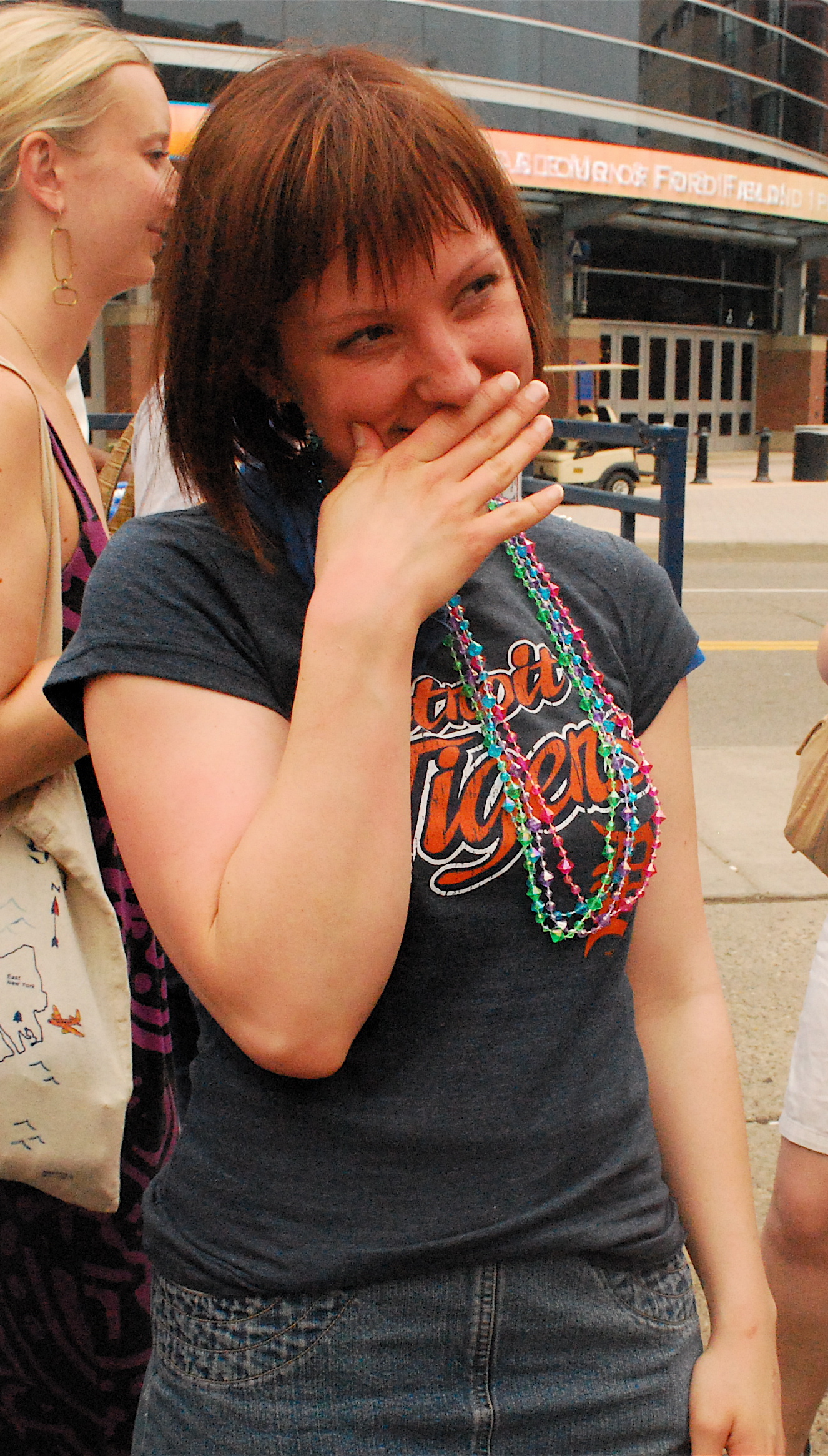|
Cheek
The cheeks () constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. ''Buccal'' means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the inside of the cheek and the teeth and gums is called the vestibule or ''buccal'' pouch or ''buccal'' cavity and forms part of the mouth. In other animals, the cheeks may also be referred to as " jowls". Structure Cheeks are fleshy in humans, the skin being suspended by the chin and the jaws, and forming the lateral wall of the human mouth, visibly touching the cheekbone below the eye. The inside of the cheek is lined with a mucous membrane (''buccal'' mucosa, part of the oral mucosa). During mastication (chewing), the cheeks and tongue between them serve to keep the food between the teeth. Clinical significance The cheek is the most common location from which a DNA sample can be taken. (Some saliva is collected from inside the mouth, e.g. using a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cheek Kissing
Cheek kissing is a ritual or social kissing gesture to indicate friendship, family relationship, perform a greeting, to confer congratulations, to comfort someone, or to show respect. Cheek kissing is very common in the Middle East, the Mediterranean, Southern Europe, Southern, Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe, the Low Countries, the Horn of Africa, Central America and South America. In other countries, including the U.S. and Japan, cheek kissing is common as well at an international meeting between head of the state, heads of state and First Lady, First Ladies or members of royal family, royal and Imperial House of Japan, the Imperial families. Depending on the local culture, cheek kissing may be considered appropriate among family members as well as friends and acquaintances: a man and a woman, two women, or two men. The last has different degrees of familiarity. In Eastern Europe, male–female and female–female cheek kissing is a standard greeting among friends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
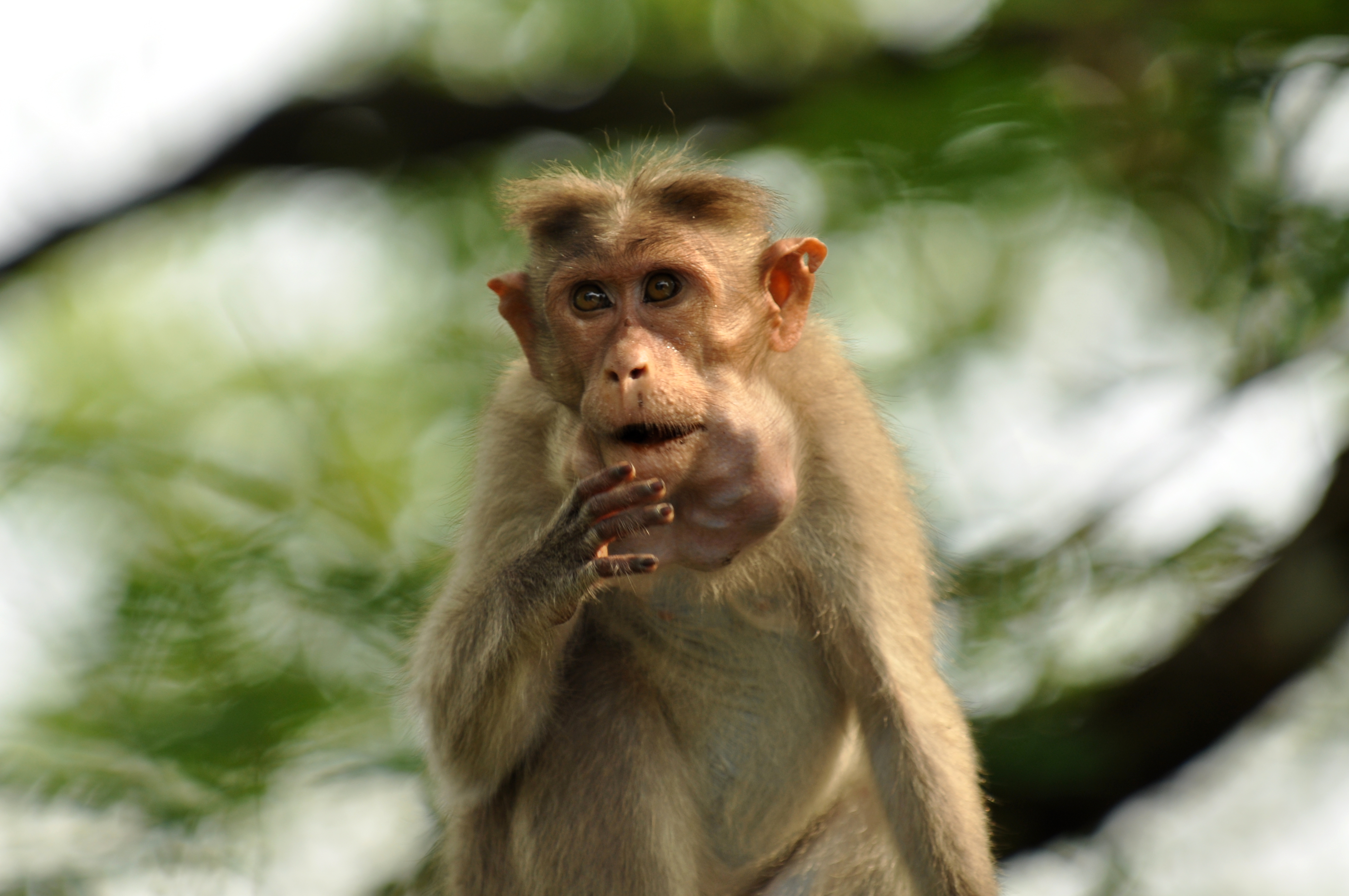
Buccal Pouch
Cheek pouches are pockets on both sides of the head of some mammals between the jaw and the cheek. They can be found on mammals including the platypus, some rodents, and most monkeys, as well as the marsupial koala. The cheek pouches of chipmunks can reach the size of their body when full. Description and function Cheek pouches are located in the thickness of the flange on both sides of the head of some mammals. Monkeys have open cheek pouches within the oral cavity, but they open out in some rodents of America. Hence the name "diplostomes" is associated with them, which means "two mouths." In some rodents, such as hamsters, the cheek pouches are remarkably developed; they form two bags ranging from the mouth to the front of the shoulders. Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire described that some bats of the genus '' Nycteris'' have an amazing form of cheek pouches, as they have a narrow opening, through which the bat can introduce air, closing the nasal canal through a special mech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cheek Augmentation
Cheek augmentation is a cosmetic surgical procedure that is intended to emphasize the cheeks on a person's face. To augment the cheeks, a plastic surgeon may place a solid implant over the cheekbone. Injections with the patients' own fat or a soft tissue filler, like Restylane, are also popular. Rarely, various cuts to the zygomatic bone (cheekbone) may be performed. Cheek augmentation is commonly combined with other procedures, such as a face lift or chin augmentation. Implants Materials Cheek implants can be made of a variety of materials. The most common material is solid silicone. In addition, two popular options are high-density porous polyethylene, marketed as '' Medpor'', and ePTFE (expanded polytetrafluoroethylene), better known as '' Gore-Tex''. Both Medpor and ePTFE are inert substances, providing better integration with the underlying tissue and bone than solid silicone. However, in the case of Medpor, the implants' integration and ingrowth with the underlying tissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jowl
The cheeks () constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. ''Buccal'' means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the inside of the cheek and the teeth and gums is called the vestibule or ''buccal'' pouch or ''buccal'' cavity and forms part of the mouth. In other animals, the cheeks may also be referred to as " jowls". Structure Cheeks are fleshy in humans, the skin being suspended by the chin and the jaws, and forming the lateral wall of the human mouth, visibly touching the cheekbone below the eye. The inside of the cheek is lined with a mucous membrane (''buccal'' mucosa, part of the oral mucosa). During mastication (chewing), the cheeks and tongue between them serve to keep the food between the teeth. Clinical significance The cheek is the most common location from which a DNA sample can be taken. (Some saliva is collected from inside the mouth, e.g. using a cott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oral Mucosa
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed '' lamina propria''. The oral cavity has sometimes been described as a mirror that reflects the health of the individual. Changes indicative of disease are seen as alterations in the oral mucosa lining the mouth, which can reveal systemic conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiency, or the local effects of chronic tobacco or alcohol use. The oral mucosa tends to heal faster and with less scar formation compared to the skin. The underlying mechanism remains unknown, but research suggests that extracellular vesicles might be involved. Classification Oral mucosa can be divided into three main categories based on function and histology: * ''Lining mucosa'', nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, found almost everywhere else in the oral cavity, including the: ** ''Alveolar mucosa'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cheekbone
In the human skull, the zygomatic bone (from ), also called cheekbone or malar bone, is a paired irregular bone, situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forming part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit (anatomy), orbit, of the temporal fossa and the infratemporal fossa. It presents a malar and a temporal surface; four Process (anatomy), processes (the frontosphenoidal, orbital, maxillary, and temporal), and four borders. Etymology The term ''zygomatic'' derives from the Ancient Greek , ''zygoma'', meaning "yoke". The zygomatic bone is occasionally referred to as the zygoma, but this term may also refer to the zygomatic arch. Structure Surfaces The ''malar surface'' is convex and perforated near its center by a small aperture, the zygomaticofacial foramen, for the passage of the zygomaticofacial nerve and vessels; below this foramen is a slight elevation, which gives origin to the Zygomaticus major muscle, zygomaticus muscle. The ''temporal surface'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hamster
Hamsters are rodents (order Rodentia) belonging to the subfamily Cricetinae, which contains 19 species classified in seven genera. They have become established as popular small pets. The best-known species of hamster is the golden or Syrian hamster (''Mesocricetus auratus''), which is the type most commonly kept as a pet. Other hamster species commonly kept as pets are the three species of dwarf hamster, Campbell's dwarf hamster (''Phodopus campbelli''), the winter white dwarf hamster (''Phodopus sungorus'') and the Roborovski hamster (''Phodopus roborovskii''), and the less common Chinese hamster (''Cricetulus griseus''). Hamsters feed primarily on seeds, fruits, vegetation, and occasionally burrowing insects. In the wild, they are crepuscular: they forage during the twilight hours. In captivity, however, they are known to live a conventionally nocturnal lifestyle, waking around sundown to feed and exercise. Physically, they are stout-bodied with distinguishing features ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Blushing
Blushing or erubescence is the reddening of a person's face due to psychological reasons. It is normally involuntary and triggered by emotional stress associated with passion, embarrassment, shyness, fear, anger, or romantic stimulation. Severe blushing is also common in people who have social anxiety in which the person experiences extreme and persistent anxiety in social and performance situations. Description Blushing is generally distinguished, despite a close physiological relation, from flushing, which is more intensive and extends over more of the body and seldom has a mental source. Idiopathic craniofacial erythema is a medical condition where a person blushes strongly with little or no provocation. People who have social phobia are particularly prone to idiopathic craniofacial erythema. Physiology A blush is a reddening of the cheeks and forehead brought about by increased capillary blood flow in the skin. It can also extend to the ears, neck and upper chest, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
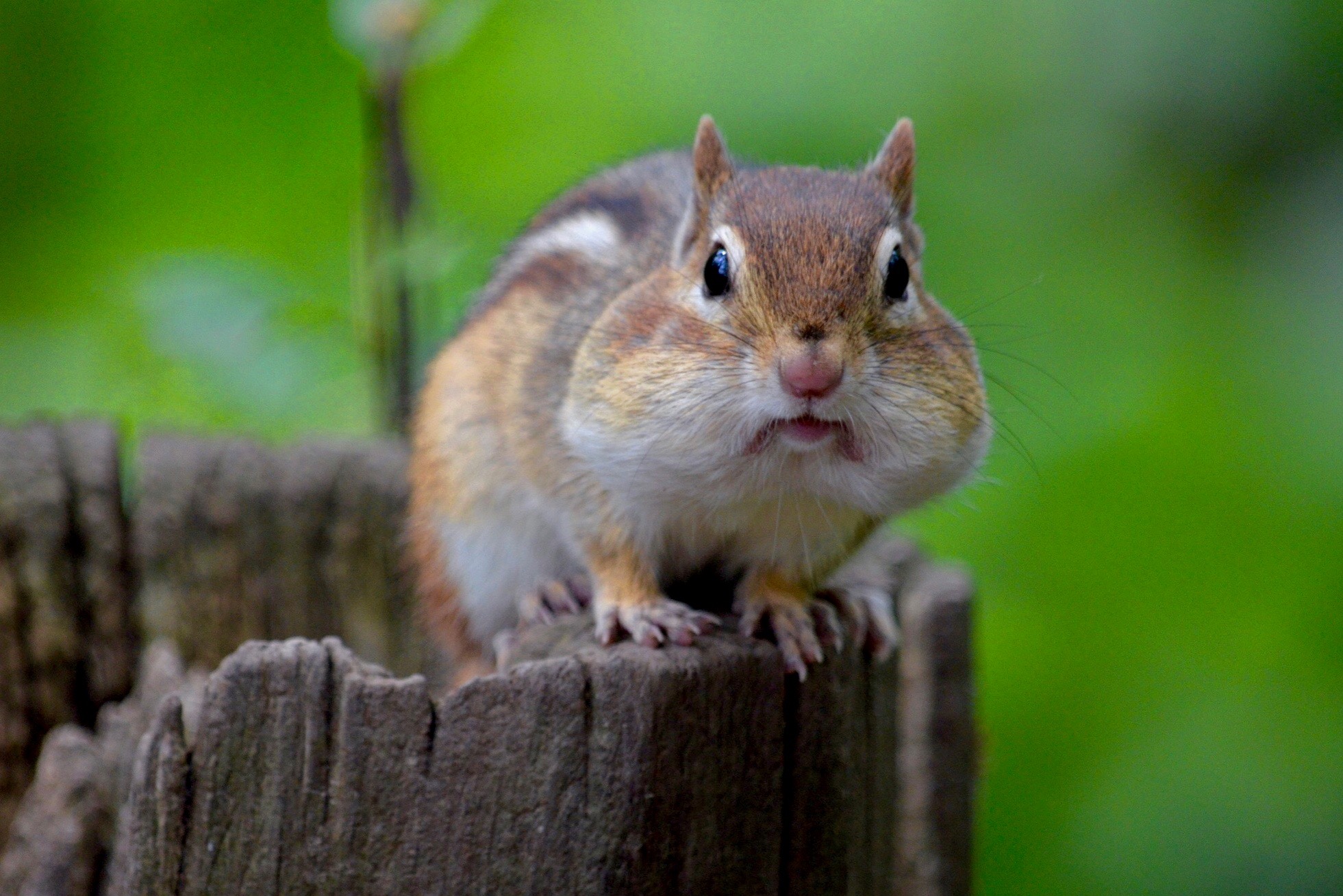
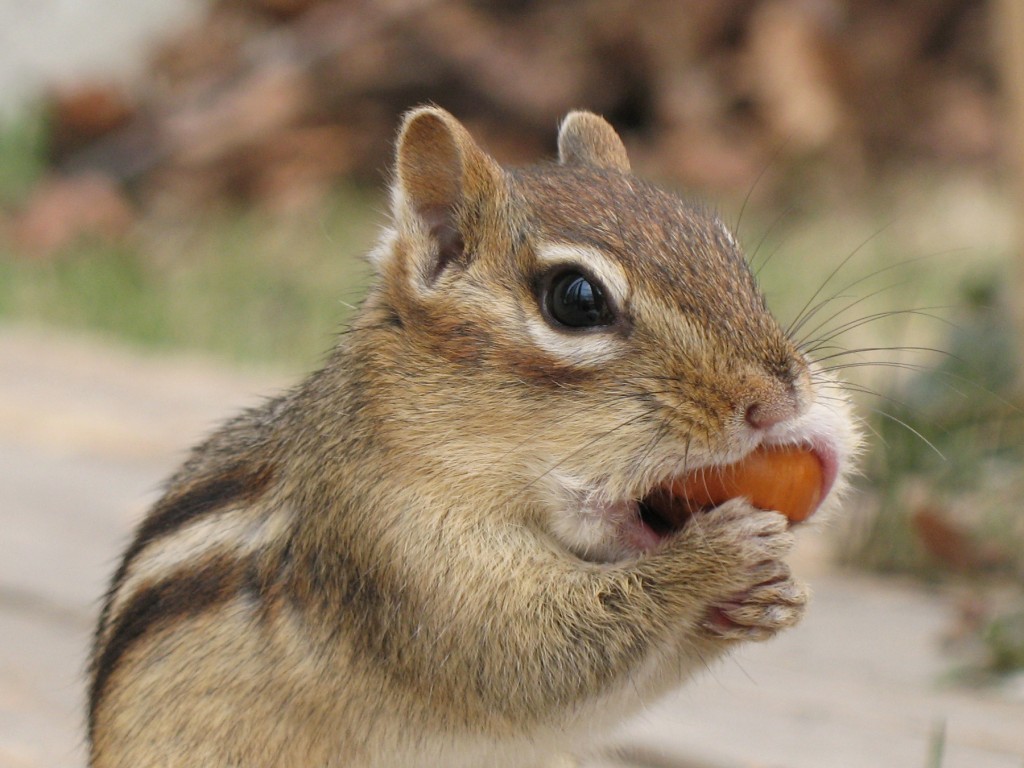
Chipmunk With Full Cheeks
Chipmunks are small, striped rodents of subtribe Tamiina. Chipmunks are found in North America, with the exception of the Siberian chipmunk which is found primarily in Asia. Taxonomy and systematics Chipmunks are classified as four genera: ''Tamias'', of which the eastern chipmunk (''T. striatus'') is the only living member; ''Eutamias'', of which the Siberian chipmunk (''E. sibiricus'') is the only living member; ''Nototamias'', which consists of three extinct species, and ''Neotamias'', which includes the 23 remaining, mostly western North American, species. These classifications were treated as subgenera due to the chipmunks' morphological similarities. As a result, most taxonomies over the twentieth century have placed the chipmunks into a single genus. Joseph C. Moore reclassified chipmunks to form a subtribe Tamiina in a 1959 study, and this classification has been supported by studies of mitochondrial DNA. The common name originally may have been spelled "chitmunk", fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zygomaticus Major Muscle
The zygomaticus major muscle is a muscle of the face. It arises from either zygomatic arch (cheekbone); it inserts at the corner of the mouth. It is innervated by branches of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII). It is a muscle of facial expression, which draws the angle of the mouth superiorly and posteriorly to allow one to smile. Bifid zygomaticus major muscle is a notable variant, and may cause cheek dimples. Structure Origin The zygomaticus major muscle originates from the superior margin of the lateral surface of the temporal process of zygomatic bone, just anterior to the zygomaticotemporal suture. Insertion It inserts at the corner of the mouth by blending with the levator anguli oris muscle, the orbicularis oris muscle, and the deeper muscular structures. Nerve supply The muscle receives motor innervation from the buccal branch and zygomatic branch of the facial nerve (CN VII). Vasculature The muscle receives arterial supply from the superior labi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Buccal Nerve
The buccal nerve (long buccal nerve) is a sensory nerve of the face arising from the mandibular nerve (CN V3) (which is itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve). It conveys sensory information from the skin of the cheek, and parts of the oral mucosa, periodontium, and gingiva. Structure Origin The buccal nerve is a branch of the anterior division of the mandibular nerve (CN V3). It is the only sensory branch of the anterior division. Course and relations After branching from the anterior trunk of the mandibular nerve (CN V3), the buccal nerve passes between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle, underneath the tendon of the temporalis muscle. It then passes anterior to the ramus of the mandible to first course deep to the masseter muscle, and finally anteroinferiorly upon surface of the buccinator muscle before piercing this muscle. Communications It connects with the buccal branches of the facial nerve on the surface of the buccinator muscle. It gives off m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |