|
Imaging Spectroscopy
In imaging spectroscopy (also hyperspectral imaging or spectral imaging) each pixel of an image acquires many bands of light intensity data from the spectrum, instead of just the three bands of the RGB color model. More precisely, it is the simultaneous acquisition of spatially coregistered images in many spectrally contiguous bands. Some spectral images contain only a few image planes of a spectral data cube, while others are better thought of as full spectra at every location in the image. For example, solar physicists use the spectroheliograph to make images of the Sun built up by scanning the slit of a spectrograph, to study the behavior of surface features on the Sun; such a spectroheliogram may have a spectral resolution of over 100,000 (\lambda / \Delta \lambda) and be used to measure local motion (via the Doppler shift) and even the magnetic field (via the Zeeman splitting The Zeeman effect (; ) is the effect of splitting of a spectral line into several component ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multispectral Image
Multispectral imaging captures image data within specific wavelength ranges across the electromagnetic spectrum. The wavelengths may be separated by filters or detected with the use of instruments that are sensitive to particular wavelengths, including light from frequencies beyond the visible light range, i.e. infrared and ultra-violet. It can allow extraction of additional information the human eye fails to capture with its visible receptors for red, green and blue. It was originally developed for military target identification and reconnaissance. Early space-based imaging platforms incorporated multispectral imaging technology to map details of the Earth related to coastal boundaries, vegetation, and landforms. Multispectral imaging has also found use in document and painting analysis. Multispectral imaging measures light in a small number (typically 3 to 15) of spectral bands. Hyperspectral imaging is a special case of spectral imaging where often hundreds of contiguous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Bands
Spectral bands are parts of the electromagnetic spectrum of specific wavelengths, which can be filtered by a standard filter. In nuclear physics, spectral bands are referred to the emission of polyatomic systems, including condensed materials, large molecules, etc. Each spectral line corresponds to one level in the atom splits in the molecules. When the number of atoms is large, one gets a continuum of energy levels, the so-called "spectral bands". They are often labeled in the same way as the monatomic lines. The bands may overlap. In general, the energy spectrum can be given by a density function, describing the number of energy levels of the quantum system for a given interval. Spectral bands have constant density, and when the bands overlap, the corresponding densities are added. Band spectra is the name given to a group of lines that are closely spaced and arranged in a regular sequence that appears to be a band. It is a colored band, separated by dark spaces on the two sides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
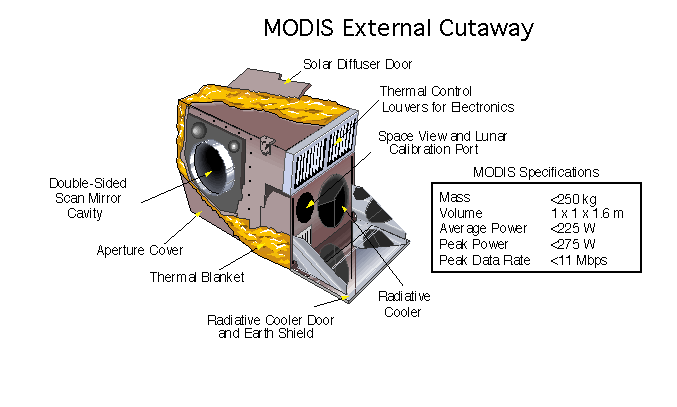
MODIS
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) is a satellite-based sensor used for earth and climate measurements. There are two MODIS sensors in Earth orbit: one on board the Terra (EOS AM) satellite, launched by NASA in 1999; and one on board the Aqua (EOS PM) satellite, launched in 2002. MODIS has now been replaced by the VIIRS, which first launched in 2011 aboard the Suomi NPP satellite. The MODIS instruments were built by Santa Barbara Remote Sensing. They capture data in 36 spectral bands ranging in wavelength from 0.4 μm to 14.4 μm and at varying spatial resolutions (2 bands at 250 m, 5 bands at 500 m and 29 bands at 1 km). Together the instruments image the entire Earth every 1 to 2 days. They are designed to provide measurements in large-scale global dynamics including changes in Earth's cloud cover, radiation budget and processes occurring in the oceans, on land, and in the lower atmosphere. Support and calibration is provided by the MO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Physics
Molecular physics is the study of the physical properties of molecules and molecular dynamics. The field overlaps significantly with physical chemistry, chemical physics, and quantum chemistry. It is often considered as a sub-field of atomic, molecular, and optical physics. Research groups studying molecular physics are typically designated as one of these other fields. Molecular physics addresses phenomena due to both molecular structure and individual atomic processes within molecules. Like atomic physics, it relies on a combination of classical and quantum mechanics to describe interactions between electromagnetic radiation and matter. Experiments in the field often rely heavily on techniques borrowed from atomic physics, such as spectroscopy and scattering. Molecular Structure In a molecule, both the electrons and nuclei experience similar-scale forces from the Coulomb interaction. However, the nuclei remain at nearly fixed locations in the molecule while the electrons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Spectroscopy
Modern spectroscopy in the Western world started in the 17th century. New designs in optics, specifically prisms, enabled systematic observations of the solar spectrum. Isaac Newton first applied the word ''spectrum'' to describe the rainbow of colors that combine to form white light. During the early 1800s, Joseph von Fraunhofer conducted experiments with dispersive spectrometers that enabled spectroscopy to become a more precise and quantitative scientific technique. Since then, spectroscopy has played and continues to play a significant role in chemistry, physics and astronomy. Fraunhofer observed and measured dark lines in the Sun's spectrum, which now bear his name although several of them were observed earlier by Wollaston. Origins and experimental development The Romans were already familiar with the ability of a prism to generate a rainbow of colors. Newton is traditionally regarded as the founder of spectroscopy, but he was not the first scientist who studied and reporte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |