|
Anaphase
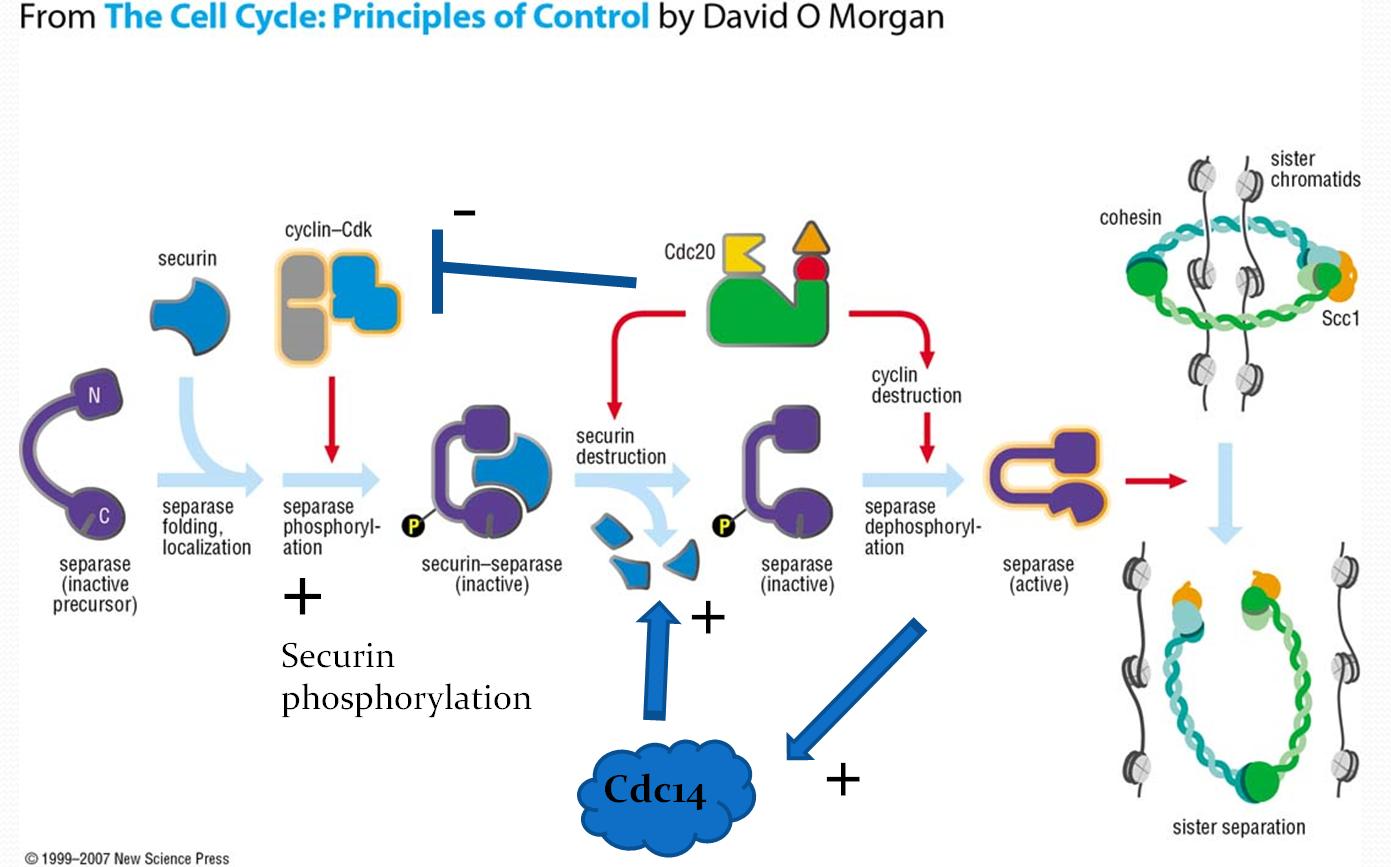
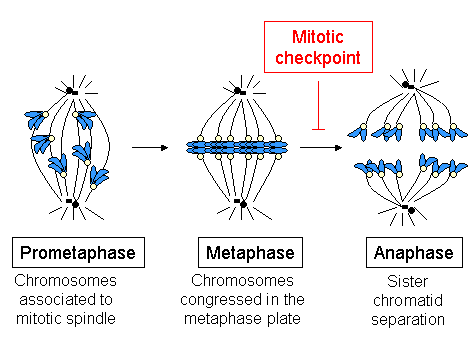
Anaphase () is the stage of mitosis after the process of metaphase, when replicated chromosomes are split and the newly-copied chromosomes (daughter chromatids) are moved to opposite poles of the cell. Chromosomes also reach their overall maximum condensation in late anaphase, to help chromosome segregation and the re-formation of the nucleus. Anaphase starts when the anaphase promoting complex marks an Chaperone (protein), inhibitory chaperone called securin for destruction by Ubiquitin, ubiquitylating it. Securin is a protein which inhibits a protease known as separase. The destruction of securin unleashes separase which then breaks down cohesin, a protein responsible for holding sister chromatids together. At this point, three subclasses of microtubule unique to mitosis are involved in creating the forces necessary to separate the chromatids: kinetochore microtubules, interpolar microtubules, and Aster_(cell_biology)#Astral_microtubules, astral microtubules. The centromere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphase-promoting Complex
Anaphase-promoting complex (also called the cyclosome or APC/C) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that marks target cell cycle proteins for degradation by the 26S proteasome. The APC/C is a large complex of 11–13 subunit proteins, including a cullin (ANAPC2, Apc2) and RING (ANAPC11, Apc11) subunit much like SCF complex, SCF. Other parts of the APC/C have unknown functions but are highly Conserved sequence, conserved. It was the discovery of the APC/C (and SCF complex, SCF) and their key role in eukaryotic cell-cycle regulation that established the importance of ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis in cell biology. Once perceived as a system exclusively involved in removing damaged protein from the cell, ubiquitination and subsequent protein degradation by the proteasome is now perceived as a universal regulatory mechanism for signal transduction whose importance approaches that of protein phosphorylation. In 2014, the APC/C was mapped in 3D at a resolution of less than a nanometre, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphase Promoting Complex
Anaphase-promoting complex (also called the cyclosome or APC/C) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that marks target cell cycle proteins for degradation by the 26S proteasome. The APC/C is a large complex of 11–13 subunit proteins, including a cullin ( Apc2) and RING ( Apc11) subunit much like SCF. Other parts of the APC/C have unknown functions but are highly conserved. It was the discovery of the APC/C (and SCF) and their key role in eukaryotic cell-cycle regulation that established the importance of ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis in cell biology. Once perceived as a system exclusively involved in removing damaged protein from the cell, ubiquitination and subsequent protein degradation by the proteasome is now perceived as a universal regulatory mechanism for signal transduction whose importance approaches that of protein phosphorylation. In 2014, the APC/C was mapped in 3D at a resolution of less than a nanometre, which also uncovered its secondary structure. This findin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Separase
Separase, also known as separin, is a cysteine protease responsible for triggering anaphase by hydrolysing cohesin, which is the protein responsible for binding sister chromatids during the early stage of anaphase. In humans, separin is encoded by the ''ESPL1'' gene. History In ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae, S. cerevisiae'', separase is encoded by the ''esp1'' gene. Esp1 was discovered by Kim Nasmyth and coworkers in 1998. In 2021, structures of human separase were determined in complex with either securin or CDK1-cyclin B1-CKS1 using cryo-EM by scientists of the University of Geneva. Function Stable cohesion between sister chromatids before anaphase and their timely separation during anaphase are critical for cell division and chromosome inheritance. In vertebrates, sister chromatid cohesion is released in 2 steps via distinct mechanisms. The first step involves phosphorylation of STAG1 or STAG2 in the cohesin complex. The second step involves cleavage of the cohesin subuni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetochore
A kinetochore (, ) is a flared oblique-shaped protein structure associated with duplicated chromatids in eukaryotic cells where the spindle fibers, which can be thought of as the ropes pulling chromosomes apart, attach during cell division to pull sister chromatids apart. The kinetochore assembles on the centromere and links the chromosome to microtubule polymers from the mitotic spindle during mitosis and meiosis. The term kinetochore was first used in a footnote in a 1934 Cytology book by Lester W. Sharp and commonly accepted in 1936. Sharp's footnote reads: "The convenient term ''kinetochore'' (= movement place) has been suggested to the author by J. A. Moore", likely referring to John Alexander Moore who had joined Columbia University as a freshman in 1932. Monocentric organisms, including vertebrates, fungi, and most plants, have a single centromeric region on each chromosome which assembles a single, localized kinetochore. Holocentric organisms, such as nematodes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Securin
Securin is a protein involved in control of the metaphase-anaphase transition and anaphase onset. Following bi-orientation of chromosome pairs and inactivation of the spindle checkpoint system, the underlying regulatory system, which includes securin, produces an abrupt stimulus that induces highly synchronous chromosome separation in anaphase. Securin and Separase Securin is initially present in the cytoplasm and binds to separase, a protease that degrades the cohesin rings that link the two sister chromatids. Separase is vital for onset of anaphase. This securin-separase complex is maintained when securin is phosphorylated by Cdk1, inhibiting ubiquitination. When bound to securin, separase is not functional. In addition, both securin and separase are well conserved proteins (Figure 1). Note that separase cannot function without initially forming the securin-separase complex. This is because securin helps properly fold separase into the functional conformation. However, yeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Mitosis is preceded by the S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is followed by telophase and cytokinesis, which divide the cytoplasm, organelles, and cell membrane of one cell into two new cell (biology), cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic phase (M phase) of a cell cycle—the cell division, division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telophase
Telophase () is the final stage in both meiosis and mitosis in a eukaryotic cell. During telophase, the effects of prophase and prometaphase (the nucleolus and nuclear membrane disintegrating) are reversed. As chromosomes reach the cell poles, a nuclear envelope is re-assembled around each set of chromatids, the nucleoli reappear, and chromosomes begin to decondense back into the expanded chromatin that is present during interphase. The mitotic spindle is disassembled and remaining spindle microtubules are depolymerized. Telophase accounts for approximately 2% of the cell cycle's duration. Cytokinesis typically begins before late telophase and, when complete, segregates the two daughter nuclei between a pair of separate daughter cells. Telophase is primarily driven by the dephosphorylation of mitotic cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) substrates. Dephosphorylation of Cdk substrates The phosphorylation of the protein targets of M-Cdks (Mitotic Cyclin-dependent Kinases) drives sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphase
Anaphase () is the stage of mitosis after the process of metaphase, when replicated chromosomes are split and the newly-copied chromosomes (daughter chromatids) are moved to opposite poles of the cell. Chromosomes also reach their overall maximum condensation in late anaphase, to help chromosome segregation and the re-formation of the nucleus. Anaphase starts when the anaphase promoting complex marks an Chaperone (protein), inhibitory chaperone called securin for destruction by Ubiquitin, ubiquitylating it. Securin is a protein which inhibits a protease known as separase. The destruction of securin unleashes separase which then breaks down cohesin, a protein responsible for holding sister chromatids together. At this point, three subclasses of microtubule unique to mitosis are involved in creating the forces necessary to separate the chromatids: kinetochore microtubules, interpolar microtubules, and Aster_(cell_biology)#Astral_microtubules, astral microtubules. The centromere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cohesin
Cohesin is a protein complex that mediates Establishment of sister chromatid cohesion, sister chromatid cohesion, homologous recombination, and Topologically associating domain, DNA looping. Cohesin is formed of SMC3, SMC1A, SMC1, RAD21, SCC1 and SCC3 (STAG1, SA1 or STAG2, SA2 in humans). Cohesin holds sister chromatids together after DNA replication until anaphase when removal of cohesin leads to separation of sister chromatids. The complex forms a ring-like structure and it is believed that sister chromatids are held together by entrapment inside the cohesin ring. Cohesin is a member of the SMC proteins, SMC family of protein complexes which includes Condensin, Nucleoid#MukBEF, MukBEF and SMC-ScpAB. Cohesin was separately discovered in budding yeast (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'') both by Douglas Koshland and Kim Nasmyth in 1997. Structure and subunits Cohesin is a multi-subunit protein complex, made up of SMC1, SMC3, RAD21 and SCC3 (SA1 or SA2). SMC1 and SMC3 are members of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaphase
Metaphase ( and ) is a stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle in which chromosomes are at their second-most condensed and coiled stage (they are at their most condensed in anaphase). These chromosomes, carrying genetic information, align in the equator of the cell between the spindle poles at the metaphase plate, before being separated into each of the two daughter nuclei. This alignment marks the beginning of metaphase. Metaphase accounts for approximately 4% of the cell cycle's duration. In metaphase, microtubules from both duplicated centrosomes on opposite poles of the cell have completed attachment to kinetochores on condensed chromosomes. The centromeres of the chromosomes convene themselves on the metaphase plate, an imaginary line that is equidistant from the two spindle poles. This even alignment is due to the counterbalance of the pulling powers generated by the opposing kinetochore microtubules, analogous to a tug-of-war between two people of equal strength, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |