|
Common Frog
The common frog or grass frog (''Rana temporaria''), also known as the European common frog, European common brown frog, European grass frog, European Holarctic true frog, European pond frog or European brown frog or simply the frog, is a semi-aquatic amphibian of the family Ranidae, found throughout much of Europe as far north as Scandinavia and as far east as the Urals, except for most of the Iberian Peninsula, southern Italy, and the southern Balkans. The farthest west it can be found is Ireland. It is also found in Asia, and eastward to Japan. The nominative, and most common, subspecies ''Rana temporaria temporaria'' is a largely terrestrial frog native to Europe. It is distributed throughout northern Europe and can be found in Ireland, the Isle of Lewis and as far east as Japan. Common frogs metamorphose through three distinct developmental life stages — aquatic larva, terrestrial juvenile, and adult. They have corpulent bodies with a rounded snout, webbed feet an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rana Temporaria Tadpoles Eating 8
Rana may refer to: Astronomy * Rana (crater), a crater on Mars * Delta Eridani or Rana, a star Films * Rana (2012 film), an Indian Kannada-language action drama * Rana, a 1998 Telugu-language action film directed by A. Kodandarami Reddy * Rana (cancelled film), an unfinished Indian film by K. S. Ravikumar People and characters * Rana (clan), a clan of Gurjars in Punjab & Kashmir * Rana (name), a given name and surname (including a list of people and characters with the name) * Rana dynasty, a ruling dynasty in Nepal (1846–1951) Places * Rana, Burkina Faso, a town in Boulkiemdé Province * Raná (Chrudim District), a municipality and village in Pardubice Region, Czech Republic * Raná (Louny District), a municipality and village in Ústí nad Labem Region, Czech Republic *Rana Municipality, a municipality in Nordland County, Norway * Råna, a mountain in Møre og Romsdal County, Norway * Rana Colony, a town in Punjab Province, Pakistan * Ra'na, a former village in Palest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia. The Alpine arch extends from Nice on the western Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean to Trieste on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Vienna at the beginning of the Pannonian Basin. The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrust fault, thrusting and Fold (geology), folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains 82 peaks higher than List of Alpine four-thousanders, . The altitude and size of the range affect the climate in Europe; in the mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebrides, Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles (Orkney and Shetland), and over six thousand smaller islands. They have a total area of and a combined population of almost 72 million, and include two sovereign states, the Republic of Ireland (which covers roughly five-sixths of Ireland), and the United Kingdom, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The Channel Islands, off the north coast of France, are normally taken to be part of the British Isles, even though geographically they do not form part of the archipelago. Under the UK Interpretation Act 1978, the Channel Islands are clarified as forming part of the British Islands, not to be confused with the British Isles. The oldest rocks are 2.7 billion years old and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hibernating
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic reduction entered by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It is most commonly used to pass through winter months – called overwintering. Although traditionally reserved for "deep" hibernators such as rodents, the term has been redefined to include animals such as bears and is now applied based on active metabolic suppression rather than any absolute decline in body temperature. Many experts believe that the processes of daily torpor and hibernation form a continuum and use similar mechanisms. The equivalent during the summer months is aestivation. Hibernation functions to conserve energy when sufficient food is not available. To achieve this energy saving, an endothermic animal decreases its metabolic rate and thereby its body temperature. Hibernation may last days, weeks, or months—depending on the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
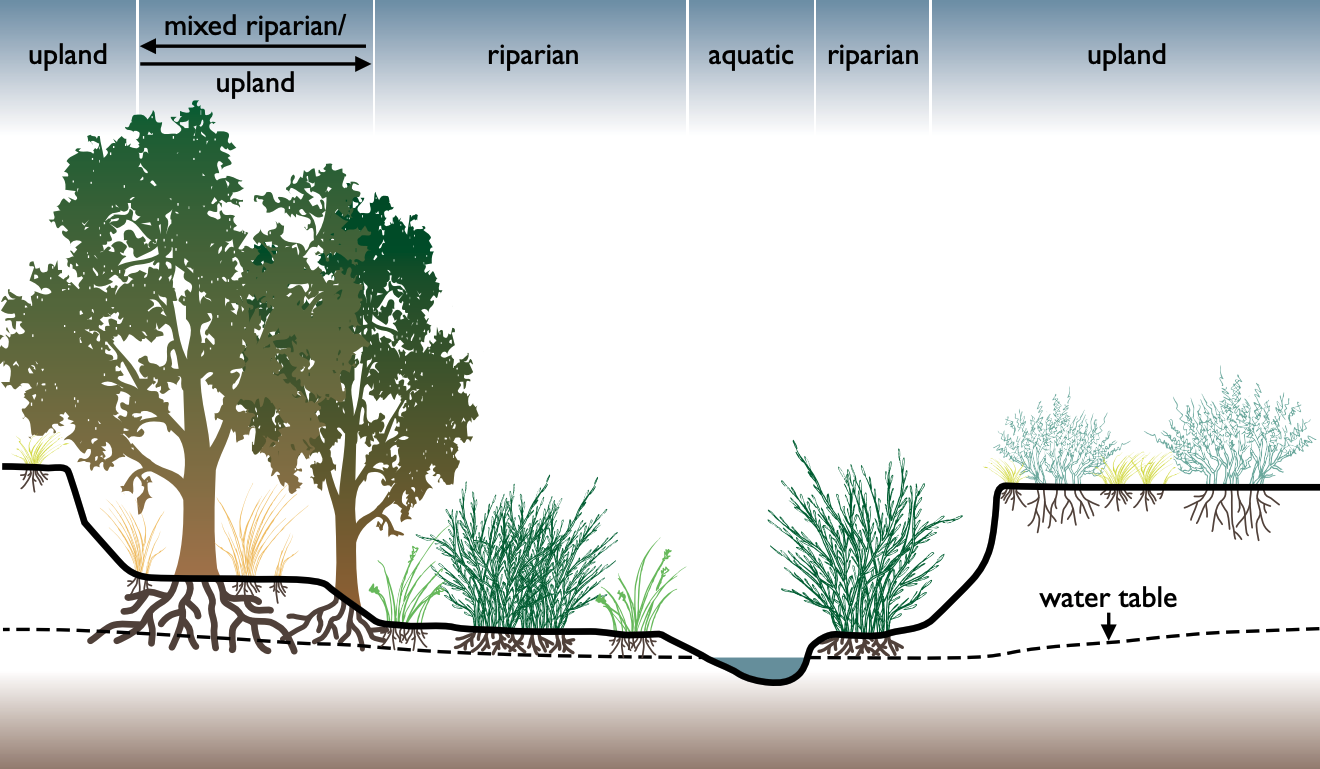
Riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin '' ripa'', meaning " river bank". Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on terrestrial and semiaquatic fauna as well as aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, and even non-vegetative areas. Riparian zones may be natural or engineered for soil stabilization or restoration. These zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition. Three variants of ecological niche are described by It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of Resource (biology), resources and competitors (for example, by growing when resources are abundant, and when predators, parasites and pathogens are scarce) and how it in turn alters those same factors (for example, limiting access to resources by other organisms, acting as a food source for predators and a consumer of prey). "The type and number of variables comprising the dimensions of an environmental niche vary from one species to another [and] the relative importance of particular environmental variables for a species may vary according to the geographic and biotic contexts". See also Chapter 2: Concepts of niches, pp. 7 ''ff'' A Grinnellian niche is determined by the habitat in which a species lives and its accompanying Behavioral ecology, behavioral adaptations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially in the soils. Wetlands form a transitional zone between waterbodies and dry lands, and are different from other terrestrial or aquatic ecosystems due to their vegetation's roots having adapted to oxygen-poor waterlogged soils. They are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as habitats to a wide range of aquatic and semi-aquatic plants and animals, with often improved water quality due to plant removal of excess nutrients such as nitrates and phosphorus. Wetlands exist on every continent, except Antarctica. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or saltwater. The main types of wetland are defined based on the dominant plants and the source of the water. For example, ''marshes'' ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuptial Pad
A nuptial pad (also known as thumb pad, or nuptial excrescence) is a secondary sex characteristic present on some mature male frogs and salamanders. Triggered by androgen hormones, this breeding gland (a type of mucous gland) appears as a spiked epithelial swelling on the forearm and prepollex that aids with grip, which is used primarily by males to grasp (or clasp) females during amplexus. They can also be used in male–male combat in some species. Historical background Austrian biologist Paul Kammerer experimented on midwife toads' nuptial pads. He used the offspring's apparent enlargening from generation-to-generation as evidence of Lamarckian evolution. Examples Many amphibian species manifest nuptial pads for use in amplexus, an example being the rough-skinned newt The rough-skinned newt or roughskin newt (''Taricha granulosa'') is a North American newt known for the strong toxin exuded from its skin. Appearance A stocky newt with rounded snout, it ranges from l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Toad
The common toad, European toad, or in Anglophone parts of Europe, simply the toad (''Bufo bufo'', from Latin ''bufo'' "toad"), is a toad found throughout most of Europe (with the exception of Ireland, Iceland, parts of Scandinavia, and some List of islands in the Mediterranean, Mediterranean islands), in the western part of North Asia, and in a small portion of Northwest Africa. It is one of a group of closely related animals that are descended from a common ancestral line of toads and which form a species complex. The toad is an inconspicuous animal as it usually lies hidden during the day. It becomes active at dusk and spends the night hunting for the invertebrates on which it feeds. It moves with a slow, ungainly walk or short jumps, and has greyish-brown skin covered with wart-like lumps. Although toads are usually solitary animals, in the breeding season, large numbers of toads converge on certain breeding ponds, where the males compete to mate with the females. Eggs are laid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moor Frog
The moor frog (''Rana arvalis'') is a slim, reddish-brown, semiaquatic amphibian native to Europe and Asia. Moor frogs are known for their ability to freeze solid and survive thawing. The frog makes use of various cryoprotectants i.e. Antifreeze protein, antifreeze that decrease its internal freezing temperature. The species is distributed over a large range, covering a significant portion of Eurasia. Male moor frogs are known to turn blue temporarily during the height of mating season. This coloration is assumed to signal a mate's Mate choice, fitness. Moor frogs typically mate through Multi-male group, multimale amplexus a form of Polyandry in animals, polyandry. The moor frog Spawn (biology), spawns its eggs in large batches in still bodies of acidic waters. Human-caused pollution is causing excessive Freshwater acidification, acidification of habitat which harms egg health. The moor frog's habitat is also under destruction due to a variety of other Anthropogenic hazard, anthr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |