|
2002
After the September 11 attacks of the previous year, foreign policy and international relations were generally united in combating al-Qaeda and other terrorist organizations. The United States especially was a leading force in combating terrorist groups. 2002 also saw the signing and establishment of many international agreements and institutions, most notably the International Criminal Court, the African Union, the Russian-American Strategic Offensive Reductions Treaty, and the Eurozone. The global economy, partly due to the September 11 attacks, generally stagnated or declined. Stock indices, such as the American Dow Jones Industrial Average and the Japanese Nikkei 225 both ended the year lower than they had started. In the later parts of 2002, the world saw the beginning of a SARS epidemic, which would go on to affect mostly China, Europe, and North America. Population The world population on January 1, 2002, was estimated to be 6.272 billion people, and it inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
September 11 Attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners scheduled to travel from the Northeastern United States to California. The hijackers crashed the first two planes into the Twin Towers of the World Trade Center in New York City, and the third plane into the Pentagon (the headquarters of the United States military) in Arlington County, Virginia. The fourth plane was intended to hit a federal government building in Washington, D.C., but crashed in a field following a passenger revolt. The attacks killed nearly 3,000 people and instigated the war on terror. The first impact was that of American Airlines Flight 11. It was crashed into the North Tower of the World Trade Center complex in Lower Manhattan at 8:46 a.m. Seventeen minutes later, at 9:03, the World Trade Center� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategic Offensive Reductions Treaty
The Treaty Between the United States of America and the Russian Federation on Strategic Offensive Reductions (SORT), also known as the Treaty of Moscow, was a strategic arms reduction treaty between the United States and Russia that was in force from June 2003 until February 2011 when it was superseded by the New START treaty. At the time, SORT was positioned as "represent ngan important element of the new strategic relationship" between the two countries with both parties agreeing to limit their nuclear arsenal to between 1,700 and 2,200 operationally deployed warheads each. It was signed in Moscow on 24 May 2002. After ratification by the U.S. Senate and the State Duma, SORT came into force on 1 June 2003. It would have expired on 31 December 2012 if not superseded by New START. Either party could have withdrawn from the treaty upon giving three months written notice to the other. Mutual nuclear disarmament SORT was one in a long line of treaties and negotiations on mut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNITA
The National Union for the Total Independence of Angola ( pt, União Nacional para a Independência Total de Angola, abbr. UNITA) is the second-largest political party in Angola. Founded in 1966, UNITA fought alongside the Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) in the Angolan War for Independence (1961–1975) and then against the MPLA in the ensuing civil war (1975–2002). The war was one of the most prominent Cold War proxy wars, with UNITA receiving military aid initially from People's Republic of China from 1966 until October 1975 and later from the United States and apartheid South Africa while the MPLA received support from the Soviet Union and its allies, especially Cuba. Until 1996, UNITA was funded through Angolan diamond mines in both Lunda Norte and Lunda Sul along the Cuango River valley, especially the Catoca mine, which was Angola's only Kimberlite mine at that time. Valdemar Chidondo served as Chief of Staff in the government of UNITA, pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angolan Civil War
The Angolan Civil War ( pt, Guerra Civil Angolana) was a civil war in Angola, beginning in 1975 and continuing, with interludes, until 2002. The war immediately began after Angola became independent from Portugal in November 1975. The war was a power struggle between two former anti-colonial guerrilla movements, the communist People's Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) and the turned anti-communist National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA). The war was used as a surrogate battleground for the Cold War by rival states such as the Soviet Union, Cuban intervention in Angola, Cuba, History of South Africa#Apartheid era (1948–1994), South Africa, and the United States. The MPLA and UNITA had different roots in Angolan society and mutually incompatible leaderships, despite their shared aim of ending colonial rule. A third movement, the National Front for the Liberation of Angola (FNLA), having fought the MPLA with UNITA during the war for independenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eelam War III
Eelam War III is the name given to the third phase of armed conflict between the Sri Lankan military and the separatist Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE). After the period of 100 days cease-fire the hostilities broke out on 19 April 1995. The LTTE - Sea Tigers planted explosives in two gun boats known as SLNS 'Sooraya' and 'Ranasuru', and blew them up. Also, a new weapon "Stinger", a shoulder-launched anti-aircraft missile was used in this conflict by the LTTE. This was used to take down two Sri Lankan Air Force AVRO aircraft flying over the Jaffna peninsula. Eelam War III also marked the rising success of the LTTE, as they managed to capture key districts such as Kilinochchi and Mullaitivu, and took over the Elephant Pass base. By the end of Eelam War III, the LTTE had control of nearly 30% of the entire island. Major military operations (in chronological order) * 19 April 1995: The LTTE sinks SLNS Sooraya and SLNS Ranasuru ending peace talks. * 28 June 1995 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Liberian Civil War
The Second Liberian Civil War was a conflict in the West African nation of Liberia lasted from 1999 to 2003. It was preceded by the First Liberian Civil War, which ended in 1996. President Charles Taylor came to power in 1997 after victory in the First Liberian Civil War which led to two years of peace. The Liberians United for Reconciliation and Democracy (LURD), an anti-Taylor rebel group backed by the government of Guinea, invaded northern Liberia in April 1999. LURD made gradual gains against Taylor in the north and began approaching the capital Monrovia by early 2002. The Movement for Democracy in Liberia (MODEL), a second anti-Taylor rebel group, invaded southern Liberia in early 2003 and quickly conquered most of the south. Taylor, controlling only a third of Liberia and under pressure from the Siege of Monrovia, resigned in August 2003 and fled to Nigeria. The Accra Comprehensive Peace Agreement was signed by the warring parties a week later, marking the political end of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
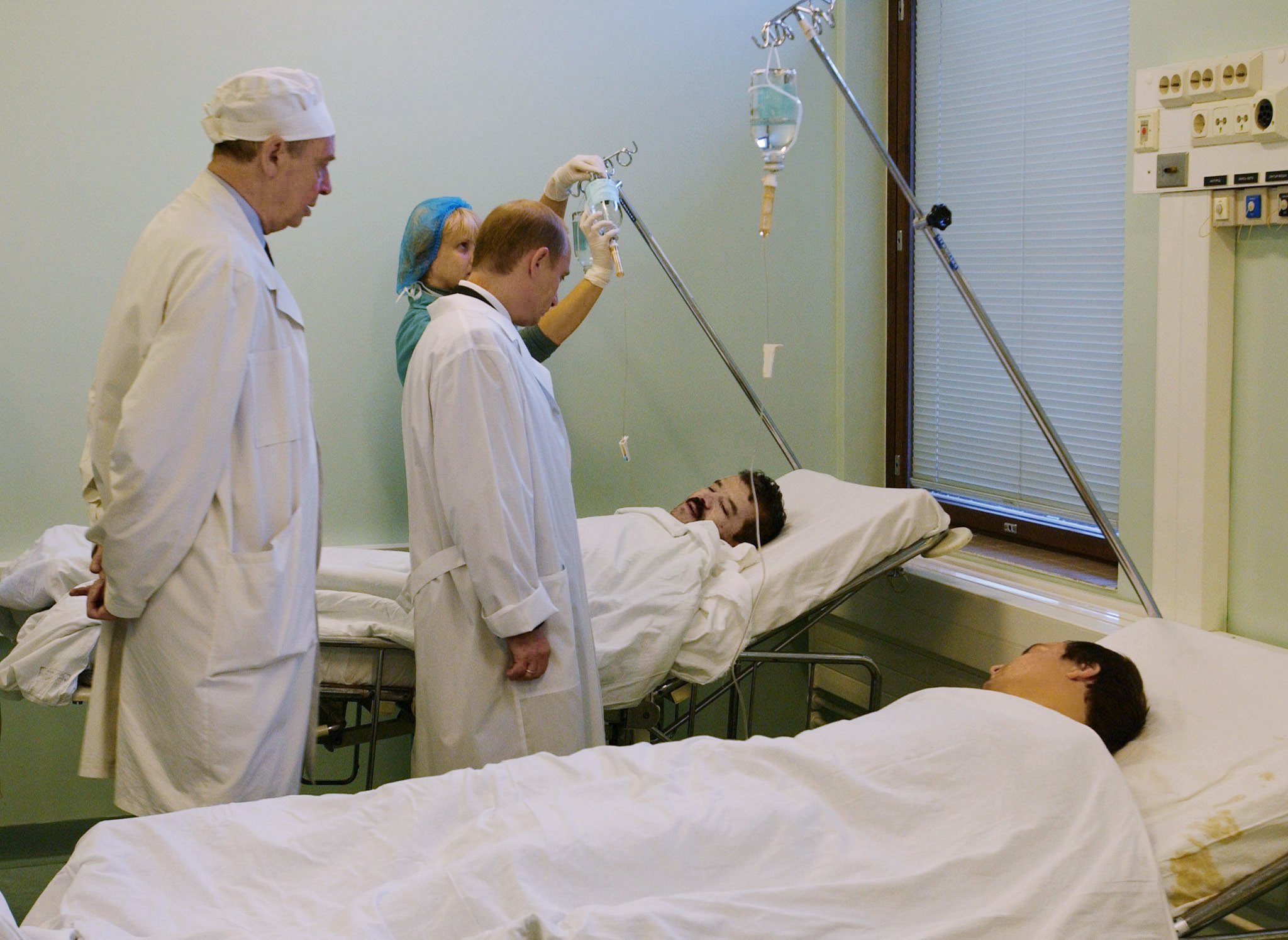
Moscow Theater Hostage Crisis
The Moscow theater hostage crisis (also known as the 2002 Nord-Ost siege) was the seizure of the crowded Dubrovka Theater by Chechen terrorists on 23 October 2002, which involved 850 hostages and ended with Russian security services killing or causing the death of at least 170 people. The attackers, led by Movsar Barayev, claimed allegiance to the Islamist separatist movement in Chechnya. They demanded the withdrawal of Russian forces from Chechnya and an end to the Second Chechen War. Due to the layout of the theater, special forces would have had to fight through of corridor and advance up a well-defended staircase before they could reach the hall in which the hostages were held. The attackers had numerous explosives, with the most powerful in the center of the auditorium. Spetsnaz operators from Federal Security Service (FSB) Alpha and Vympel, supported by a Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs (MVD) SOBR unit, pumped a chemical agent into the building's ventilation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mil Mi-26
The Mil Mi-26 (russian: link=no, Миль Ми-26, NATO reporting name: Halo) is a Soviet/Russian heavy transport helicopter. Its product code is ''Izdeliye 90''. Operated by both military and civilian operators, it is the largest and most powerful helicopter to have gone into serial production. Design and development Following the incomplete development of the heavier Mil Mi-12 (prototypes known as Mil V-12) in the early 1970s, work began on a new heavy-lift helicopter, designated as the ''Izdeliye 90'' ("Project 90") and later allocated designation ''Mi-26''. The new design was required to have an empty weight less than half its maximum takeoff weight. The helicopter was designed by Marat Tishchenko, protégé of Mikhail Mil, founder of the OKB-329 design bureau. The Mi-26 was designed to replace earlier Mi-6 and Mi-12 heavy lift helicopters and act as a heavy-lift helicopter for military and civil use, having twice the cabin space and payload of the Mi-6, then the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2002 Khankala Mi-26 Crash
On 19 August 2002, a group of Chechen separatists armed with a man-portable air-defense system brought down a Russian Mil Mi-26 helicopter in a minefield, which resulted in the death of 127 Russian soldiers in the greatest loss of life in the history of helicopter aviation. It was also the most deadly aviation disaster ever suffered by the Russian Armed Forces, as well as its worst loss of life in a single day since the 1999 start of the Second Chechen War. Attack On 19 August 2002, Chechen separatist fighters launched a Russian-made 9K38 Igla shoulder-fired, heat-seeking surface-to-air missile which hit an overloaded Mil Mi-26 heavy transport helicopter of the 487th Separate Helicopter Regiment, causing it to crash-land and burn at Khankala military air base near Chechnya's capital city of Grozny. The helicopter was ferrying 142 soldiers and officers belonging to various units, mostly from the 20th Guards Motor Rifle Division, from the Russian Air Force base at Mozdok, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
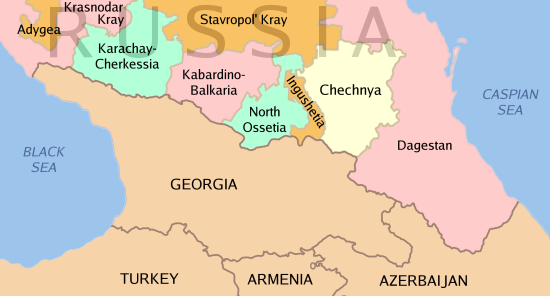
Second Chechen War
The Second Chechen War (russian: Втора́я чече́нская война́, ) took place in Chechnya and the border regions of the North Caucasus between the Russian Federation and the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, from August 1999 to April 2009. In August 1999, Islamist fighters from Chechnya infiltrated Russia's Dagestan region, violating Russia's borders. During the initial campaign, Russian military and pro-Russian Chechen paramilitary forces faced Chechen separatists in open combat and seized the Chechen capital Grozny after a winter siege that lasted from December 1999 until February 2000. Russia established direct rule over Chechnya in May 2000 although Chechen militant resistance throughout the North Caucasus region continued to inflict heavy Russian casualties and challenge Russian political control over Chechnya for several years. Both sides carried out attacks against civilians. These attacks drew international condemnation. In mid-2000, the Russian g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepalese Civil War
The Nepalese Civil War was a protracted armed conflict that took place in the former Kingdom of Nepal from 1996 to 2006. It saw fighting between the Nepalese royal government and the Communist Party of Nepal (Maoist) throughout the country. The conflict began on 13 February 1996, when the Communist Party of Nepal initiated an insurgency with the stated purpose of overthrowing the Nepalese monarchy and establishing a people's republic; it ended with the signing of the Comprehensive Peace Accord on 21 November 2006. The insurgency was characterized by numerous war crimes and crimes against humanity, including summary executions, massacres, purges, kidnappings, and mass rapes. It resulted in the deaths of over 17,000 people, including civilians, insurgents, and army and police personnel; and the internal displacement of hundreds of thousands of people, mostly throughout rural Nepal. The Truth and Reconciliation Commission has received about 63,000 complaints, as reported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |