|
Argument (linguistics)
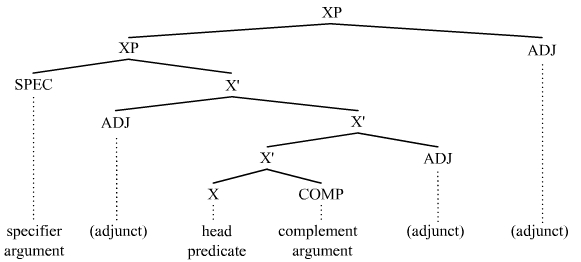
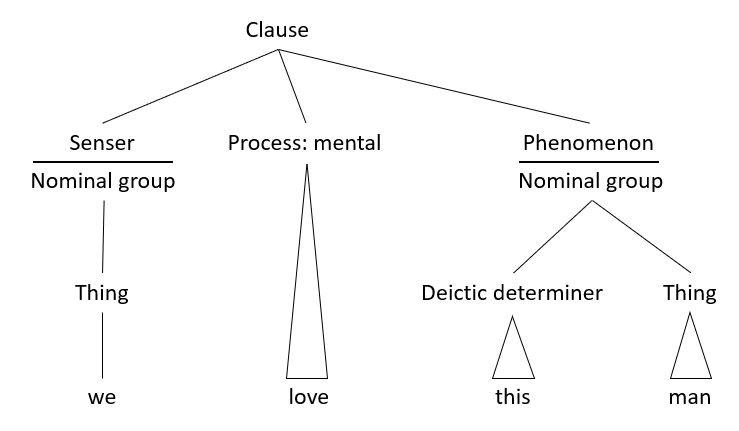
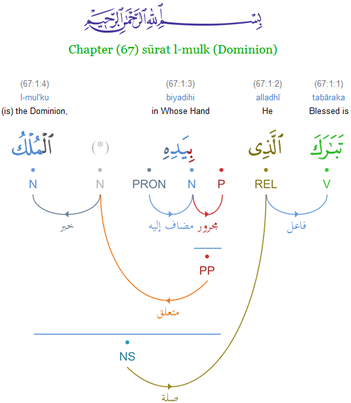
In linguistics, an argument is an expression that helps complete the meaning of a predicate (grammar), predicate, the latter referring in this context to a main verb and its auxiliaries. In this regard, the ''Complement (linguistics), complement'' is a closely related concept. Most predicates take one, two, or three arguments. A predicate and its arguments form a ''predicate-argument structure''. The discussion of predicates and arguments is associated most with (content) verbs and noun phrases (NPs), although other syntactic category, syntactic categories can also be construed as predicates and as arguments. Arguments must be distinguished from adjunct (grammar), adjuncts. While a predicate needs its arguments to complete its meaning, the adjuncts that appear with a predicate are optional; they are not necessary to complete the meaning of the predicate. Most theories of syntax and semantics acknowledge arguments and adjuncts, although the terminology varies, and the distinction is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incorporation (linguistics)
In linguistics, incorporation is a phenomenon by which a grammatical category, such as a verb, forms a compound with its direct object (object incorporation) or adverbial modifier, while retaining its original syntactic function. The inclusion of a noun qualifies the verb, narrowing its scope rather than making reference to a specific entity. Incorporation is central to many polysynthetic languages such as those found in North America, Siberia and northern Australia. However, polysynthesis does not necessarily imply incorporation (Mithun 2009), and the presence of incorporation does not imply that the language is polysynthetic. Examples of incorporation English Although incorporation does not occur regularly, English uses it sometimes: ''breastfeed'', and direct object incorporation, as in ''babysit''. Etymologically, such verbs in English are usually back-formations: the verbs ''breastfeed'' and ''babysit'' are formed from the adjective ''breast-fed'' and the noun ''bab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). Diverse approaches, such as generative grammar and functional grammar, offer unique perspectives on syntax, reflecting its complexity and centrality to understanding human language. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from the ancient Greek word , meaning an orderly or systematic arrangement, which consists of (''syn-'', "together" or "alike"), and (''táxis'', "arrangement"). In Hellenistic Greek, this also specifically developed a use referring to the grammatical order of words, with a slightly altered spelling: . The English term, which first appeared in 1548, is partly borrowed from Latin () and Greek, though the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Theories Of Grammar
Functional linguistics is an approach to the study of language characterized by taking systematically into account the speaker's and the hearer's side, and the communicative needs of the speaker and of the given language community. Linguistic functionalism spawned in the 1920s to 1930s from Ferdinand de Saussure's systematic structuralist approach to language (1916). Functionalism sees functionality of language and its elements to be the key to understanding linguistic processes and structures. Functional theories of language propose that since language is fundamentally a tool, it is reasonable to assume that its structures are best analyzed and understood with reference to the functions they carry out. These include the tasks of conveying meaning and contextual information. Functional theories of grammar belong to structural and, broadly, humanistic linguistics, considering language as being created by the community, and linguistics as relating to systems theory. Functional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argumentation Theory
Argumentation theory is the interdisciplinary study of how conclusions can be supported or undermined by premises through logical reasoning. With historical origins in logic, dialectic, and rhetoric, argumentation theory includes the arts and sciences of civil debate, dialogue, conversation, and persuasion. It studies rules of inference, logic, and procedural rules in both artificial and real-world settings. Argumentation includes various forms of dialogue such as deliberation and negotiation which are concerned with collaborative decision-making procedures. It also encompasses eristic dialogue, the branch of social debate in which victory over an opponent is the primary goal, and didactic dialogue used for teaching. This discipline also studies the means by which people can express and rationally resolve or at least manage their disagreements. Argumentation is a daily occurrence, such as in public debate, science, and law. For example in law, in courts by the judge, the partie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argument2
An argument is a series of sentences, statements, or propositions some of which are called premises and one is the conclusion. The purpose of an argument is to give reasons for one's conclusion via justification, explanation, and/or persuasion. Arguments are intended to determine or show the degree of truth or acceptability of another statement called a conclusion. The process of crafting or delivering arguments, argumentation, can be studied from three main perspectives: the logical, the dialectical and the rhetorical perspective. In logic, an argument is usually expressed not in natural language but in a symbolic formal language, and it can be defined as any group of propositions of which one is claimed to follow from the others through deductively valid inferences that preserve truth from the premises to the conclusion. This logical perspective on argument is relevant for scientific fields such as mathematics and computer science. Logic is the study of the forms of reasoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependency Grammar
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern Grammar, grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of Phrase structure grammar, phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a Head (linguistics), head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb, finite verb phrase constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-bar Theory
In linguistics, X-bar theory is a model of phrase structure and a theory of syntactic category formation that proposes a universal schema for how phrases are organized. It suggests that all phrases share a common underlying structure, regardless of their specific category (noun phrase, verb phrase, etc.). This structure, known as the X-bar schema, is based on the idea that every phrase (XP, X phrase) has a Head (linguistics), head, which determines the type (syntactic category) of the phrase (X). The theory was first proposed by Noam Chomsky in 1970Chomsky, Noam (1970). Remarks on Nominalization. In: R. Jacobs and P. Rosenbaum (eds.) ''Reading in English Transformational Grammar'', 184–221. Waltham: Ginn. reformulating the ideas of Zellig Harris (1951), and further developed by Ray Jackendoff (1974, 1977a, 1977bJackendoff, Ray (1977b) Constraints on Phrase Structure Rules, in P. W. Culicover, T. Wasow & A. Akmajian (eds.), ''Formal Syntax'', Academic Press, New York, pp. 249– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase Structure Grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue ( Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in the Chomsky hierarchy: context-sensitive grammars or context-free grammars. In a broader sense, phrase structure grammars are also known as ''constituency grammars''. The defining character of phrase structure grammars is thus their adherence to the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation of dependency grammars. History In 1956, Chomsky wrote, "A phrase-structure grammar is defined by a finite vocabulary (alphabet) Vp, and a finite set Σ of initial strings in Vp, and a finite set F of rules of the form: X → Y, where X and Y are strings in Vp." Constituency relation In linguistics, phrase structure grammars are all those grammars that are based on the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constituent (linguistics)
In syntactic analysis, a constituent is a word or a group of words that function as a single unit within a hierarchical structure. The constituent structure of sentences is identified using ''tests for constituents''. These tests apply to a portion of a sentence, and the results provide evidence about the constituent structure of the sentence. Many constituents are phrases. A phrase is a sequence of one or more words (in some theories two or more) built around a head lexical item and working as a unit within a sentence. A word sequence is shown to be a phrase/constituent if it exhibits one or more of the behaviors discussed below. The analysis of constituent structure is associated mainly with phrase structure grammars, although dependency grammars also allow sentence structure to be broken down into constituent parts. Tests for constituents in English Tests for constituents are diagnostics used to identify sentence structure. There are numerous tests for constituents that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Language
is the principal language of the Japonic languages, Japonic language family spoken by the Japanese people. It has around 123 million speakers, primarily in Japan, the only country where it is the national language, and within the Japanese diaspora worldwide. The Japonic family also includes the Ryukyuan languages and the variously classified Hachijō language. There have been many Classification of the Japonic languages, attempts to group the Japonic languages with other families such as Ainu languages, Ainu, Austronesian languages, Austronesian, Koreanic languages, Koreanic, and the now discredited Altaic languages, Altaic, but none of these proposals have gained any widespread acceptance. Little is known of the language's prehistory, or when it first appeared in Japan. Chinese documents from the 3rd century AD recorded a few Japanese words, but substantial Old Japanese texts did not appear until the 8th century. From the Heian period (794–1185), extensive waves of Sino-Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |