|
Hyperlexia
Hyperlexia is a syndrome characterized by a child's precocious ability to read. It was initially identified by Norman E. Silberberg and Margaret C. Silberberg (1967), who defined it as the precocious ability to read words without prior training in learning to read, typically before the age of five. They indicated that children with hyperlexia have a significantly higher word-decoding ability than their reading comprehension levels. Children with hyperlexia also present with an intense fascination for written material at a very early age. Hyperlexic children are characterized by word-reading ability well above what would be expected given their age. First named and scientifically described in 1967, it can be viewed as an ability in which word recognition ability goes far above expected levels of skill. Some hyperlexics, however, have trouble understanding speech. Some experts believe that most children with hyperlexia, or perhaps even all of them, lie on the autism spectrum. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echolalia
Echolalia is the unsolicited repetition of vocalizations made by another person; when repeated by the same person, it is called palilalia. In its profound form it is automatic and effortless. It is one of the echophenomena, closely related to echopraxia, the automatic repetition of movements made by another person; both are "subsets of imitative behavior" whereby sounds or actions are imitated "without explicit awareness". Echolalia may be an immediate reaction to a stimulus or may be delayed. Echolalia occurs in many cases of autism spectrum disorder and Tourette syndrome. It may also occur in several other neurological conditions such as some forms of dementia or stroke-related aphasia. The word "echolalia" is derived from the Greek (''ēchō''), meaning "echo" or "to repeat", and (''laliá'') meaning "speech" or "talk" (of onomatopoeic origin, from the verb (''laléo''), meaning "to talk"). Signs and symptoms Echolalia can be categorized as either immediate (occurrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darold Treffert
Darold A. Treffert (March 12, 1933 – December 14, 2020) was an American psychiatrist and research director who specialized in the epidemiology of autism spectrum disorders and savant syndrome. He lived in Fond du Lac, Wisconsin. He was on the staff at Agnesian HealthCare and served on the Board of Trustees of Marian University. Treffert was a clinical professor at the University of Wisconsin Medical School. He was also a clinical professor at University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee. Education Treffert first attended Bethany Lutheran College where he focused on pre-medical courses and earned an associate in arts degree in 1953. He received his medical doctorate in 1958 from the University of Wisconsin Medical School. He interned in Eugene, Oregon, and then completed a residency in psychiatry at University Hospitals (now University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics) in Madison, Wisconsin. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William-Adolphe Bouguereau (1825-1905) - The Difficult Lesson (1884)
William-Adolphe Bouguereau (; 30 November 1825 – 19 August 1905) was a French Academic art, academic painter. In his realistic genre paintings, he used mythological themes, making modern interpretations of Classicism, classical subjects, with an emphasis on the female human body. During his life, he enjoyed significant popularity in France and the United States, was given numerous official honors, and received top prices for his work. As the quintessential salon painter of his generation, he was reviled by the Impressionism, Impressionist avant-garde. By the early twentieth century, Bouguereau and his art fell out of favor with the public, due in part to changing tastes. In the 1980s, a revival of interest in figure painting led to a rediscovery of Bouguereau and his work. He finished 822 known paintings, but the whereabouts of many are Lost artworks, still unknown. Life and career Formative years William-Adolphe Bouguereau was born in La Rochelle, France, on 30 November 1825, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communicate
Communication is commonly defined as the transmission of information. Its precise definition is disputed and there are disagreements about whether unintentional or failed transmissions are included and whether communication not only transmits meaning but also creates it. Models of communication are simplified overviews of its main components and their interactions. Many models include the idea that a source uses a coding system to express information in the form of a message. The message is sent through a channel to a receiver who has to decode it to understand it. The main field of inquiry investigating communication is called communication studies. A common way to classify communication is by whether information is exchanged between humans, members of other species, or non-living entities such as computers. For human communication, a central contrast is between verbal and non-verbal communication. Verbal communication involves the exchange of messages in linguistic form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor Of Optometry
Optometry is the healthcare practice concerned with examining the eyes for visual defects, prescribing corrective lenses, and detecting eye abnormalities. In the United States and Canada, optometrists are those that hold a post-baccalaureate four-year Doctor of Optometry degree. They are trained and licensed to practice medicine for eye related conditions, in addition to providing refractive (optical) eye care. Within their scope of practice, optometrists are considered physicians and bill medical insurance(s) (example: Medicare) accordingly. In the United Kingdom, optometrists may also provide medical care (e.g. prescribe medications and perform various surgeries) for eye-related conditions in addition to providing refractive care. The Doctor of Optometry degree is rarer in the UK. Many optometrists participate in academic research for eye-related conditions and diseases. In addition to prescribing glasses and contact lenses for vision related deficiencies, optometrists are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebecca Williamson Brown
Rebecca () appears in the Hebrew Bible as the wife of Isaac and the mother of Jacob and Esau. According to biblical tradition, Rebecca's father was Bethuel the Aramean from Paddan Aram, also called Aram-Naharaim. Rebecca's brother was Laban (Bible), Laban the Aramean, and she was the granddaughter of Milcah and Nahor, son of Terah, Nahor, the brother of Abraham. Rebecca and Isaac were one of the four couples that some believe are buried in the Cave of the Patriarchs, the other three being Adam and Eve, Abraham and Sarah, and Jacob and Leah. Most scholars have considered Rebecca's historicity uncertain. Early life After the Binding of Isaac, Sarah died. After taking care of her burial, Abraham went about finding a wife for his son Isaac, who was already 37 years old. He commanded his servant (whom the Torah commentators identify as Eliezer of Damascus) to journey to Aram Naharaim to select a bride from his own family, rather than engage Isaac to a local Canaanite girl. Abraham s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splinter Skill
A splinter skill is an "ability to do a specific task that does not generalize to other tasks", according to ''Occupational Therapy for Physical Dysfunction''. Cheatum and Hammond define them as skills learned that are above the child's age. Jacks writes that they are skills that are not "an integral part of the orderly sequential development"; that is, skills mastered before they are developmentally expected. According to Ayres and Robbins, an example is "the ability to play a particular piece on the piano without having the generalized ability to play the piano". References Skills Learning {{developmental-psych-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotypical
The neurodiversity paradigm is a framework for understanding human brain function that considers the diversity within sensory processing, motor abilities, social comfort, cognition, and focus as neurobiological differences. This diversity falls on a spectrum of neurocognitive differences. The neurodiversity paradigm argues that diversity in neurocognition is part of humanity and that some neurodivergences generally classified as disorders, such as autism, are differences with strengths and weaknesses as well as disabilities that are not necessarily pathological. The neurodiversity movement started in the late 1980s and early 1990s with the start of Autism Network International. Much of the correspondence that led to the formation of the movement happened over autism conferences, namely the autistic-led Autreat, penpal lists, and Usenet. The framework grew out of the disability rights movement and builds on the social model of disability, arguing that disability partly arises ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Skills
A social skill is any competence facilitating interaction and communication with others where social rules and relations are created, communicated, and changed in verbal and nonverbal ways. The process of learning these skills is called socialization. Lack of such skills can cause ''social awkwardness''. Interpersonal skills are actions used to effectively interact with others. Interpersonal skills relate to categories of dominance vs. submission, love vs. hate, affiliation vs. aggression, and control vs. autonomy (Leary, 1957). Positive interpersonal skills include entertainment, persuasion, active listening, showing care, delegation, hospitality and stewardship, among others. Social psychology, an academic discipline focused on research relating to social functioning, studies how interpersonal skills are learned through societal-based changes in attitude, thinking, and behavior. Enumeration and categorization Social skills are the tools that enable people to communicate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
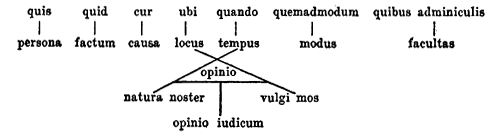
Five Ws
The Five Ws is a checklist used in journalism to ensure that the News style#Lead, lead contains all the essential points of a story. As far back as 1913, reporters were taught that the lead should answer these questions: * ''Who?''asking about a person or other agent * ''What?''asking about an object or action * ''When?''asking about a time * ''Where?''asking about a place * ''Why?''asking about a reason or cause In modern times, journalism students are still taught that these are the fundamental five questions of newswriting. Reporters also use the "5 Ws" to guide research and interviews and to raise important ethical questions, such as "How do you know that?". Nomenclature There are many other names for this checklist. Some common ones are: The Five W's and H, The 5 W's of Journalism, Six Honest-Serving Men. Usage outside of journalism In the United Kingdom (excluding Scotland), the Five Ws are used in Key Stage 2 and Key Stage 3 lessons (ages 7–14). In data analyti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Delay
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing. Human language is characterized by its cultural and historical diversity, with significant variations observed between cultures and across time. Human languages possess the properties of productivity and displacement, which enable the creation of an infinite number of sentences, and the ability to refer to objects, events, and ideas that are not immediately present in the discourse. The use of human language relies on social convention and is acquired through learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pragmatics
In linguistics and the philosophy of language, pragmatics is the study of how Context (linguistics), context contributes to meaning. The field of study evaluates how human language is utilized in social interactions, as well as the relationship between the interpreter and the interpreted. Linguists who specialize in pragmatics are called pragmaticians. The field has been represented since 1986 by the International Pragmatics Association (IPrA). Pragmatics encompasses phenomena including implicature, speech acts, relevance theory, relevance and Conversation analysis, conversation,Mey, Jacob L. (1993) ''Pragmatics: An Introduction''. Oxford: Blackwell (2nd ed. 2001). as well as nonverbal communication. Theories of pragmatics go hand-in-hand with theories of semantics, which studies aspects of meaning, and syntax, which examines sentence structures, principles, and relationships. The ability to understand another speaker's intended meaning is called ''pragmatic competence''. In 1938 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |