|
Analogue Modelling (geology)
Analogue modelling is a laboratory experimental method using uncomplicated physical models (such as a sandbox) with certain simple scales of time and length to model geological scenarios and simulate geodynamic evolutions. There are numerous limitations affecting the direct study of the Earth. Firstly, the timescales of geodynamic processes are exceptionally long (millions of years), and most of the processes started long before human records. Secondly, the length scales of geodynamic processes are enormous (thousands of kilometres), and most of them happen at depth within the Earth. Thus, scientists began making proportional small-scale simulations of features in the natural world to test geological ideas. Analogue models can directly show the whole structural pattern in 3D and cross-section. They are helpful in understanding the internal structures and the progressive development of Earth's deforming regions. Analogue modelling has been widely used for geodynamic analysis and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Bodies Modelling
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their Geochronology, absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben with normal faulting and rift-flank uplifts mainly on one side. Where rifts remain above sea level they form a rift valley, which may be filled by water forming a rift lake. The axis of the rift area may contain volcanic rocks, and active volcanism is a part of many, but not all, active rift systems. Major rifts occur along the central axis of most mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust and lithosphere is created along a divergent boundary between two tectonic plates. ''Failed rifts'' are the result of continental rifting that failed to continue to the point of break-up. Typically the transition from rifting to spreading develops at a triple junction where three converging rifts meet over a hotspot. Two of these evolve to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open System (systems Theory)
An open system is a system that has external interactions. Such interactions can take the form of information, energy, or material transfers into or out of the system boundary, depending on the discipline which defines the concept. An open system is contrasted with the concept of an isolated system which exchanges neither energy, matter, nor information with its environment. An open system is also known as a flow system. The concept of an open system was formalized within a framework that enabled one to interrelate the theory of the organism, thermodynamics, and evolutionary theory. This concept was expanded upon with the advent of information theory and subsequently systems theory. Today the concept has its applications in the natural and social sciences. In the natural sciences an open system is one whose border is permeable to both energy and mass. By contrast, a closed system is permeable to energy but not to matter. The definition of an open system assumes that there a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed System
A closed system is a natural physical system that does not allow transfer of matter in or out of the system, althoughin the contexts of physics, chemistry, engineering, etc.the transfer of energy (e.g. as work or heat) is allowed. Physics In classical mechanics In nonrelativistic classical mechanics, a closed system is a physical system that does not exchange any matter with its surroundings, and is not subject to any net force whose source is external to the system. A closed system in classical mechanics would be equivalent to an isolated system in thermodynamics. Closed systems are often used to limit the factors that can affect the results of a specific problem or experiment. In thermodynamics In thermodynamics, a closed system can exchange energy (as heat or work) but not matter, with its surroundings. An isolated system cannot exchange any heat, work, or matter with the surroundings, while an open system can exchange energy and matter. (This scheme of definition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid opposing the weight of a partially or fully immersed object (which may be also be a parcel of fluid). In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus, the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the Displacement (fluid), displaced fluid. For this reason, an object with average density greater than the surrounding fluid tends to sink because its weight is greater than the weight of the fluid it displaces. If the objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
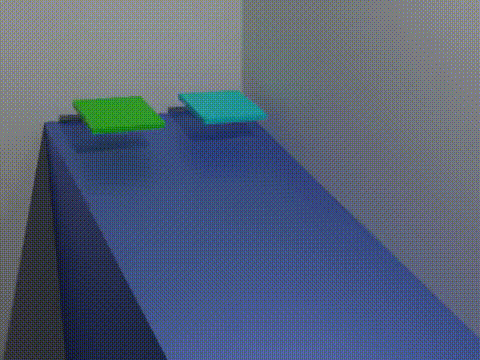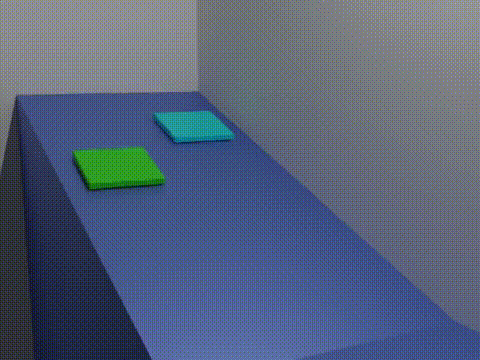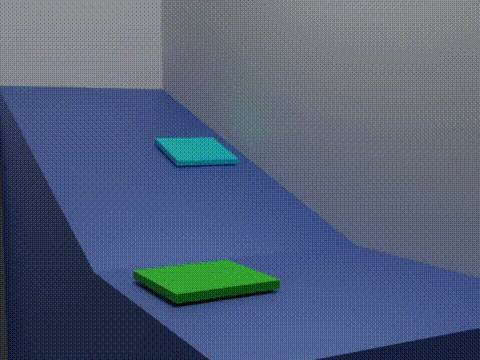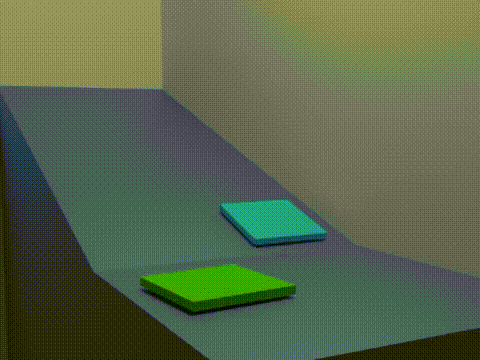
Analogue Modelling Of Fold-thrust Belt System
Analog or analogue may refer to: Computing and electronics * Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable ** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals *** Analog electronics, circuits which use analog signals **** Analog computer, a computer that uses analog signals ** Analog recording, information recorded using an analog signal * Functional analog (electronic), a system that fulfills the same function as another * Structural analog (electronic), a system that has the same structure as another Entertainment Albums and songs * ''Analog'' (album), an album by Eureka Farm * "Analog" (song), a song by Tyler, The Creator, featuring Hodgy Beats, from ''Goblin'' * ''Analogue'' (album), a 2005 album by A-ha ** "Analogue" (All I Want), the title track of the 2005 album by A-ha Books and magazines * ''Analog Science Fiction and Fact'', a science-fiction magazine * ''ANALOG Computing'', a 1981–1989 magazine about Atari computers * '' An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be used: \rho = \frac, where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance, the density is equal to its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium is the densest known element at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different systems of units, it is sometimes replaced by the dimensionless quantity "relative den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density Contrast
Density contrast is a parameter used in galaxy formation to indicate where there are local enhancements in matter density. :\Delta=\frac It is believed that after inflation, although the universe was mostly uniform, some regions were slightly denser than others with contrast densities on the order of 1 trillionth. As the horizon distance expanded, the enclosed causally connected (i.e. gravitationally connected) masses increased until they reached the Jeans mass and began to collapse, which allowed galaxies, galaxy clusters A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. Clusters consist of galax ..., superclusters, and filaments to form. References Physical cosmology Inflation (cosmology) {{physical-cosmology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stokes' Law
In fluid dynamics, Stokes' law gives the frictional force – also called drag force – exerted on spherical objects moving at very small Reynolds numbers in a viscous fluid. It was derived by George Gabriel Stokes in 1851 by solving the Stokes flow limit for small Reynolds numbers of the Navier–Stokes equations.Batchelor (1967), p. 233. Statement of the law The force of viscosity on a small sphere moving through a viscous fluid is given by: :_ = - 6 \pi \mu R where (in SI units): * _ is the frictional force – known as Stokes' drag – acting on the interface between the fluid and the particle (newtons, kg m s−2); * (some authors use the symbol ) is the dynamic viscosity ( Pascal-seconds, kg m−1 s−1); * is the radius of the spherical object (meters); * is the flow velocity relative to the object (meters per second). Note the minus sign in the equation, the drag force points in the opposite direction to the relative velocity: drag opposes the motion. Stokes' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauchy Momentum Equation
The Cauchy momentum equation is a vector partial differential equation put forth by Augustin-Louis Cauchy that describes the non-relativistic momentum transport in any continuum. Main equation In convective (or Lagrangian) form the Cauchy momentum equation is written as: \frac = \frac 1 \rho \nabla \cdot \boldsymbol + \mathbf where * \mathbf is the flow velocity vector field, which depends on time and space, (unit: \mathrm) * t is time, (unit: \mathrm) * \frac is the material derivative of \mathbf, equal to \partial_t\mathbf + \mathbf\cdot \nabla\mathbf, (unit: \mathrm) * \rho is the density at a given point of the continuum (for which the continuity equation holds), (unit: \mathrm) * \boldsymbol is the stress tensor, (unit: \mathrm) * \mathbf=\beginf_x\\ f_y\\ f_z\end is a vector containing all of the accelerations caused by body forces (sometimes simply gravitational acceleration), (unit: \mathrm) * \nabla\cdot\boldsymbol= \begin \dfrac + \dfrac + \dfrac \\ \dfrac + \dfra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of the processes involved is called tribology, and has a history of more than 2000 years. Friction can have dramatic consequences, as illustrated by the use of friction created by rubbing pieces of wood together to start a fire. Another important consequence of many types of friction can be wear, which may lead to performance degradation or damage to components. It is known that frictional energy losses account for about 20% of the total energy expenditure of the world. As briefly discussed later, there are many different contributors to the retarding force in friction, ranging from asperity deformation to the generation of charges and changes in local structure. When two bodies in contact move relative to each other, due to these variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscous Force
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. Thus its SI units are newton-seconds per metre squared, or pascal-seconds. Viscosity quantifies the internal frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's center line than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube with a constant rate of flow, the strengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |