
*
*
*
Other sources
AI & ML in FusionAI & ML in Fusion, video lecture
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Presidential Address to the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Later published as
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
* David Autor, Autor, David H., "Why Are There Still So Many Jobs? The History and Future of Workplace Automation" (2015) 29(3) ''Journal of Economic Perspectives'' 3.
*
* Boyle, James
The Line: AI and the Future of Personhood MIT Press, 2024.
* Kenneth Cukier, Cukier, Kenneth, "Ready for Robots? How to Think about the Future of AI", ''Foreign Affairs'', vol. 98, no. 4 (July/August 2019), pp. 192–198. George Dyson (science historian), George Dyson, historian of computing, writes (in what might be called "Dyson's Law") that "Any system simple enough to be understandable will not be complicated enough to behave intelligently, while any system complicated enough to behave intelligently will be too complicated to understand." (p. 197.) Computer scientist Alex Pentland writes: "Current machine learning, AI machine-learning algorithms are, at their core, dead simple stupid. They work, but they work by brute force." (p. 198.)
*
*
* Gertner, Jon. (2023) "Wikipedia's Moment of Truth: Can the online encyclopedia help teach A.I. chatbots to get their facts right — without destroying itself in the process?" ''New York Times Magazine'' (July 18, 2023
online
* Gleick, James, "The Fate of Free Will" (review of Kevin J. Mitchell, ''Free Agents: How Evolution Gave Us Free Will'', Princeton University Press, 2023, 333 pp.), ''The New York Review of Books'', vol. LXXI, no. 1 (18 January 2024), pp. 27–28, 30. "Agency (philosophy), Agency is what distinguishes us from machines. For biological creatures, reason and motivation, purpose come from acting in the world and experiencing the consequences. Artificial intelligences – disembodied, strangers to blood, sweat, and tears – have no occasion for that." (p. 30.)
* Halpern, Sue, "The Coming Tech Autocracy" (review of Verity Harding, ''AI Needs You: How We Can Change AI's Future and Save Our Own'', Princeton University Press, 274 pp.; Gary Marcus, ''Taming Silicon Valley: How We Can Ensure That AI Works for Us'', MIT Press, 235 pp.; Daniela Rus and Gregory Mone, ''The Mind's Mirror: Risk and Reward in the Age of AI'', Norton, 280 pp.; Madhumita Murgia, ''Code Dependent: Living in the Shadow of AI'', Henry Holt, 311 pp.), ''The New York Review of Books'', vol. LXXI, no. 17 (7 November 2024), pp. 44–46. "'We can't realistically expect that those who hope to get rich from AI are going to have the interests of the rest of us close at heart,' ... writes [Gary Marcus]. 'We can't count on governments driven by campaign finance contributions [from tech companies] to push back.'... Marcus details the demands that citizens should make of their governments and the tech company, tech companies. They include Transparency (behavior), transparency on how AI systems work; compensation for individuals if their data [are] used to train LLMs (
large language model
A large language model (LLM) is a language model trained with self-supervised machine learning on a vast amount of text, designed for natural language processing tasks, especially language generation.
The largest and most capable LLMs are g ...
)s and the right to consent to this use; and the ability to hold tech companies liable for the harms they cause by eliminating Section 230, imposing cash penalties, and passing stricter product liability laws... Marcus also suggests... that a new, AI-specific federal agency, akin to the FDA, the FCC, or the Federal Trade Commission, FTC, might provide the most robust oversight.... [T]he Fordham University, Fordham law professor Chinmayi Sharma... suggests... establish[ing] a professional licensing regime for engineers that would function in a similar way to medical licenses, malpractice suits, and the Hippocratic oath in medicine. 'What if, like doctors,' she asks..., 'AI engineers also vowed to Primum non nocere, do no harm?'" (p. 46.)
*
* Hughes-Castleberry, Kenna, "A Murder Mystery Puzzle: The literary puzzle ''Cain's Jawbone'', which has stumped humans for decades, reveals the limitations of natural-language-processing algorithms", ''Scientific American'', vol. 329, no. 4 (November 2023), pp. 81–82. "This murder mystery competition has revealed that although NLP (natural-language processing) models are capable of incredible feats, their abilities are very much limited by the amount of context (linguistics), context they receive. This [...] could cause [difficulties] for researchers who hope to use them to do things such as analyze ancient languages. In some cases, there are few historical records on long-gone civilizations to serve as training data for such a purpose." (p. 82.)
* Immerwahr, Daniel, "Your Lying Eyes: People now use A.I. to generate fake videos indistinguishable from real ones. How much does it matter?", ''The New Yorker'', 20 November 2023, pp. 54–59. "If by 'deepfakes' we mean realistic videos produced using artificial intelligence that actually deceive people, then they barely exist. The fakes aren't deep, and the deeps aren't fake. [...] A.I.-generated videos are not, in general, operating in our media as counterfeited evidence. Their role better resembles that of cartoons, especially smutty ones." (p. 59.)
* Johnston, John (2008) ''The Allure of Machinic Life: Cybernetics, Artificial Life, and the New AI'', MIT Press.
*
*
* Leffer, Lauren, "The Risks of Trusting AI: We must avoid humanizing machine-learning models used in scientific research", ''Scientific American'', vol. 330, no. 6 (June 2024), pp. 80–81.
* Jill Lepore, Lepore, Jill, "The Chit-Chatbot: Is talking with a machine a conversation?", ''The New Yorker'', 7 October 2024, pp. 12–16.
*
* Marcus, Gary, "Artificial Confidence: Even the newest, buzziest systems of artificial general intelligence are stymmied by the same old problems", ''Scientific American'', vol. 327, no. 4 (October 2022), pp. 42–45.
*
* Introduced Deep Q-learning, DQN, which produced human-level performance on some Atari games.
* Eyal Press, Press, Eyal, "In Front of Their Faces: Does facial-recognition technology lead police to ignore contradictory evidence?", ''The New Yorker'', 20 November 2023, pp. 20–26.
*
* Roivainen, Eka, "AI's IQ:
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a generative artificial intelligence chatbot developed by OpenAI and released on November 30, 2022. It uses large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4o as well as other Multimodal learning, multimodal models to create human-like re ...
aced a [standard intelligence] test but showed that
intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as t ...
cannot be measured by IQ alone", ''Scientific American'', vol. 329, no. 1 (July/August 2023), p. 7. "Despite its high IQ,
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a generative artificial intelligence chatbot developed by OpenAI and released on November 30, 2022. It uses large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4o as well as other Multimodal learning, multimodal models to create human-like re ...
fails at tasks that require real humanlike reasoning or an understanding of the physical and social world.... ChatGPT seemed unable to reason logically and tried to rely on its vast database of... facts derived from online texts."
* Scharre, Paul, "Killer Apps: The Real Dangers of an AI Arms Race", ''Foreign Affairs'', vol. 98, no. 3 (May/June 2019), pp. 135–144. "Today's AI technologies are powerful but unreliable. Rules-based systems cannot deal with circumstances their programmers did not anticipate. Learning systems are limited by the data on which they were trained. AI failures have already led to tragedy. Advanced autopilot features in cars, although they perform well in some circumstances, have driven cars without warning into trucks, concrete barriers, and parked cars. In the wrong situation, AI systems go from supersmart to superdumb in an instant. When an enemy is trying to manipulate and hack an AI system, the risks are even greater." (p. 140.)
*
*
*
* Ben Tarnoff, Tarnoff, Ben, "The Labor Theory of AI" (review of Matteo Pasquinelli, ''The Eye of the Master: A Social History of Artificial Intelligence'', Verso, 2024, 264 pp.), ''The New York Review of Books'', vol. LXXII, no. 5 (27 March 2025), pp. 30–32. The reviewer, Ben Tarnoff, writes: "The strangeness at the heart of the generative AI boom is that nobody really knows how the technology works. We know how the
large language model
A large language model (LLM) is a language model trained with self-supervised machine learning on a vast amount of text, designed for natural language processing tasks, especially language generation.
The largest and most capable LLMs are g ...
s within
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a generative artificial intelligence chatbot developed by OpenAI and released on November 30, 2022. It uses large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4o as well as other Multimodal learning, multimodal models to create human-like re ...
and its counterparts are trained, even if we don't always know which data they're being trained on: they are asked to predict the next string of characters in a sequence. But exactly how they arrive at any given prediction is a mystery. The computations that occur inside the model are simply too intricate for any human to comprehend." (p. 32.)
* Ashish Vaswani, Vaswani, Ashish, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar et al. "Attention is all you need." Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017). Seminal paper on
transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ...
s.
* Vincent, James, "Horny Robot Baby Voice: James Vincent on AI chatbots", ''London Review of Books'', vol. 46, no. 19 (10 October 2024), pp. 29–32. "[AI chatbot] programs are made possible by new technologies but rely on the timelelss human tendency to anthropomorphise." (p. 29.)
*
External links
*
{{Authority control
Artificial intelligence, *
Computational fields of study
Computational neuroscience
Cybernetics
Data science
Formal sciences
Intelligence by type
 There are several kinds of machine learning.
There are several kinds of machine learning.  Affective computing is a field that comprises systems that recognize, interpret, process, or simulate human feeling, emotion, and mood. For example, some
Affective computing is a field that comprises systems that recognize, interpret, process, or simulate human feeling, emotion, and mood. For example, some  Local search uses
Local search uses 

 The regulation of artificial intelligence is the development of public sector policies and laws for promoting and regulating AI; it is therefore related to the broader regulation of algorithms. The regulatory and policy landscape for AI is an emerging issue in jurisdictions globally. According to AI Index at Stanford, the annual number of AI-related laws passed in the 127 survey countries jumped from one passed in 2016 to 37 passed in 2022 alone. Between 2016 and 2020, more than 30 countries adopted dedicated strategies for AI. Most EU member states had released national AI strategies, as had Canada, China, India, Japan, Mauritius, the Russian Federation, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, U.S., and Vietnam. Others were in the process of elaborating their own AI strategy, including Bangladesh, Malaysia and Tunisia. The Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence was launched in June 2020, stating a need for AI to be developed in accordance with human rights and democratic values, to ensure public confidence and trust in the technology. Henry Kissinger, Eric Schmidt, and Daniel Huttenlocher published a joint statement in November 2021 calling for a government commission to regulate AI. In 2023, OpenAI leaders published recommendations for the governance of superintelligence, which they believe may happen in less than 10 years. In 2023, the United Nations also launched an advisory body to provide recommendations on AI governance; the body comprises technology company executives, government officials and academics. In 2024, the Council of Europe created the first international legally binding treaty on AI, called the "Framework Convention on Artificial Intelligence and Human Rights, Democracy and the Rule of Law". It was adopted by the European Union, the United States, the United Kingdom, and other signatories.
In a 2022 Ipsos survey, attitudes towards AI varied greatly by country; 78% of Chinese citizens, but only 35% of Americans, agreed that "products and services using AI have more benefits than drawbacks". A 2023 Reuters/Ipsos poll found that 61% of Americans agree, and 22% disagree, that AI poses risks to humanity. In a 2023 Fox News poll, 35% of Americans thought it "very important", and an additional 41% thought it "somewhat important", for the federal government to regulate AI, versus 13% responding "not very important" and 8% responding "not at all important".
In November 2023, the first global AI Safety Summit was held in Bletchley Park in the UK to discuss the near and far term risks of AI and the possibility of mandatory and voluntary regulatory frameworks. 28 countries including the United States, China, and the European Union issued a declaration at the start of the summit, calling for international co-operation to manage the challenges and risks of artificial intelligence. In May 2024 at the AI Seoul Summit, 16 global AI tech companies agreed to safety commitments on the development of AI.
The regulation of artificial intelligence is the development of public sector policies and laws for promoting and regulating AI; it is therefore related to the broader regulation of algorithms. The regulatory and policy landscape for AI is an emerging issue in jurisdictions globally. According to AI Index at Stanford, the annual number of AI-related laws passed in the 127 survey countries jumped from one passed in 2016 to 37 passed in 2022 alone. Between 2016 and 2020, more than 30 countries adopted dedicated strategies for AI. Most EU member states had released national AI strategies, as had Canada, China, India, Japan, Mauritius, the Russian Federation, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, U.S., and Vietnam. Others were in the process of elaborating their own AI strategy, including Bangladesh, Malaysia and Tunisia. The Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence was launched in June 2020, stating a need for AI to be developed in accordance with human rights and democratic values, to ensure public confidence and trust in the technology. Henry Kissinger, Eric Schmidt, and Daniel Huttenlocher published a joint statement in November 2021 calling for a government commission to regulate AI. In 2023, OpenAI leaders published recommendations for the governance of superintelligence, which they believe may happen in less than 10 years. In 2023, the United Nations also launched an advisory body to provide recommendations on AI governance; the body comprises technology company executives, government officials and academics. In 2024, the Council of Europe created the first international legally binding treaty on AI, called the "Framework Convention on Artificial Intelligence and Human Rights, Democracy and the Rule of Law". It was adopted by the European Union, the United States, the United Kingdom, and other signatories.
In a 2022 Ipsos survey, attitudes towards AI varied greatly by country; 78% of Chinese citizens, but only 35% of Americans, agreed that "products and services using AI have more benefits than drawbacks". A 2023 Reuters/Ipsos poll found that 61% of Americans agree, and 22% disagree, that AI poses risks to humanity. In a 2023 Fox News poll, 35% of Americans thought it "very important", and an additional 41% thought it "somewhat important", for the federal government to regulate AI, versus 13% responding "not very important" and 8% responding "not at all important".
In November 2023, the first global AI Safety Summit was held in Bletchley Park in the UK to discuss the near and far term risks of AI and the possibility of mandatory and voluntary regulatory frameworks. 28 countries including the United States, China, and the European Union issued a declaration at the start of the summit, calling for international co-operation to manage the challenges and risks of artificial intelligence. In May 2024 at the AI Seoul Summit, 16 global AI tech companies agreed to safety commitments on the development of AI.
 Thought-capable artificial beings have appeared as storytelling devices since antiquity,AI in myth: and have been a persistent theme in science fiction.
A common Trope (literature), trope in these works began with Mary Shelley's ''Frankenstein'', where a human creation becomes a threat to its masters. This includes such works as 2001: A Space Odyssey (novel), Arthur C. Clarke's and 2001: A Space Odyssey, Stanley Kubrick's ''2001: A Space Odyssey'' (both 1968), with HAL 9000, the murderous computer in charge of the ''Discovery One'' spaceship, as well as ''The Terminator'' (1984) and ''The Matrix'' (1999). In contrast, the rare loyal robots such as Gort from ''The Day the Earth Stood Still'' (1951) and Bishop from ''Aliens (film), Aliens'' (1986) are less prominent in popular culture.
Isaac Asimov introduced the Three Laws of Robotics in many stories, most notably with the "Multivac" super-intelligent computer. Asimov's laws are often brought up during lay discussions of machine ethics; while almost all artificial intelligence researchers are familiar with Asimov's laws through popular culture, they generally consider the laws useless for many reasons, one of which is their ambiguity.
Several works use AI to force us to confront the fundamental question of what makes us human, showing us artificial beings that have sentience, the ability to feel, and thus to suffer. This appears in Karel Čapek's ''R.U.R.'', the films ''A.I. Artificial Intelligence'' and ''Ex Machina (film), Ex Machina'', as well as the novel ''Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep?'', by Philip K. Dick. Dick considers the idea that our understanding of human subjectivity is altered by technology created with artificial intelligence.
Thought-capable artificial beings have appeared as storytelling devices since antiquity,AI in myth: and have been a persistent theme in science fiction.
A common Trope (literature), trope in these works began with Mary Shelley's ''Frankenstein'', where a human creation becomes a threat to its masters. This includes such works as 2001: A Space Odyssey (novel), Arthur C. Clarke's and 2001: A Space Odyssey, Stanley Kubrick's ''2001: A Space Odyssey'' (both 1968), with HAL 9000, the murderous computer in charge of the ''Discovery One'' spaceship, as well as ''The Terminator'' (1984) and ''The Matrix'' (1999). In contrast, the rare loyal robots such as Gort from ''The Day the Earth Stood Still'' (1951) and Bishop from ''Aliens (film), Aliens'' (1986) are less prominent in popular culture.
Isaac Asimov introduced the Three Laws of Robotics in many stories, most notably with the "Multivac" super-intelligent computer. Asimov's laws are often brought up during lay discussions of machine ethics; while almost all artificial intelligence researchers are familiar with Asimov's laws through popular culture, they generally consider the laws useless for many reasons, one of which is their ambiguity.
Several works use AI to force us to confront the fundamental question of what makes us human, showing us artificial beings that have sentience, the ability to feel, and thus to suffer. This appears in Karel Čapek's ''R.U.R.'', the films ''A.I. Artificial Intelligence'' and ''Ex Machina (film), Ex Machina'', as well as the novel ''Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep?'', by Philip K. Dick. Dick considers the idea that our understanding of human subjectivity is altered by technology created with artificial intelligence.