|
Eigenfunction
In mathematics, an eigenfunction of a linear operator ''D'' defined on some function space is any non-zero function f in that space that, when acted upon by ''D'', is only multiplied by some scaling factor called an eigenvalue. As an equation, this condition can be written as Df = \lambda f for some scalar eigenvalue \lambda. The solutions to this equation may also be subject to boundary conditions that limit the allowable eigenvalues and eigenfunctions. An eigenfunction is a type of eigenvector. Eigenfunctions In general, an eigenvector of a linear operator ''D'' defined on some vector space is a nonzero vector in the domain of ''D'' that, when ''D'' acts upon it, is simply scaled by some scalar value called an eigenvalue. In the special case where ''D'' is defined on a function space, the eigenvectors are referred to as eigenfunctions. That is, a function ''f'' is an eigenfunction of ''D'' if it satisfies the equation where λ is a scalar. The solutions to Equation may also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthonormal Basis
In mathematics, particularly linear algebra, an orthonormal basis for an inner product space V with finite Dimension (linear algebra), dimension is a Basis (linear algebra), basis for V whose vectors are orthonormal, that is, they are all unit vectors and Orthogonality_(mathematics), orthogonal to each other. For example, the standard basis for a Euclidean space \R^n is an orthonormal basis, where the relevant inner product is the dot product of vectors. The Image (mathematics), image of the standard basis under a Rotation (mathematics), rotation or Reflection (mathematics), reflection (or any orthogonal transformation) is also orthonormal, and every orthonormal basis for \R^n arises in this fashion. An orthonormal basis can be derived from an orthogonal basis via Normalize (linear algebra), normalization. The choice of an origin (mathematics), origin and an orthonormal basis forms a coordinate frame known as an ''orthonormal frame''. For a general inner product space V, an orthono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilbert Space
In mathematics, a Hilbert space is a real number, real or complex number, complex inner product space that is also a complete metric space with respect to the metric induced by the inner product. It generalizes the notion of Euclidean space. The inner product allows lengths and angles to be defined. Furthermore, Complete metric space, completeness means that there are enough limit (mathematics), limits in the space to allow the techniques of calculus to be used. A Hilbert space is a special case of a Banach space. Hilbert spaces were studied beginning in the first decade of the 20th century by David Hilbert, Erhard Schmidt, and Frigyes Riesz. They are indispensable tools in the theories of partial differential equations, mathematical formulation of quantum mechanics, quantum mechanics, Fourier analysis (which includes applications to signal processing and heat transfer), and ergodic theory (which forms the mathematical underpinning of thermodynamics). John von Neumann coined the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
In linear algebra, an eigenvector ( ) or characteristic vector is a vector that has its direction unchanged (or reversed) by a given linear transformation. More precisely, an eigenvector \mathbf v of a linear transformation T is scaled by a constant factor \lambda when the linear transformation is applied to it: T\mathbf v=\lambda \mathbf v. The corresponding eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic root is the multiplying factor \lambda (possibly a negative or complex number). Geometrically, vectors are multi-dimensional quantities with magnitude and direction, often pictured as arrows. A linear transformation rotates, stretches, or shears the vectors upon which it acts. A linear transformation's eigenvectors are those vectors that are only stretched or shrunk, with neither rotation nor shear. The corresponding eigenvalue is the factor by which an eigenvector is stretched or shrunk. If the eigenvalue is negative, the eigenvector's direction is reversed. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermitian Matrix
In mathematics, a Hermitian matrix (or self-adjoint matrix) is a complex square matrix that is equal to its own conjugate transpose—that is, the element in the -th row and -th column is equal to the complex conjugate of the element in the -th row and -th column, for all indices and : A \text \quad \iff \quad a_ = \overline or in matrix form: A \text \quad \iff \quad A = \overline . Hermitian matrices can be understood as the complex extension of real symmetric matrices. If the conjugate transpose of a matrix A is denoted by A^\mathsf, then the Hermitian property can be written concisely as A \text \quad \iff \quad A = A^\mathsf Hermitian matrices are named after Charles Hermite, who demonstrated in 1855 that matrices of this form share a property with real symmetric matrices of always having real eigenvalues. Other, equivalent notations in common use are A^\mathsf = A^\dagger = A^\ast, although in quantum mechanics, A^\ast typically means the complex conjugate onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirac Delta Function
In mathematical analysis, the Dirac delta function (or distribution), also known as the unit impulse, is a generalized function on the real numbers, whose value is zero everywhere except at zero, and whose integral over the entire real line is equal to one. Thus it can be Heuristic, represented heuristically as \delta (x) = \begin 0, & x \neq 0 \\ , & x = 0 \end such that \int_^ \delta(x) dx=1. Since there is no function having this property, modelling the delta "function" rigorously involves the use of limit (mathematics), limits or, as is common in mathematics, measure theory and the theory of distribution (mathematics), distributions. The delta function was introduced by physicist Paul Dirac, and has since been applied routinely in physics and engineering to model point masses and instantaneous impulses. It is called the delta function because it is a continuous analogue of the Kronecker delta function, which is usually defined on a discrete domain and takes values ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sturm–Liouville Theory
In mathematics and its applications, a Sturm–Liouville problem is a second-order linear ordinary differential equation of the form \frac \left (x) \frac\right+ q(x)y = -\lambda w(x) y for given functions p(x), q(x) and w(x), together with some boundary conditions at extreme values of x. The goals of a given Sturm–Liouville problem are: * To find the for which there exists a non-trivial solution to the problem. Such values are called the ''eigenvalues'' of the problem. * For each eigenvalue , to find the corresponding solution y = y(x) of the problem. Such functions y are called the '' eigenfunctions'' associated to each . Sturm–Liouville theory is the general study of Sturm–Liouville problems. In particular, for a "regular" Sturm–Liouville problem, it can be shown that there are an infinite number of eigenvalues each with a unique eigenfunction, and that these eigenfunctions form an orthonormal basis of a certain Hilbert space of functions. This theory is important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drum Vibration Mode12
The drum is a member of the percussion group of musical instruments. In the Hornbostel–Sachs classification system, it is a membranophone. Drums consist of at least one membrane, called a drumhead or drum skin, that is stretched over a shell and struck, either directly with the player's hands, or with a percussion mallet, to produce sound. There is usually a resonant head on the underside of the drum. Other techniques have been used to cause drums to make sound, such as the thumb roll. Drums are the world's oldest and most ubiquitous musical instruments, and the basic design has remained virtually unchanged for thousands of years. Drums may be played individually, with the player using a single drum, and some drums such as the djembe are almost always played in this way. Others are normally played in a set of two or more, all played by one player, such as bongo drums and timpani. A number of different drums together with cymbals form the basic modern drum kit. Many d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
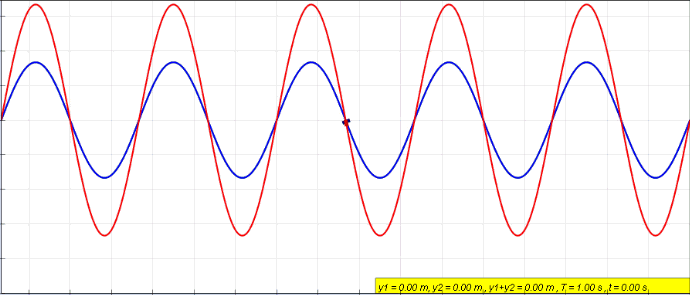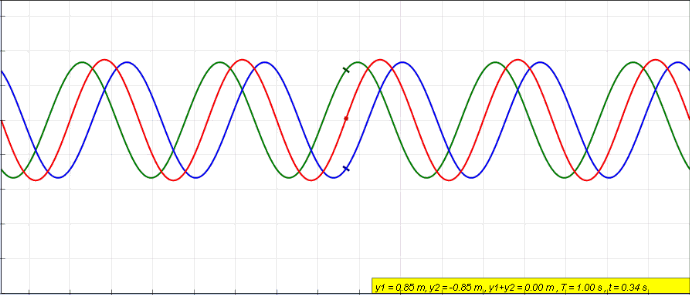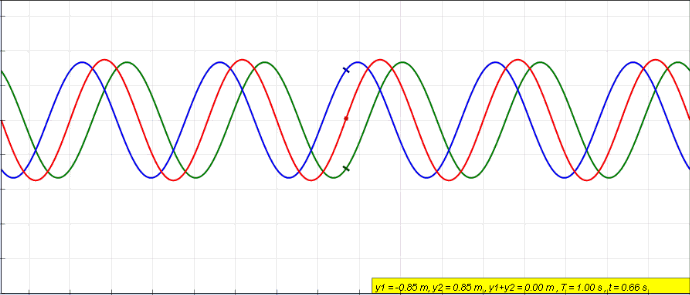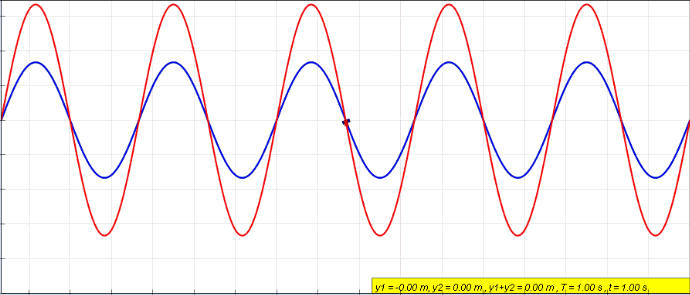
Standing Wave
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect to time, and the oscillations at different points throughout the wave are in phase. The locations at which the absolute value of the amplitude is minimum are called node (physics), nodes, and the locations where the absolute value of the amplitude is maximum are called antinodes. Standing waves were first described scientifically by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday observed Faraday wave, standing waves on the surface of a liquid in a vibrating container. Franz Melde coined the term "standing wave" (German: ''stehende Welle'' or ''Stehwelle'') around 1860 and demonstrated the phenomenon in his classic experiment with vibrating strings. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the direction opposite to the movement of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-adjoint Operator
In mathematics, a self-adjoint operator on a complex vector space ''V'' with inner product \langle\cdot,\cdot\rangle is a linear map ''A'' (from ''V'' to itself) that is its own adjoint. That is, \langle Ax,y \rangle = \langle x,Ay \rangle for all x, y ∊ ''V''. If ''V'' is finite-dimensional with a given orthonormal basis, this is equivalent to the condition that the matrix of ''A'' is a Hermitian matrix, i.e., equal to its conjugate transpose ''A''. By the finite-dimensional spectral theorem, ''V'' has an orthonormal basis such that the matrix of ''A'' relative to this basis is a diagonal matrix with entries in the real numbers. This article deals with applying generalizations of this concept to operators on Hilbert spaces of arbitrary dimension. Self-adjoint operators are used in functional analysis and quantum mechanics. In quantum mechanics their importance lies in the Dirac–von Neumann formulation of quantum mechanics, in which physical observables such as position, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Instrument
In musical instrument classification, string instruments, or chordophones, are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer strums, plucks, strikes or sounds the strings in varying manners. Musicians play some string instruments, like Guitar, guitars, by plucking the String (music), strings with their fingers or a plectrum, plectrum (pick), and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow (music), bow, like Violin, violins. In some keyboard (music), keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |