Cerebral Cortex on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the
 The cerebral cortex is the outer covering of the surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres and is folded into peaks called
The cerebral cortex is the outer covering of the surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres and is folded into peaks called

 The
The
 Blood supply to the cerebral cortex is part of the cerebral circulation. Cerebral arteries supply the blood that perfuses the cerebrum. This arterial blood carries oxygen, glucose, and other nutrients to the cortex. Cerebral veins drain the deoxygenated blood, and metabolic wastes including carbon dioxide, back to the heart.
The main arteries supplying the cortex are the
Blood supply to the cerebral cortex is part of the cerebral circulation. Cerebral arteries supply the blood that perfuses the cerebrum. This arterial blood carries oxygen, glucose, and other nutrients to the cortex. Cerebral veins drain the deoxygenated blood, and metabolic wastes including carbon dioxide, back to the heart.
The main arteries supplying the cortex are the 
 The cerebral cortex is composed of a heterogenous population of cells that give rise to different cell types. The majority of these cells are derived from radial glia migration that form the different cell types of the neocortex and it is a period associated with an increase in neurogenesis. Similarly, the process of neurogenesis regulates lamination to form the different layers of the cortex. During this process there is an increase in the restriction of cell fate that begins with earlier progenitors giving rise to any cell type in the cortex and later progenitors giving rise only to
The cerebral cortex is composed of a heterogenous population of cells that give rise to different cell types. The majority of these cells are derived from radial glia migration that form the different cell types of the neocortex and it is a period associated with an increase in neurogenesis. Similarly, the process of neurogenesis regulates lamination to form the different layers of the cortex. During this process there is an increase in the restriction of cell fate that begins with earlier progenitors giving rise to any cell type in the cortex and later progenitors giving rise only to
 The layered structure of the mature cerebral cortex is formed during development. The first pyramidal neurons generated migrate out of the ventricular zone and subventricular zone, together with reelin-producing Cajal–Retzius neurons, from the preplate. Next, a cohort of neurons migrating into the middle of the preplate divides this transient layer into the superficial marginal zone, which will become layer I of the mature neocortex, and the subplate, forming a middle layer called the cortical plate. These cells will form the deep layers of the mature cortex, layers five and six. Later born neurons migrate radially into the cortical plate past the deep layer neurons, and become the upper layers (two to four). Thus, the layers of the cortex are created in an inside-out order. The only exception to this inside-out sequence of neurogenesis occurs in the layer I of
The layered structure of the mature cerebral cortex is formed during development. The first pyramidal neurons generated migrate out of the ventricular zone and subventricular zone, together with reelin-producing Cajal–Retzius neurons, from the preplate. Next, a cohort of neurons migrating into the middle of the preplate divides this transient layer into the superficial marginal zone, which will become layer I of the mature neocortex, and the subplate, forming a middle layer called the cortical plate. These cells will form the deep layers of the mature cortex, layers five and six. Later born neurons migrate radially into the cortical plate past the deep layer neurons, and become the upper layers (two to four). Thus, the layers of the cortex are created in an inside-out order. The only exception to this inside-out sequence of neurogenesis occurs in the layer I of
 The map of functional cortical areas, which include primary motor and visual cortex, originates from a ' protomap', which is regulated by molecular signals such as fibroblast growth factor FGF8 early in embryonic development. These signals regulate the size, shape, and position of cortical areas on the surface of the cortical primordium, in part by regulating gradients of
The map of functional cortical areas, which include primary motor and visual cortex, originates from a ' protomap', which is regulated by molecular signals such as fibroblast growth factor FGF8 early in embryonic development. These signals regulate the size, shape, and position of cortical areas on the surface of the cortical primordium, in part by regulating gradients of
 The association areas are the parts of the cerebral cortex that do not belong to the primary regions. They function to produce a meaningful perception, perceptual experience of the world, enable us to interact effectively, and support abstract thinking and language. The parietal lobe, parietal, Temporal lobe, temporal, and
The association areas are the parts of the cerebral cortex that do not belong to the primary regions. They function to produce a meaningful perception, perceptual experience of the world, enable us to interact effectively, and support abstract thinking and language. The parietal lobe, parietal, Temporal lobe, temporal, and
 Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, show as a marker, an atrophy of the grey matter of the cerebral cortex.
Other Central nervous system disease, diseases of the central nervous system include neurological disorders such as epilepsy, movement disorders, and Aphasia#Boston classification, different types of aphasia (difficulties in speech expression or comprehension).
Brain damage from disease or trauma, can involve damage to a specific lobe such as in frontal lobe disorder, and associated functions will be affected. The blood–brain barrier that serves to protect the brain from infection can become compromised allowing entry to pathogens.
The prenatal development, developing fetus is susceptible to a range of environmental factors that can cause birth defects and problems in later development. Maternal alcohol consumption for example can cause fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Other factors that can cause neurodevelopment disorders are Environmental toxicants and fetal development, toxicants such as drugs, and exposure to radiation as from X-rays. Infections can also affect the development of the cortex. A viral infection is one of the causes of lissencephaly, which results in a smooth cortex without
Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, show as a marker, an atrophy of the grey matter of the cerebral cortex.
Other Central nervous system disease, diseases of the central nervous system include neurological disorders such as epilepsy, movement disorders, and Aphasia#Boston classification, different types of aphasia (difficulties in speech expression or comprehension).
Brain damage from disease or trauma, can involve damage to a specific lobe such as in frontal lobe disorder, and associated functions will be affected. The blood–brain barrier that serves to protect the brain from infection can become compromised allowing entry to pathogens.
The prenatal development, developing fetus is susceptible to a range of environmental factors that can cause birth defects and problems in later development. Maternal alcohol consumption for example can cause fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Other factors that can cause neurodevelopment disorders are Environmental toxicants and fetal development, toxicants such as drugs, and exposure to radiation as from X-rays. Infections can also affect the development of the cortex. A viral infection is one of the causes of lissencephaly, which results in a smooth cortex without
File:Lateral surface of cerebral cortex - gyri.png, Lateral surface of the human cerebral cortex
File:Medial surface of cerebral cortex - entorhinal cortex.png, Medial surface of the human cerebral cortex
Brainmaps-macaque-hippocampus.jpg, Tissue slice from the brain of an adult macaque monkey. The cerebral cortex is depicted in dark violet.
"The primary visual cortex"
Webvision: Comprehensive article about the structure and function of the primary visual cortex.
"Basic cell types"
Webvision: Image of the basic cell types of the monkey cerebral cortex.
Cerebral Cortex – Cell Centered Database
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cerebral Cortex Cerebral cortex,
cerebrum
The cerebrum (: cerebra), telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres) as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfac ...
of the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
in humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
and other mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s. It is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
, and plays a key role in attention
Attention or focus, is the concentration of awareness on some phenomenon to the exclusion of other stimuli. It is the selective concentration on discrete information, either subjectively or objectively. William James (1890) wrote that "Atte ...
, perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous syste ...
, awareness
In philosophy and psychology, awareness is the perception or knowledge of something. The concept is often synonymous with consciousness. However, one can be aware of something without being explicitly conscious of it, such as in the case of bli ...
, thought
In their most common sense, the terms thought and thinking refer to cognitive processes that can happen independently of sensory stimulation. Their most paradigmatic forms are judging, reasoning, concept formation, problem solving, and de ...
, memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembe ...
, language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing syste ...
, and consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is awareness of a state or object, either internal to oneself or in one's external environment. However, its nature has led to millennia of analyses, explanations, and debate among philosophers, scientists, an ...
.
The six-layered neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, ...
makes up approximately 90% of the cortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
, with the allocortex
The allocortex (from Latin allo-, meaning other, and cortex, meaning bark or crust), or heterogenetic cortex, is one of the two types of cerebral cortex in the brain, together with the neocortex. In the human brain, the allocortex is the much sm ...
making up the remainder. The cortex is divided into left and right parts by the longitudinal fissure, which separates the two cerebral hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres ...
s that are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental ...
and other commissural fibers
The commissural fibers or transverse fibers are axons that connect the two hemispheres of the brain. Huge numbers of commissural fibers make up the commissural tracts in the brain, the largest of which is the corpus callosum.
In contrast to ...
. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, cortical folding is crucial for the brain circuitry and its functional organisation. In mammals with small brains, there is no folding and the cortex is smooth.
A fold or ridge in the cortex is termed a gyrus
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (: gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; : sulcus). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals.
...
(plural gyri) and a groove is termed a sulcus (plural sulci). These surface convolutions appear during fetal development and continue to mature after birth through the process of gyrification
Gyrification is the process of forming the characteristic folds of the cerebral cortex. The peak of such a fold is called a ''gyrus'' (pl. ''gyri''), and its trough is called a ''Sulcus (neuroanatomy), sulcus'' (pl. ''sulci''). The neurons of the ...
. In the human brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the nervous system, and with the spinal cord, comprises the central nervous system. It consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. The brain controls most of the activi ...
, the majority of the cerebral cortex is not visible from the outside, but buried in the sulci. The major sulci and gyri mark the divisions of the cerebrum into the lobes of the brain
The lobes of the brain are the four major identifiable regions of the human cerebral cortex, and they comprise the surface of each hemisphere of the cerebrum. The two hemispheres are roughly symmetrical in structure, and are connected by the c ...
. The four major lobes are the frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes. Other lobes are the limbic lobe, and the insular cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe, parietal and frontal lobes) within each brain hemisphere ...
often referred to as the ''insular lobe''.
There are between 14 and 16 billion neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s in the human cerebral cortex. These are organised into horizontal cortical layers, and radially into cortical column
A cortical column is a group of neurons forming a cylindrical structure through the cerebral cortex of the brain perpendicular to the cortical surface. The structure was first identified by Vernon Benjamin Mountcastle in 1957. He later identified c ...
s and minicolumns. Cortical areas have specific functions such as movement in the motor cortex
The motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, motor control, control, and execution of voluntary movements.
The motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the posterior precentral gyrus immediately ...
, and sight in the visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalam ...
. The motor cortex is primarily located in the precentral gyrus, and the visual cortex is located in the occipital lobe.
Structure
 The cerebral cortex is the outer covering of the surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres and is folded into peaks called
The cerebral cortex is the outer covering of the surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres and is folded into peaks called gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (: gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulcus (neuroanatomy), sulci (depressions or furrows; : sulcus). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in huma ...
, and grooves called sulci. In the human brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the nervous system, and with the spinal cord, comprises the central nervous system. It consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. The brain controls most of the activi ...
, it is between 2 and 3-4 mm. thick, and makes up 40% of the brain's mass. 90% of the cerebral cortex is the six-layered neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, ...
whilst the other 10% is made up of the three/four-layered allocortex
The allocortex (from Latin allo-, meaning other, and cortex, meaning bark or crust), or heterogenetic cortex, is one of the two types of cerebral cortex in the brain, together with the neocortex. In the human brain, the allocortex is the much sm ...
. There are between 14 and 16 billion neurons in the cortex. These cortical neurons are organized radially in cortical column
A cortical column is a group of neurons forming a cylindrical structure through the cerebral cortex of the brain perpendicular to the cortical surface. The structure was first identified by Vernon Benjamin Mountcastle in 1957. He later identified c ...
s, and minicolumns, in the horizontally organized layers of the cortex.
The neocortex is separable into different regions of cortex known in the plural as cortices, and include the motor cortex
The motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, motor control, control, and execution of voluntary movements.
The motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the posterior precentral gyrus immediately ...
and visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalam ...
. About two thirds of the cortical surface is buried in the sulci and the insular cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe, parietal and frontal lobes) within each brain hemisphere ...
is completely hidden. The cortex is thickest over the top of a gyrus and thinnest at the bottom of a sulcus.
Folds
The cerebral cortex is folded in a way that allows a large surface area of neural tissue to fit within the confines of theneurocranium
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, brain-pan, or brainbox, is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the cal ...
. When unfolded in the human, each hemispheric cortex has a total surface area of about . The folding is inward away from the surface of the brain, and is also present on the medial surface of each hemisphere within the longitudinal fissure. Most mammals have a cerebral cortex that is convoluted with the peaks known as gyri and the troughs or grooves known as sulci. Some small mammals including some small rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal specie ...
s have smooth cerebral surfaces without gyrification
Gyrification is the process of forming the characteristic folds of the cerebral cortex. The peak of such a fold is called a ''gyrus'' (pl. ''gyri''), and its trough is called a ''Sulcus (neuroanatomy), sulcus'' (pl. ''sulci''). The neurons of the ...
.
Lobes
The larger sulci and gyri mark the divisions of the cortex of the cerebrum into thelobes of the brain
The lobes of the brain are the four major identifiable regions of the human cerebral cortex, and they comprise the surface of each hemisphere of the cerebrum. The two hemispheres are roughly symmetrical in structure, and are connected by the c ...
. There are four main lobes: the frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a Sulcus (neur ...
, parietal lobe
The parietal lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.
The parietal lobe integra ...
, temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pr ...
, and occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin , 'behind', and , 'head'.
The occipital lobe is the ...
. The insular cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe, parietal and frontal lobes) within each brain hemisphere ...
is often included as the insular lobe. The limbic lobe is a rim of cortex on the medial side of each hemisphere and is also often included. There are also three lobules of the brain described: the paracentral lobule, the superior parietal lobule, and the inferior parietal lobule.
Thickness
For species of mammals, larger brains (in absolute terms, not just in relation to body size) tend to have thicker cortices. The smallest mammals, such asshrew
Shrews ( family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to dif ...
s, have a neocortical thickness of about 0.5 mm; the ones with the largest brains, such as humans and fin whales, have thicknesses of 2–4 mm. There is an approximately logarithm
In mathematics, the logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, must be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of to base is , because is to the rd power: . More generally, if , the ...
ic relationship between brain weight and cortical thickness.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain (MRI) makes it possible to get a measure for the thickness of the human cerebral cortex and relate it to other measures. The thickness of different cortical areas varies but in general, sensory cortex is thinner than motor cortex. One study has found some positive association between the cortical thickness and intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as t ...
.
Another study has found that the somatosensory cortex is thicker in migraine patients, though it is not known if this is the result of migraine attacks, the cause of them or if both are the result of a shared cause.
A later study using a larger patient population reports no change in the cortical thickness in patients with migraine.
A genetic disorder of the cerebral cortex, whereby decreased folding in certain areas results in a microgyrus, where there are four layers instead of six, is in some instances seen to be related to dyslexia
Dyslexia (), previously known as word blindness, is a learning disability that affects either reading or writing. Different people are affected to different degrees. Problems may include difficulties in spelling words, reading quickly, wri ...
.
Layers of neocortex

 The
The neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, ...
is formed of six layers, numbered I to VI, from the outermost layer I – near to the pia mater, to the innermost layer VI – near to the underlying white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called Nerve tract, tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distr ...
. Each cortical layer has a characteristic distribution of different neurons and their connections with other cortical and subcortical regions. There are direct connections between different cortical areas and indirect connections via the thalamus.
One of the clearest examples of cortical layering is the line of Gennari in the primary visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus ...
. This is a band of whiter tissue that can be observed with the naked eye in the calcarine sulcus of the occipital lobe. The line of Gennari is composed of axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences) is a long, slender cellular extensions, projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, ...
s bringing visual information from the thalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of ...
into layer IV of the visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalam ...
.
Staining
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the Microscope, microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissue (biology), tissues), in cytology (microscopic ...
cross-sections of the cortex to reveal the position of neuronal cell bodies and the intracortical axon tracts allowed neuroanatomists in the early 20th century to produce a detailed description of the ''laminar structure of the cortex'' in different species. The work of Korbinian Brodmann (1909) established that the mammalian neocortex is consistently divided into six layers.
Layer I
Layer I is the molecular layer, and contains few scattered neurons, including GABAergic rosehip neurons. Layer I consists largely of extensions of apical dendritic tufts ofpyramidal neurons
Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal cells are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cort ...
and horizontally oriented axons, as well as glial cells. During development, Cajal–Retzius cells and subpial granular layer cells are present in this layer. Also, some spiny stellate cells can be found here. Inputs to the apical tufts are thought to be crucial for the ''feedback'' interactions in the cerebral cortex involved in associative learning and attention.
While it was once thought that the input to layer I came from the cortex itself, it is now known that layer I across the cerebral cortex receives substantial input from ''matrix'' or M-type thalamus cells, as opposed to ''core'' or C-type that go to layer IV.
It is thought that layer I serves as a central hub for collecting and processing widespread information. It integrates ascending sensory inputs with top-down expectations, regulating how sensory perceptions align with anticipated outcomes. Further, layer I sorts, directs, and combines excitatory inputs, integrating them with neuromodulatory signals. Inhibitory interneurons, both within layer I and from other cortical layers, gate these signals. Together, these interactions dynamically calibrate information flow throughout the neocortex, shaping perceptions and experiences.
Layer II
Layer II, the external granular layer, contains smallpyramidal neurons
Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal cells are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cort ...
and numerous stellate neurons.
Layer III
Layer III, the external pyramidal layer, contains predominantly small and medium-size pyramidal neurons, as well as non-pyramidal neurons with vertically oriented intracortical axons; layers I through III are the main target of commissural corticocortical afferents, and layer III is the principal source of corticocortical efferents.Layer IV
Layer IV, the internal granular layer, contains different types of stellate and pyramidal cells, and is the main target of thalamocortical afferents from thalamus type C neurons (core-type) as well as intra-hemispheric corticocortical afferents. The layers above layer IV are also referred to as supragranular layers (layers I-III), whereas the layers below are referred to as infragranular layers (layers V and VI). African elephants,cetaceans
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla that includes whales, dolphins and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively c ...
, and hippopotamus
The hippopotamus (''Hippopotamus amphibius;'' ; : hippopotamuses), often shortened to hippo (: hippos), further qualified as the common hippopotamus, Nile hippopotamus and river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Sahar ...
do not have a layer IV with axons which would terminate there going instead to the inner part of layer III.
Layer V
Layer V, the internal pyramidal layer, contains large pyramidal neurons. Axons from these leave the cortex and connect with subcortical structures including thebasal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into externa ...
. In the primary motor cortex of the frontal lobe, layer V contains giant pyramidal cells called Betz cells, whose axons travel through the internal capsule
The internal capsule is a paired white matter structure, as a two-way nerve tract, tract, carrying afferent nerve fiber, ascending and efferent nerve fiber, descending axon, fibers, to and from the cerebral cortex. The internal capsule is situate ...
, the brain stem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is co ...
, and the spinal cord forming the corticospinal tract
The corticospinal tract is a white matter motor pathway starting at the cerebral cortex that terminates on lower motor neurons and interneurons in the spinal cord, controlling movements of the limbs and trunk. There are more than one million neu ...
, which is the main pathway for voluntary motor control.
Layer VI
Layer VI, the polymorphic layer or multiform layer, contains few large pyramidal neurons and many small spindle-like pyramidal and multiform neurons; layer VI sends efferent fibers to the thalamus, establishing a very precise reciprocal interconnection between the cortex and the thalamus. That is, layer VI neurons from one cortical column connect with thalamus neurons that provide input to the same cortical column. These connections are both excitatory and inhibitory. Neurons send excitatory fibers to neurons in the thalamus and also send collaterals to the thalamic reticular nucleus that inhibit these same thalamus neurons or ones adjacent to them. One theory is that because the inhibitory output is reduced by cholinergic input to the cerebral cortex, this provides thebrainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
with adjustable "gain control for the relay of lemniscal inputs".
Columns
The cortical layers are not simply stacked one over the other; there exist characteristic connections between different layers and neuronal types, which span all the thickness of the cortex. These cortical microcircuits are grouped intocortical column
A cortical column is a group of neurons forming a cylindrical structure through the cerebral cortex of the brain perpendicular to the cortical surface. The structure was first identified by Vernon Benjamin Mountcastle in 1957. He later identified c ...
s and minicolumns. It has been proposed that the minicolumns are the basic functional units of the cortex. In 1957, Vernon Mountcastle showed that the functional properties of the cortex change abruptly between laterally adjacent points; however, they are continuous in the direction perpendicular to the surface. Later works have provided evidence of the presence of functionally distinct cortical columns in the visual cortex (Hubel and Wiesel, 1959), auditory cortex,
and associative cortex.
Cortical areas that lack a layer IV are called agranular. Cortical areas that have only a rudimentary layer IV are called dysgranular. Information processing within each layer is determined by different temporal dynamics with that in layers II/III having a slow 2 Hz oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
while that in layer V has a fast 10–15 Hz oscillation.
Types of cortex
Based on the differences in laminar organization the cerebral cortex can be classified into two types, the large area ofneocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, ...
which has six cell layers, and the much smaller area of allocortex
The allocortex (from Latin allo-, meaning other, and cortex, meaning bark or crust), or heterogenetic cortex, is one of the two types of cerebral cortex in the brain, together with the neocortex. In the human brain, the allocortex is the much sm ...
that has three or four layers:
* The neocortex is also known as the isocortex or neopallium and is the part of the mature cerebral cortex with six distinct layers. Examples of neocortical areas include the granular primary motor cortex, and the striate primary visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus ...
. The neocortex has two subtypes, the ''true isocortex'' and the proisocortex which is a transitional region between the isocortex and the regions of the periallocortex.
* The allocortex is the part of the cerebral cortex with three or four layers, and has three subtypes, the paleocortex
In anatomy of animals, the paleocortex, or paleopallium, is a region within the telencephalon in the vertebrate brain. This type of cerebral cortex, cortical tissue consists of three cortical laminae (layers of perikaryon, neuronal cell bodies). I ...
with three cortical laminae, the archicortex which has four or five, and a transitional area adjacent to the allocortex, the periallocortex. Examples of allocortex are the olfactory cortex and the hippocampus
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the ...
.
There is a transitional area between the neocortex and the allocortex called the paralimbic cortex, where layers 2, 3 and 4 are merged. This area incorporates the proisocortex of the neocortex and the periallocortex of the allocortex. In addition, the cerebral cortex may be classified into four lobes: the frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a Sulcus (neur ...
, temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pr ...
, the parietal lobe
The parietal lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.
The parietal lobe integra ...
, and the occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin , 'behind', and , 'head'.
The occipital lobe is the ...
, named from their overlying bones of the skull.
Blood supply and drainage
 Blood supply to the cerebral cortex is part of the cerebral circulation. Cerebral arteries supply the blood that perfuses the cerebrum. This arterial blood carries oxygen, glucose, and other nutrients to the cortex. Cerebral veins drain the deoxygenated blood, and metabolic wastes including carbon dioxide, back to the heart.
The main arteries supplying the cortex are the
Blood supply to the cerebral cortex is part of the cerebral circulation. Cerebral arteries supply the blood that perfuses the cerebrum. This arterial blood carries oxygen, glucose, and other nutrients to the cortex. Cerebral veins drain the deoxygenated blood, and metabolic wastes including carbon dioxide, back to the heart.
The main arteries supplying the cortex are the anterior cerebral artery
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from th ...
, the middle cerebral artery
The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral artery, cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches an ...
, and the posterior cerebral artery
The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, as well as the medial and inferior aspects of the temporal lobe of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the d ...
. The anterior cerebral artery supplies the anterior portions of the brain, including most of the frontal lobe. The middle cerebral artery supplies the parietal lobes, temporal lobes, and parts of the occipital lobes. The middle cerebral artery splits into two branches to supply the left and right hemisphere, where they branch further. The posterior cerebral artery supplies the occipital lobes.
The circle of Willis is the main blood system that deals with blood supply in the cerebrum and cerebral cortex.

Development
Theprenatal development
Prenatal development () involves the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal de ...
of the cerebral cortex is a complex and finely tuned process called corticogenesis, influenced by the interplay between genes and the environment.
Neural tube
The cerebral cortex develops from the most anterior part, the forebrain region, of theneural tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural folds become elevated, ...
. The neural plate
In embryology, the neural plate is a key Development of the human body, developmental structure that serves as the basis for the nervous system. Cranial to the primitive node of the embryonic primitive streak, Ectoderm, ectodermal tissue thickens ...
folds and closes to form the neural tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural folds become elevated, ...
. From the cavity inside the neural tube develops the ventricular system, and, from the neuroepithelial cells of its walls, the neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s and glia of the nervous system. The most anterior (front, or cranial) part of the neural plate, the prosencephalon, which is evident before neurulation
Neurulation refers to the folding process in vertebrate embryos, which includes the transformation of the neural plate into the neural tube. The embryo at this stage is termed the neurula.
The process begins when the notochord induces the formati ...
begins, gives rise to the cerebral hemispheres and later cortex.
Cortical neuron development
Cortical neurons are generated within the ventricular zone, next to the ventricles. At first, this zone contains neural stem cells, that transition toradial glial cell
Radial glial cells, or radial glial progenitor cells (RGPs), are Bipolar neuron, bipolar-shaped progenitor cells that are responsible for producing all of the neurons in the cerebral cortex. RGPs also produce certain lineages of glia, including as ...
s–progenitor cells, which divide to produce glial cells and neurons.
Radial glia
 The cerebral cortex is composed of a heterogenous population of cells that give rise to different cell types. The majority of these cells are derived from radial glia migration that form the different cell types of the neocortex and it is a period associated with an increase in neurogenesis. Similarly, the process of neurogenesis regulates lamination to form the different layers of the cortex. During this process there is an increase in the restriction of cell fate that begins with earlier progenitors giving rise to any cell type in the cortex and later progenitors giving rise only to
The cerebral cortex is composed of a heterogenous population of cells that give rise to different cell types. The majority of these cells are derived from radial glia migration that form the different cell types of the neocortex and it is a period associated with an increase in neurogenesis. Similarly, the process of neurogenesis regulates lamination to form the different layers of the cortex. During this process there is an increase in the restriction of cell fate that begins with earlier progenitors giving rise to any cell type in the cortex and later progenitors giving rise only to neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s of superficial layers. This differential cell fate creates an inside-out topography in the cortex with younger neurons in superficial layers and older neurons in deeper layers. In addition, laminar neurons are stopped in S or G2 phase in order to give a fine distinction between the different cortical layers. Laminar differentiation is not fully complete until after birth since during development laminar neurons are still sensitive to extrinsic signals and environmental cues.
Although the majority of the cells that compose the cortex are derived locally from radial glia there is a subset population of neurons that migrate from other regions. Radial glia give rise to neurons that are pyramidal in shape and use glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
as a neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
, however these migrating cells contribute neurons that are stellate-shaped and use GABA as their main neurotransmitter. These GABAergic neurons are generated by progenitor cells in the medial ganglionic eminence (MGE) that migrate tangentially to the cortex via the subventricular zone. This migration of GABAergic neurons is particularly important since GABA receptors are excitatory during development. This excitation is primarily driven by the flux of chloride ions through the GABA receptor, however in adults chloride concentrations shift causing an inward flux of chloride that hyperpolarizes postsynaptic neurons.
The glial fibers produced in the first divisions of the progenitor cells are radially oriented, spanning the thickness of the cortex from the ventricular zone to the outer, pial surface, and provide scaffolding for the migration of neurons outwards from the ventricular zone.
At birth there are very few dendrite
A dendrite (from Ancient Greek language, Greek δένδρον ''déndron'', "tree") or dendron is a branched cytoplasmic process that extends from a nerve cell that propagates the neurotransmission, electrochemical stimulation received from oth ...
s present on the cortical neuron's cell body, and the axon is undeveloped. During the first year of life the dendrites become dramatically increased in number, such that they can accommodate up to a hundred thousand synaptic connections with other neurons. The axon can develop to extend a long way from the cell body.
Asymmetric division
The first divisions of the progenitor cells are symmetric, which duplicates the total number of progenitor cells at each mitotic cycle. Then, some progenitor cells begin to divide asymmetrically, producing one postmitotic cell that migrates along the radial glial fibers, leaving the ventricular zone, and one progenitor cell, which continues to divide until the end of development, when it differentiates into aglial cell
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) and in the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. The neuroglia make up ...
or an ependymal cell. As the G1 phase
The G1 phase, gap 1 phase, or growth 1 phase, is the first of four phases of the cell cycle that takes place in eukaryotic cell division. In this part of interphase, the cell synthesizes Messenger RNA, mRNA and proteins in preparation for subsequ ...
of mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
is elongated, in what is seen as selective cell-cycle lengthening, the newly born neurons migrate to more superficial layers of the cortex. The migrating daughter cells become the pyramidal cells of the cerebral cortex. The development process is time ordered and regulated by hundreds of genes and epigenetic regulatory mechanisms.
Layer organization
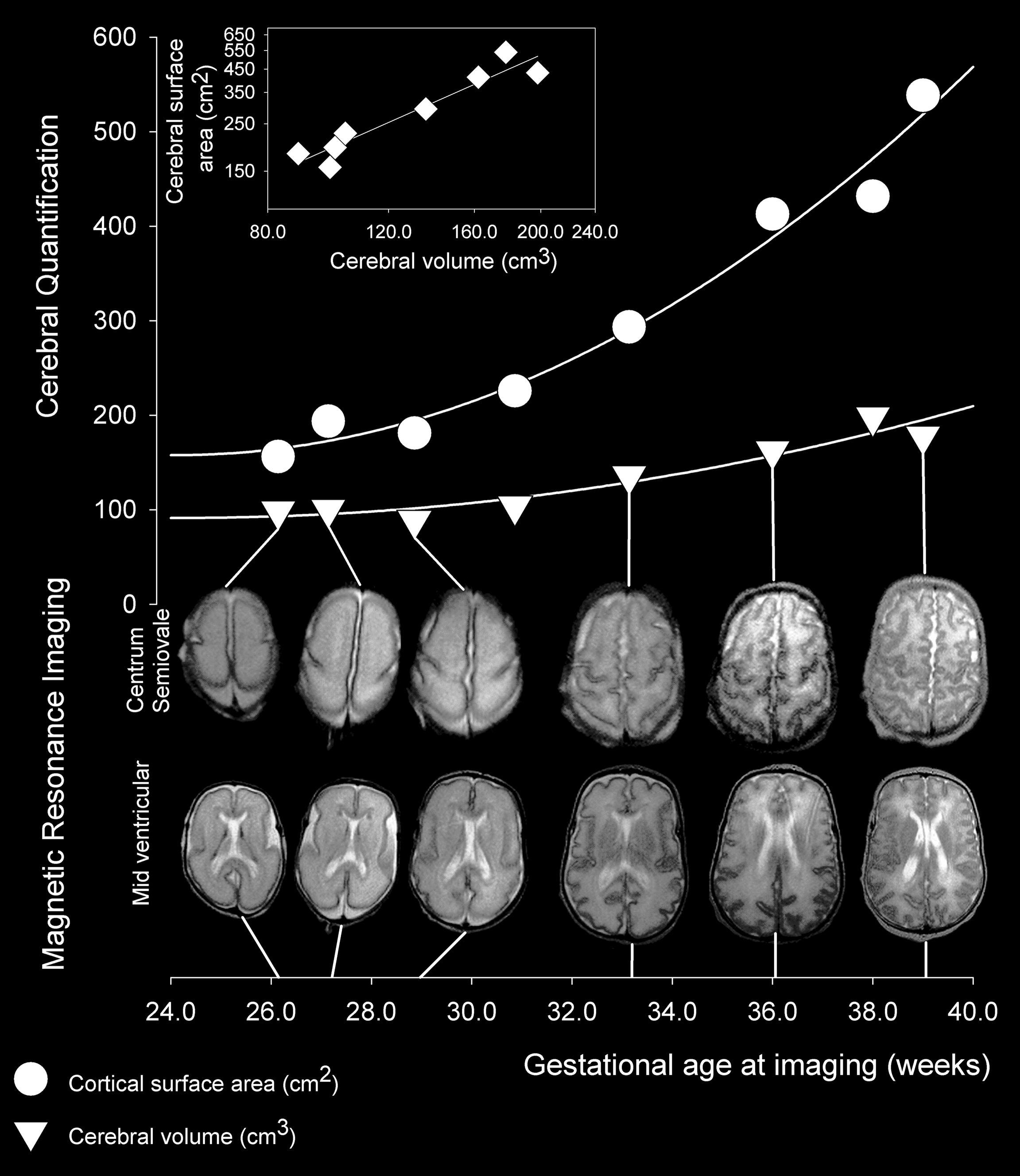
 The layered structure of the mature cerebral cortex is formed during development. The first pyramidal neurons generated migrate out of the ventricular zone and subventricular zone, together with reelin-producing Cajal–Retzius neurons, from the preplate. Next, a cohort of neurons migrating into the middle of the preplate divides this transient layer into the superficial marginal zone, which will become layer I of the mature neocortex, and the subplate, forming a middle layer called the cortical plate. These cells will form the deep layers of the mature cortex, layers five and six. Later born neurons migrate radially into the cortical plate past the deep layer neurons, and become the upper layers (two to four). Thus, the layers of the cortex are created in an inside-out order. The only exception to this inside-out sequence of neurogenesis occurs in the layer I of
The layered structure of the mature cerebral cortex is formed during development. The first pyramidal neurons generated migrate out of the ventricular zone and subventricular zone, together with reelin-producing Cajal–Retzius neurons, from the preplate. Next, a cohort of neurons migrating into the middle of the preplate divides this transient layer into the superficial marginal zone, which will become layer I of the mature neocortex, and the subplate, forming a middle layer called the cortical plate. These cells will form the deep layers of the mature cortex, layers five and six. Later born neurons migrate radially into the cortical plate past the deep layer neurons, and become the upper layers (two to four). Thus, the layers of the cortex are created in an inside-out order. The only exception to this inside-out sequence of neurogenesis occurs in the layer I of primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
s, in which, in contrast to rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal specie ...
s, neurogenesis continues throughout the entire period of corticogenesis.
Cortical patterning
 The map of functional cortical areas, which include primary motor and visual cortex, originates from a ' protomap', which is regulated by molecular signals such as fibroblast growth factor FGF8 early in embryonic development. These signals regulate the size, shape, and position of cortical areas on the surface of the cortical primordium, in part by regulating gradients of
The map of functional cortical areas, which include primary motor and visual cortex, originates from a ' protomap', which is regulated by molecular signals such as fibroblast growth factor FGF8 early in embryonic development. These signals regulate the size, shape, and position of cortical areas on the surface of the cortical primordium, in part by regulating gradients of transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
expression, through a process called cortical patterning. Examples of such transcription factors include the genes EMX2 and PAX6. Together, both transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
s form an opposing gradient of expression. Pax6 is highly expressed at the rostral lateral pole, while Emx2 is highly expressed in the caudomedial pole. The establishment of this gradient is important for proper development. For example, mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
s in Pax6 can cause expression levels of Emx2 to expand out of its normal expression domain, which would ultimately lead to an expansion of the areas normally derived from the caudal medial cortex, such as the visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalam ...
. On the contrary, if mutations in Emx2 occur, it can cause the Pax6-expressing domain to expand and result in the frontal and Motor cortex, motor cortical regions enlarging. Therefore, researchers believe that similar gradients and Cell signaling, signaling centers next to the cortex could contribute to the regional expression of these transcription factors.
Two very well studied patterning signals for the cortex include Fibroblast growth factor, FGF and retinoic acid. If FGFs are Protein production, misexpressed in different areas of the developing cortex, cortical patterning is disrupted. Specifically, when FGF8, Fgf8 is increased in the Anatomical terms of location, anterior pole, Emx2 is Downregulation and upregulation, downregulated and a caudal (anatomical term), caudal shift in the cortical region occurs. This ultimately causes an expansion of the rostral regions. Therefore, Fgf8 and other FGFs play a role in the regulation of expression of Emx2 and Pax6 and represent how the cerebral cortex can become specialized for different functions.
Rapid expansion of the cortical surface area is regulated by the amount of self-renewal of radial glial cell
Radial glial cells, or radial glial progenitor cells (RGPs), are Bipolar neuron, bipolar-shaped progenitor cells that are responsible for producing all of the neurons in the cerebral cortex. RGPs also produce certain lineages of glia, including as ...
s and is partly regulated by Fibroblast growth factor, FGF and Notch signaling pathway, Notch genes. During the period of cortical neurogenesis and layer formation, many higher mammals begin the process of gyrification
Gyrification is the process of forming the characteristic folds of the cerebral cortex. The peak of such a fold is called a ''gyrus'' (pl. ''gyri''), and its trough is called a ''Sulcus (neuroanatomy), sulcus'' (pl. ''sulci''). The neurons of the ...
, which generates the characteristic folds of the cerebral cortex. Gyrification is regulated by a DNA-associated protein Trnp1 and by FGF and Sonic hedgehog, SHH signaling.
Evolution
Of all the different brain regions, the cerebral cortex shows the largest evolutionary variation and has evolved most recently. In contrast to the highly conserved circuitry of the medulla oblongata, for example, which serves critical functions such as regulation of heart and respiration rates, many areas of the cerebral cortex are not strictly necessary for survival. Thus, the evolution of the cerebral cortex has seen the advent and modification of new functional areas—particularly association areas that do not directly receive input from outside the cortex. A key theory of cortical evolution is embodied in the radial unit hypothesis and related protomap hypothesis, first proposed by Rakic. This theory states that new cortical areas are formed by the addition of new radial units, which is accomplished at the stem cell level. The protomap hypothesis states that the cellular and molecular identity and characteristics of neurons in each cortical area are specified by cortical stem cells, known asradial glial cell
Radial glial cells, or radial glial progenitor cells (RGPs), are Bipolar neuron, bipolar-shaped progenitor cells that are responsible for producing all of the neurons in the cerebral cortex. RGPs also produce certain lineages of glia, including as ...
s, in a primordial map. This map is controlled by secreted signaling proteins and downstream transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
s.
Function

Connections
The cerebral cortex is connected to various subcortical structures such as thethalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of ...
and the basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into externa ...
, sending information to them along efferent nerve fiber, efferent connections and receiving information from them via afferent nerve fiber, afferent connections. Most sensory information is routed to the cerebral cortex via the thalamus. Olfactory information, however, passes through the olfactory bulb to the olfactory cortex (piriform cortex). The majority of connections are from one area of the cortex to another, rather than from subcortical areas; Valentino Braitenberg, Braitenberg and Schüz (1998) claim that in primary sensory areas, at the cortical level where the input fibers terminate, up to 20% of the synapses are supplied by extracortical afferents but that in other areas and other layers the percentage is likely to be much lower.
Cortical areas
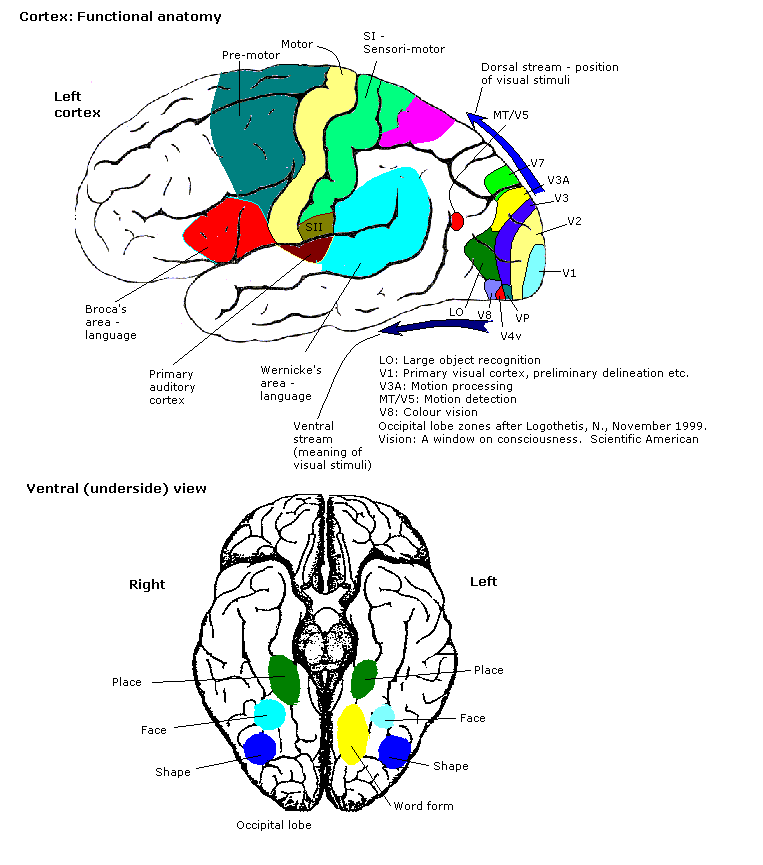
The whole of the cerebral cortex was divided into 52 different areas in an early presentation by Korbinian Brodmann. These areas, known as Brodmann areas, are based on their cytoarchitecture but also relate to various functions. An example is Brodmann area 17, which is theprimary visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus ...
.
In more general terms the cortex is typically described as comprising three parts: sensory, motor, and association areas.
Sensory areas
The sensory areas are the cortical areas that receive and process information from the senses. Parts of the cortex that receive sensory inputs from thethalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of ...
are called primary sensory areas. The senses of vision, hearing, and touch are served by the primary visual cortex, primary auditory cortex and primary somatosensory cortex respectively. In general, the two hemispheres receive information from the opposite (contralateral) side of the Human body, body. For example, the right primary somatosensory cortex receives information from the left limbs, and the right visual cortex receives information from the left visual receptive field, field.
The organization of sensory maps in the cortex reflects that of the corresponding sensing organ, in what is known as a Topographic map (Neuroanatomy), topographic map. Neighboring points in the primary visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalam ...
, for example, correspond to neighboring points in the retina. This topographic map is called a retinotopy, retinotopic map. In the same way, there exists a tonotopy, tonotopic map in the primary auditory cortex and a somatotopy, somatotopic map in the primary sensory cortex. This last topographic map of the body onto the posterior central gyrus has been illustrated as a deformed human representation, the somatosensory Cortical homunculus, homunculus, where the size of different body parts reflects the relative density of their innervation. Areas with much sensory innervation, such as the fingertips and the lips, require more cortical area to process finer sensation.
Motor areas
The motor areas are located in both hemispheres of the cortex. The motor areas are very closely related to the control of voluntary movements, especially fine fragmented movements performed by the hand. The right half of the motor area controls the left side of the body, and vice versa. Two areas of the cortex are commonly referred to as motor: * Primary motor cortex, which ''executes'' voluntary movements * Supplementary motor areas and premotor cortex, which ''select'' voluntary movements. In addition, motor functions have been described for: * Posterior parietal cortex, which guides voluntary movements in space * Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, which decides which voluntary movements to make according to higher-order instructions, rules, and self-generated thoughts. Just underneath the cerebral cortex are interconnected subcortical masses of grey matter calledbasal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into externa ...
(or nuclei). The basal ganglia receive input from the substantia nigra of the midbrain and motor areas of the cerebral cortex, and send signals back to both of these locations. They are involved in motor control. They are found lateral to the thalamus. The main components of the basal ganglia are the caudate nucleus, the putamen, the globus pallidus, the substantia nigra, the nucleus accumbens, and the subthalamic nucleus. The putamen and globus pallidus are also collectively known as the lentiform nucleus, because together they form a lens-shaped body. The putamen and caudate nucleus are also collectively called the corpus striatum after their striped appearance.
Association areas
 The association areas are the parts of the cerebral cortex that do not belong to the primary regions. They function to produce a meaningful perception, perceptual experience of the world, enable us to interact effectively, and support abstract thinking and language. The parietal lobe, parietal, Temporal lobe, temporal, and
The association areas are the parts of the cerebral cortex that do not belong to the primary regions. They function to produce a meaningful perception, perceptual experience of the world, enable us to interact effectively, and support abstract thinking and language. The parietal lobe, parietal, Temporal lobe, temporal, and occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin , 'behind', and , 'head'.
The occipital lobe is the ...
s – all located in the posterior part of the cortex – integrate sensory information and information stored in memory. The frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a Sulcus (neur ...
or prefrontal association complex is involved in planning actions and movement, as well as abstract thought. Globally, the association areas are organized as distributed networks. Each network connects areas distributed across widely spaced regions of the cortex. Distinct networks are positioned adjacent to one another yielding a complex series of interwoven networks. The specific organization of the association networks is debated with evidence for interactions, hierarchical relationships, and competition between networks.
In humans, association networks are particularly important to language function. In the past it was theorized that language abilities are localized in Broca's area in areas of the left inferior frontal gyrus, Brodmann area 44, BA44 and Brodmann area 45, BA45, for language expression and in Wernicke's area Brodmann area, BA22, for language reception. However, the processes of language expression and reception have been shown to occur in areas other than just those structures around the lateral sulcus, including the frontal lobe, basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into externa ...
, cerebellum, and pons.
Clinical significance
 Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, show as a marker, an atrophy of the grey matter of the cerebral cortex.
Other Central nervous system disease, diseases of the central nervous system include neurological disorders such as epilepsy, movement disorders, and Aphasia#Boston classification, different types of aphasia (difficulties in speech expression or comprehension).
Brain damage from disease or trauma, can involve damage to a specific lobe such as in frontal lobe disorder, and associated functions will be affected. The blood–brain barrier that serves to protect the brain from infection can become compromised allowing entry to pathogens.
The prenatal development, developing fetus is susceptible to a range of environmental factors that can cause birth defects and problems in later development. Maternal alcohol consumption for example can cause fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Other factors that can cause neurodevelopment disorders are Environmental toxicants and fetal development, toxicants such as drugs, and exposure to radiation as from X-rays. Infections can also affect the development of the cortex. A viral infection is one of the causes of lissencephaly, which results in a smooth cortex without
Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, show as a marker, an atrophy of the grey matter of the cerebral cortex.
Other Central nervous system disease, diseases of the central nervous system include neurological disorders such as epilepsy, movement disorders, and Aphasia#Boston classification, different types of aphasia (difficulties in speech expression or comprehension).
Brain damage from disease or trauma, can involve damage to a specific lobe such as in frontal lobe disorder, and associated functions will be affected. The blood–brain barrier that serves to protect the brain from infection can become compromised allowing entry to pathogens.
The prenatal development, developing fetus is susceptible to a range of environmental factors that can cause birth defects and problems in later development. Maternal alcohol consumption for example can cause fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Other factors that can cause neurodevelopment disorders are Environmental toxicants and fetal development, toxicants such as drugs, and exposure to radiation as from X-rays. Infections can also affect the development of the cortex. A viral infection is one of the causes of lissencephaly, which results in a smooth cortex without gyrification
Gyrification is the process of forming the characteristic folds of the cerebral cortex. The peak of such a fold is called a ''gyrus'' (pl. ''gyri''), and its trough is called a ''Sulcus (neuroanatomy), sulcus'' (pl. ''sulci''). The neurons of the ...
.
A type of electrocorticography called cortical stimulation mapping is an invasive procedure that involves placing electrodes directly onto the exposed brain in order to localise the functions of specific areas of the cortex. It is used in clinical and therapeutic applications including pre-surgical mapping.
Genes associated with cortical disorders
There are a number of genetic mutations that can cause a wide range of genetic disorders of the cerebral cortex, including microcephaly, schizencephaly and types of lissencephaly. Chromosome abnormality, Chromosome abnormalities can also result causing a number of neurodevelopmental disorders such as fragile X syndrome and Rett syndrome. MCPH1 codes for microcephalin, and disorders in this and in ASPM (gene), ASPM are associated with microcephaly. Mutations in the gene NBS1 that codes for nibrin can cause Nijmegen breakage syndrome, characterised by microcephaly. Mutations in EMX2, and COL4A1 are associated with schizencephaly, a condition marked by the absence of large parts of the cerebral hemispheres.History
In 1909, Korbinian Brodmann distinguished 52 different regions of the cerebral cortex based on their cytoarchitecture. These are known as Brodmann areas. Rafael Lorente de Nó, a student of Santiago Ramon y Cajal, identified more than 40 different types of cortical neurons based on the distribution of their dendrites and axons.Other animals
The cerebral cortex is derived from the pallium (neuroanatomy), pallium, a layered structure found in the prosencephalon, forebrain of all vertebrates. The basic form of the pallium is a cylindrical layer enclosing fluid-filled ventricles. Around the circumference of the cylinder are four zones, the dorsal pallium, medial pallium, ventral pallium, and lateral pallium, which are thought to be Homology (biology), homologous to theneocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, ...
, hippocampus
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the ...
, amygdala, and piriform cortex, olfactory cortex, respectively.
In Avian brain, avian brains, evidence suggests the avian pallium's neuroarchitecture to be reminiscent of the mammalian cerebral cortex. The avian pallium has also been suggested to be an equivalent neural basis for Animal consciousness, consciousness.
Until recently no counterpart to the cerebral cortex had been recognized in invertebrates. However, a study published in the journal ''Cell'' in 2010, based on gene expression profiles, reported strong affinities between the cerebral cortex and the mushroom bodies of the Nereididae, ragworm ''Platynereis dumerilii''. Mushroom bodies are structures in the brains of many types of worms and arthropods that are known to play important roles in learning and memory; the genetic evidence indicates a common evolutionary origin, and therefore indicates that the origins of the earliest precursors of the cerebral cortex date back to the Precambrian era.
Additional images
See also
* Brain–computer interface * Cortical dysplasia * Cortical homunculus * Eloquent cortex * EMX1 * Gray matter heterotopia * Limbic system * List of regions in the human brain * Insular cortexReferences
External links
* *"The primary visual cortex"
Webvision: Comprehensive article about the structure and function of the primary visual cortex.
"Basic cell types"
Webvision: Image of the basic cell types of the monkey cerebral cortex.
Cerebral Cortex – Cell Centered Database
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cerebral Cortex Cerebral cortex,