|
MGluRs
The metabotropic glutamate receptors, or mGluRs, are a type of glutamate receptor that are active through an indirect metabotropic receptor, metabotropic process. They are members of the group C GPCR family, group C family of G-protein-coupled receptors, or GPCRs. Like all glutamate receptor (biochemistry), receptors, mGluRs bind with glutamate, an amino acid that functions as an excitatory neurotransmitter. Function and structure The mGluRs perform a variety of functions in the central and peripheral nervous systems: For example, they are involved in learning, memory, anxiety, and the perception of pain. They are found in pre- and postsynaptic neurons in synapses of the hippocampus, cerebellum, and the cerebral cortex, as well as other parts of the brain and in peripheral tissues. Like other metabotropic receptors, mGluRs have G protein-coupled receptor, seven transmembrane domains that span the cell membrane. Unlike ionotropic receptors, metabotropic glutamate receptors are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamate Receptor
Glutamate receptors are synaptic and non synaptic receptors located primarily on the membranes of neuronal and glial cells. Glutamate (the conjugate base of glutamic acid) is abundant in the human body, but particularly in the nervous system and especially prominent in the human brain where it is the body's most prominent neurotransmitter, the brain's main excitatory neurotransmitter, and also the precursor for GABA, the brain's main inhibitory neurotransmitter. Glutamate receptors are responsible for the glutamate-mediated postsynaptic excitation of neural cells, and are important for neural communication, memory formation, learning, and regulation. Glutamate receptors are implicated in a number of neurological conditions. Their central role in excitotoxicity and prevalence in the central nervous system has been linked or speculated to be linked to many neurodegenerative diseases, and several other conditions have been further linked to glutamate receptor gene muta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
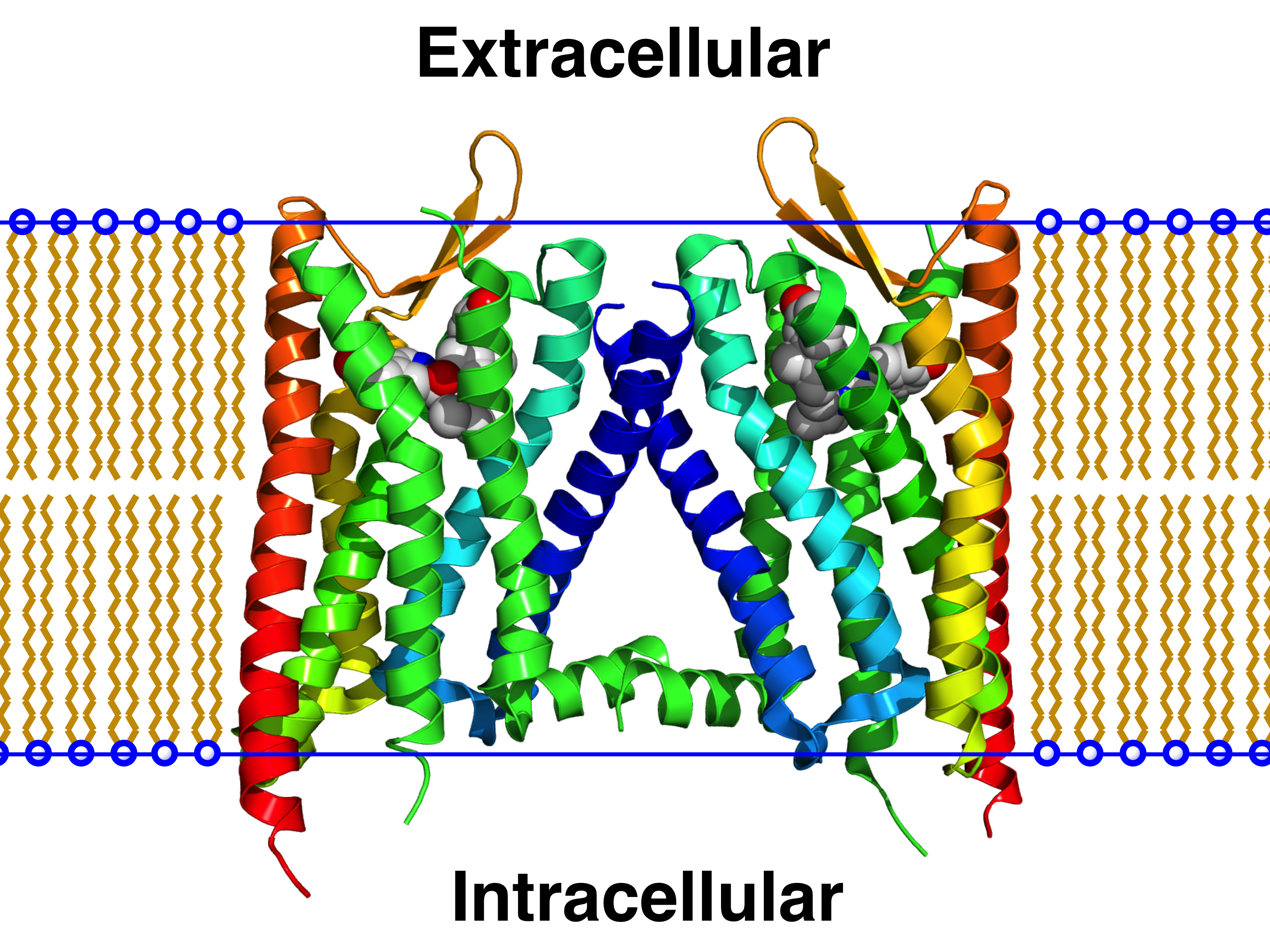
GRM1
The glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1, also known as GRM1, is a human gene which encodes the metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR1) protein. Function L-Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and activates both ligand-gated ion channel, ionotropic and Metabotropic glutamate receptor, metabotropic glutamate receptors. Glutamatergic neurotransmission is involved in most aspects of normal brain function and can be perturbed in many neuropathologic conditions. The metabotropic glutamate receptors are a family of G protein-coupled receptors, that have been divided into 3 groups on the basis of sequence homology, putative signal transduction mechanisms, and pharmacologic properties. Group I, which includes GRM1 alongside Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5, GRM5, have been shown to activate phospholipase C. Group II includes Metabotropic glutamate receptor 2, GRM2 and Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3, GRM3 while Group III includes Meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large protein family, group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell (biology), cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops (three extracellular loops interacting with ligand molecules, three intracellular loops interacting with G proteins, an N-terminus, N-terminal extracellular region and a C-terminal intracellular region) of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) licence/ref> Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The six-layered neocortex makes up approximately 90% of the Cortex (anatomy), cortex, with the allocortex making up the remainder. The cortex is divided into left and right parts by the longitudinal fissure, which separates the two cerebral hemispheres that are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum and other commissural fibers. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the neurocranium, cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, gyrification, cortical folding is crucial for the Neural circuit, brain circuitry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an Receptor antagonist, antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology The word originates from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''agōnistēs''), "contestant; champion; rival" < (''agōn''), "contest, combat; exertion, struggle" < (''agō''), "I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive." Types of agonists Receptor (biochemistry), Receptors can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as hormones and neurotransmitters) or exogenous agonists (such as medication, drugs), resulting in a biological response. A physiological agonism an ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPCR Oligomer
A GPCR oligomer is a protein complex that consists of a small number ( ''oligoi'' "a few", ''méros'' "part, piece, component") of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). It is held together by covalent bonds or by intermolecular forces. The subunits within this complex are called protomers, while unconnected receptors are called monomers. Receptor homomers consist of identical protomers, while heteromers consist of different protomers. Receptor homodimers – which consist of two identical GPCRs – are the simplest homomeric GPCR oligomers. Receptor heterodimers – which consist of two different GPCRs – are the simplest heteromeric GPCR oligomers. The existence of receptor oligomers is a general phenomenon, whose discovery has superseded the prevailing paradigmatic concept of the function of receptors as plain monomers, and has far-reaching implications for the understanding of neurobiological diseases as well as for the development of drugs. Discovery For a long time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmission
Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron (the presynaptic neuron), and bind to and react with the receptors on the dendrites of another neuron (the postsynaptic neuron) a short distance away. Changes in the concentration of ions, such as Ca2+, Na+, K+, underlie both chemical and electrical activity in the process. The increase in calcium levels is essential and can be promoted by protons. A similar process occurs in retrograde neurotransmission, where the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron release retrograde neurotransmitters (e.g., endocannabinoids; synthesized in response to a rise in intracellular calcium levels) that signal through receptors that are located on the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron, mainly at GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses. Neurotransmission is regulated by severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presynaptic Inhibition
Presynaptic inhibition is a phenomenon in which an inhibitory neuron provides synaptic input to the axon of another neuron ( axo-axonal synapse) to make it less likely to fire an action potential. Presynaptic inhibition occurs when an inhibitory neurotransmitter, like GABA, acts on GABA receptors on the axon terminal. Or when endocannabinoids act as retrograde messengers by binding to presynaptic CB1 receptors, thereby indirectly modulating GABA and the excitability of dopamine neurons by reducing it and other presynaptic released neurotransmitters. Presynaptic inhibition is ubiquitous among sensory neurons. Function Sensory stimuli, such as pain, proprioception, and somatosensation, are sensed by primary afferent fibers. Somatosensory neurons encode information about the body's current state (e.g. temperature, pain, pressure, position, etc.). For vertebrate animals, these primary afferent fibers form synapses onto the spinal cord, specifically in the dorsal horn area, onto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Excitability
Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron (the presynaptic neuron), and bind to and react with the receptors on the dendrites of another neuron (the postsynaptic neuron) a short distance away. Changes in the concentration of ions, such as Ca2+, Na+, K+, underlie both chemical and electrical activity in the process. The increase in calcium levels is essential and can be promoted by protons. A similar process occurs in retrograde neurotransmission, where the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron release retrograde neurotransmitters (e.g., endocannabinoids; synthesized in response to a rise in intracellular calcium levels) that signal through receptors that are located on the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron, mainly at GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses. Neurotransmission is regulated by several dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channels
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion transporter proteins: # The rate of ion transport thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |