|
Castration
Castration is any action, surgery, surgical, chemical substance, chemical, or otherwise, by which a male loses use of the testicles: the male gonad. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy (excision of both testicles), while chemical castration uses pharmaceutical drugs to deactivate the testes. Some forms of castration cause sterilization (medicine), sterilization (permanently preventing the castrated person or animal from reproduction, reproducing); it also greatly reduces the production of hormones, such as testosterone and estrogen. Surgical castration in animals is often called neutering. #Other animals, Castration of animals is intended to favor a desired development of the animal or of its habits, as an anaphrodisiac or to prevent overpopulation. The parallel of castration for female animals is spaying. Castration may also refer medically to oophorectomy in female humans and animals. The term ''castration'' may also be sometimes used to refer to emasculation where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Castration
Chemical castration is castration via anaphrodisiac drugs, whether to reduce libido and sexual activity, management of cancer, to treat cancer, or otherwise. Unlike orchiectomy, surgical castration, where the gonads are removed through an incision in the body,"Can Castration Be a Solution for Sex Offenders? Man Who Mutilated Himself in Jail Thinks So, but Debate on Its Effectiveness Continues in Va., Elsewhere" by Candace Rondeaux for the Washington Post, July 5, 2006 chemical castration does not remove organs and is not a form of Human sterilization (surgical procedure), sterilization. Chemical castration is general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
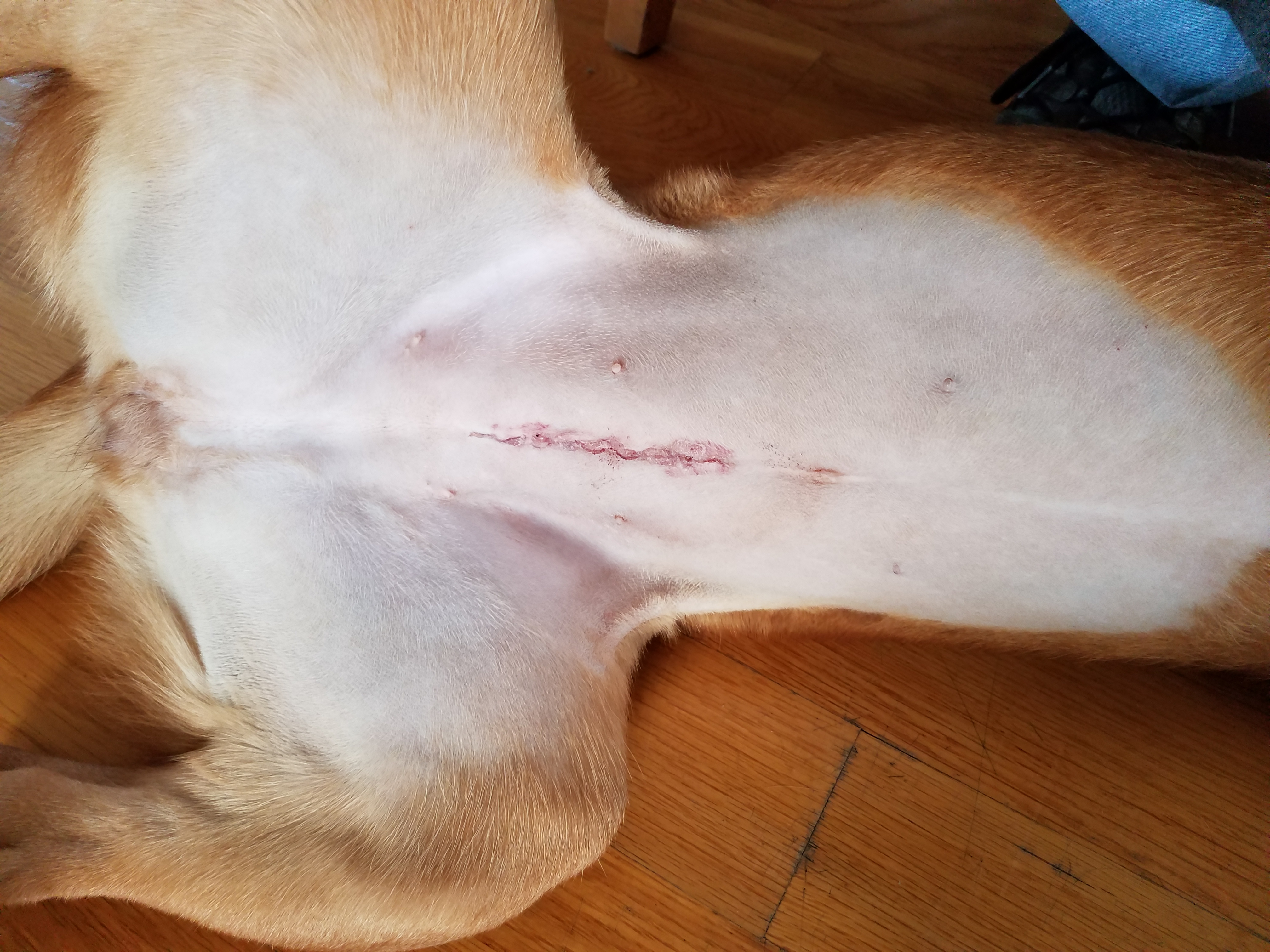
Spaying
Neutering, from the Latin ('of neither sex'), is the removal of a non-human animal's reproductive organ, either all of it or a considerably large part. The male-specific term is castration, while spaying is usually reserved for female animals. Colloquially, both terms are often referred to as fixing. In male horses, castrating is referred to as gelding. An animal that has not been neutered is sometimes referred to as entire or intact. Often the term ''neuter ng' is used to specifically mean castration, e.g. in phrases like "spay and neuter". Neutering is the most common method for animal sterilization. Humane societies, animal shelters, and rescue groups urge pet owners to have their pets neutered to prevent the births of unwanted litters, which contribute to the overpopulation of unwanted animals in the rescue system. Many countries require that all adopted cats and dogs be sterilized before going to their new homes. Methods of sterilization Females (spaying) Spaying is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutering
Neutering, from the Latin ('of neither sex'), is the removal of a non-human animal's sex organ, reproductive organ, either all of it or a considerably large part. The male-specific term is castration, while spaying is usually reserved for female animals. Colloquially, both terms are often referred to as fixing. In male horses, castrating is referred to as gelding. An animal that has not been neutered is sometimes referred to as entire or intact. Often the term ''neuter[ing]'' is used to specifically mean castration, e.g. in phrases like "spay and neuter". Neutering is the most common method for animal Sterilization (medicine), sterilization. humane society, Humane societies, animal shelters, and rescue groups urge pet owners to have their pets neutered to prevent the births of unwanted Litter (zoology), litters, which contribute to the Overpopulation of domestic pets, overpopulation of unwanted animals in the rescue system. Many countries require that all adopted cats and dogs be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the neoplasm, uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Abnormal growth of the prostate tissue is usually detected through Screening (medicine), screening tests, typically blood tests that check for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels. Those with high levels of PSA in their blood are at increased risk for developing prostate cancer. Diagnosis requires a prostate biopsy, biopsy of the prostate. If cancer is present, the pathologist assigns a Gleason score; a higher score represents a more dangerous tumor. Medical imaging is performed to look for cancer that has spread outside the prostate. Based on the Gleason score, PSA levels, and imaging results, a cancer case is assigned a cancer staging, stage 1 to 4. A higher stage signifies a more advanced, more dangerous disease. Most prostate tumors remain small and cause no health problems. These are managed with active surveillance of prostate cancer, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oophorectomy
Oophorectomy (; from Greek , , 'egg-bearing' and , , 'a cutting out of'), historically also called ''ovariotomy'', is the surgical removal of an ovary or ovaries. The surgery is also called ovariectomy, but this term is mostly used in reference to non-human animals, e.g. the surgical removal of ovaries from laboratory animals. Removal of the ovaries of females is the biological equivalent of castration of males; the term ''castration'' is only occasionally used in the medical literature to refer to oophorectomy of women. In veterinary medicine, the removal of ovaries and uterus is called ovariohysterectomy ( spaying) and is a form of sterilization. The first reported successful human oophorectomy was carried out by (Sir) Sydney Jones at Sydney Infirmary, Australia, in 1870. Partial oophorectomy or ovariotomy is a term sometimes used to describe a variety of surgeries such as ovarian cyst removal, or resection of parts of the ovaries. This kind of surgery is fertility-preser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castration In Ancient Rome
Sexual attitudes and behaviors in ancient Rome are indicated by Roman art, art, Latin literature, literature, and Corpus Inscriptionum Latinarum, inscriptions, and to a lesser extent by classical archaeology, archaeological remains such as erotic artifacts and Roman architecture, architecture. It has sometimes been assumed that "unlimited sexual license" was characteristic of ancient Rome, but sexuality was not excluded as a concern of the ''mos maiorum'', the traditional social norms that affected public, private, and military life. ''Pudor'', "shame, modesty", was a regulating factor in behavior, as were legal strictures on certain sexual transgressions in both the Roman Republic, Republican and Roman Empire, Imperial periods. The Roman censor, censors—Roman magistrate, public officials who determined the Social class in ancient Rome, social rank of individuals—had the power to remove Roman citizenship, citizens from the Roman senate, senatorial or equestrian order for sex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchidectomy
Orchiectomy (also named orchidectomy) is a surgical procedure in which one or both testicles are removed. The surgery can be performed for various reasons: *treatment for testicular cancer *as part of gender-affirming surgery for transgender women *as management for advanced prostate cancer *to remove damaged testes after testicular torsion. *after a trauma or complex rupture of the tunica albuginea. *as a treatment for post vasectomy pain syndrome. Less frequently, orchiectomy may be performed following a trauma, or due to wasting away of one or more testicles. Procedure Simple orchiectomy A simple orchiectomy is commonly performed as part of gender-affirming surgery for transgender women, or as palliative treatment for advanced cases of prostate cancer. A simple orchiectomy may also be required in the event of testicular torsion. For the procedure, the person lies flat on an operating table with the penis taped against the abdomen. The nurse shaves a small area for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchiectomy
Orchiectomy (also named orchidectomy) is a surgery, surgical procedure in which one or both testicles are removed. The surgery can be performed for various reasons: *treatment for testicular cancer *as part of gender-affirming surgery for transgender women *as management for advanced prostate cancer *to remove damaged testes after testicular torsion. *after a trauma or complex rupture of the tunica albuginea. *as a treatment for post vasectomy pain syndrome. Less frequently, orchiectomy may be performed following a trauma, or due to wasting away of one or more testicles. Procedure Simple orchiectomy A simple orchiectomy is commonly performed as part of gender-affirming surgery for transgender women, or as palliative treatment for advanced cases of prostate cancer. A simple orchiectomy may also be required in the event of testicular torsion. For the procedure, the person lies flat on an operating table with the Human penis, penis taped against the abdomen. The nurse shaves a sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emasculation
Emasculation is the removal of the external male sex organs, which includes both the penis and the scrotum, the latter of which contains the testicles. It is distinct from castration, where only the testicles are removed. Although the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, the potential medical consequences of emasculation are more extensive due to the complications arising from the removal of the penis. There are a range of religious, cultural, punitive, and personal reasons why someone may choose to emasculate themselves or another person. The term ''emasculation'' may be used in a metaphorical sense, referring to the perceived loss of attributes traditionally associated with masculinity, such as strength, power, or autonomy. Method There are several different methods of emasculation. Both the penis and testicles may be removed simultaneously using a sharp instrument, such as a knife or razor or swords. Non-crushing vascular clamps may also be used in medical surgery to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Offender
A sex offender (sexual offender, sex abuser, or sexual abuser) is a person who has committed a Sex and the law, sex crime. What constitutes a sex crime differs by culture and legal jurisdiction. The majority of convicted sex offenders have convictions for crimes of a sexual nature; however, some sex offenders have simply violated a law contained in a sexual category. Some of the serious crimes which result in a mandatory sex-offender classification are sexual assault, statutory rape, bestiality, child sexual abuse, incest, and rape. Some sex offenders are deemed too dangerous to society to be released and are subjected to civil confinementindefinite continuing incarceration, which is supposed to, but does not always, provide meaningful treatment to the offender. sex offender registries in the United States, Sex offender registration laws in the United States may also classify less serious offenses as sexual offenses requiring sex offender registration. In some states public urin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicles
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone. The release of testosterone is regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland. Sperm production is controlled by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary gland and by testosterone produced within the gonads. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and comparing it to ellipsoids (an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristics such as increased muscle and bone mass, and the growth of androgenic hair, body hair. It is associated with increased aggression, sex drive, Dominance hierarchy, dominance, courtship display, and a wide range of behavioral characteristics. In addition, testosterone in both sexes is involved in health and well-being, where it has a significant effect on overall mood, cognition, social and sexual behavior, metabolism and energy output, the cardiovascular system, and in the prevention of osteoporosis. Insufficient levels of testosterone in men may lead to abnormalities including frailty, accumulation of adipose fat tissue within the body, anxiety and depression, sexual performance issues, and bone loss. Excessiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |