|
Cyclophosphine
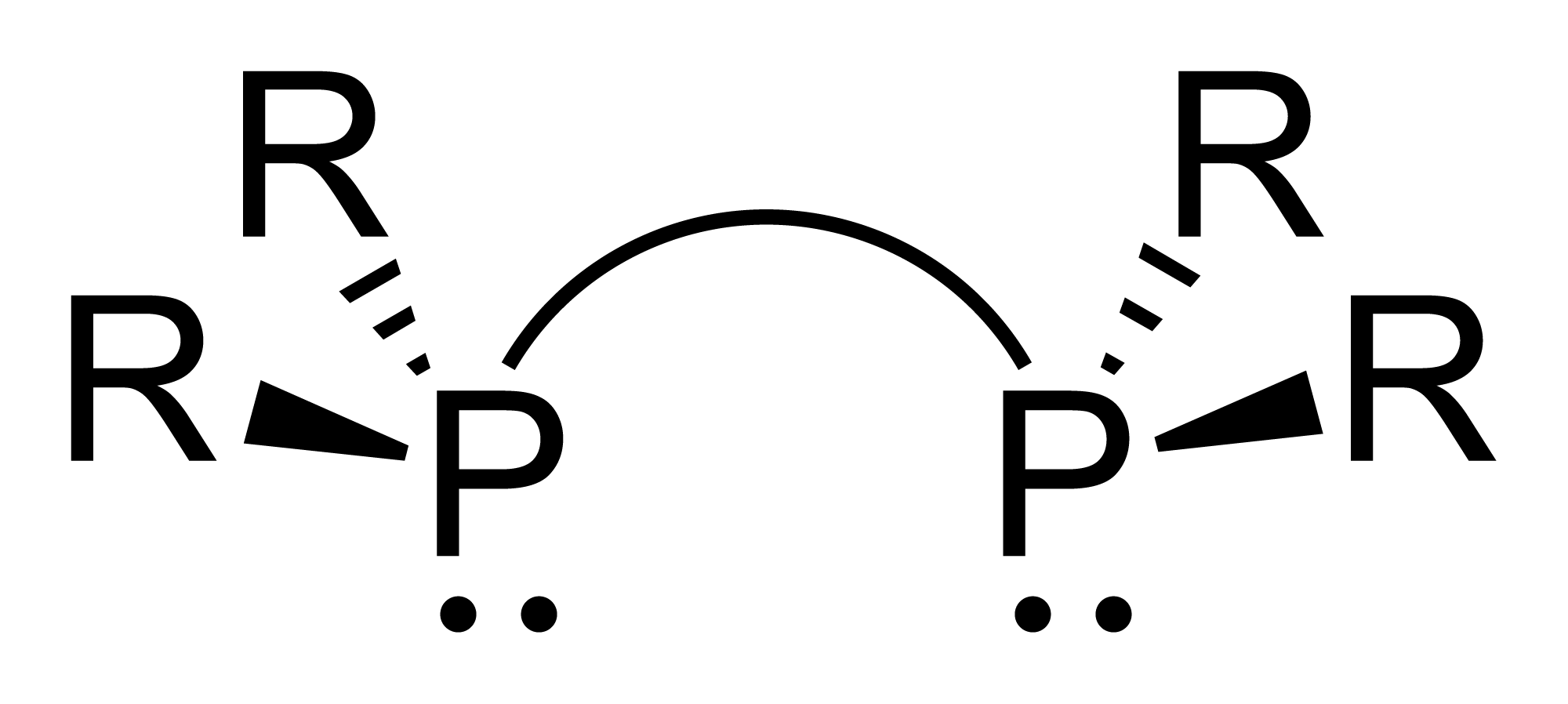
Cyclopentaphosphine is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is prepared by the hydrolysis of cyclo-. Although only of theoretical interest, is parent of many related cyclic polyphosphines that are the subject of research. Organic cyclophosphines Organic cyclophosphanes are a family of organophosphorus compounds with the formula (RP)n where R is an organic substituent. Many examples are known. They are white, air-sensitive solids which have good solubility in organic solvents. Well-characterized examples are known for ring sizes 3–6. The three-membered rings feature bulky substituents, e.g., [''tert''-BuP]3. The cyclophosphines can be prepared by several methods, one involves reductive coupling of dichlorophosphines: : Isomerism The structures are complicated by the slow pyramidal inversion at phosphorus(III). In principle, many isomers are possible for ''cyclo''-, but usually only one is observed. All phenyl substituents are equatorial in ''cyclo''-.{{cite j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphorus Compound
Organophosphorus chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organophosphorus compounds, which are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX (nerve agent), VX nerve agents. Phosphorus, like nitrogen, is in pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, and thus phosphorus compounds and nitrogen compounds have many similar properties. The definition of organophosphorus compounds is variable, which can lead to confusion. In industrial and environmental chemistry, an organophosphorus compound need contain only an organic substituent, but need not have a direct phosphorus-carbon (P-C) bond. Thus a large proportion of pesticides (e.g., malathion), are often included in this class of compounds. Phosphorus can adopt a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep Mantle (geology), mantle remain active areas of investigation. All allotropes (structurally different pure forms of an element) and some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, graphene, etc.), carbon monoxide , carbon dioxide , carbides, and salt (chemistry), salts of inorganic anions such as carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, thiocyanates, isothiocyanates, etc. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it cannot occur within life, living things. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chem , a place in Finland
{{disambig ...
Chem may refer to: *Chemistry *Chemical * ''Chem'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press *Post apocalyptic slang for "drugs", medicinal or otherwise in the Fallout video game series. In Ancient Egyptian usage: * ''Khem'' (also spelt ''Chem''), the Egyptian word for "black" *Min (god), in the past erroneously named ''Khem'' CHEM may refer to : *A metabolic panel: for instance, CHEM-7, which is the basic metabolic panel * CHEM-DT, a Canadian television channel See also * Chemo (other) * Kem (other) *Kemi Kemi (; ; ; ) is a cities of Finland, town and municipalities of Finland, municipality of Finland. It is located approximately from the city of Tornio and the Finland–Sweden border, Swedish border. The distance to Oulu is to the south and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramidal Inversion
In chemistry, pyramidal inversion (also umbrella inversion) is a fluxional process in compounds with a pyramidal molecule, such as ammonia (NH3) "turns inside out". It is a rapid oscillation of the atom and substituents, the molecule or ion passing through a planar transition state. For a compound that would otherwise be chiral due to a stereocenter, pyramidal inversion allows its enantiomers to racemize. The general phenomenon of pyramidal inversion applies to many types of molecules, including carbanions, amines, phosphines, arsines, stibines, and sulfoxides. Energy barrier The identity of the inverting atom has a dominating influence on the barrier. Inversion of ammonia is rapid at room temperature, inverting 30 billion times per second. Three factors contribute to the rapidity of the inversion: a low energy barrier (24.2 kJ/mol; 5.8 kcal/mol), a narrow barrier width (distance between geometries), and the low mass of hydrogen atoms, which combine to give a further 80-f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenyl
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula , and is often represented by the symbol Ph (archaically φ) or Ø. The phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen atom, which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional group. A phenyl group has six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the remaining carbon bonded to a substituent. Phenyl groups are commonplace in organic chemistry. Although often depicted with alternating double and single bonds, the phenyl group is chemically aromatic and has equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring. Nomenclature Usually, a "phenyl group" is synonymous with and is represented by the symbol Ph (archaically, Φ), or Ø. Benzene is sometimes denoted as PhH. Phenyl groups are generally attached to other atoms or groups. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphines
Organophosphines are organophosphorus compounds with the formula PR''n''H3−''n'', where R is an organic substituent. These compounds can be classified according to the value of ''n'': primary phosphines (''n'' = 1), secondary phosphines (''n'' = 2), tertiary phosphines (''n'' = 3). All adopt pyramidal structures. Organophosphines are generally colorless, lipophilic liquids or solids. The parent of the organophosphines is phosphine (PH3). Annette Schier and Hubert Schmidbaur"P-Donor Ligands" in Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. 1° vs 2° vs 3° phosphines Organophophines are classified according to the number of organic substituents. Primary phosphines Primary (1°) phosphines, with the formula RPH2, in principle are derived by alkylation of phosphine. Some simple alkyl derivatives such as methylphosphine (CH3PH2) can be prepared by alkylation of phosphine in the presence of base: : (M = Li, Na, K) A more common syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |