|
Monochloramine
Monochloramine, often called chloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula NH2Cl. Together with dichloramine (NHCl2) and nitrogen trichloride (NCl3), it is one of the three chloramines of ammonia. It is a colorless liquid at its melting point of , but it is usually handled as a dilute aqueous solution, in which form it is sometimes used as a disinfectant. Chloramine is too unstable to have its boiling point measured. Water treatment Chloramine is used as a disinfectant for water. It is less aggressive than chlorine and more stable against light than hypochlorites. Drinking water disinfection Chloramine is commonly used in low concentrations as a secondary disinfectant in municipal water distribution systems as an alternative to chlorination. This application is increasing. Chlorine (referred to in water treatment as free chlorine) is being displaced by chloramine—to be specific, monochloramine—which is much less reactive and does not dissipate as rapidly as free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Trichloride
Nitrogen trichloride, also known as trichloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula . This yellow, oily, and explosive liquid is most commonly encountered as a product of chemical reactions between ammonia-derivatives and chlorine (for example, in swimming pools). Alongside monochloramine and dichloramine, trichloramine is responsible for the distinctive 'chlorine smell' associated with swimming pools, where the compound is readily formed as a product from hypochlorous acid reacting with ammonia and other nitrogenous substances in the water, such as urea from urine. Preparation and occurrence The compound is generated by treatment of ammonium chloride with calcium hypochlorite. When prepared in an aqueous-dichloromethane mixture, the trichloramine is extracted into the nonaqueous phase. Intermediates in this conversion include monochloramine and dichloramine, and , respectively. Nitrogen trichloride, trademarked as Agene, was at one time used to bleach flour, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichloramine
Dichloramine (IUPAC name: ''Azonous dichloride'') is a reactive inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is one of the three chloramines of ammonia, the others being monochloramine () and nitrogen trichloride (). This yellow gas is unstable and reacts with many materials. It is formed by a reaction between ammonia and chlorine or sodium hypochlorite. It is a byproduct formed during the synthesis of monochloramine and nitrogen trichloride. Synthesis Dichloramine can be prepared by a reaction between monochloramine and chlorine or sodium hypochlorite: : Reactions Dichloramine reacts with the hydroxide ion, which can be present in water or comes from water molecules, to yield nitroxyl and the chloride ion The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pro .... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Trichloride
Nitrogen trichloride, also known as trichloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula . This yellow, oily, and explosive liquid is most commonly encountered as a product of chemical reactions between ammonia-derivatives and chlorine (for example, in swimming pools). Alongside monochloramine and dichloramine, trichloramine is responsible for the distinctive 'chlorine smell' associated with swimming pools, where the compound is readily formed as a product from hypochlorous acid reacting with ammonia and other nitrogenous substances in the water, such as urea from urine. Preparation and occurrence The compound is generated by treatment of ammonium chloride with calcium hypochlorite. When prepared in an aqueous-dichloromethane mixture, the trichloramine is extracted into the nonaqueous phase. Intermediates in this conversion include monochloramine and dichloramine, and , respectively. Nitrogen trichloride, trademarked as Agene, was at one time used to bleach flour, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichloramine
Dichloramine (IUPAC name: ''Azonous dichloride'') is a reactive inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is one of the three chloramines of ammonia, the others being monochloramine () and nitrogen trichloride (). This yellow gas is unstable and reacts with many materials. It is formed by a reaction between ammonia and chlorine or sodium hypochlorite. It is a byproduct formed during the synthesis of monochloramine and nitrogen trichloride. Synthesis Dichloramine can be prepared by a reaction between monochloramine and chlorine or sodium hypochlorite: : Reactions Dichloramine reacts with the hydroxide ion, which can be present in water or comes from water molecules, to yield nitroxyl and the chloride ion The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pro .... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidizing agent, oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Electronegativity#Pauling electronegativity, Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval Alchemy, alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride Salt (chemistry), salts like ammonium chloride (sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride (common salt), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and . However, the nature of fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and is a precursor for numeous chemicals. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many chemicals. In many countries, it is classified as an List of extremely hazardous substances, extremely hazardous substance. Ammonia is toxic, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
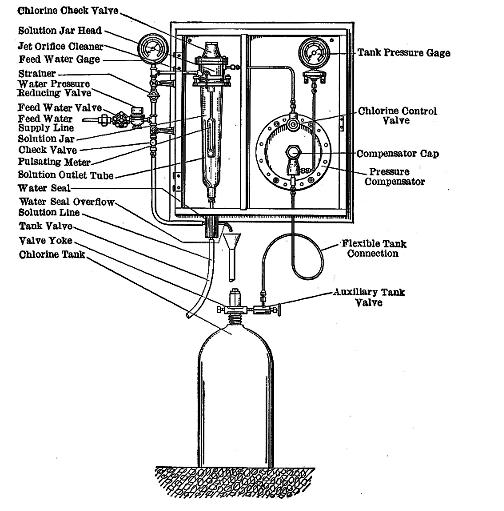
Water Chlorination
Water chlorination is the process of adding chlorine or chlorine compounds such as sodium hypochlorite to water. This method is used to kill bacteria, viruses and other microbes in water. In particular, chlorination is used to prevent the spread of waterborne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and typhoid. History In a paper published in 1894, it was formally proposed to add chlorine to water to render it "germ-free". Two other authorities endorsed this proposal and published it in many other papers in 1895. Early attempts at implementing water chlorination at a water treatment plant were made in 1893 in Hamburg, Germany. In 1897 the town of Maidstone, England was the first to have its entire water supply treated with chlorine. Permanent water chlorination began in 1905, when a faulty slow sand filter and a contaminated water supply caused a serious typhoid fever epidemic in Lincoln, England. Alexander Cruickshank Houston used chlorination of the water to stop the epidem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypochlorite
In chemistry, hypochlorite, or chloroxide is an oxyanion with the chemical formula ClO−. It combines with a number of cations to form hypochlorite salts. Common examples include sodium hypochlorite (household bleach) and calcium hypochlorite (a component of bleaching powder, swimming pool "chlorine"). The Cl–O distance in ClO− is 1.69 Å. The name can also refer to esters of hypochlorous acid, namely organic compounds with a ClO– group covalently bound to the rest of the molecule. The principal example is ''tert''-butyl hypochlorite, which is a useful chlorinating agent. Most hypochlorite salts are handled as aqueous solutions. Their primary applications are as bleaching, disinfection, and water treatment agents. They are also used in chemistry for chlorination and oxidation reactions. Reactions Acid reaction Acidification of hypochlorites generates hypochlorous acid, which exists in an equilibrium with chlorine. A lowered pH (i.e. towards acid) drives the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
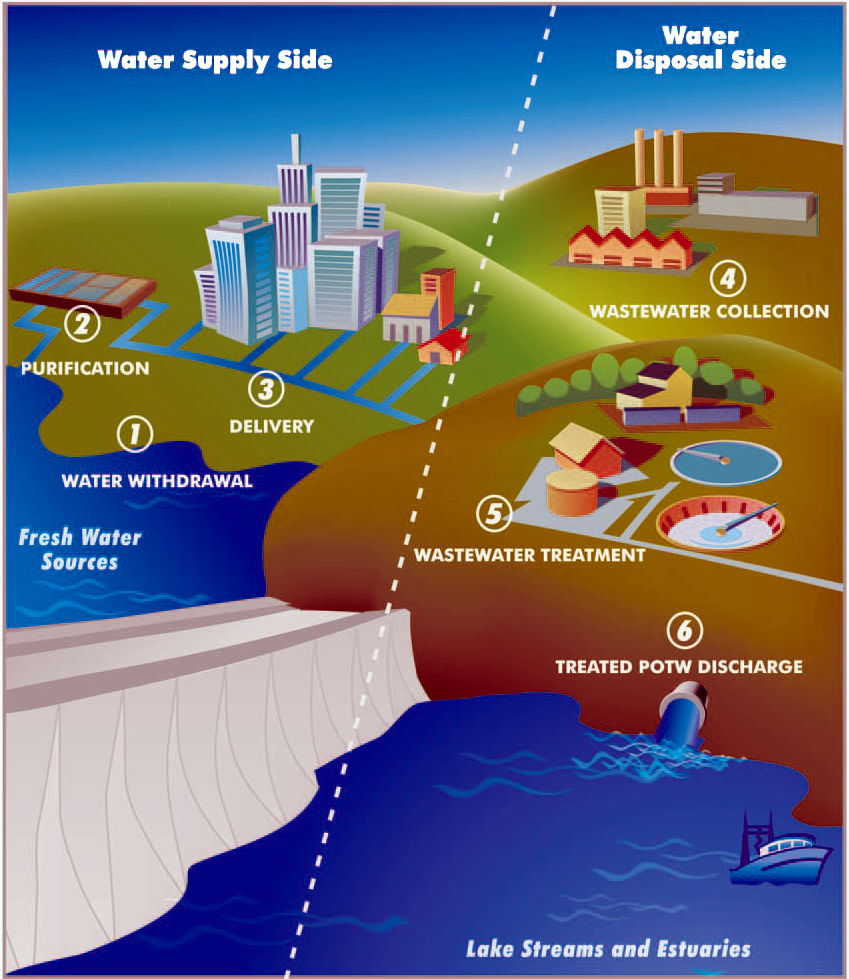
Water Supply Network
A water supply network or water supply system is a system of engineered hydrologic and hydraulic components that provide water supply. A water supply system typically includes the following: # A drainage basin (see water purification – sources of drinking water) # A raw water collection point (above or below ground) where the water accumulates, such as a lake, a river, or groundwater from an underground aquifer. Raw water may be transferred using uncovered ground-level aqueducts, covered tunnels, or underground water pipes to water purification facilities. # Water purification facilities. Treated water is transferred using water pipes (usually underground). # Water storage facilities such as reservoirs, water tanks, or water towers. Smaller water systems may store the water in cisterns or pressure vessels. Tall buildings may also need to store water locally in pressure vessels in order for the water to reach the upper floors. # Additional water pressurizing compone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloramines
Chloramines refer to derivatives of ammonia and organic amines wherein one or more N−H bonds have been replaced by N−Cl bonds. Two classes of compounds are considered: inorganic chloramines and organic chloramines. Chloramines are the most widely used members of the halamines. Inorganic chloramines Inorganic chloramines comprise three compounds: monochloramine (NH2Cl), dichloramine (NHCl2), and nitrogen trichloride (NCl3). Monochloramine is of broad significance as a disinfectant for water. Inorganic chloramines are produced by the reaction of ammonia and hypochlorous acid or chlorine. An urban legend claims that mixing household bleach (aqueous sodium hypochlorite) with ammonia-based cleaners releases chlorine gas or mustard gas; in reality, the gas produced by the reaction is a mixture of inorganic chloramines. Organic chloramines 144px, ''N''-Chloropiperidine is a rare example of an organic chloramine. 144px, Chloramine-T is often referred to as a chloramine, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and is a precursor for numeous chemicals. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many chemicals. In many countries, it is classified as an List of extremely hazardous substances, extremely hazardous substance. Ammonia is toxic, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |