Japanese language on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
is the principal language of the Japonic language family spoken by the
 The Chinese writing system was imported to Japan from
The Chinese writing system was imported to Japan from
 Early Middle Japanese is the Japanese of the
Early Middle Japanese is the Japanese of the
''hyōjungo'' and ''kyōtsūgo'' ) are almost the same. ''Hyōjungo'' or ''kyōtsūgo'' is a conception that forms the counterpart of dialect. This normative language was born after the from the language spoken in the higher-class areas of Tokyo (see Yamanote). ''Hyōjungo'' is taught in schools and used on television and in official communications. It is the version of Japanese discussed in this article.
used in formal texts, is different compared to the , used in everyday speech. The two systems have different rules of grammar and some variance in vocabulary. ''Bungo'' was the main method of writing Japanese until about 1900; since then ''kōgo'' gradually extended its influence and the two methods were both used in writing until the 1940s. ''Bungo'' still has some relevance for historians, literary scholars, and lawyers (many Japanese laws that survived
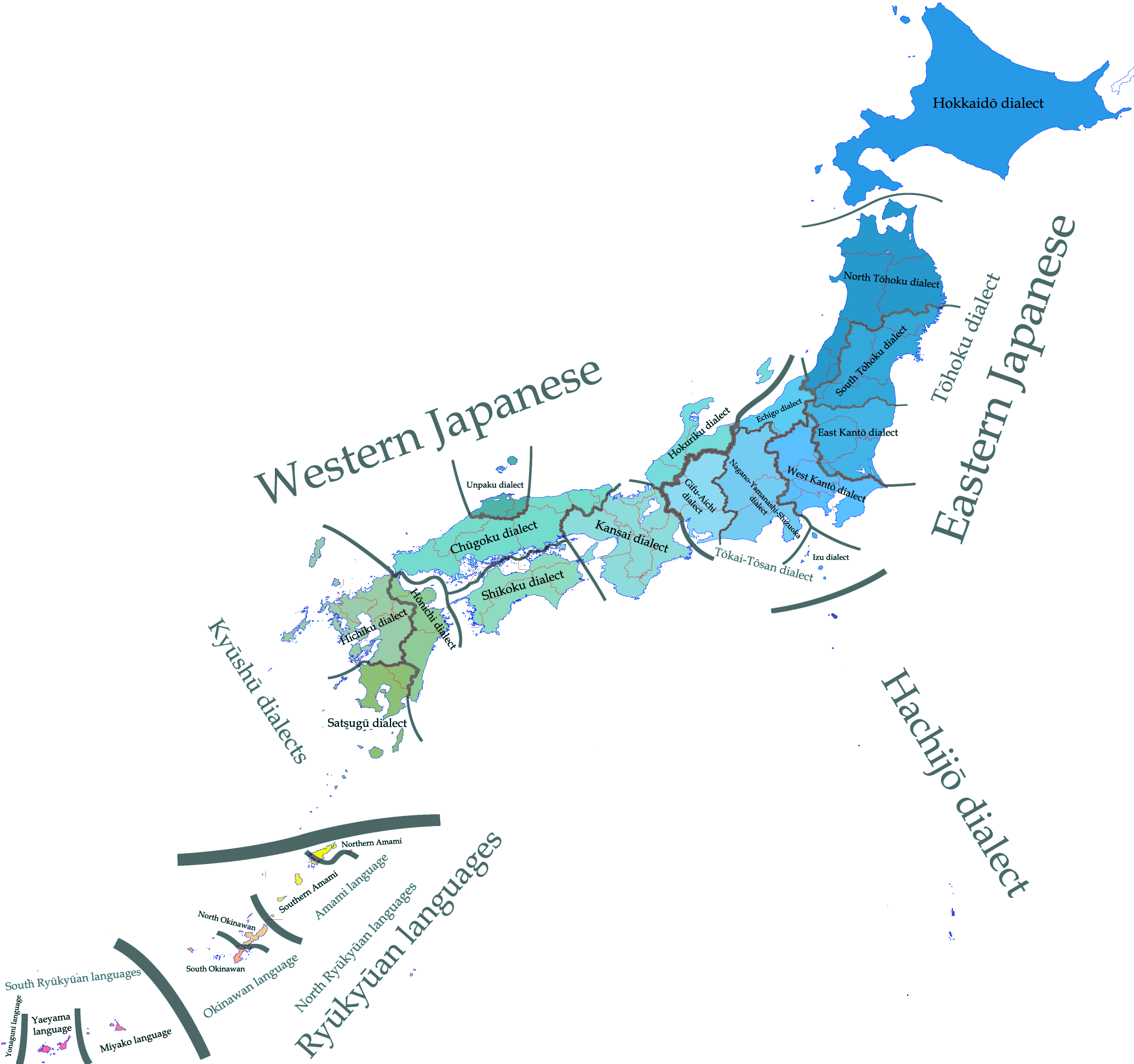 Japanese dialects typically differ in terms of
Japanese dialects typically differ in terms of
 At first, the Japanese wrote in
At first, the Japanese wrote in
"Sotomayor, Denzel Washington, GE CEO Speak to Graduates"
C-SPAN (US). 30 May 2011; retrieved 2011-05-30 International interest in the Japanese language dates from the 19th century but has become more prevalent following Japan's economic bubble of the 1980s and the global popularity of
"Japanese"
in ''Dictionary of Languages: the Definitive Reference to More than 400 Languages.'' New York: Columbia University Press. ; * * * * Kuno, Susumu (1973). ''The structure of the Japanese language''. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. . * Kuno, Susumu. (1976). "Subject, theme, and the speaker's empathy: A re-examination of relativization phenomena", in Charles N. Li (Ed.), ''Subject and topic'' (pp. 417–444). New York: Academic Press. . * McClain, Yoko Matsuoka. (1981). ''Handbook of modern Japanese grammar:'' 'Kōgo Nihon bumpō'' Tokyo: Hokuseido Press. . * Miller, Roy (1967). ''The Japanese language''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. * Miller, Roy (1980). ''Origins of the Japanese language: Lectures in Japan during the academic year, 1977–78''. Seattle: University of Washington Press. . * Mizutani, Osamu; & Mizutani, Nobuko (1987). ''How to be polite in Japanese:'' 'Nihongo no keigo'' Tokyo:
National Institute for Japanese Language and Linguistics
Japanese Language Student's Handbook
(archived 2 January 2010) {{Authority control Agglutinative languages Languages attested from the 8th century Languages of Japan Languages of Palau Subject–object–verb languages Syllable-timed languages
Japanese people
are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago. Japanese people constitute 97.4% of the population of the country of Japan. Worldwide, approximately 125 million people are of Japanese descent, making them list of contempora ...
. It has around 123 million speakers, primarily in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, the only country where it is the national language
'' ''
A national language is a language (or language variant, e.g. dialect) that has some connection— de facto or de jure—with a nation. The term is applied quite differently in various contexts. One or more languages spoken as first languag ...
, and within the Japanese diaspora
The Japanese diaspora and its individual members, known as Nikkei (, ) or as Nikkeijin (, ), comprise the Japanese people, Japanese emigration, emigrants from Japan (and their Kinship, descendants) residing in a country outside Japan. Emigration ...
worldwide.
The Japonic family also includes the Ryukyuan languages
The , also Lewchewan or Luchuan (), are the indigenous languages of the Ryukyu Islands, the southernmost part of the Japanese archipelago. Along with the Japanese language and the Hachijō language, they make up the Japonic language family.
Ju ...
and the variously classified Hachijō language
The small group of , natively called , depending on classification, either are the most divergent form of Japanese dialects, Japanese, or comprise a branch of Japonic languages (alongside mainland Japanese, Northern Ryukyuan languages, Northern Ry ...
. There have been many attempts to group the Japonic languages with other families such as Ainu, Austronesian, Koreanic, and the now discredited Altaic, but none of these proposals have gained any widespread acceptance.
Little is known of the language's prehistory, or when it first appeared in Japan. Chinese documents from the 3rd century AD recorded a few Japanese words, but substantial Old Japanese texts did not appear until the 8th century. From the Heian period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kammu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means in Japanese. It is a ...
(794–1185), extensive waves of Sino-Japanese vocabulary
Sino-Japanese vocabulary, also known as , is a subset of Japanese vocabulary that originated in Chinese language, Chinese or was created from elements borrowed from Chinese. Most Sino-Japanese words were borrowed in the 5th–9th centuries AD, from ...
entered the language, affecting the phonology
Phonology (formerly also phonemics or phonematics: "phonemics ''n.'' 'obsolescent''1. Any procedure for identifying the phonemes of a language from a corpus of data. 2. (formerly also phonematics) A former synonym for phonology, often pre ...
of Early Middle Japanese. Late Middle Japanese (1185–1600) saw extensive grammatical changes and the first appearance of European loanwords. The basis of the standard dialect
A standard language (or standard variety, standard dialect, standardized dialect or simply standard) is any language variety that has undergone substantial codification in its grammar, lexicon, writing system, or other features and that stands ...
moved from the Kansai region to the Edo region (modern Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most ...
) in the Early Modern Japanese period (early 17th century–mid 19th century). Following the end of Japan's self-imposed isolation in 1853, the flow of loanword
A loanword (also a loan word, loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language (the recipient or target language), through the process of borrowing. Borrowing is a metaphorical term t ...
s from European languages increased significantly, and words from English roots have proliferated.
Japanese is an agglutinative, mora-timed language with relatively simple phonotactics
Phonotactics (from Ancient Greek 'voice, sound' and 'having to do with arranging') is a branch of phonology that deals with restrictions in a language on the permissible combinations of phonemes. Phonotactics defines permissible syllable struc ...
, a pure vowel system, phonemic vowel and consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract, except for the h sound, which is pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Examples are and pronou ...
length, and a lexically significant pitch-accent. Word order is normally subject–object–verb with particles marking the grammatical function of words, and sentence structure is topic–comment. Sentence-final particles are used to add emotional or emphatic impact, or form questions. Nouns have no grammatical number
In linguistics, grammatical number is a Feature (linguistics), feature of nouns, pronouns, adjectives and verb agreement (linguistics), agreement that expresses count distinctions (such as "one", "two" or "three or more"). English and many other ...
or gender
Gender is the range of social, psychological, cultural, and behavioral aspects of being a man (or boy), woman (or girl), or third gender. Although gender often corresponds to sex, a transgender person may identify with a gender other tha ...
, and there are no articles. Verbs are conjugated, primarily for tense and voice
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound produ ...
, but not person
A person (: people or persons, depending on context) is a being who has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations suc ...
. Japanese adjectives are also conjugated. Japanese has a complex system of honorifics, with verb forms and vocabulary to indicate the relative status of the speaker, the listener, and persons mentioned.
The Japanese writing system
The modern Japanese writing system uses a combination of Logogram, logographic kanji, which are adopted Chinese characters, and Syllabary, syllabic kana. Kana itself consists of a pair of syllabary, syllabaries: hiragana, used primarily for n ...
combines Chinese characters
Chinese characters are logographs used Written Chinese, to write the Chinese languages and others from regions historically influenced by Chinese culture. Of the four independently invented writing systems accepted by scholars, they represe ...
, known as , with two unique syllabaries
In the linguistic study of written languages, a syllabary is a set of written symbols that represent the syllables or (more frequently) morae which make up words.
A symbol in a syllabary, called a syllabogram, typically represents an (option ...
(or moraic scripts) derived by the Japanese from the more complex Chinese characters: ( or , 'simple characters') and ( or , 'partial characters'). Latin script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Gree ...
( ) is also used in a limited fashion (such as for imported acronyms) in Japanese writing. The numeral system
A numeral system is a writing system for expressing numbers; that is, a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set, using digits or other symbols in a consistent manner.
The same sequence of symbols may represent differe ...
uses mostly Arabic numerals
The ten Arabic numerals (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9) are the most commonly used symbols for writing numbers. The term often also implies a positional notation number with a decimal base, in particular when contrasted with Roman numera ...
, but also traditional Chinese numerals
Chinese numerals are words and characters used to denote numbers in written Chinese.
Today, speakers of Chinese languages use three written numeral systems: the system of Arabic numerals used worldwide, and two indigenous systems. The more fami ...
.
History
Prehistory
Proto-Japonic, the common ancestor of the Japanese andRyukyuan languages
The , also Lewchewan or Luchuan (), are the indigenous languages of the Ryukyu Islands, the southernmost part of the Japanese archipelago. Along with the Japanese language and the Hachijō language, they make up the Japonic language family.
Ju ...
, is thought to have been brought to Japan by settlers coming from the Korean peninsula sometime in the early- to mid-4th century BC (the Yayoi period
The Yayoi period (弥生時代, ''Yayoi jidai'') (c. 300 BC – 300 AD) is one of the major historical periods of the Japanese archipelago. It is generally defined as the era between the beginning of food production in Japan and the emergence o ...
), replacing the languages of the original Jōmon inhabitants, including the ancestor of the modern Ainu language. Because writing had yet to be introduced from China, there is no direct evidence, and anything that can be discerned about this period must be based on internal reconstruction from Old Japanese, or comparison
Comparison or comparing is the act of evaluating two or more things by determining the relevant, comparable characteristics of each thing, and then determining which characteristics of each are similar to the other, which are different, and t ...
with the Ryukyuan languages and Japanese dialects.
Old Japanese
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (; ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BCE to 660 CE. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla. While the three kingdoms were in separate existence, Baekje had the h ...
around the start of the fifth century, alongside Buddhism. The earliest texts were written in Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese is the language in which the classics of Chinese literature were written, from . For millennia thereafter, the written Chinese used in these works was imitated and iterated upon by scholars in a form now called Literary ...
, although some of these were likely intended to be read as Japanese using the method, and show influences of Japanese grammar such as Japanese word order. The earliest text, the , dates to the early eighth century, and was written entirely in Chinese characters, which are used to represent, at different times, Chinese, ''kanbun'', and Old Japanese. As in other texts from this period, the Old Japanese sections are written in Man'yōgana, which uses ''kanji
are logographic Chinese characters, adapted from Chinese family of scripts, Chinese script, used in the writing of Japanese language, Japanese. They were made a major part of the Japanese writing system during the time of Old Japanese and are ...
'' for their phonetic as well as semantic values.
Based on the Man'yōgana system, Old Japanese can be reconstructed as having 88 distinct morae. Texts written with Man'yōgana use two different sets of ''kanji'' for each of the morae now pronounced , , , , , , , , , , , and . (The has 88, but all later texts have 87. The distinction between mo1 and mo2 apparently was lost immediately following its composition.) This set of morae shrank to 67 in Early Middle Japanese, though some were added through Chinese influence. Man'yōgana also has a symbol for , which merges with before the end of the period.
Several fossilizations of Old Japanese grammatical elements remain in the modern language – the genitive particle ''tsu'' (superseded by modern ''no'') is preserved in words such as ''matsuge'' ("eyelash", lit. "hair of the eye"); modern ''mieru'' ("to be visible") and ''kikoeru'' ("to be audible") retain a mediopassive suffix -''yu(ru)'' (''kikoyu'' → ''kikoyuru'' (the attributive form, which slowly replaced the plain form starting in the late Heian period) → ''kikoeru'' (all verbs with the ''shimo-nidan'' conjugation pattern underwent this same shift in Early Modern Japanese)); and the genitive particle ''ga'' remains in intentionally archaic speech.
Early Middle Japanese
 Early Middle Japanese is the Japanese of the
Early Middle Japanese is the Japanese of the Heian period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kammu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means in Japanese. It is a ...
, from 794 to 1185. It formed the basis for the literary standard of Classical Japanese, which remained in common use until the early 20th century.
During this time, Japanese underwent numerous phonological developments, in many cases instigated by an influx of Chinese loanwords. These included phonemic length distinction for both consonants
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract, except for the h sound, which is pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Examples are and pronou ...
and vowels, palatal consonants (e.g. ''kya'') and labial consonant clusters (e.g. ''kwa''), and closed syllables
A syllable is a basic unit of organization within a sequence of speech sounds, such as within a word, typically defined by linguists as a ''nucleus'' (most often a vowel) with optional sounds before or after that nucleus (''margins'', which are ...
. This had the effect of changing Japanese into a mora-timed language.
Late Middle Japanese
Late Middle Japanese covers the years from 1185 to 1600, and is normally divided into two sections, roughly equivalent to theKamakura period
The is a period of History of Japan, Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura, Kanagawa, Kamakura by the first ''shōgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the G ...
and the Muromachi period
The , also known as the , is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate ( or ), which was officially established in 1338 by the first Muromachi ...
, respectively. The later forms of Late Middle Japanese are the first to be described by non-native sources, in this case the Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
and Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related organizations in the Catholic Church, founded or inspired by the Italian saint Francis of Assisi. They include three independent Religious institute, religious orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor bei ...
missionaries; and thus there is better documentation of Late Middle Japanese phonology than for previous forms (for instance, the '' Arte da Lingoa de Iapam''). Among other sound changes, the sequence merges to , in contrast with ; is reintroduced from Chinese; and merges with . Some forms rather more familiar to Modern Japanese speakers begin to appear – the continuative ending -''te'' begins to reduce onto the verb (e.g. ''yonde'' for earlier ''yomite''), the -k- in the final mora of adjectives drops out (''shiroi'' for earlier ''shiroki''); and some forms exist where modern standard Japanese has retained the earlier form (e.g. ''hayaku'' > ''hayau'' > ''hayɔɔ'', where modern Japanese just has ''hayaku'', though the alternative form is preserved in the standard greeting ''o-hayō gozaimasu'' "good morning"; this ending is also seen in ''o-medetō'' "congratulations", from ''medetaku'').
Late Middle Japanese has the first loanwords from European languages – now-common words borrowed into Japanese in this period include ''pan'' ("bread") and ''tabako'' ("tobacco", now "cigarette"), both from Portuguese.
Modern Japanese
Modern Japanese is considered to begin with theEdo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
(which spanned from 1603 to 1867). Since Old Japanese, the ''de facto'' standard Japanese had been the Kansai dialect, especially that of Kyoto
Kyoto ( or ; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan's largest and most populous island of Honshu. , the city had a population of 1.46 million, making it t ...
. However, during the Edo period, Edo (now Tokyo) developed into the largest city in Japan, and the Edo-area dialect became standard Japanese. Since the end of Japan's self-imposed isolation in 1853, the flow of loanwords from European languages has increased significantly. The period since 1945 has seen many words borrowed from other languagessuch as German (e.g. 'temporary job', 'vaccine'), Portuguese ( 'sponge cake') and English. Many English loan words especially relate to technologyfor example, 'personal computer', 'internet', and 'camera'. Due to the large quantity of English loanwords, modern Japanese has developed a distinction between and , and and , with the latter in each pair only found in loanwords, eg. for party or for Disney.
Geographic distribution
Although Japanese is spoken almost exclusively in Japan, it has also been spoken outside of the country. Before and duringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, through Japanese annexation of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
and Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
, as well as partial occupation of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, and various Pacific islands, locals in those countries learned Japanese as the language of the empire. As a result, many elderly people in these countries can still speak Japanese.
Japanese emigrant communities (the largest of which are to be found in Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
, with 1.4 million to 1.5 million Japanese immigrants and descendants, according to Brazilian IBGE data, more than the 1.2 million of the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
) sometimes employ Japanese as their primary language. Approximately 12% of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
residents speak Japanese, with an estimated 12.6% of the population of Japanese ancestry in 2008. Japanese emigrants can also be found in Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
, Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
(especially in the eastern states), Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
(especially in Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
, where 1.4% of the population has Japanese ancestry), the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
(notably in Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, where 16.7% of the population has Japanese ancestry, and California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
), and the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
(particularly in Davao Region
Davao Region, formerly called Southern Mindanao (; ), is an Regions of the Philippines, administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region XI. Situated at the southeastern portion of Mindanao, enclosing Davao Gulf, it comprises fiv ...
and the Province of Laguna).
Official status
Japanese has no official status in Japan, but is the ''de facto''national language
'' ''
A national language is a language (or language variant, e.g. dialect) that has some connection— de facto or de jure—with a nation. The term is applied quite differently in various contexts. One or more languages spoken as first languag ...
of the country. There is a form of the language considered standard: , meaning "standard Japanese", or , "common language", or even "Tokyo dialect" at times. The meanings of the two terms (World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
are still written in ''bungo'', although there are ongoing efforts to modernize their language). ''Kōgo'' is the dominant method of both speaking and writing Japanese today, although ''bungo'' grammar and vocabulary are occasionally used in modern Japanese for effect.
Japanese is, along with Palauan and English, an official language of Angaur
, or in Palauan, is an island and state in the Island country, island nation of Palau.
History
Angaur was traditionally divided among some eight clans. Traditional features within clan areas represent important symbols giving identity to fam ...
, Palau
Palau, officially the Republic of Palau, is an island country in the Micronesia subregion of Oceania in the western Pacific Ocean. The Republic of Palau consists of approximately 340 islands and is the western part of the Caroline Islands ...
according to the 1982 state constitution. At the time it was written, many of the elders participating in the process had been educated in Japanese during the South Seas Mandate over the island, as shown by the 1958 census of the Trust Territory of the Pacific which found that 89% of Palauans born between 1914 and 1933 could speak and read Japanese. However, as of the 2005 Palau census, no residents of Angaur were reported to speak Japanese at home.
Dialects and mutual intelligibility
 Japanese dialects typically differ in terms of
Japanese dialects typically differ in terms of pitch accent
A pitch-accent language is a type of language that, when spoken, has certain syllables in words or morphemes that are prominent, as indicated by a distinct contrasting pitch (music), pitch (tone (linguistics), linguistic tone) rather than by vol ...
, inflectional morphology, vocabulary
A vocabulary (also known as a lexicon) is a set of words, typically the set in a language or the set known to an individual. The word ''vocabulary'' originated from the Latin , meaning "a word, name". It forms an essential component of languag ...
, and particle usage. Some even differ in vowel
A vowel is a speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract, forming the nucleus of a syllable. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness a ...
and consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract, except for the h sound, which is pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Examples are and pronou ...
inventories, although this is less common.
In terms of mutual intelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between different but related language varieties in which speakers of the different varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. Mutual intelli ...
, a survey in 1967 found that the four most unintelligible dialects (excluding Ryūkyūan languages and Tōhoku dialects) to students from Greater Tokyo were the Kiso dialect (in the deep mountains of Nagano Prefecture
is a Landlocked country, landlocked Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshu. Nagano Prefecture has a population of 2,007,682 () and has a geographic area of . Nagano Prefecture borders Niigata Prefecture ...
), the Himi dialect (in Toyama Prefecture), the Kagoshima dialect
The , often referred to as the , is a group of dialects or dialect continuum of the Japanese language spoken mainly within the area of the former Ōsumi and Satsuma provinces now incorporated into the southwestern prefecture of Kagoshima. It ...
and the Maniwa dialect (in Okayama Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Chūgoku region of Honshu. Okayama Prefecture has a population of 1,826,059 (1 February 2025) and has a geographic area of 7,114 Square kilometre, km2 (2,746 sq mi). Okayama Prefecture ...
). The survey was based on 12- to 20-second-long recordings of 135 to 244 phoneme
A phoneme () is any set of similar Phone (phonetics), speech sounds that are perceptually regarded by the speakers of a language as a single basic sound—a smallest possible Phonetics, phonetic unit—that helps distinguish one word fr ...
s, which 42 students listened to and translated word-for-word. The listeners were all Keio University students who grew up in the Kantō region
The is a geography, geographical region of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. In a common definition, the region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures of Japan, prefectures: Chiba Prefecture, Chiba, Gunma Prefe ...
.
There are some language islands in mountain villages or isolated islands such as Hachijō-jima island, whose dialects are descended from Eastern Old Japanese. Dialects of the Kansai region
The or the lies in the southern-central region of Japan's main island Honshū. The region includes the prefectures of Nara, Wakayama, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo and Shiga, often also Mie, sometimes Fukui, Tokushima and Tottori. The metropol ...
are spoken or known by many Japanese, and Osaka
is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the List of cities in Japan, third-most populous city in J ...
dialect in particular is associated with comedy (see Kansai dialect). Dialects of Tōhoku and North Kantō are associated with typical farmers.
The Ryūkyūan languages, spoken in Okinawa and the Amami Islands
The The name ''Amami-guntō'' was standardized on February 15, 2010. Prior to that, another name, ''Amami shotō'' (奄美諸島), was also used. is a Japanese archipelago in the Satsunan Islands, which is part of the Ryukyu Islands, and is sout ...
(administratively part of Kagoshima
, is the capital Cities of Japan, city of Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 583,966 in 285,992 households, and a population density of 1100 persons per km2. The total area of the city is .
Etymology
While the ...
), are distinct enough to be considered a separate branch of the Japonic family; not only is each language unintelligible to Japanese speakers, but most are unintelligible to those who speak other Ryūkyūan languages. However, in contrast to linguists, many ordinary Japanese people tend to consider the Ryūkyūan languages as dialects of Japanese.
The imperial court also seems to have spoken an unusual variant of the Japanese of the time, most likely the spoken form of Classical Japanese, a writing style that was prevalent during the Heian period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kammu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means in Japanese. It is a ...
, but began to decline during the late Meiji period
The was an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868, to July 30, 1912. The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonizatio ...
. The Ryūkyūan languages are classified by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
as 'endangered', as young people mostly use Japanese and cannot understand the languages. Okinawan Japanese is a variant of Standard Japanese influenced by the Ryūkyūan languages, and is the primary dialect spoken among young people in the Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the or the , are a chain of Japanese islands that stretch southwest from Kyushu to Geography of Taiwan, Taiwan: the Ryukyu Islands are divided into the Satsunan Islands (Ōsumi Islands, Ōsumi, Tokara Islands, Tokara and A ...
.
Modern Japanese has become prevalent nationwide (including the Ryūkyū islands) due to education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education als ...
, mass media
Mass media include the diverse arrays of media that reach a large audience via mass communication.
Broadcast media transmit information electronically via media such as films, radio, recorded music, or television. Digital media comprises b ...
, and an increase in mobility within Japan, as well as economic integration.
Classification
Japanese is a member of the Japonic language family, which also includes theRyukyuan languages
The , also Lewchewan or Luchuan (), are the indigenous languages of the Ryukyu Islands, the southernmost part of the Japanese archipelago. Along with the Japanese language and the Hachijō language, they make up the Japonic language family.
Ju ...
spoken in the Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the or the , are a chain of Japanese islands that stretch southwest from Kyushu to Geography of Taiwan, Taiwan: the Ryukyu Islands are divided into the Satsunan Islands (Ōsumi Islands, Ōsumi, Tokara Islands, Tokara and A ...
. As these closely related languages are commonly treated as dialects of the same language, Japanese is sometimes called a language isolate
A language isolate is a language that has no demonstrable genetic relationship with any other languages. Basque in Europe, Ainu and Burushaski in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, Haida and Zuni in North America, Kanoê in South America, and Tiwi ...
.
According to Martine Robbeets, Japanese has been subject to more attempts to show its relation to other languages than any other language in the world. Since Japanese first gained the consideration of linguists in the late 19th century, attempts have been made to show its genealogical relation to languages or language families such as Ainu, Korean, Chinese, Tibeto-Burman, Uralic, Altaic (or Ural-Altaic), Austroasiatic, Austronesian and Dravidian. At the fringe, some linguists have even suggested a link to Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
, including Greek, or to Sumerian. Main modern theories try to link Japanese either to northern Asian languages, like Korean or the proposed larger Altaic family, or to various Southeast Asian languages, especially Austronesian. None of these proposals have gained wide acceptance (and the Altaic family itself is now considered controversial). As it stands, only the link to Ryukyuan has wide support.
Other theories view the Japanese language as an early creole language
A creole language, or simply creole, is a stable form of contact language that develops from the process of different languages simplifying and mixing into a new form (often a pidgin), and then that form expanding and elaborating into a full-fl ...
formed through inputs from at least two distinct language groups, or as a distinct language of its own that has absorbed various aspects from neighboring languages.
Phonology
Vowels
Japanese has five vowels, andvowel length
In linguistics, vowel length is the perceived or actual length (phonetics), duration of a vowel sound when pronounced. Vowels perceived as shorter are often called short vowels and those perceived as longer called long vowels.
On one hand, many ...
is phonemic, with each having both a short and a long version. Elongated vowels are usually denoted with a line over the vowel (a macron) in rōmaji, a repeated vowel character in hiragana
is a Japanese language, Japanese syllabary, part of the Japanese writing system, along with ''katakana'' as well as ''kanji''.
It is a phonetic lettering system. The word ''hiragana'' means "common" or "plain" kana (originally also "easy", ...
, or a chōonpu succeeding the vowel in katakana
is a Japanese syllabary, one component of the Japanese writing system along with hiragana, kanji and in some cases the Latin script (known as rōmaji).
The word ''katakana'' means "fragmentary kana", as the katakana characters are derived fr ...
. is compressed rather than protruded, or simply unrounded.
Consonants
Some Japanese consonants have severalallophone
In phonology, an allophone (; from the Greek , , 'other' and , , 'voice, sound') is one of multiple possible spoken soundsor '' phones''used to pronounce a single phoneme in a particular language. For example, in English, the voiceless plos ...
s, which may give the impression of a larger inventory of sounds. However, some of these allophones have since become phonemic. For example, in the Japanese language up to and including the first half of the 20th century, the phonemic sequence was palatalized and realized phonetically as , approximately ; however, now and are distinct, as evidenced by words like "Western-style tea" and "social status".
The "r" of the Japanese language is of particular interest, ranging between an apical central tap and a lateral approximant. The "g" is also notable; unless it starts a sentence, it may be pronounced , in the Kanto prestige dialect and in other eastern dialects.
The phonotactics
Phonotactics (from Ancient Greek 'voice, sound' and 'having to do with arranging') is a branch of phonology that deals with restrictions in a language on the permissible combinations of phonemes. Phonotactics defines permissible syllable struc ...
of Japanese are relatively simple. The syllable structure is (C)(G)V(C), that is, a core vowel surrounded by an optional onset consonant, a glide and either the first part of a geminate consonant (/, represented as Q) or a moraic nasal in the coda (/, represented as N).
The nasal is sensitive to its phonetic environment and assimilates to the following phoneme, with pronunciations including . Onset-glide clusters only occur at the start of syllables but clusters across syllables are allowed as long as the two consonants are the moraic nasal followed by a homorganic consonant.
Japanese also includes a pitch accent
A pitch-accent language is a type of language that, when spoken, has certain syllables in words or morphemes that are prominent, as indicated by a distinct contrasting pitch (music), pitch (tone (linguistics), linguistic tone) rather than by vol ...
, which is not represented in moraic writing; for example ("chopsticks") and ("bridge") are both spelled , and are only differentiated by the tone contour.
Writing system
History
Literacy was introduced to Japan in the form of the Chinese writing system, by way ofBaekje
Baekje or Paekche (; ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BCE to 660 CE. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla. While the three kingdoms were in separate existence, Baekje had the h ...
before the 5th century AD. Using this script, the Japanese king Bu presented a petition to Emperor Shun of Song in AD 478. After the ruin of Baekje, Japan invited scholars from China to learn more of the Chinese writing system. Japanese emperors gave an official rank to Chinese scholars (/) and spread the use of Chinese characters during the 7th and 8th centuries.
Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese is the language in which the classics of Chinese literature were written, from . For millennia thereafter, the written Chinese used in these works was imitated and iterated upon by scholars in a form now called Literary ...
, with Japanese names represented by characters used for their meanings and not their sounds. Later, during the 7th century AD, the Chinese-sounding phoneme principle was used to write pure Japanese poetry and prose, but some Japanese words were still written with characters for their meaning and not the original Chinese sound. This was the beginning of Japanese as a written language in its own right. By this time, the Japanese language was already very distinct from the Ryukyuan languages
The , also Lewchewan or Luchuan (), are the indigenous languages of the Ryukyu Islands, the southernmost part of the Japanese archipelago. Along with the Japanese language and the Hachijō language, they make up the Japonic language family.
Ju ...
.
An example of this mixed style is the , which was written in AD 712. Japanese writers then started to use Chinese characters to write Japanese in a style known as ''man'yōgana'', a syllabic script which used Chinese characters for their sounds in order to transcribe the words of Japanese speech mora by mora.
Over time, a writing system evolved. Chinese characters
Chinese characters are logographs used Written Chinese, to write the Chinese languages and others from regions historically influenced by Chinese culture. Of the four independently invented writing systems accepted by scholars, they represe ...
(kanji
are logographic Chinese characters, adapted from Chinese family of scripts, Chinese script, used in the writing of Japanese language, Japanese. They were made a major part of the Japanese writing system during the time of Old Japanese and are ...
) were used to write either words borrowed from Chinese, or Japanese words with the same or similar meanings. Chinese characters were also used to write grammatical elements; these were simplified, and eventually became two moraic scripts: hiragana
is a Japanese language, Japanese syllabary, part of the Japanese writing system, along with ''katakana'' as well as ''kanji''.
It is a phonetic lettering system. The word ''hiragana'' means "common" or "plain" kana (originally also "easy", ...
and katakana
is a Japanese syllabary, one component of the Japanese writing system along with hiragana, kanji and in some cases the Latin script (known as rōmaji).
The word ''katakana'' means "fragmentary kana", as the katakana characters are derived fr ...
which were developed based on Man'yōgana. Some scholars claim that Manyogana originated from Baekje, but this hypothesis is denied by mainstream Japanese scholars.
Hiragana and katakana were first simplified from kanji, and hiragana, emerging somewhere around the 9th century, was mainly used by women. Hiragana was seen as an informal language, whereas katakana and kanji were considered more formal and were typically used by men and in official settings. However, because of hiragana's accessibility, more and more people began using it. Eventually, by the 10th century, hiragana was used by everyone.
Modern Japanese is written in a mixture of three main systems: kanji, characters of Chinese origin used to represent both Chinese loanword
A loanword (also a loan word, loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language (the recipient or target language), through the process of borrowing. Borrowing is a metaphorical term t ...
s into Japanese and a number of native Japanese morpheme
A morpheme is any of the smallest meaningful constituents within a linguistic expression and particularly within a word. Many words are themselves standalone morphemes, while other words contain multiple morphemes; in linguistic terminology, this ...
s; and two syllabaries
In the linguistic study of written languages, a syllabary is a set of written symbols that represent the syllables or (more frequently) morae which make up words.
A symbol in a syllabary, called a syllabogram, typically represents an (option ...
: hiragana and katakana. The Latin script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Gree ...
(or ''rōmaji'' in Japanese) is used to a certain extent, such as for imported acronyms and to transcribe Japanese names and in other instances where non-Japanese speakers need to know how to pronounce a word (such as "ramen" at a restaurant). Arabic numerals are much more common than the kanji numerals when used in counting, but kanji numerals are still used in compounds, such as .
Historically, attempts to limit the number of kanji in use commenced in the mid-19th century, but government did not intervene until after Japan's defeat in the Second World War. During the post-war occupation (and influenced by the views of some U.S. officials), various schemes including the complete abolition of kanji and exclusive use of rōmaji were considered. The ''jōyō kanji
The are those kanji listed on the , officially announced by the Japanese Ministry of Education. The current List of jōyō kanji, list of 2,136 characters was issued in 2010. It is a slightly modified version of the tōyō kanji, kanji, which ...
'' ("common use kanji"), originally called '' tōyō kanji'' (kanji for general use) scheme arose as a compromise solution.
Japanese students begin to learn kanji from their first year at elementary school. A guideline created by the Japanese Ministry of Education, the list of ''kyōiku kanji
The are kanji which Japanese elementary school students should learn from first through sixth grade. Also known as , these kanji are listed on the . The table is developed and maintained by the Japanese Ministry of Education (MEXT). Although t ...
'' ("education kanji", a subset of ''jōyō kanji
The are those kanji listed on the , officially announced by the Japanese Ministry of Education. The current List of jōyō kanji, list of 2,136 characters was issued in 2010. It is a slightly modified version of the tōyō kanji, kanji, which ...
''), specifies the 1,006 simple characters a child is to learn by the end of sixth grade. Children continue to study another 1,130 characters in junior high school, covering in total 2,136 ''jōyō kanji''. The official list of ''jōyō kanji'' has been revised several times, but the total number of officially sanctioned characters has remained largely unchanged.
As for kanji for personal names, the circumstances are somewhat complicated. ''Jōyō kanji'' and '' jinmeiyō kanji'' (an appendix of additional characters for names) are approved for registering personal names. Names containing unapproved characters are denied registration. However, as with the list of ''jōyō kanji'', criteria for inclusion were often arbitrary and led to many common and popular characters being disapproved for use. Under popular pressure and following a court decision holding the exclusion of common characters unlawful, the list of ''jinmeiyō kanji'' was substantially extended from 92 in 1951 (the year it was first decreed) to 983 in 2004. Furthermore, families whose names are not on these lists were permitted to continue using the older forms.
Hiragana
''Hiragana
is a Japanese language, Japanese syllabary, part of the Japanese writing system, along with ''katakana'' as well as ''kanji''.
It is a phonetic lettering system. The word ''hiragana'' means "common" or "plain" kana (originally also "easy", ...
'' are used for words without kanji representation, for words no longer written in kanji, for replacement of rare kanji that may be unfamiliar to intended readers, and also following kanji to show conjugational endings. Because of the way verbs (and adjectives) in Japanese are conjugated, kanji alone cannot fully convey Japanese tense and mood, as kanji cannot be subject to variation when written without losing their meaning. For this reason, hiragana are appended to kanji to show verb and adjective conjugations. Hiragana used in this way are called okurigana. Hiragana can also be written in a superscript called furigana
is a Japanese reading aid consisting of smaller kana (syllabic characters) printed either above or next to kanji (logographic characters) or other characters to indicate their pronunciation. It is one type of ruby text. Furigana is also know ...
above or beside a kanji to show the proper reading. This is done to facilitate learning, as well as to clarify particularly old or obscure (or sometimes invented) readings.
Katakana
''Katakana
is a Japanese syllabary, one component of the Japanese writing system along with hiragana, kanji and in some cases the Latin script (known as rōmaji).
The word ''katakana'' means "fragmentary kana", as the katakana characters are derived fr ...
'', like hiragana, constitute a syllabary
In the Linguistics, linguistic study of Written language, written languages, a syllabary is a set of grapheme, written symbols that represent the syllables or (more frequently) mora (linguistics), morae which make up words.
A symbol in a syllaba ...
; katakana are primarily used to write foreign words, plant and animal names, and for emphasis. For example, "Australia" has been adapted as , and "supermarket" has been adapted and shortened into .
Grammar
Sentence structure
Japanese word order is classified as subject–object–verb. Unlike manyIndo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
, the only strict rule of word order is that the verb must be placed at the end of a sentence (possibly followed by sentence-end particles). This is because Japanese sentence elements are marked with particles that identify their grammatical functions.
The basic sentence structure is topic–comment. Once the topic has been stated using the particle , it is normally omitted in subsequent sentences, and the next use of ''wa'' will change the topic. For instance, someone may begin a conversation with a sentence that includes . Each person may say a number of comments regarding Tanaka as the topic, and someone could change the topic to Naoko with a sentence including .
As these example translations illustrate, a sentence may include a topic, but the topic is not part of sentence's core statement. Japanese is often called a topic-prominent language because of its strong tendency to indicate the topic separately from the subject, and the two do not always coincide. That is, a sentence might not involve the topic directly at all. To replicate this effect in English, consider "As for Naoko, people are rude." The topic, "Naoko," provides context to the comment about the subject, "people," and the sentence as a whole indicates that "people are rude" is a statement relevant to Naoko. However, the sentence's comment does not describe Naoko directly at all, and whatever the sentence indicates about Naoko is an inference. The topic is not the core of the sentence; the core of the sentence is always the comment.
In a basic comment, the subject is marked with the particle , and the rest of the comment describes the subject. For example, in , ''ga'' indicates that "elephant" is the subject of the sentence. Context determines whether the speaker means a single elephant or elephants plural. The copula ends the sentence, indicating that the subject is equivalent to the rest of the comment. Here, ''doubutsu'' means ''animal''. Therefore, the sentence means " heelephant is nanimal" or "Elephants are animals." A basic comment can end in three ways: with the copula ''da'', with a different verb, or with an adjective ending in the kana . A sentence ending might also be decorated with particles that alter the way the sentence is meant to be interpreted, as in . This is also why ''da'' is replaced with when the speaker is talking to someone they do not know well: it makes the sentence more polite.
Often, ''ga'' implies distinction of the subject within the topic, so the previous example comment would make the most sense within a topic where not all of the relevant subjects were animals. For example, in , the particle ''wa'' indicates the topic is ''kono ganbutsu'' ("this toy" or "these toys"). In English, if there are many toys and one is an elephant, this could mean "Among these toys, heelephant is nanimal." That said, if the subject is clearly a subtopic, this differentiation effect may or may not be relevant, such as in . The equivalent sentence, "As for the Japanese language, grammar is easy," might be a general statement that Japanese grammar is easy or a statement that grammar is an especially easy feature of the Japanese language. Context should reveal which.
Because ''ga'' marks the subject of the sentence but the sentence overall is intended to be relevant to the topic indicated by ''wa'', translations of Japanese into English often elide the difference between these particles. For example, the phrase ''watashi wa zou ga suki da'' literally means "As for myself, elephants are likeable." The sentence about myself describes elephants as having a likeable quality. From this, it is clear that I like elephants, and this sentence is often translated into English as "I like elephants." However, to do so changes the subject of the sentence (from "Elephant" to "I") and the verb (from "is" to "like"); it does not reflect Japanese grammar.
Japanese grammar tends toward brevity; the subject or object of a sentence need not be stated and pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (Interlinear gloss, glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase.
Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts of speech, but so ...
s may be omitted if they can be inferred from context. In the example above, ''zou ga doubutsu da'' would mean " heelephant is nanimal", while ''doubutsu da'' by itself would mean " heyare animals." In especially casual speech, many speakers would omit the copula, leaving the noun ''doubutsu'' to mean " hey areanimals." A single verb can be a complete sentence: . In addition, since adjectives can form the predicate in a Japanese sentence (below), a single adjective can be a complete sentence: ).
Nevertheless, unlike the topic, the subject is always implied: all sentences which omit a ''ga'' particle must have an implied subject that could be specified with a ''ga'' particle. For example, means "As for this cat, tis Loki." An equivalent sentence might read , meaning "As for this cat, this is Loki." However, in the same way it is unusual to state the subject twice in the English sentence, it is unusual to specify that redundant subject in Japanese. Rather than replace the redundant subject with a word like "it," the redundant subject is omitted from the Japanese sentence. It is obvious from the context that the first sentence refers to the cat by the name "Loki," and the explicit subject of the second sentence contributes no information.
While the language has some words that are typically translated as pronouns, these are not used as frequently as pronouns in some Indo-European languages, and function differently. In some cases, Japanese relies on special verb forms and auxiliary verbs to indicate the direction of benefit of an action: "down" to indicate the out-group gives a benefit to the in-group, and "up" to indicate the in-group gives a benefit to the out-group. Here, the in-group includes the speaker and the out-group does not, and their boundary depends on context. For example, means " e/she/theyexplained tto e/us. Similarly, means " /weexplained tto im/her/them. Such beneficiary auxiliary verbs thus serve a function comparable to that of pronouns and prepositions in Indo-European languages to indicate the actor and the recipient of an action.
Japanese "pronouns" also function differently from most modern Indo-European pronouns (and more like nouns) in that they can take modifiers as any other noun may. For instance, one does not say in English:
The amazed he ran down the street. (grammatically incorrect insertion of a pronoun)But one ''can'' grammatically say essentially the same thing in Japanese:
This is partly because these words evolved from regular nouns, such as "you" ( "lord"), "you" ( "that side, yonder"), and "I" ( "servant"). This is why some linguists do not classify Japanese "pronouns" as pronouns, but rather as referential nouns, much like Spanish (contracted from , "your ( majestic plural) grace") or Portuguese (from ). Japanese personal pronouns are generally used only in situations requiring special emphasis as to who is doing what to whom. The choice of words used as pronouns is correlated with the sex of the speaker and the social situation in which they are spoken: men and women alike in a formal situation generally refer to themselves as or (also , hyper-polite form), while men in rougher or intimate conversation are much more likely to use the word or ''boku''. Similarly, different words such as ''anata'', ''kimi'', and (, more formally "the one before me") may refer to a listener depending on the listener's relative social position and the degree of familiarity between the speaker and the listener. When used in different social relationships, the same word may have positive (intimate or respectful) or negative (distant or disrespectful) connotations. Japanese often use titles of the person referred to where pronouns would be used in English. For example, when speaking to one's teacher, it is appropriate to use , but inappropriate to use ''anata''. This is because ''anata'' is used to refer to people of equal or lower status, and one's teacher has higher status.Transliteration: (grammatically correct)
Inflection and conjugation
Japanese nouns have no grammatical number, gender or article aspect. The noun may refer to a single book or several books; can mean "person" or "people", and can be "tree" or "trees". Where number is important, it can be indicated by providing a quantity (often with a counter word) or (rarely) by adding a suffix, or sometimes by duplication (e.g. , , usually written with an iteration mark as ). Words for people are usually understood as singular. Thus ''Tanaka-san'' usually means ''Mx Tanaka''. Words that refer to people and animals can be made to indicate a group of individuals through the addition of a collective suffix (a noun suffix that indicates a group), such as ''-tachi'', but this is not a true plural: the meaning is closer to the English phrase "and company". A group described as ''Tanaka-san-tachi'' may include people not named Tanaka. Some Japanese nouns are effectively plural, such as ''hitobito'' "people" and ''wareware'' "we/us", while the word ''tomodachi'' "friend" is considered singular, although plural in form. Verbs are conjugated to show tenses, of which there are two: past and non-past, which is used for the present and the future. For verbs that represent an ongoing process, the ''-te iru'' form indicates a continuous (or progressive) aspect, similar to the suffix ''ing'' in English. For others that represent a change of state, the ''-te iru'' form indicates a perfect aspect. For example, ''kite iru'' means "They have come (and are still here)", but ''tabete iru'' means "They are eating". Questions (both with an interrogative pronoun and yes/no questions) have the same structure as affirmative sentences, but with intonation rising at the end. In the formal register, the question particle ''-ka'' is added. For example, becomes . In a more informal tone sometimes the particle is added instead to show a personal interest of the speaker: ''Dōshite konai-no?'' "Why aren't (you) coming?". Some simple queries are formed simply by mentioning the topic with an interrogative intonation to call for the hearer's attention: ''Kore wa?'' "(What about) this?"; () "(What's your) name?". Negatives are formed by inflecting the verb. For example, becomes . Plain negative forms are ''i''-adjectives (see below) and inflect as such, e.g. . The so-called ''-te'' verb form is used for a variety of purposes: either progressive or perfect aspect (see above); combining verbs in a temporal sequence (''Asagohan o tabete sugu dekakeru'' "I'll eat breakfast and leave at once"), simple commands, conditional statements and permissions (''Dekakete-mo ii?'' "May I go out?"), etc. The word ''da'' (plain), ''desu'' (polite) is the copula verb. It corresponds to the English verb ''is'' and marks tense when the verb is conjugated into its past form ''datta'' (plain), ''deshita'' (polite). This comes into use because only ''i''-adjectives and verbs can carry tense in Japanese. Two additional common verbs are used to indicate existence ("there is") or, in some contexts, property: ''aru'' (negative ''nai'') and ''iru'' (negative ''inai''), for inanimate and animate things, respectively. For example, ''Neko ga iru'' "There's a cat", ''Ii kangae-ga nai'' " haven't got a good idea". The verb "to do" (''suru'', polite form ''shimasu'') is often used to make verbs from nouns (''ryōri suru'' "to cook", ''benkyō suru'' "to study", etc.) and has been productive in creating modern slang words. Japanese also has a huge number of compound verbs to express concepts that are described in English using a verb and an adverbial particle (e.g. ''tobidasu'' "to fly out, to flee", from ''tobu'' "to fly, to jump" + ''dasu'' "to put out, to emit"). There are three types of adjectives (see Japanese adjectives): # , or ''i'' adjectives, which have a conjugating ending . An example of this is , which can become past ( "it was hot"), or negative ( "it is not hot"). ''nai'' is also an ''i'' adjective, which can become past (i.e., "it was not hot"). #: "a hot day". # , or ''na'' adjectives, which are followed by a form of the copula, usually ''na''. For example, ''hen'' (strange) #: "a strange person". # , also called true adjectives, such as ''ano'' "that" #: "that mountain". Both ''keiyōshi'' and ''keiyōdōshi'' may predicate sentences. For example,Both inflect, though they do not show the full range of conjugation found in true verbs. The ''rentaishi'' in Modern Japanese are few in number, and unlike the other words, are limited to directly modifying nouns. They never predicate sentences. Examples include ''ookina'' "big", ''kono'' "this", ''iwayuru'' "so-called" and ''taishita'' "amazing". Both ''keiyōdōshi'' and ''keiyōshi'' form"The rice is hot." "He's strange."
adverb An adverb is a word or an expression that generally modifies a verb, an adjective, another adverb, a determiner, a clause, a preposition, or a sentence. Adverbs typically express manner, place, time, frequency, degree, or level of certainty by ...
s, by following with ''ni'' in the case of ''keiyōdōshi'':
"become strange",and by changing ''i'' to ''ku'' in the case of ''keiyōshi'':
"become hot".The grammatical function of nouns is indicated by
postposition
Adpositions are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositions (which precede their complemen ...
s, also called particles. These include for example:
* for the nominative case
In grammar, the nominative case ( abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case, or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb, or (in Latin and formal variants ...
.
: "He did it."
* for the accusative case
In grammar, the accusative case ( abbreviated ) of a noun is the grammatical case used to receive the direct object of a transitive verb.
In the English language, the only words that occur in the accusative case are pronouns: "me", "him", "he ...
.
: "What will (you) eat?"
* for the dative case
In grammar, the dative case ( abbreviated , or sometimes when it is a core argument) is a grammatical case used in some languages to indicate the recipient or beneficiary of an action, as in "", Latin for "Maria gave Jacob a drink". In this examp ...
.
: "Please give it to Mx Tanaka."
: It is also used for the lative case, indicating a motion to a location.
: "I want to go to Japan."
* However, is more commonly used for the lative case.
: "Won't you go to the party?"
* for the genitive case
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive ca ...
, or nominalizing phrases.
: "my camera"
: "(I) like going skiing."
* for the topic. It can co-exist with the case markers listed above, and it overrides ''ga'' and (in most cases) ''o''.
: (literally) "As for me, sushi is good." The nominative marker ''ga'' after ''watashi'' is hidden under ''wa''.
Note: The subtle difference between ''wa'' and ''ga'' in Japanese cannot be derived from the English language as such, because the distinction between sentence topic and subject is not made there. While ''wa'' indicates the topic, which the rest of the sentence describes or acts upon, it carries the implication that the subject indicated by ''wa'' is not unique, or may be part of a larger group.
''Ikeda-san wa yonjū-ni sai da.'' "As for Mx Ikeda, they are forty-two years old." Others in the group may also be of that age.Absence of ''wa'' often means the subject is the focus of the sentence.
''Ikeda-san ga yonjū-ni sai da.'' "It is Mx Ikeda who is forty-two years old." This is a reply to an implicit or explicit question, such as "who in this group is forty-two years old?"
Politeness
Japanese has an extensive grammatical system to express politeness and formality. This reflects the hierarchical nature of Japanese society. The Japanese language can express differing levels of social status. The differences in social position are determined by a variety of factors including job, age, experience, or even psychological state (e.g., a person asking a favour tends to do so politely). The person in the lower position is expected to use a polite form of speech, whereas the other person might use a plainer form. Strangers will also speak to each other politely. Japanese children begin learning and using polite speech in basic forms from an early age, but their use of more formal and sophisticated polite speech becomes more common and expected as they enter their teenage years and start engaging in more adult-like social interactions. See '' uchi–soto''. Whereas is commonly aninflection
In linguistic Morphology (linguistics), morphology, inflection (less commonly, inflexion) is a process of word formation in which a word is modified to express different grammatical category, grammatical categories such as grammatical tense, ...
al system, and often employ many special honorific and humble alternate verbs: ''iku'' "go" becomes ''ikimasu'' in polite form, but is replaced by ''irassharu'' in honorific speech and ''ukagau'' or ''mairu'' in humble speech.
The difference between honorific and humble speech is particularly pronounced in the Japanese language. Humble language is used to talk about oneself or one's own group (company, family) whilst honorific language is mostly used when describing the interlocutor and their group. For example, the ''-san'' suffix ("Mr", "Mrs", "Miss", or "Mx") is an example of honorific language. It is not used to talk about oneself or when talking about someone from one's company to an external person, since the company is the speaker's in-group. When speaking directly to one's superior in one's company or when speaking with other employees within one's company about a superior, a Japanese person will use vocabulary and inflections of the honorific register to refer to the in-group superior and their speech and actions. When speaking to a person from another company (i.e., a member of an out-group), however, a Japanese person will use the plain or the humble register to refer to the speech and actions of their in-group superiors. In short, the register used in Japanese to refer to the person, speech, or actions of any particular individual varies depending on the relationship (either in-group or out-group) between the speaker and listener, as well as depending on the relative status of the speaker, listener, and third-person referents.
Most noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an Object (grammar), object or Subject (grammar), subject within a p ...
s in the Japanese language may be made polite by the addition of ''o-'' or ''go-'' as a prefix. ''o-'' is generally used for words of native Japanese origin, whereas ''go-'' is affixed to words of Chinese derivation. In some cases, the prefix has become a fixed part of the word, and is included even in regular speech, such as ''gohan'' 'cooked rice; meal.' Such a construction often indicates deference to either the item's owner or to the object itself. For example, the word ''tomodachi'' 'friend,' would become ''o-tomodachi'' when referring to the friend of someone of higher status (though mothers often use this form to refer to their children's friends). On the other hand, a polite speaker may sometimes refer to ''mizu'' 'water' as ''o-mizu'' to show politeness.
Vocabulary
There are three main sources of words in the Japanese language: the or ; ; and . The original language of Japan, or at least the original language of a certain population that was ancestral to a significant portion of the historical and present Japanese nation, was the so-called or infrequently , i.e. " Yamato words"), which in scholarly contexts is sometimes referred to as ( or rarely , i.e. the " Wa language"). In addition to words from this original language, present-day Japanese includes a number of words that were either borrowed from Chinese or constructed from Chinese roots following Chinese patterns. These words, known as , entered the language from the 5th century onwards by contact with Chinese culture. According to the Japanese dictionary, ''kango'' comprise 49.1% of the total vocabulary, ''wago'' make up 33.8%, other foreign words or account for 8.8%, and the remaining 8.3% constitute hybridized words or that draw elements from more than one language. There are also a great number of words ofmimetic
Mimesis (; , ''mīmēsis'') is a term used in literary criticism and philosophy that carries a wide range of meanings, including ''imitatio'', imitation, Similarity (philosophy), similarity, receptivity, representation (arts), representation, m ...
origin in Japanese, with Japanese having a rich collection of sound symbolism, both onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia (or rarely echoism) is a type of word, or the process of creating a word, that phonetics, phonetically imitates, resembles, or suggests the sound that it describes. Common onomatopoeias in English include animal noises such as Oin ...
for physical sounds, and more abstract words. A small number of words have come into Japanese from the Ainu language. ''Tonakai'' (reindeer
The reindeer or caribou (''Rangifer tarandus'') is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, subarctic, tundra, taiga, boreal, and mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. It is the only re ...
), ''rakko'' ( sea otter) and '' shishamo'' ( smelt, a type of fish) are well-known examples of words of Ainu origin.
Words of different origins occupy different registers in Japanese. Like Latin-derived words in English, ''kango'' words are typically perceived as somewhat formal or academic compared to equivalent Yamato words. Indeed, it is generally fair to say that an English word derived from Latin/French roots typically corresponds to a Sino-Japanese word in Japanese, whereas an Anglo-Saxon word would best be translated by a Yamato equivalent.
Incorporating vocabulary from European languages
There are over 250 languages indigenous to Europe, and most belong to the Indo-European language family. Out of a total European population of 744 million as of 2018, some 94% are native speakers of an Indo-European language. The three larges ...
, ''gairaigo'', began with borrowings from Portuguese in the 16th century, followed by words from Dutch during Japan's long isolation of the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
. With the Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored Imperial House of Japan, imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Althoug ...
and the reopening of Japan in the 19th century, words were borrowed from German, French, and English. Today most borrowings are from English.
In the Meiji era, the Japanese also coined many neologisms using Chinese roots and morphology to translate European concepts; these are known as '' wasei-kango'' (Japanese-made Chinese words). Many of these were then imported into Chinese, Korean, and Vietnamese via their kanji in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. For example, , and are words derived from Chinese roots that were first created and used by the Japanese, and only later borrowed into Chinese and other East Asian languages. As a result, Japanese, Chinese, Korean, and Vietnamese share a large common corpus of vocabulary in the same way many Greek- and Latin-derived words – both inherited or borrowed into European languages, or modern coinages from Greek or Latin roots – are shared among modern European languages – see classical compound
Neoclassical compounds are compound words composed from combining forms (which act as affixes or stems) derived from Classical_language#Classical_studies, classical languages (classical Latin or ancient Greek) root (linguistics), roots. Neo-Lati ...
.
In the past few decades, '' wasei-eigo'' ("made-in-Japan English") has become a prominent phenomenon. Words such as (< ''one'' + ''pattern'', "to be in a rut", "to have a one-track mind") and (< ''skin'' + ''-ship'', "physical contact"), although coined by compounding English roots, are nonsensical in most non-Japanese contexts; exceptions exist in nearby languages such as Korean however, which often use words such as ''skinship'' and ''rimokon'' (remote control) in the same way as in Japanese.
The popularity of many Japanese cultural exports has made some native Japanese words familiar in English, including ''emoji
An emoji ( ; plural emoji or emojis; , ) is a pictogram, logogram, ideogram, or smiley embedded in text and used in electronic messages and web pages. The primary function of modern emoji is to fill in emotional cues otherwise missing from type ...
, futon, haiku
is a type of short form poetry that originated in Japan. Traditional Japanese haiku consist of three phrases composed of 17 Mora (linguistics), morae (called ''On (Japanese prosody), on'' in Japanese) in a 5, 7, 5 pattern; that include a ''kire ...
, judo
is an unarmed gendai budō, modern Japanese martial art, combat sport, Olympic sport (since 1964), and the most prominent form of jacket wrestling competed internationally.『日本大百科全書』電子版【柔道】(CD-ROM version of Encyc ...
, kamikaze, karaoke, karate
(; ; Okinawan language, Okinawan pronunciation: ), also , is a martial arts, martial art developed in the Ryukyu Kingdom. It developed from the Okinawan martial arts, indigenous Ryukyuan martial arts (called , "hand"; ''tī'' in Okinawan) un ...
, ninja
A , or was a spy and infiltrator in pre-modern Japan. The functions of a ninja included siege and infiltration, ambush, reconnaissance, espionage, deception, and later bodyguarding.Kawakami, pp. 21–22 Antecedents may have existed as ear ...
, origami, rickshaw'' (from ), ''samurai
The samurai () were members of the warrior class in Japan. They were originally provincial warriors who came from wealthy landowning families who could afford to train their men to be mounted archers. In the 8th century AD, the imperial court d ...
, sayonara, Sudoku, sumo
is a form of competitive full-contact wrestling where a ''rikishi'' (wrestler) attempts to force his opponent out of a circular ring (''dohyō'') or into touching the ground with any body part other than the soles of his feet (usually by th ...
, sushi
is a traditional Japanese dish made with , typically seasoned with sugar and salt, and combined with a variety of , such as seafood, vegetables, or meat: raw seafood is the most common, although some may be cooked. While sushi comes in n ...
, tofu
or bean curd is a food prepared by Coagulation (milk), coagulating soy milk and then pressing the resulting curds into solid white blocks of varying softness: ''silken'', ''soft'', ''firm'', and ''extra (or super) firm''. It originated in Chin ...
, tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from , ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions (including detonations, ...
, tycoon''. See list of English words of Japanese origin
Words of Japanese origin have entered many languages. Some words are simple transliterations of Japanese language words for concepts inherent to Japanese culture. The words on this page are an incomplete list of words which are listed in major En ...
for more.
Gender in the Japanese language
Depending on the speakers’ gender, different linguistic features might be used. The typical lect used by females is called and the one used by males is called . ''Joseigo'' and ''danseigo'' are different in various ways, including first-person pronouns (such as ''watashi'' or ''atashi'' for women and for men) and sentence-final particles (such as , , or for ''joseigo'', or , , or for ''danseigo''). In addition to these specific differences, expressions and pitch can also be different. For example, ''joseigo'' is more gentle, polite, refined, indirect, modest, and exclamatory, and often accompanied by raised pitch.Kogal slang
In the 1990s, the traditional feminine speech patterns and stereotyped behaviors were challenged, and a popular culture of “naughty” teenage girls emerged, called , sometimes referenced in English-language materials as “kogal”. Their rebellious behaviors, deviant language usage, the particular make-up called , and the fashion became objects of focus in the mainstream media. Although kogal slang was not appreciated by older generations, the ''kogyaru'' continued to create terms and expressions. Kogal culture also changed Japanese norms of gender and the Japanese language.Non-native study
Many major universities throughout the world provide Japanese language courses, and a number of secondary and even primary schools worldwide offer courses in the language. This is a significant increase from beforeWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
; in 1940, only 65 Americans not of Japanese descent were able to read, write, and understand the language. Beate Sirota Gordon commencement address at Mills College, 14 May 2011"Sotomayor, Denzel Washington, GE CEO Speak to Graduates"
C-SPAN (US). 30 May 2011; retrieved 2011-05-30 International interest in the Japanese language dates from the 19th century but has become more prevalent following Japan's economic bubble of the 1980s and the global popularity of
Japanese popular culture
Japanese popular culture includes Cinema of Japan, Japanese cinema, Japanese cuisine, cuisine, Television in Japan, television programs, anime, manga, Video gaming in Japan, video games, Music of Japan, music, and doujinshi, all of which retain ol ...
(such as anime
is a Traditional animation, hand-drawn and computer animation, computer-generated animation originating from Japan. Outside Japan and in English, ''anime'' refers specifically to animation produced in Japan. However, , in Japan and in Ja ...
and video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
s) since the 1990s. As of 2015, more than 3.6 million people studied the language worldwide, primarily in East and Southeast Asia. Nearly one million Chinese, 745,000 Indonesians, 556,000 South Koreans and 357,000 Australians studied Japanese in lower and higher educational institutions. Between 2012 and 2015, considerable growth of learners originated in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
(20.5%), Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
(34.1%), Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
(38.7%) and the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
(54.4%).
The Japanese government provides standardized tests to measure spoken and written comprehension of Japanese for second language learners; the most prominent is the Japanese-Language Proficiency Test (JLPT), which features five levels of exams. The JLPT is offered twice a year.
Example text
Article 1 of the ''Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the Human rights, rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN Drafting of the Universal D ...
'' in Japanese:
See also
* Aizuchi * Culture of Japan * Japanese dictionary * Japanese exonyms * Japanese language and computers *Japanese literature
Japanese literature throughout most of its history has been influenced by cultural contact with neighboring Asian literatures, most notably China and its literature. Early texts were often written in pure Classical Chinese or , a Chinese-Japa ...
* Japanese name
in modern times consist of a family name (surname) followed by a given name. Japanese names are usually written in kanji, where the pronunciation follows a special set of rules. Because parents when naming children, and foreigners when adoptin ...
* Japanese punctuation
* Japanese profanity
* Japanese Sign Language family
* Japanese words and words derived from Japanese in other languages at Wiktionary, Wikipedia's sibling project
* Classical Japanese
* Romanization of Japanese
** Hepburn romanization
is the main system of Romanization of Japanese, romanization for the Japanese language. The system was originally published in 1867 by American Christian missionary and physician James Curtis Hepburn as the standard in the first edition of h ...
* Rendaku
* Yojijukugo
*Other:
** History of writing in Vietnam
Notes
References
Citations
Works cited
* Bloch, Bernard (1946). Studies in colloquial Japanese I: Inflection. ''Journal of the American Oriental Society'', ''66'', pp. 97–130. * Bloch, Bernard (1946). Studies in colloquial Japanese II: Syntax. ''Language'', ''22'', pp. 200–248. * Chafe, William L. (1976). Giveness, contrastiveness, definiteness, subjects, topics, and point of view. In C. Li (Ed.), ''Subject and topic'' (pp. 25–56). New York: Academic Press. . * Dalby, Andrew. (2004)"Japanese"
in ''Dictionary of Languages: the Definitive Reference to More than 400 Languages.'' New York: Columbia University Press. ; * * * * Kuno, Susumu (1973). ''The structure of the Japanese language''. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. . * Kuno, Susumu. (1976). "Subject, theme, and the speaker's empathy: A re-examination of relativization phenomena", in Charles N. Li (Ed.), ''Subject and topic'' (pp. 417–444). New York: Academic Press. . * McClain, Yoko Matsuoka. (1981). ''Handbook of modern Japanese grammar:'' 'Kōgo Nihon bumpō'' Tokyo: Hokuseido Press. . * Miller, Roy (1967). ''The Japanese language''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. * Miller, Roy (1980). ''Origins of the Japanese language: Lectures in Japan during the academic year, 1977–78''. Seattle: University of Washington Press. . * Mizutani, Osamu; & Mizutani, Nobuko (1987). ''How to be polite in Japanese:'' 'Nihongo no keigo'' Tokyo:
The Japan Times
''The Japan Times'' is Japan's largest and oldest English-language daily newspaper. It is published by , a subsidiary of News2u Holdings, Inc. It is headquartered in the in Kioicho, Chiyoda, Tokyo.
History
''The Japan Times'' was launched by ...
. .
*
*
*
* Shibamoto, Janet S. (1985). ''Japanese women's language''. New York: Academic Press. . Graduate Level
* (pbk).
* Tsujimura, Natsuko (1996). ''An introduction to Japanese linguistics''. Cambridge, MA: Blackwell Publishers. (hbk); (pbk). Upper Level Textbooks
* Tsujimura, Natsuko (Ed.) (1999). ''The handbook of Japanese linguistics''. Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers. . Readings/Anthologies
*
Further reading
* * * * * *External links
National Institute for Japanese Language and Linguistics
Japanese Language Student's Handbook
(archived 2 January 2010) {{Authority control Agglutinative languages Languages attested from the 8th century Languages of Japan Languages of Palau Subject–object–verb languages Syllable-timed languages