|
Data Fabrication
In science, scientific inquiry and academia, academic research, data fabrication is the intentional misrepresentation of research results. As with other forms of scientific misconduct, it is the intent to deceive that marks fabrication as unethical, and thus different from scientists pathological science, deceiving themselves. There are many ways data can be fabricated. Experimental data can be fabricated by reporting experiments that were never conducted, and accurate data can be manipulated or misrepresented to suit a desired outcome. One of the biggest problems with this form of scientific fraud is that "university investigations into research misconduct are often inadequate, opaque and poorly conducted. They challenge the idea that institutions can police themselves on research integrity." Sometimes intentional fabrication can be difficult to distinguish from unintentional academic incompetence or malpractice. Examples of this include the failure to account for measurement erro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984), then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996) and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007), is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by multinational company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, the company operates several laboratories in the United States and around the world. Researchers working at Bell Laboratories are credited with the development of radio astronomy, the transistor, the laser, the photovoltaic cell, the charge-coupled device (CCD), information theory, the Unix operating system, and the programming languages B, C, C++, S, SNOBOL, AWK, AMPL, and others. Nine Nobel Prizes have been awarded for work completed at Bell Laboratories. Bell Labs had its origin in the complex corporate organization of the Bell System telephone conglomerate. In the late 19th century, the laboratory began as the Western Electric Engineering Department, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
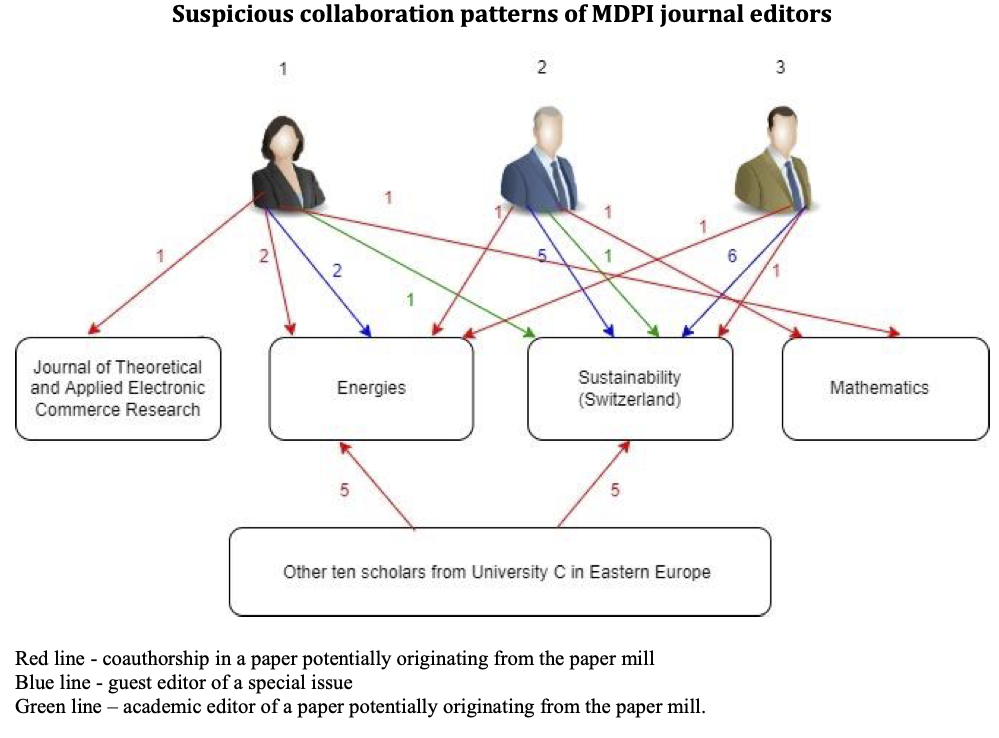
Research Paper Mill
In research, a paper mill is a "profit oriented, unofficial and potentially illegal organisation that produces and sells authorship on research manuscripts. In some cases, paper mills are sophisticated operations that sell authorship positions on legitimate research, but in many cases the papers contain fraudulent data and can be heavily plagiarized or otherwise unprofessional. According to a report from ''Nature'', thousands of papers in academic journals have been traced to paper mills from China, Iran and Russia, and some journals are revamping their review processes." It is a problem of research ethics and research integrity affecting academic publishing (academic writing, scientific writing Scientific writing is writing for science. English-language scientific writing originated in the 14th century, with the language later becoming the dominant medium for the field. Style conventions for scientific writing vary, with different focu ... and medical writing). It is an instan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junk Science
The expression junk science is used to describe scientific data, research, or analysis considered by the person using the phrase to be spurious or fraudulent. The concept is often invoked in political and legal contexts where facts and scientific results have a great amount of weight in making a determination. It usually conveys a pejorative connotation that the research has been untowardly driven by political, ideological, financial, or otherwise unscientific motives. The concept was popularized in the 1990s in relation to expert testimony in civil litigation. More recently, invoking the concept has been a tactic to criticize research on the harmful environmental or public health effects of corporate activities, and occasionally in response to such criticism. Author Dan Agin in his book ''Junk Science'' harshly criticized those who deny the basic premise of global warming, In some contexts, junk science is counterposed to the "sound science" or "solid science" that favors one' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derek Freeman
John Derek Freeman (15 August 1916 – 6 July 2001) was a New Zealand anthropologist knownTuzin, page 1013. for #Freeman_vs._Mead:_A_self_described_heresy, his criticism of Margaret Mead's work on Samoan society, as described in her 1928 ethnography ''Coming of Age in Samoa''. His attack "ignited controversy of a scale, visibility, and ferocity never before seen in anthropology." Freeman initially became interested in Franz Boas, Boasian cultural anthropology while an undergraduate in Wellington, and later went to live and work as a teacher in Samoa. After entering the Royal New Zealand Naval Volunteer Reserve, New Zealand Naval Reserve in World War II, he did graduate training with British social anthropologists Meyer Fortes and Raymond Firth at London School of Economics. He did two and a half years of fieldwork in Borneo studying the Iban people. His 1953 doctoral dissertation described the relations between Iban agriculture and kinship practices. Returning to Borneo in 1961 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |