Sézary Disease on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sézary disease, or Sézary syndrome, is a type of
 Sézary disease and
Sézary disease and
Sezary Syndrome lymphoma information
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sezary's Disease Lymphoma Lymphoid-related cutaneous conditions Syndromes
cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a class of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a type of cancer of the immune system. Unlike most non-Hodgkin lymphomas (which are generally B cell, B-cell-related), CTCL is caused by a mutation of T cells. The ma ...
that was first described by Albert Sézary. The affected T cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
s, known as Sézary's cells or Lutzner cells, have pathological quantities of mucopolysaccharide
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosacchari ...
s. Sézary disease is sometimes considered a late stage of mycosis fungoides
Mycosis fungoides, also known as Alibert-Bazin syndrome or granuloma fungoides, is the most common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It generally affects the skin, but may progress internally over time. Symptoms include rash, tumors, skin lesio ...
with lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In c ...
.
Signs and symptoms
 Sézary disease and
Sézary disease and mycosis fungoides
Mycosis fungoides, also known as Alibert-Bazin syndrome or granuloma fungoides, is the most common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It generally affects the skin, but may progress internally over time. Symptoms include rash, tumors, skin lesio ...
are cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a class of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a type of cancer of the immune system. Unlike most non-Hodgkin lymphomas (which are generally B cell, B-cell-related), CTCL is caused by a mutation of T cells. The ma ...
s having a primary manifestation in the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
. The disease's origin is a peripheral CD4+ T-lymphocyte, although rarer CD8+/CD4- cases have been observed. Epidermotropism (lymphocytes residing in the epidermis) by neoplastic
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
CD4+ lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and ...
with the formation of Pautrier's microabscesses is the hallmark sign of the disease. Although the condition can affect people of all ages, it is commonly diagnosed in adults over age 60. The dominant signs and symptoms of the disease are:
# Generalized erythroderma
Erythroderma is an inflammatory skin disease with erythema, redness and scaling that affects nearly the entire cutaneous surface.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 436. . This te ...
– redness of the skin
# Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In c ...
– swollen, enlarged lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
s
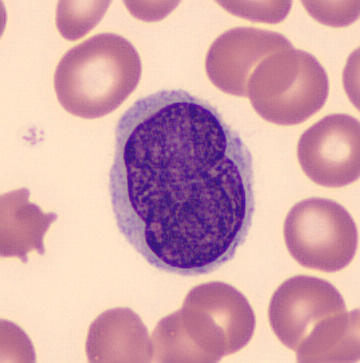
# Atypical T cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
s – malignant lymphocytes known as "Sézary cells" seen in the peripheral blood with typical cerebriform nuclei (brain-shaped, convoluted nuclei)
# Hepatosplenomegaly
Hepatosplenomegaly (commonly abbreviated HSM) is the simultaneous enlargement of both the liver (hepatomegaly) and the spleen (splenomegaly). Hepatosplenomegaly can occur as the result of acute viral hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis, and his ...
– enlarged liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
and spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
# Palmoplantar keratoderma
Palmoplantar keratodermas are a heterogeneous group of skin disorders characterized by abnormal thickening (scleroderma) of the stratum corneum of the palms and soles.
Autosomal recessive, dominant, X-linked, and acquired forms have all been de ...
– thickening of the palms of the hands, and soles of the feet
Diagnosis
Those who have Sézary disease often present skin lesions that do not heal with normal medication. A blood test generally reveals any change in the levels of lymphocytes in the blood, which is often associated with acutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a class of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a type of cancer of the immune system. Unlike most non-Hodgkin lymphomas (which are generally B cell, B-cell-related), CTCL is caused by a mutation of T cells. The ma ...
. Finally, a biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample ...
of a skin lesion can be performed to rule out any other causes.
The immunohistochemical features are very similar to those presented in mycosis fungoides except for the following differences:
# More monotonous cellular infiltrates (large, clustered atypical pagetoid cells) in Sézary syndrome
# Sometimes absent epidermotropism
# Increased lymph node involvement with infiltrates of Sézary syndrome.
Treatment
Treatment typically includes some combination ofphotodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a form of phototherapy involving light and a photosensitizing chemical substance used in conjunction with molecular oxygen to elicit cell death ( phototoxicity).
PDT is used in treating acne, wet age-related macula ...
, radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
, chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
, and biologic therapy.
Treatments are often used in combination with phototherapy
Light therapy, also called phototherapy or bright light therapy is the exposure to direct sunlight or artificial light at controlled wavelengths in order to treat a variety of medical disorders, including seasonal affective disorder (SAD), circ ...
and chemotherapy, though pure chemotherapy is rarely used today. No single treatment type has revealed clear-cut benefits in comparison to others, treatment for all cases remains problematic.
Radiation therapy
A number of types of radiation therapy may be used includingtotal skin electron therapy
Total may refer to:
Mathematics
* Total, the summation of a set of numbers
* Total order, a partial order without incomparable pairs
* Total relation, which may also mean
** connected relation (a binary relation in which any two elements are comp ...
. While this therapy does not generally result in systemic toxic effects it can produce side effects involving the skin. It is only available at a few institutions.
Chemotherapy
Romidepsin,vorinostat
Vorinostat (International Nonproprietary Name, rINN), also known as suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (suberic acid, suberoyl+aniline, anilide+hydroxamic acid abbreviated as SAHA), is a member of a larger class of compounds that inhibit histone de ...
and a few others are a second-line drug for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a class of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a type of cancer of the immune system. Unlike most non-Hodgkin lymphomas (which are generally B cell, B-cell-related), CTCL is caused by a mutation of T cells. The ma ...
. Mogamulizumab
Mogamulizumab, sold under the brand name Poteligeo, is a humanized, afucosylated monoclonal antibody targeting CC chemokine receptor type 4 (CCR4). It is given by injection into a vein.
The most common side effects include rash, infusion-rel ...
has been approved in Japan and the United States.
The FDA has approved denileukin diftitox-cxdl (Lymphir) for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) after at least 1 prior systemic therapy. LYMPHIR (denileukin diftitox-cxcl)
Injection 300 mcg is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory Stage I-III cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) after at least one prior systemic therapy.
Epidemiology
In the Western population, there are around 3 cases of Sézary syndrome per 1,000,000 people. Sézary disease is more common in males with a ratio of 2:1, and the mean age of diagnosis is between 55 and 60 years of age.See also
*List of cutaneous conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the Human body, body and composed of Human skin, skin, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function o ...
References
External links
Sezary Syndrome lymphoma information
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sezary's Disease Lymphoma Lymphoid-related cutaneous conditions Syndromes