|
Mogamulizumab
Mogamulizumab, sold under the brand name Poteligeo, is a humanized, afucosylated monoclonal antibody targeting CC chemokine receptor type 4 (CCR4). It is given by injection into a vein. The most common side effects include rash, infusion-related reactions, fatigue, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, and upper respiratory tract infection. Mogamulizumab was approved for medical use in Japan in 2012. It was approved for medical use in the United States and the European Union in 2018. It was approved for medical use in Canada in 2022. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical uses Mogamulizumab is indicated for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory mycosis fungoides or Sézary syndrome after at least one prior systemic therapy. History The precursor to mogamulizumab was a mouse anti-human CCR4 IgG1 mAb (KM2160), that was made in 1996 in a collaboration between Kouji Matsushima of University of Tokyo and Kyow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCR4
C-C chemokine receptor type 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCR4'' gene. CCR4 has also been designated CD194 ( cluster of differentiation 194). The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the G protein-coupled receptor family. It is a receptor for the following CC chemokines: * CCL2 (MCP-1) * CCL4 (MIP-1) * CCL5 (RANTES) * CCL17 (TARC) * CCL22 (Macrophage-derived chemokine) Chemokines are a group of small structurally related proteins that regulate cell trafficking of various types of leukocytes. The chemokines also play fundamental roles in the development, homeostasis, and function of the immune system, and they have effects on cells of the central nervous system as well as on endothelial cells involved in angiogenesis or angiostasis. CCR4 is a cell-surface protein and should not be confused with the unrelated carbon catabolite repression-negative on TATA-less ( CCR4-Not), a nuclear protein complex that regulates gene expression. Clinical signifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
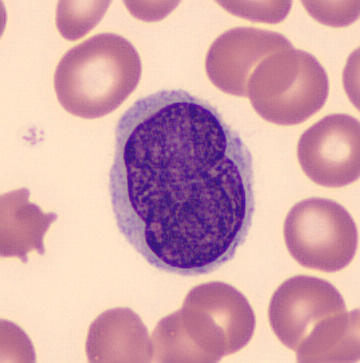
Sézary Disease
Sézary disease, or Sézary syndrome, is a type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma that was first described by Albert Sézary. The affected T cells, known as Sézary's cells or Lutzner cells, have pathological quantities of mucopolysaccharides. Sézary disease is sometimes considered a late stage of mycosis fungoides with lymphadenopathy. Signs and symptoms Sézary disease and mycosis fungoides are cutaneous T-cell lymphomas having a primary manifestation in the skin. The disease's origin is a peripheral CD4+ T-lymphocyte, although rarer CD8+/CD4- cases have been observed. Epidermotropism (lymphocytes residing in the epidermis) by neoplastic CD4+ lymphocytes with the formation of Pautrier's microabscesses is the hallmark sign of the disease. Although the condition can affect people of all ages, it is commonly diagnosed in adults over age 60. The dominant signs and symptoms of the disease are: # Generalized erythroderma – redness of the skin # Lymphadenopathy – swollen, enlarg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a class of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a type of cancer of the immune system. Unlike most non-Hodgkin lymphomas (which are generally B-cell-related), CTCL is caused by a mutation of T cells. The cancerous T cells in the body initially migrate to the skin, causing various lesions to appear. These lesions change shape as the disease progresses, typically beginning as what appears to be a rash which can be very itchy and eventually forming plaques and tumors before spreading to other parts of the body. Signs and symptoms The presentation depends if it is mycosis fungoides or Sézary syndrome, the most common, though not the only types. Among the symptoms for the aforementioned types are: enlarged lymph nodes, an enlarged liver and spleen, and non-specific dermatitis. Cause The cause of CTCL remains largely unknown, but several external risk factors have been proposed as potential triggers and promoters of the disease. These include the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afucosylated Monoclonal Antibodies
Afucosylated monoclonal antibodies are monoclonal antibodies engineered so that the oligosaccharides in the Fc region of the antibody do not have any fucose sugar units. When antibodies are afucosylated, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) is increased. Background Most approved monoclonal antibodies are of the IgG1 isotype, where two N-linked biantennary complex-type oligosaccharides are bound to the Fc region. The Fc region exercises the effector function of ADCC through its interaction with leukocyte receptors of the FcγR family. ADCC is important in the efficacy of cancer antibodies, but with many approved cancer antibodies there is less ADCC than could be desired due to nonspecific IgG competing with the drugs for binding to FcγIIIa on natural killer cells. Afucosylated monoclonal antibodies overcome this problem through improved FcγIIIa binding. Approaches The Swiss company GlycArt Biotechnology developed a system using CHO cells, where the cells were engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adult T-cell Leukemia/lymphoma
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL or ATLL) is a rare cancer of the immune system's T-cells caused by human T cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type 1 ( HTLV-1). All ATL cells contain integrated HTLV-1 provirus further supporting that causal role of the virus in the cause of the neoplasm. A small number of HTLV-1 individuals progress to develop ATL with a long latency period between infection and ATL development. ATL is categorized into four subtypes: acute, smoldering, lymphoma-type, and chronic. Acute and lymphoma-type are known to particularly be aggressive with poorer prognosis. Globally, the retrovirus HTLV-1 is estimated to infect 20 million people per year with the incidence of ATL approximately 0.05 per 100,000 per year with endemic regions such as regions of Japan, as high as 27 per 100,000 per year. However, cases have increased in non-endemic regions with highest incidence of HTLV-1 in southern/northern islands of Japan, Caribbean, Central and South America, intertropic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyowa Hakko Kirin
is a Japanese pharmaceutical and biotechnology company under the Kirin Holdings, and is among the 40 largest in the world by revenue. The company is headquartered in Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo and is a member of the Nikkei 225 stock index. History On July 1, 1949 the forerunner of the present company, Kyowa Hakko Kogyo Co., Ltd. is established. The company merged with Kirin Pharma Co., Ltd., on October 1, 2008 to form Kyowa Hakko Kirin with plans to spin off the bio-chemical business into Kyowa Hakko Bio. On July 11, 2014, the KHK subsidiary, ProStrakan Group (based in Scotland), acquired Archimedes Pharma from the Novo Nordisk Foundation for $394 million In 2019, Kirin Holdings acquired 95% stake in Kyowa Hakko Bio which is Kyowa Kirin's subsidiary corporation. The entity was renamed "Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd.", replacing its prior name of Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd. In November 2022, Kyowa Kirin announced plans to spin its international established medicines portfolio into a new jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water per os, by mouth. It may also be used to administer pharmaceutical drug, medications or other medical therapy such as blood transfusion, blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amgen
Amgen Inc. (formerly Applied Molecular Genetics Inc.) is an American multinational biopharmaceutical Corporation, company headquartered in Thousand Oaks, California. As one of the world's largest independent biotechnology companies, Amgen has approximately 24,000 staff in total as of 2022. The name "AMGen" is a portmanteau of the company's original name, Applied Molecular Genetics, which became the official name of the company in 1983 (three years after incorporation and coincident with its initial public offering). The company is listed on the Nasdaq Global Select Market under the ticker symbol "AMGN", as well as a component of the Nasdaq-100, the Dow Jones Industrial Average, and the S&P 100 and S&P 500, 500 indices. History Amgen was established in Thousand Oaks in 1980, as Applied Molecular Genetics.Baker, Pam (2002). ''Thousand Oaks Westlake Village: A Contemporary Portrait''. Community Communications, Inc., p. 37. . Amgen was backed by a small group of venture capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ventricles of the brain. CSF is mostly produced by specialized Ependyma, ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. It is also produced by ependymal cells in the lining of the ventricles. In humans, there is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day. CSF acts as a shock absorber, cushion or buffer, providing basic mechanical and immune system, immunological protection to the brain inside the Human skull, skull. CSF also serves a vital function in the cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow. CSF occupies the subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater) and the ventricular system around and inside t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycosis Fungoides
Mycosis fungoides, also known as Alibert-Bazin syndrome or granuloma fungoides, is the most common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It generally affects the skin, but may progress internally over time. Symptoms include rash, tumors, skin lesions, and itchy skin. While the cause remains unclear, most cases are not hereditary. Most cases are in people over 20 years of age, and it is more common in men than women. Treatment options include sunlight exposure, ultraviolet light, topical corticosteroids, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of mycosis fungoides are categorized into three clinical stages: the patch stage, the plaque stage, and the tumour stage. The patch stage is defined by flat, reddish patches of varying sizes that may have a wrinkled appearance. They can also look yellowish in people with darker skin. The plaque stage follows the patch stage of mycosis fungoides. It is characterized by the presence of raised lesions that appear reddis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drug
An orphan drug is a medication, pharmaceutical agent that is developed to treat certain rare medical conditions. An orphan drug would not be profitable to produce without government assistance, due to the small population of patients affected by the conditions. The conditions that orphan drugs are used to treat are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy that depends on the legislation (if there is any) of the country. Designation of a drug as an orphan drug has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug medical research, research and development. Examples of this can be that in the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakthrough Therapy
Breakthrough therapy is a United States Food and Drug Administration designation that expedites drug development that was created by Congress under Section 902 of the 9 July 2012 Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act. The FDA's "breakthrough therapy" designation is not intended to imply that a drug is actually a "breakthrough" or that there is high-quality evidence of treatment efficacy for a particular condition; rather, it allows the FDA to grant priority review to drug candidates if preliminary clinical trials indicate that the therapy may offer substantial treatment advantages over existing options for patients with serious or life-threatening diseases. The FDA has other mechanisms for expediting the review and approval process for promising drugs, including fast track designation, accelerated approval, and priority review. Requirements A breakthrough therapy designation can be assigned to a drug if "it is a drug which is intended alone or in combination wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |