|
Low Magic
(, ) is a type of European sorcery, often referred to as witchcraft, that has been transmitted through grimoires—books containing instructions for performing magical practices. The term "goetia" finds its origins in the Greek word "goes", which originally denoted Divination, diviners, Magic (supernatural)#Magicians, magicians, healers, and Oracle, seers. Initially, it held a connotation of low magic, implying fraudulent or deceptive ''mageia'' as opposed to theurgy, which was regarded as divine magic. Grimoires, also known as "books of spells" or "spellbooks", serve as instructional manuals for various magical endeavors. They cover crafting magical objects, casting spells, performing divination, and summoning supernatural entities, such as angels, Spirit (supernatural entity), spirits, deities, and demons. Although the term "grimoire" originates from Europe, similar magical texts have been found in diverse cultures across the world. The history of grimoires can be traced ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
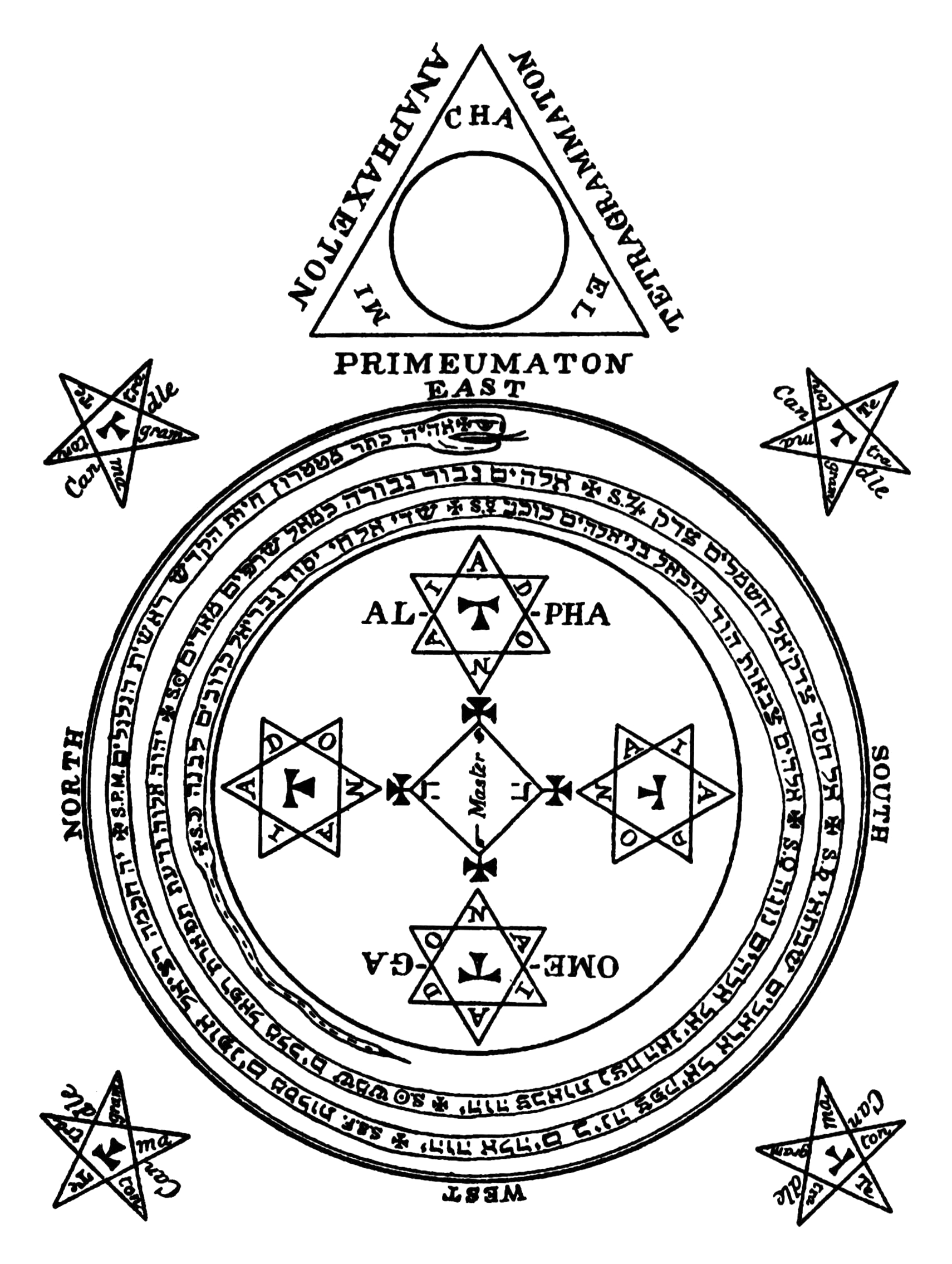
Circle Of Solomon And Triangle Of Solomon From The Lesser Key Of Solomon
A circle is a shape consisting of all point (geometry), points in a plane (mathematics), plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the Centre (geometry), centre. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is called the radius. The length of a line segment connecting two points on the circle and passing through the centre is called the diameter. A circle bounds a region of the plane called a Disk (mathematics), disc. The circle has been known since before the beginning of recorded history. Natural circles are common, such as the full moon or a slice of round fruit. The circle is the basis for the wheel, which, with related inventions such as gears, makes much of modern machinery possible. In mathematics, the study of the circle has helped inspire the development of geometry, astronomy and calculus. Terminology * Annulus (mathematics), Annulus: a ring-shaped object, the region bounded by two concentric circles. * Circular arc, Arc: any Connected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coptic Language
Coptic () is a dormant language, dormant Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language. It is a group of closely related Egyptian dialects, representing the most recent developments of the Ancient Egyptian language, Egyptian language, and historically spoken by the Copts, starting from the third century AD in Roman Egypt. Coptic was supplanted by Arabic as the primary Vernacular, spoken language of Egypt following the Arab conquest of Egypt and was slowly replaced over the centuries. Coptic has no native speakers today apart from a number of priests, although it remains in daily use as the Sacred language, liturgical language of the Coptic Orthodox Church and of the Coptic Catholic Church. It is written with the Coptic alphabet, a modified form of the Greek alphabet with seven additional letters borrowed from the Demotic (Egyptian), Demotic Egyptian script. The major Coptic dialects are Sahidic, Bohairic, Akhmimic, Fayyumic, Lycopolitan (Asyutic), and Oxyrhynchite. Sahidic Coptic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermeticism
Hermeticism, or Hermetism, is a philosophical and religious tradition rooted in the teachings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, a syncretism, syncretic figure combining elements of the Greek god Hermes and the Egyptian god Thoth. This system encompasses a wide range of Western esotericism, esoteric knowledge, including aspects of alchemy, astrology, and theurgy, and has significantly influenced various mystical and occult traditions throughout history. The writings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, often referred to as the ''Hermetica'', were produced over a period spanning many centuries () and may be very different in content and scope. One particular form of Hermetic teaching is the religio-philosophical system found in a specific subgroup of Hermetic writings known as the Hermetica#Religio-philosophical Hermetica, 'religio-philosophical' ''Hermetica''. The most famous of these are the ''Corpus Hermeticum'', a collection of seventeen Ancient Greek, Greek treatises written b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabbalah
Kabbalah or Qabalah ( ; , ; ) is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. It forms the foundation of Mysticism, mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal (). List of Jewish Kabbalists, Jewish Kabbalists originally developed transmissions of the primary texts of Kabbalah within the realm of Jewish tradition and often use classical Jewish scriptures to explain and demonstrate its mystical teachings. Kabbalists hold these teachings to define the inner meaning of both the Hebrew Bible and traditional rabbinic literature and their formerly concealed transmitted dimension, as well as to explain the significance of Jewish religious observances. Historically, Kabbalah emerged from earlier forms of Jewish mysticism, in 12th- to 13th-century Golden age of Jewish culture in Spain, al-Andalus (Spain) and in Hakhmei Provence, and was reinterpreted during the Jewish mystical renaissance in 16th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleister Crowley
Aleister Crowley ( ; born Edward Alexander Crowley; 12 October 1875 – 1 December 1947) was an English occultist, ceremonial magician, poet, novelist, mountaineer, and painter. He founded the religion of Thelema, identifying himself as the prophet entrusted with guiding humanity into the Aeon of Horus, Æon of Horus in the early 20th century. A prolific writer, he published widely over the course of his life. Born to a wealthy family in Royal Leamington Spa, Warwickshire, Crowley rejected his parents' fundamentalist Christian Plymouth Brethren faith to pursue an interest in Western esotericism. He was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, Trinity College at the University of Cambridge, where he focused his attention upon mountaineering and poetry, resulting in several publications. Some biographers allege that here he was recruited into a British intelligence agency, further suggesting that he remained a spy throughout his life. In 1898, he joined the esoteric Hermetic Order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eliphas Levi
Eliphaz is one of Esau's sons in the Bible. Eliphaz or Eliphas may also refer to: * Eliphaz (Job), another person in the Bible * Eliphaz Dow (1705–1755), first male executed in New Hampshire * Eliphaz Fay (1797–1854), fourth president of Waterville College (now called Colby College) * Éliphas Lévi (1810-1875), French occultist born Alphonse Louis Constant * Eliphaz Maari (born 1954), Anglican bishop who served in Ugand * Eliphas Shivute (born 1974), Namibian retired footballer See also * Eliphas Buffett House, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, on the National Register of Historic Places * * * Elifaz, Israel, a kibbutz {{given name Masculine given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heresy
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, particularly the accepted beliefs or religious law of a religious organization. A heretic is a proponent of heresy. Heresy in Heresy in Christianity, Christianity, Heresy in Judaism, Judaism, and Bid‘ah, Islam has at times been met with censure ranging from excommunication to the death penalty. Heresy is distinct from apostasy, which is the explicit renunciation of one's religion, principles or cause; and from blasphemy, which is an impious utterance or action concerning God or sacred things. Heresiology is the study of heresy. Etymology Derived from Ancient Greek ''haíresis'' (), the English ''heresy'' originally meant "choice" or "thing chosen". However, it came to mean the "party, or school, of a man's choice", and also referred to that process whereby a young person would examine various philosophies to determine how to live. The word ''heresy'' is usually used within a C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paganism
Paganism (, later 'civilian') is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Christianity, Judaism, and Samaritanism. In the time of the Roman Empire, individuals fell into the pagan class either because they were increasingly rural and provincial relative to the Christian population, or because they were not '' milites Christi'' (soldiers of Christ).J. J. O'Donnell (1977)''Paganus'': Evolution and Use, ''Classical Folia'', 31: 163–69. Alternative terms used in Christian texts were '' hellene'', '' gentile'', and '' heathen''. Ritual sacrifice was an integral part of ancient Greco-Roman religion and was regarded as an indication of whether a person was pagan or Christian. Paganism has broadly connoted the "religion of the peasantry". During and after the Middle Ages, the term ''paganism'' was applied to any non-Christian religion, and the term presumed a belief in fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testament Of Solomon
The Testament of Solomon is a pseudepigraphical composite text ascribed to King Solomon but not regarded as canonical scripture by Jews or Christian groups. It was written in the Greek language, based on precedents dating back to the early 1st millennium AD, but was likely not completed in any meaningful textual sense until sometime in the Middle Ages. In its most noteworthy recensions, the text describes how Solomon was enabled to build his temple by commanding demons by means of a magical ring that was entrusted to him by the archangel Michael. Dating and authorship Scholarly opinion on when the Testament of Solomon was written varies widely. Suggested dates for its composition range between the end of the 1st century AD and the High Middle Ages. Also disputed is whether it had a Christian or Jewish origin. Mid-twentieth century scholarship tended to agree that much of its content "reflects the first-century Judaism in Israel" and includes material much earlier than its com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudepigrapha
A pseudepigraph (also :wikt:anglicized, anglicized as "pseudepigraphon") is a false attribution, falsely attributed work, a text whose claimed author is not the true author, or a work whose real author attributed it to a figure of the past. The name of the author to whom the work is falsely attributed is often prefixed with the particle ":wikt:pseudo-, pseudo-", such as for example "pseudo-Aristotle" or "pseudo-Dionysius": these terms refer to the anonymous authors of works falsely attributed to Aristotle and Dionysius the Areopagite, respectively. In biblical studies, the term ''pseudepigrapha'' can refer to an assorted collection of Jewish religious works thought to be written 300 BCE to 300 CE. They are distinguished by Protestantism, Protestants from the deuterocanonical books (Catholic and Orthodox) or Apocrypha (Protestant), the books that appear in extant copies of the Septuagint in the fourth century or later and the Vulgate, but not in the Hebrew Bible or in Protestan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Solomon
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a constitutional monarch if his power is restrained by fixed laws. Kings are hereditary monarchs when they inherit power by birthright and elective monarchs when chosen to ascend the throne. *In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the title may refer to tribal kingship. Germanic kingship is cognate with Indo-European traditions of tribal rulership (cf. Indic ''rājan'', Gothic ''reiks'', and Old Irish '' rí'', etc.). *In the context of classical antiquity, king may translate in Latin as '' rex'' and in Greek as ''archon'' or ''basileus''. *In classical European feudalism, the title of ''king'' as the ruler of a ''kingdom'' is understood to be the highest rank in the feudal order, potentially subject, at least nominally, only to an emperor (harking back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Enoch
The Book of Enoch (also 1 Enoch; Hebrew language, Hebrew: סֵפֶר חֲנוֹךְ, ''Sēfer Ḥănōḵ''; , ) is an Second Temple Judaism, ancient Jewish Apocalyptic literature, apocalyptic religious text, ascribed by tradition to the Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch Enoch who was the father of Methuselah and the great-grandfather of Noah..Barker, Margaret. (2005) [1998]. ''The Lost Prophet: The Book of Enoch and Its Influence on Christianity''. London: SPCK; Sheffield Phoenix Press. The Book of Enoch contains unique material on the origins of demons and Nephilim, why some fallen angel, angels fell from heaven, an explanation of why the Genesis flood narrative, Genesis flood was morally necessary, and a prophetic exposition of the Millennialism, thousand-year reign of the Messiah. Three books are traditionally attributed to Enoch, including the distinct works 2 Enoch and 3 Enoch. 1 Enoch is not considered to be Biblical canon, canonical scripture by most Jewish or Christian chu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |