|
Manganese(IV) Fluoride
Manganese tetrafluoride, MnF4, is the highest fluoride of manganese. It is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used as a means of purifying elemental fluorine.. Preparation Manganese tetrafluoride was first unequivocally prepared in 1961 by the reaction of manganese(II) fluoride (or other MnII compounds) with a stream of fluorine gas at 550 °C: the MnF4 sublimes into the gas stream and condenses onto a cold finger. This is still the commonest method of preparation, although the sublimation can be avoided by operating at increased fluorine pressure (4.5–6 bar at 180–320 °C) and mechanically agitating the powder to avoid sintering of the grains.. The reaction can also be carried out starting from manganese powder in a fluidized bed. Other preparations of MnF4 include the fluorination of MnF2 with krypton difluoride, or with F2 in liquid hydrogen fluoride solution under ultraviolet light.. Manganese tetrafluoride has also been prepared (but not isolated) in an acid� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Naturwissenschaften
''The Science of Nature'', formerly ''Naturwissenschaften'', is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Springer Science+Business Media covering all aspects of the natural sciences relating to questions of biological significance. It was founded in 1913 and intended as a German-language equivalent of the English-language journal ''Nature'', at a time when German was still a dominant language of the natural sciences. The journal is now published in English. History ''Die Naturwissenschaften'' was founded in 1913 by Arnold Berliner and published by Julius Springer Verlag. Berliner intended to create a German equivalent to the English-language journal ''Nature''. The original subtitle ''Wochenschrift für die Fortschritte der Naturwissenschaften, der Medizin und der Technik'' (''Weekly Publication of the Advances in the Natural Sciences, Medicine and Technology'') was later changed to its current ''The Science of Nature''. The journal is published monthly and the ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hydrogen Fluoride
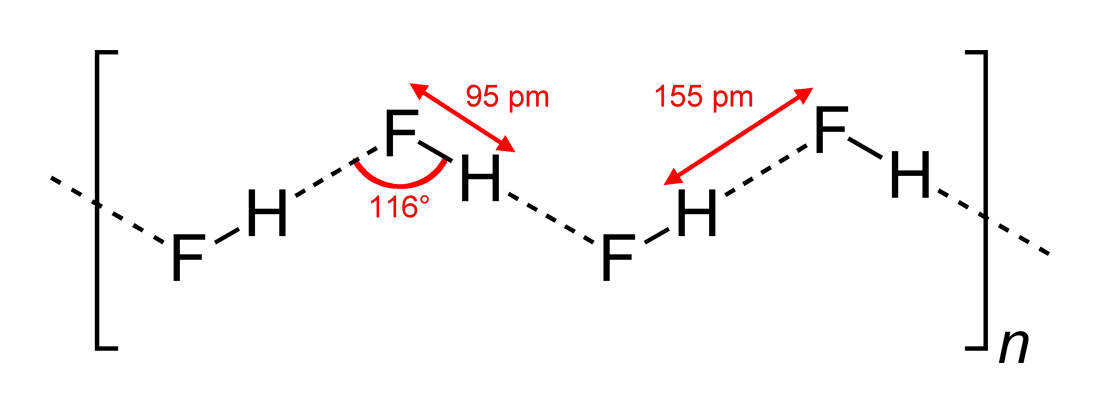
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the form of hydrofluoric acid, and is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is also widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Due to strong and extensive hydrogen bonding, it boils near room temperature, a much higher temperature than other hydrogen halides. Hydrogen fluoride is an extremely dangerous gas, forming corrosive and penetrating hydrofluoric acid upon contact with moisture. The gas can also cause blindness by rapid destruction of the corneas. History In 1771 Carl Wilhelm Scheele prepared the aqueous solution, hydrofluoric acid in large quantities, although hydrofluoric acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Moissan Cell
Ferdinand Frédéric Henri Moissan (; 28 September 1852 – 20 February 1907) was a French chemist and pharmacist who won the 1906 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work in isolating fluorine from its compounds. Among his other contributions, Moissan discovered moissanite and contributed to the development of the electric arc furnace. Moissan was one of the original members of the International Atomic Weights Committee. Biography Early life and education Moissan was born in Paris on 28 September 1852, the son of a minor officer of the Eastern Railway Company, Francis Ferdinand Moissan, and a seamstress, Joséphine Améraldine (née Mitel). In 1864 they moved to Meaux, where he attended the local school. During this time, Moissan became an apprentice clockmaker. However, in 1870, Moissan and his family moved back to Paris due to war against Prussia. Moissan was unable to receive the ''grade universitaire'' necessary to attend university. After spending a year in the army, he enr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Potassium Fluoride
Potassium fluoride is the chemical compound with the formula KF. After hydrogen fluoride, KF is the primary source of the fluoride ion for applications in manufacturing and in chemistry. It is an alkali halide salt and occurs naturally as the rare mineral carobbiite. Solutions of KF will etch glass due to the formation of soluble fluorosilicates, although HF is more effective. Preparation Potassium fluoride is prepared by reacting potassium carbonate with hydrofluoric acid. Evaporation of the solution forms crystals of potassium bifluoride. The bifluoride on heating yields potassium fluoride: : : Platinum or heat resistant plastic containers are often used for these operations. Potassium chloride converts to KF upon treatment with hydrogen fluoride. In this way, potassium fluoride is recyclable. Crystalline properties KF crystallizes in the cubic NaCl crystal structure. The lattice parameter at room temperature is 0.266 nm. Applications in organic chemistry In organic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of chemical element, elements from naturally occurring sources such as ores using an electrolytic cell. The voltage that is needed for electrolysis to occur is called the decomposition potential. The word "lysis" means to separate or break, so in terms, electrolysis would mean "breakdown via electricity." Etymology The word "electrolysis" was introduced by Michael Faraday in 1834, using the Greek language, Greek words "amber", which since the 17th century was associated with electrical phenomena, and ' meaning "dissolution". Nevertheless, electrolysis, as a tool to study chemical reactions and obtain pure chemical element, elements, precedes the coinage of the term and formal description by Faraday. History In the early nineteenth century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Xenon Hexafluoroplatinate
Xenon hexafluoroplatinate is the product of the reaction of platinum hexafluoride with xenon, in an experiment that proved the chemical reactivity of the noble gases. This experiment was performed by Neil Bartlett at the University of British Columbia, who formulated the product as "Xe+ tF6sup>−", although subsequent work suggests that Bartlett's product was probably a salt mixture and did not in fact contain this specific salt. Preparation "Xenon hexafluoroplatinate" is prepared from xenon and platinum hexafluoride (PtF6) as gaseous solutions in SF6. The reactants are combined at 77 K and slowly warmed to allow for a controlled reaction. Structure The material described originally as "xenon hexafluoroplatinate" is probably not Xe+ tF6sup>−. The main problem with this formulation is "Xe+", which would be a radical and would dimerize or abstract a fluorine atom to give XeF+. Thus, Bartlett discovered that Xe undergoes chemical reactions, but the nature and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
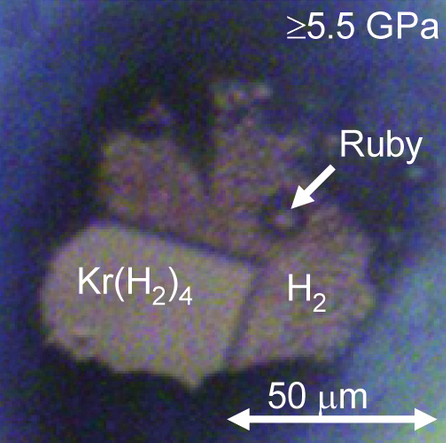
Noble-gas Compound
In chemistry, noble gas compounds are chemical compounds that include an element from the noble gases, group 8 or 18 of the periodic table. Although the noble gases are generally unreactive elements, many such compounds have been observed, particularly involving the element xenon. From the standpoint of chemistry, the noble gases may be divided into two groups: the relatively reactive krypton (ionisation energy 14.0 eV), xenon (12.1 eV), and radon (10.7 eV) on one side, and the very unreactive argon (15.8 eV), neon (21.6 eV), and helium (24.6 eV) on the other. Consistent with this classification, Kr, Xe, and Rn form compounds that can be isolated in bulk at or near standard temperature and pressure, whereas He, Ne, Ar have been observed to form true chemical bonds using spectroscopic techniques, but only when frozen into a noble gas matrix at temperatures of or lower, in supersonic jets of noble gas, or under extremely high pressures with metals. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Adducts
In chemistry, an adduct (; alternatively, a contraction of "addition product") is a product of a direct addition of two or more distinct molecules, resulting in a single reaction product containing all atoms of all components. The resultant is considered a distinct molecular species. Examples include the addition of sodium bisulfite to an aldehyde to give a sulfonate. It can be considered as a single product resulting from the direct combination of different molecules which comprises all atoms of the reactant molecules. Adducts often form between Lewis acids and Lewis bases. A good example is the formation of adducts between the Lewis acid borane and the oxygen atom in the Lewis bases, tetrahydrofuran (THF): or diethyl ether: . Many Lewis acids and Lewis bases reacting in the gas phase or in non-aqueous solvents to form adducts have been examined in the ECW model. Trimethylborane, trimethyltin chloride and bis(hexafluoroacetylacetonato)copper(II) are examples of Lewis acids t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Xenon Difluoride
Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesized. Xenon is used in flash lamps and arc lamps, and as a general anesthetic. The first excimer laser design used a xenon dimer molecule (Xe2) as the lasing medium, and the earliest laser designs used xenon flash lamps as pumps. Xenon is also used to search for hypothetical weakly interacting massive particles and as a propellant for ion thrusters in spacecraft. Naturally occurring xenon consists of seven stable isotopes and two long-lived radioactive isotopes. More than 40 unstable xenon isotopes undergo radioactive decay, and the isotope ratios of xenon are an important tool for studying the early history of the Solar System. Radioactive x ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Petroleum Ether
Petroleum ether is the petroleum fraction consisting of aliphatic hydrocarbons and boiling in the range 35–60 °C, and commonly used as a laboratory solvent. Despite the name, petroleum ether is not an ether; the term is used only figuratively, signifying extreme lightness and volatility. Properties The very lightest, most volatile liquid hydrocarbon solvents that can be bought from laboratory chemical suppliers may also be offered under the name petroleum ether. Petroleum ether consists mainly of aliphatic hydrocarbons and is usually low in aromatics. It is commonly hydrodesulfurized and may be hydrogenated to reduce the amount of aromatic and other Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated hydrocarbons. Petroleum ether bears normally a descriptive suffix giving the boiling range. Thus, from the leading international laboratory chemical suppliers it is possible to buy various petroleum ethers with boiling ranges such as 30–50 °C, 40–60 °C, 50–70& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Manganese(III) Fluoride
Manganese(III) fluoride (also known as Manganese trifluoride) is the inorganic compound with the formula MnF3. This red/purplish solid is useful for converting hydrocarbons into fluorocarbons, i.e., it is a fluorination agent. It forms a hydrate and many derivatives. Synthesis, structure and reactions MnF3 can be prepared by treating a solution of MnF2 in hydrogen fluoride with fluorine: :MnF2 + 0.5 F2 → MnF3 It can also be prepared by the reaction of elemental fluorine with a manganese(II) halide at ~250 °C.Inorganic chemistry, Catherine E. Housecroft, A.G. Sharpe, pp.711-712, section ''Manganese (III)'' googlebooks link/ref> Structure Like vanadium(III) fluoride, MnF3 features octahedral metal centers with the same average M-F bond distances. In the Mn compound, however, is distorted (and hence a monoclinic unit cell vs. a higher symmetry one) due to the Jahn-Teller effect, with pairs of Mn-F distances of 1.79, 1.91, 2.09 Å. The hydrate MnF3.3H2O is obtained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |