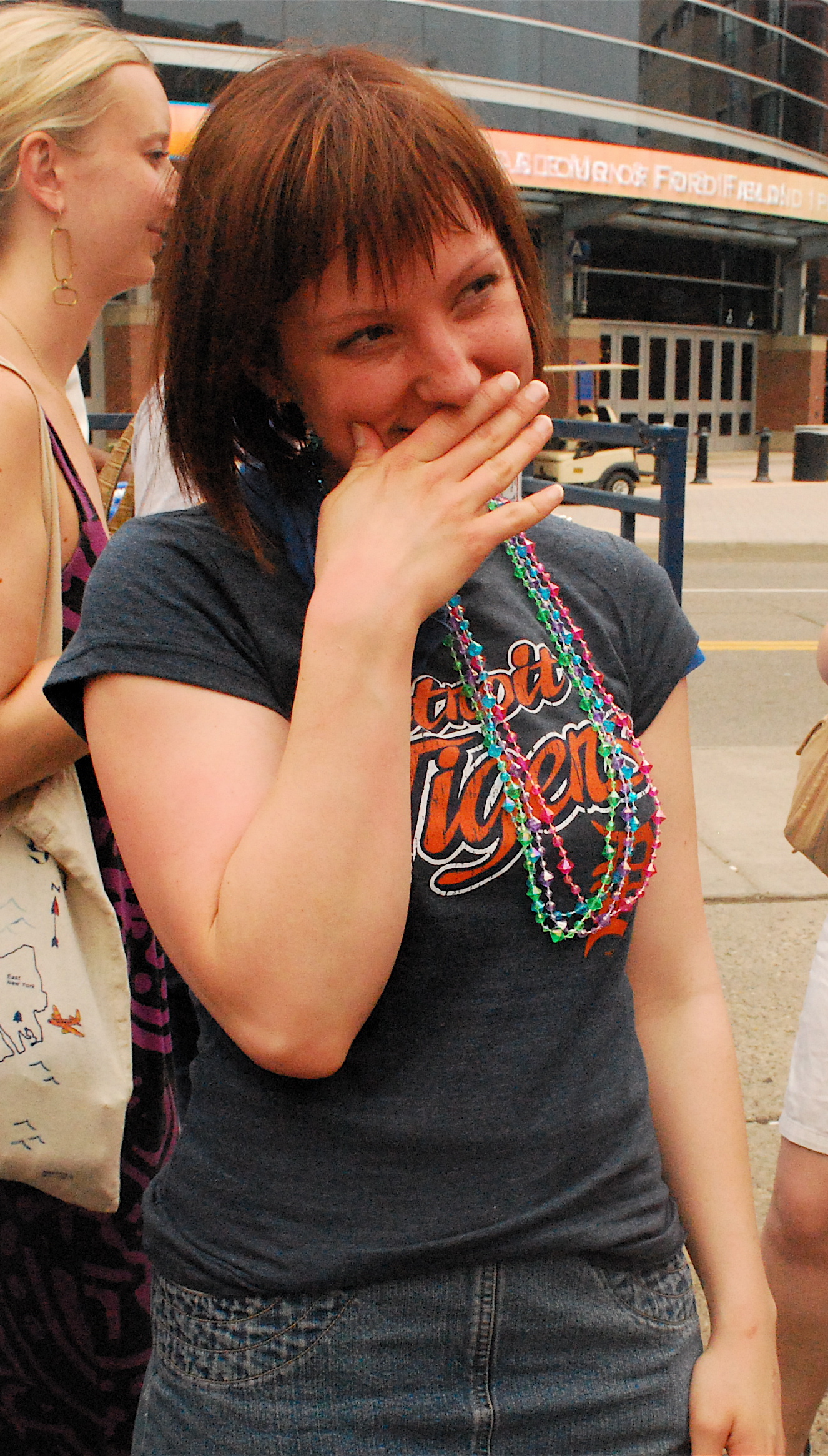|
Blushing
Blushing or erubescence is the reddening of a person's face due to psychological reasons. It is normally involuntary and triggered by emotional stress associated with passion, embarrassment, shyness, fear, anger, or romantic stimulation. Severe blushing is also common in people who have social anxiety in which the person experiences extreme and persistent anxiety in social and performance situations. Description Blushing is generally distinguished, despite a close physiological relation, from flushing, which is more intensive and extends over more of the body and seldom has a mental source. Idiopathic craniofacial erythema is a medical condition where a person blushes strongly with little or no provocation. People who have social phobia are particularly prone to idiopathic craniofacial erythema. Physiology A blush is a reddening of the cheeks and forehead brought about by increased capillary blood flow in the skin. It can also extend to the ears, neck and upper chest, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blushing Girl 0001
Blushing or erubescence is the reddening of a person's face due to Psychology, psychological reasons. It is normally involuntary and triggered by emotional Stress (biology), stress associated with Passion (emotion), passion, embarrassment, shyness, fear, anger, or Lovestruck, romantic stimulation. Severe blushing is also common in people who have social anxiety in which the person experiences extreme and persistent anxiety in social and performance situations. Description Blushing is generally distinguished, despite a close physiological relation, from Flushing (physiology), flushing, which is more intensive and extends over more of the body and seldom has a mental source. Idiopathic craniofacial erythema is a medical condition where a person blushes strongly with little or no provocation. People who have social phobia are particularly prone to idiopathic craniofacial erythema. Physiology A blush is a reddening of the cheeks and forehead brought about by increased capillary b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Anxiety
Social anxiety is the anxiety and fear specifically linked to being in social settings (i.e., interacting with others). Some categories of disorders associated with social anxiety include anxiety disorders, mood disorders, autism spectrum disorders, eating disorders, and substance use disorders. Individuals with higher levels of social anxiety often avert their gazes, show fewer facial expressions, and show difficulty with initiating and maintaining a conversation. Social anxiety commonly manifests itself in the teenage years and can be persistent throughout life; however, people who experience problems in their daily functioning for an extended period of time can develop social anxiety disorder. Trait social anxiety, the stable tendency to experience this anxiety, can be distinguished from state anxiety, the momentary response to a particular social stimulus. Half of the individuals with any social fears meet the criteria for social anxiety disorder. Age, culture, and gender ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiopathic Craniofacial Erythema
Idiopathic craniofacial erythema is a medical condition characterized by uncontrollable and frequently unprovoked facial blushing. Blushing can occur at any time and is frequently triggered by even mundane events, such as talking to friends, paying for goods in a shop, asking for directions or even simply making eye contact with another person. This medical condition characterized by severe, frequent and uncontrollable reddening of the face, which is often unprovoked. It is unknown why people are afflicted with this condition, but it is appears to be the result of an overactive sympathetic nervous system, an automatic response which sufferers have no mental control over. It is related to focal hyperhidrosis, more commonly known as excessive sweating, as it is caused by the same overactive nerves which cause excessive sweating. Sufferers of severe facial blushing commonly experience focal hyperhidrosis. Studies have also shown that patients with severe facial blushing or focal hyper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
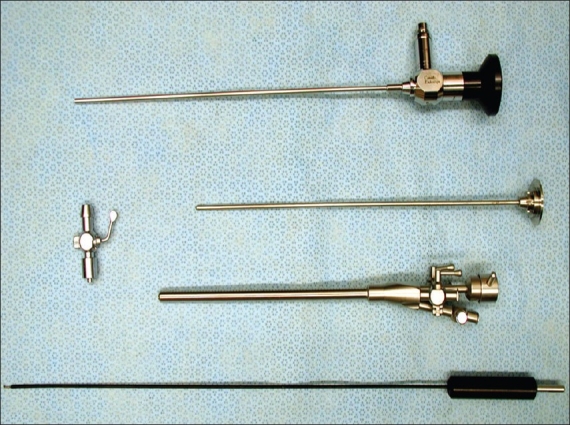
Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy
Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy (ETS) is a surgical procedure in which a portion of the sympathetic nerve trunk in the thoracic region is destroyed. ETS is used to treat excessive sweating in certain parts of the body (focal hyperhidrosis), facial flushing, Raynaud's disease and reflex sympathetic dystrophy. By far the most common complaint treated with ETS is sweaty palms ( palmar hyperhidrosis). The intervention is controversial and illegal in some jurisdictions. Like any surgical procedure, it has risks; the endoscopic sympathetic block (ESB) procedure and those procedures that affect fewer nerves have lower risks. Sympathectomy physically destroys relevant nerves anywhere in either of the two sympathetic trunks, which are long chains of nerve ganglia located bilaterally along the vertebral column (a localisation which entails a low risk of injury) responsible for various important aspects of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Each nerve trunk is broadly divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracentral Lobule
In neuroanatomy, the paracentral lobule is on the medial surface of the cerebral hemisphere and is the continuation of the precentral and postcentral gyri. The paracentral lobule controls motor and sensory innervations of the contralateral lower extremity. It is also responsible for control of blushing, defecation and urination. It includes portions of the frontal and parietal lobes: * The anterior portion of the paracentral lobule is part of the frontal lobe and contains a little portion of Brodmann's area 6 (SMA): this is because the paracentral sulcus (branch of the cingulate sulcus) does not correspond to the precentral sulcus on the medial plane. * The posterior portion is considered part of the parietal lobe and deals with somatosensory of the distal limbs. While the boundary between the lobes, the central sulcus, is easy to locate on the lateral surface of the cerebral hemispheres, this boundary is often discerned in a cytoarchetectonic manner in cases where the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy
Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy (ETS) is a surgical procedure in which a portion of the sympathetic nerve trunk in the thoracic region is destroyed. ETS is used to treat excessive sweating in certain parts of the body (focal hyperhidrosis), facial flushing, Raynaud's disease and reflex sympathetic dystrophy. By far the most common complaint treated with ETS is sweaty palms ( palmar hyperhidrosis). The intervention is controversial and illegal in some jurisdictions. Like any surgical procedure, it has risks; the endoscopic sympathetic block (ESB) procedure and those procedures that affect fewer nerves have lower risks. Sympathectomy physically destroys relevant nerves anywhere in either of the two sympathetic trunks, which are long chains of nerve ganglia located bilaterally along the vertebral column (a localisation which entails a low risk of injury) responsible for various important aspects of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Each nerve trunk is broadly divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Expression Of The Emotions In Man And Animals
''The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals'' is Charles Darwin's third major work of evolutionary theory, following ''On the Origin of Species'' (1859) and '' The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex'' (1871). Initially intended as a chapter in ''Descent of Man'', ''Expression'' grew in length and was published separately in 1872. Darwin explores the biological aspects of emotional behaviour and the animal origins of human characteristics like smiling and frowning, shrugging shoulders, lifting eyebrows in surprise, and the baring of teeth in an angry sneer. A German translation of ''Expression'' appeared in 1872, and Dutch and French versions followed in 1873 and 1874. Though ''Expression'' has never been out of print since its first publication, it has also been described as Darwin's "forgotten masterpiece". Psychologist Paul Ekman has argued that ''Expression'' is the foundational text for modern scientific psychology. Before Darwin, human emotional li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
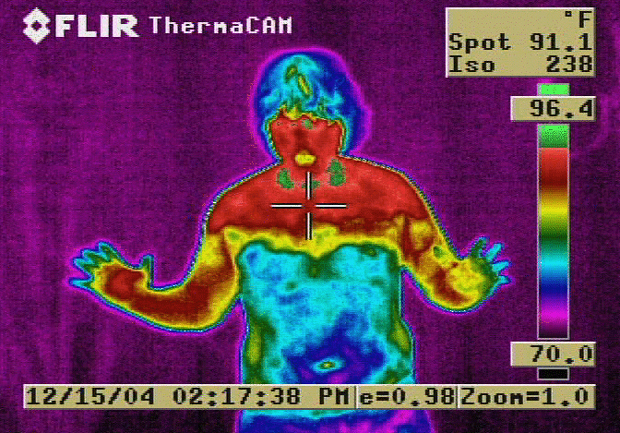
Flushing (physiology)
Flushing is to become markedly red in the face and often other areas of the skin, from various physiological conditions. Flushing is generally distinguished from blushing, since blushing is psychosomatic, milder, generally restricted to the face, cheeks or ears, and generally assumed to reflect emotional stress, such as embarrassment, anger, or romantic stimulation. Flushing is also a cardinal symptom of carcinoid syndrome—the syndrome that results from hormones (often serotonin or histamine) being secreted into systemic circulation. Causes * abrupt cessation of physical exertion (resulting in heart output in excess of current muscular need for blood flow) * abdominal cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome (ACNES), usually in patients who have had abdominal surgery * alcohol flush reaction * antiestrogens such as tamoxifen * atropine poisoning * body contact with warm or hot water (hot tub, bath, shower) * butorphanol reaction with some narcotic analgesics (since but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embarrassment
Embarrassment or awkwardness is an emotional state that is associated with mild to severe levels of discomfort, and which is usually experienced when someone commits (or thinks of) a socially unacceptable or frowned-upon act that is witnessed by or revealed to others. Frequently grouped with shame and guilt, embarrassment is considered a " self-conscious emotion", and it can have a profoundly negative impact on a person's thoughts or behavior. Usually, some perception of loss of honor or dignity (or other high-value ideals) is involved, but the embarrassment level and the type depends on the situation. Causes Embarrassment can be personal, caused by unwanted attention to private matters or personal flaws or mishaps or shyness. Some causes of embarrassment stem from personal actions, such as being caught in a lie or in making a mistake. In many cultures, being seen nude or inappropriately dressed is a particularly stressful form of embarrassment (see modesty). Personal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shyness
Shyness (also called diffidence) is the feeling of apprehension, lack of comfort, or awkwardness especially when a person is around other people. This commonly occurs in new situations or with unfamiliar people; a shy person may simply opt to avoid these situations. Although shyness can be a characteristic of people who have low self-esteem, the primary defining characteristic of shyness is a fear of what other people will think of a person's behavior. This fear of negative reactions such as being mocked, humiliated or patronized, criticized or rejected can cause a shy person to retreat. Stronger forms of shyness can be referred to as social anxiety or social phobia. Origins The initial cause of shyness varies. Scientists believe that they have located genetic data supporting the hypothesis that shyness is, at least, partially genetic. However, there is also evidence that suggests the environment in which a person is raised can also be responsible for their shyness. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenoceptor
The adrenergic receptors or adrenoceptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of many catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) produced by the body, but also many medications like beta blockers, beta-2 (β2) agonists and alpha-2 (α2) agonists, which are used to treat high blood pressure and asthma, for example. Many cells have these receptors, and the binding of a catecholamine to the receptor will generally stimulate the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). The SNS is responsible for the fight-or-flight response, which is triggered by experiences such as exercise or fear-causing situations. This response dilates pupils, increases heart rate, mobilizes energy, and diverts blood flow from non-essential organs to skeletal muscle. These effects together tend to increase physical performance momentarily. History By the turn of the 19th century, it was agreed that the stimulation of sympathetic nerves could cause dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control and cognition, cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotion, emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to motor coordination, coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine motor skill, fine movement, sense of balance, equilibrium, list of human positions, posture, and motor learning in humans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |