|
Cis-1,2-dihydroxy-4-methylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1-carboxylate Dehydrogenase
In enzymology, a cis-1,2-dihydroxy-4-methylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1-carboxylate dehydrogenase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :cis-1,2-dihydroxy-4-methylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1-carboxylate + NAD(P)+ \rightleftharpoons 4-methylcatechol + NAD(P)H + CO2 The 3 substrates of this enzyme are cis-1,2-dihydroxy-4-methylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1-carboxylate, NAD+, and NADP+, whereas its 4 products are 4-methylcatechol, NADH, NADPH, and CO2. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-CH group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is cis-1,2-dihydroxy-4-methylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1-carboxylate:NAD(P)+ oxidoreductase (decarboxylating). This enzyme participates in toluene and xylene In organic chemistry, xylene or xylol (; IUPAC name: dimethylbenzene) are any of three organic compounds with the formula . They are derived from the substitution of two hydrogen atoms with methyl group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
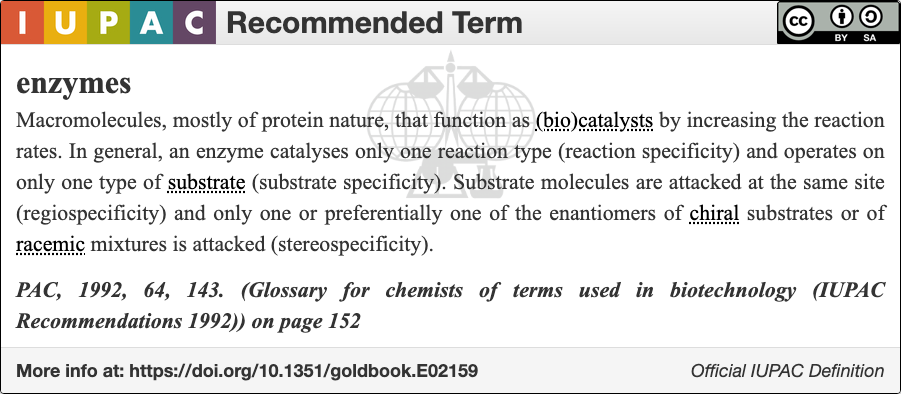
Enzymology
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at normally-encountered concentrations it is odorless. As the source of carbon in the carbon cycle, atmospheric is the primary carbon source for life on Earth. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared, infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, and seawater. It is a trace gas Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.042% (as of May 2022) having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm or about 0.028%. Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of these increased concentrations, which are the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EC 1
EC or ec may refer to: Arts and entertainment * EC Comics, an American publisher of comic books * '' Electric Circus'', a Canadian television program * Eric Clapton Stratocaster, signature model guitars by Fender Businesses and organisations Government * Environment and Climate Change Canada, a Canadian federal government department * European Commission, the executive body of the European Union * European Council, the European Union institution comprising the college of heads of state of government * European Communities, one of the three pillars of the EU * European Community, a significant component of the European Union from 1993 to 2009, renamed European Economic Community Transportation * EuroCity, a train service of the European inter-city rail network * EasyJet Europe (IATA code: EC) * Avialeasing (former IATA code: EC), a cargo airline * East Coast (train operating company), a train operating company in the UK * EC, the aircraft registration prefix for Spain Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xylene
In organic chemistry, xylene or xylol (; IUPAC name: dimethylbenzene) are any of three organic compounds with the formula . They are derived from the substitution of two hydrogen atoms with methyl groups in a benzene ring; which hydrogens are substituted determines which of three structural isomers results. It is a colorless, flammable, slightly greasy liquid of great industrial value. The mixture is referred to as both xylene and, more precisely, xylenes. Mixed xylenes refers to a mixture of the xylenes plus ethylbenzene. The four compounds have identical molecular formulas . Typically the four compounds are produced together by various catalytic reforming and pyrolysis methods. Occurrence and production Xylenes are an important petrochemical produced by catalytic reforming and also by coal carbonisation in the manufacture of coke fuel. They also occur in crude oil in concentrations of about 0.5–1%, depending on the source. Small quantities occur in gasoline and aircra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toluene
Toluene (), also known as toluol (), is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula , often abbreviated as , where Ph stands for the phenyl group. It is a colorless, water Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...-insoluble liquid with the odor associated with paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, consisting of a methyl group (CH3) attached to a phenyl group by a single bond. As such, its systematic IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry, IUPAC name is methylbenzene. Toluene is predominantly used as an industrial feedstock and a solvent. As the solvent in some types of paint thinner, permanent markers, contact cement and certain types of glue, toluene is sometimes used as a recreational inhalant and has the potential of causin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enzymes
Enzymes are listed here by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system: :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) ( Oxidoreductase) * Dehydrogenase * Luciferase * DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) ** Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase ** Diacetyl reductase ** Glycerol dehydrogenase ** Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phoshitiendopene dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase ** L-xylulose reductase ** Lactate dehydrogenase ** Malate dehydrogenase ** Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) ** Glucose oxidase ** L-gulonolactone oxidase ** Thiamine oxidase ** Xanthine oxidase * EC 1.1.4 (with a disulfide as accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually utilizes NADP+ or NAD+ as cofactors. Transmembrane oxidoreductases create electron transport chains in bacteria, chloroplasts and mitochondria, including respiratory complexes I, II and III. Some others can associate with biological membranes as peripheral membrane proteins or be anchored to the membranes through a single transmembrane helix. in Membranome database Reactions For e ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product (chemistry)
Products are the species formed from chemical reactions. During a chemical reaction, reactants are transformed into products after passing through a high energy transition state. This process results in the consumption of the reactants. It can be a spontaneous reaction or mediated by catalysts which lower the energy of the transition state, and by solvents which provide the chemical environment necessary for the reaction to take place. When represented in chemical equations, products are by convention drawn on the right-hand side, even in the case of reversible reactions. The properties of products such as their energies help determine several characteristics of a chemical reaction, such as whether the reaction is exergonic or endergonic. Additionally, the properties of a product can make it easier to extract and purify following a chemical reaction, especially if the product has a different state of matter than the reactants. Spontaneous reaction : R \rightarrow P *W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). NADPH is the redox, reduced form, whereas NADP is the redox, oxidized form. NADP is used by all forms of cellular life. NADP is essential for life because it is needed for cellular respiration. NADP differs from NAD+, NAD by the presence of an additional phosphate group on the 2' position of the ribose ring that carries the adenine Moiety (chemistry), moiety. This extra phosphate is added by NAD+ kinase, NAD+ kinase and removed by NADP+ phosphatase. Biosynthesis NADP In general, NADP+ is synthesized before NADPH is. Such a reaction usually starts with NAD+, NAD+ from either the de-novo or the salvage pathway, with NAD+ kinase, NAD+ kinase adding the extra phosphate g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |