|
Cervical Plexus
The cervical plexus is a nerve plexus of the anterior rami of the first (i.e. upper-most) four cervical spinal nerves C1-C4. The cervical plexus provides motor innervation to some muscles of the neck, and the diaphragm; it provides sensory innervation to parts of the head, neck, and chest. Anatomy They are located laterally to the transverse processes between prevertebral muscles from the medial side and vertebral (m. scalenus, m. levator scapulae, m. splenius cervicis) from lateral side. There is anastomosis with accessory nerve, hypoglossal nerve and sympathetic trunk. It is located in the neck, deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The branches of the cervical plexus emerge from the posterior triangle at the nerve point, a point which lies midway on the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid. Relations The cervical plexus is situated deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, internal jugular vein, and deep cervical fascia. It is situated anterior to the mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Nerves
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. Structure Each spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, formed from the combination of nerve root fibers from its dorsal and ventral roots. The dorsal root is the afferent sensory root and carries sensory information to the brain. The ventral root is the efferent motor root and carries motor information from the brain. The spinal nerve emerges from the spinal column through an opening ( intervertebral foramen) between adjace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Cervical Fascia
The deep cervical fascia (or fascia colli in older texts) lies under cover of the platysma, and invests the muscles of the neck; it also forms sheaths for the carotid vessels, and for the structures situated in front of the vertebral column. Its attachment to the hyoid bone prevents the formation of a dewlap. The investing portion of the fascia is attached behind to the ligamentum nuchæ and to the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra. The ''alar fascia'' is a portion of the ''deep cervical fascia''. Divisions The deep cervical fascia is often divided into a superficial, middle, and deep layer. The superficial layer is also known as the investing layer of deep cervical fascia. It envelops the trapezius, sternocleidomastoid, and muscles of facial expression. It also contains the submandibular and parotid salivary gland as well as the muscles of mastication (the masseter, pterygoid, and temporalis muscles). The middle layer is also known as the pretracheal fas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternohyoid
The sternohyoid muscle is a bilaterally paired, long, thin, narrow strap muscle of the anterior neck. It is one of the infrahyoid muscles. It is innervated by the ansa cervicalis. It acts to depress the hyoid bone. The sternohyoid muscle is a flat muscle located on both sides of the neck, part of the infrahyoid muscle group. It originates from the medial edge of the clavicle, sternoclavicular ligament, and posterior side of the manubrium, and ascends to attach to the body of the hyoid bone. The sternohyoid muscle, along with other infrahyoid muscles, functions to depress the hyoid bone, which is important for activities such as speaking, chewing, and swallowing. Additionally, this muscle group contributes to the protection of the trachea, esophagus, blood vessels, and thyroid gland. The sternohyoid muscle also plays a minor role in head movements. Structure The sternohyoid muscle is one of the paired strap muscles of the infrahyoid muscles. The muscle is directed superome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternothyroid
The sternothyroid muscle (or sternothyroideus) is an infrahyoid muscle of the neck. It acts to depress the hyoid bone. Structure The two muscles are in contact with each other proximally (close to their origin), but diverge distally (towards their insertions). Origin The sternothyroid arises from the posterior surface of the manubrium of the sternum from the midline to the notch for the first rib (inferior to the origin of the sternohyoid muscle), and the posterior margin of the first costal cartilage. Insertion It inserts onto the oblique line of the lamina of thyroid cartilage. Innervation The sternothyroid muscle receives motor innervation from branches of the ansa cervicalis (ultimately derived from cervical spinal nerves C1-C3). Relations The sternothyroid muscle is shorter and wider than the sternohyoid muscle and is situated deep to and partially medial to it. Variations The muscle may be absent or doubled. It may issue accessory slips to the thyrohyoid mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
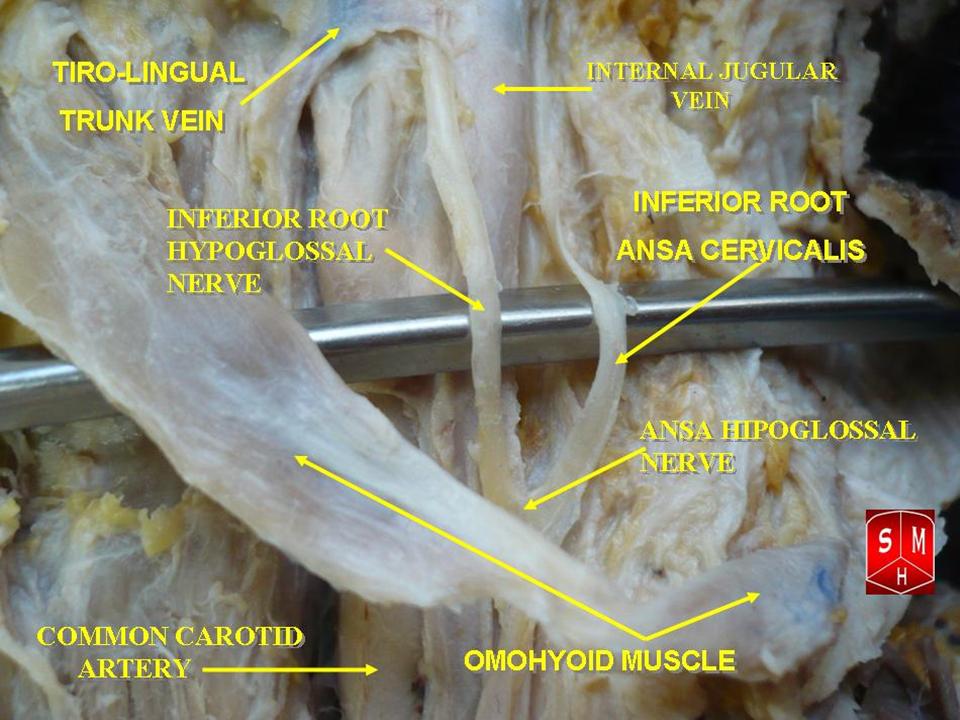
Ansa Cervicalis
The ansa cervicalis (or ansa hypoglossi in older literature) is a loop formed by muscular branches of the cervical plexus formed by branches of cervical spinal nerves C1-C3. The ansa cervicalis has two roots - a superior root (formed by branch of C1) and an inferior root (formed by union of branches of C2 and C3) - that unite distally, forming a loop. It is situated anterior to the carotid sheath. Branches of the ansa cervicalis innervate three of the four infrahyoid muscles: the sternothyroid, sternohyoid, and omohyoid muscles (note that the thyrohyoid muscle is the one infrahyoid muscle not innervated by the ansa cervicalis - it is instead innervated by cervical spinal nerve 1 via a separate thyrohyoid branch). Its name means "handle of the neck" in Latin. Anatomy The ansa cervicalis is typically embedded within the anterior wall of the carotid sheath anterior to the internal jugular vein. Superior root The superior root of the ansa cervicalis (formerly known as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraclavicular Nerves
The supraclavicular nerve is a cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the cervical plexus that arises from the third and fourth cervical (spinal) nerves. It emerges from beneath the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, then split into multiple branches. Together, these innervate the skin over the shoulder. The supraclavicular nerve can be blocked during shoulder surgery. Anatomy Origin The supraclavicular nerve is a branch of the cervical plexus that arises from cervical (spinal) nerves C3-C4 with the predominant contribution from C4. Course It emerges at the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle alongside the other three cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus, then promptly divides into several branches. The nerves descend in the posterior triangle of the neck beneath the platysma muscle and the deep cervical fascia. Near the clavicle, the supraclavicular nerves perforate the fascia and the platysma muscle to become cutaneous. They are arranged, ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Cervical Nerve
The transverse cervical nerve (superficial cervical or cutaneous cervical) is a cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the cervical plexus that arises from the second and third cervical spinal nerves (C2-C3). It curves around the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus muscle, then pierces the fascia of the neck before dividing into two branches. It provides sensory innervation to the front of the neck. Anatomy Course and relations It curves around the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus muscle about its middle, and, passing obliquely forward beneath the external jugular vein to the anterior border of the muscle, it perforates the deep cervical fascia before dividing into an ascending branch and a descending branch beneath the platysma. The ascending branch communicates with the cervical branch of the facial nerve The cervical branch of the facial nerve is a nerve in the neck. It is a branch of the facial nerve (VII). It supplies the platysma muscle, among other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ear Canal
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the auricle to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter. Structure The human ear canal is divided into two parts. The elastic cartilage part forms the outer third of the canal; its anterior and lower wall are cartilaginous, whereas its superior and back wall are fibrous. The cartilage is the continuation of the cartilage framework of auricle. The cartilaginous portion of the ear canal contains small hairs and specialized sweat glands, called apocrine glands, which produce cerumen ( ear wax). The bony part forms the inner two thirds. The bony part is much shorter in children and is only a ring (''annulus tympanicus'') in the newborn. The layer of epithelium encompassing the bony portion of the ear canal is much thinner and therefore, more sensitive in comparison to the cartilaginous portion. Size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Acoustic Meatus
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the auricle to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter. Structure The human ear canal is divided into two parts. The elastic cartilage part forms the outer third of the canal; its anterior and lower wall are cartilaginous, whereas its superior and back wall are fibrous. The cartilage is the continuation of the cartilage framework of auricle. The cartilaginous portion of the ear canal contains small hairs and specialized sweat glands, called apocrine glands, which produce cerumen ( ear wax). The bony part forms the inner two thirds. The bony part is much shorter in children and is only a ring (''annulus tympanicus'') in the newborn. The layer of epithelium encompassing the bony portion of the ear canal is much thinner and therefore, more sensitive in comparison to the cartilaginous portion. Size a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinna (anatomy)
The auricle or auricula is the visible part of the ear that is outside the head. It is also called the pinna (Latin for 'wing' or ' fin', : pinnae), a term that is used more in zoology. Structure The diagram shows the shape and location of most of these components: * '' antihelix'' forms a 'Y' shape where the upper parts are: ** ''Superior crus'' (to the left of the ''fossa triangularis'' in the diagram) ** ''Inferior crus'' (to the right of the ''fossa triangularis'' in the diagram) * ''Antitragus'' is below the ''tragus'' * ''Aperture'' is the entrance to the ear canal * ''Auricular sulcus'' is the depression behind the ear next to the head * ''Concha'' is the hollow next to the ear canal * Conchal angle is the angle that the back of the ''concha'' makes with the side of the head * ''Crus'' of the helix is just above the ''tragus'' * ''Cymba conchae'' is the narrowest end of the ''concha'' * External auditory meatus is the ear canal * ''Fossa triangularis'' is the depression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Auricular Nerve
The great auricular nerve is a Cutaneous nerve, cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the head. It originates from the second and third spinal nerve, cervical (spinal) nerves (C2-C3) of the cervical plexus. It provides sensory innervation to the skin over the parotid gland and the Mastoid part of the temporal bone, mastoid process, parts of the outer ear, and to the parotid gland and its parotid fascia, fascia. Pain resulting from parotitis is caused by an impingement on the great auricular nerve. Structure The great auricular nerve is the largest of the ascending branches of the cervical plexus. Origin It arises from the second and third cervical (spinal) nerves (C2-C3), with the predominant contribution coming from C2. Course and relations The great auricular nerve is a large trunk that ascends almost vertically over the sternocleidomastoid. It winds around the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, then perforates the deep fascia before ascending alongside the exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Occipital
The lesser occipital nerve (or small occipital nerve) is a cutaneous spinal nerve of the cervical plexus. It arises from second cervical (spinal) nerve (C2) (along with the greater occipital nerve). It innervates the skin of the back of the upper neck and of the scalp posterior to the ear. Structure Origin It arises from the (lateral branch of the ventral ramus) of cervical spinal nerve C2; it (sources differ) receives or may also receive fibres from cervical spinal nerve C3. It originates between the atlas, and axis. The lesser occipital nerve is one of the four cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus. Course and relations It curves around the accessory nerve (CN XI) to come to course anterior to it. It then curves around and ascends along the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle; rarely, it may pierce the muscle. Near the cranium, it perforates the deep cervical fascia. It is continued upwards along the scalp posterior to the auricle. It divides i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |