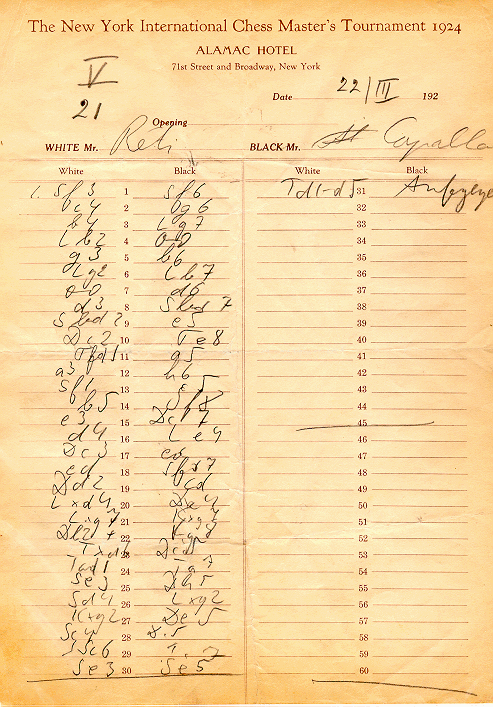|
Zukertort Opening
The Zukertort Opening is a chess opening named after Johannes Zukertort that begins with the move: :1. Nf3 Sometimes the name "Réti Opening" is used for the opening move 1.Nf3, although most sources define the Réti more narrowly as the sequence 1.Nf3 d5 2.c4. A flank opening, it is the third most popular of the twenty legal opening moves White has, behind only 1.e4 and 1.d4. The move has been described by Edmar Mednis as a "perfect and flexible opening" and by others such as Aron Nimzowitsch as "certainly the most solid move, whereas moves such as 1.e4 and 1.d4 are both 'committal' and 'compromising'." The game can transpose into many other openings that usually start with 1.e4, 1.d4, or 1.c4. If Black is not careful, there is the risk of running unprepared into a highly theoretical opening, e.g. after 1.Nf3 c5 White can play 2.e4 leading to the mainline Sicilian Defense. Other common transpositions are to various lines of the Queen's Gambit Declined (after e.g. 1.Nf3 d5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Réti Opening
The Réti Opening is a hypermodern chess opening whose "traditional" or "classic method" begins with the moves: :1. Nf3 d5 :2. c4 White attacks Black's pawn from the , which may occasion 2...dxc4. White may couple this plan with a kingside fianchetto (g3 and Bg2) to create pressure on the light squares in the . The opening is named after Czechoslovakian chess player Richard Réti (1889–1929). The opening is in the spirit of the hypermodernism movement that Réti championed, with the center being dominated from the wings rather than by direct occupation. If White fianchettoes both bishops, castles kingside, and refrains from occupying the center with pawns, the result may be described as the Réti system. In the ''Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'', Réti Opening is classified as codes A04–A09, where it is closely associated with the King's Indian Attack. History According to Réti, the opening was introduced into master play in the early part of 1923. Schiller, Eric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Opening
The English Opening is a chess opening that begins with the move: :1. c4 A flank opening, it is the fourth most popular and, according to various databases, one of the four most successful of White's twenty possible first moves. White begins the fight for the by staking a claim to the d5-square from the wing, in hypermodern style. Although many lines of the English have a distinct character, the opening is often used as a transpositional device in much the same way as 1.Nf3 – to avoid such highly regarded responses to 1.d4 as the Nimzo-Indian and Grünfeld Defences — and is considered reliable and flexible. The English derives its name from the leading 19th century English master Howard Staunton, who played it during his 1843 match with Saint-Amant and at London 1851, the first international tournament. It did not inspire Staunton's contemporaries and caught on only in the twentieth century. It is now recognised as a opening that may be used to reach both classical an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chess Openings
This is a list of chess openings, organized by the ''Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'' () code. In 1966, Chess Informant categorized the chess openings into five broad areas ("A" through "E"), with each of those broken down into one hundred subcategories ("00" through "99"). The openings were published in five volumes of ''ECO'', with volumes labeled "A" through "E". This is a list of chess openings by the ''ECO'' classification. A – Flank openings * White first moves other than 1.e4, 1.d4 (A00–A39) * 1.d4 without 1...d5, 1...Nf6 or 1...f5: Atypical replies to 1.d4 (A40–A44) * 1.d4 Nf6 without 2.c4: Atypical replies to 1...Nf6 (A45–A49) * 1.d4 Nf6 2.c4 without 2...e6 or 2...g6: Atypical Indian systems (A50–A79) * 1.d4 f5: Dutch Defence (A80–A99) A00–A39 White first moves other than 1.e4, 1.d4: *A00 Irregular Openings :* Anderssen's Opening: 1.a3 ::* Anderssen's Opening, Polish Gambit: 1...a5 2.b4 :::* Bugayev Attack 2...e5 ::* Anderssen's Opening, Creepy Crawl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staunton Gambit
The Staunton Gambit is a chess opening characterised by the moves: :1. d4 f5 (the Dutch Defence) :2. e4!? White sacrifices a pawn for quick development, hoping to launch an attack against Black's , which has been somewhat weakened by 1...f5. Black can decline the gambit with 2...d6, transposing to the Balogh Defence, but accepting the pawn with 2...fxe4 is considered stronger. Although the Staunton Gambit was once a feared weapon for White, it is rarely played today, since theory has shown how to neutralise it, and White scores only about 50 percent. The '' ECO'' codes for Staunton Gambit are A82 and A83. Gambit accepted After 2...fxe4, play usually proceeds 3.Nc3 Nf6. Main line: 4.Bg5 The main line runs 4.Bg5, first played by Howard Staunton against Bernhard Horwitz in London, 1846. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London System
The London System, also known as the Mason Variation, is an in chess where White opens with 1.d4 but does not play the Queen's Gambit, instead opting to rapidly develop the . This often results in a . The London System can be used against virtually any Black defense and thus comprises a smaller body of opening theory than many other openings. Although it has a reputation as a opening, the London System has faced criticism for its lack of . The rapid of the dark-squared bishop in the London System can be contrasted to the Colle System, in which the queen's bishop often remains on c1 during the opening phase of the game. Origin British player James Mason was the first well-known proponent of the London System. His contemporaries include Johannes Zukertort, Adolf Anderssen, and William Steinitz. The London System came to prominence in an international tournament held in Central Hall, Westminster from July 31 to August 19, 1922, which would later be known as the 1922 London to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Defense
In the game of chess, Indian Defence or Indian Game is a broad term for a group of chess opening, openings characterised by the moves: :1. b:Chess Opening Theory/1. d4, d4 b:Chess Opening Theory/1. d4/1...Nf6, Nf6 They are all to varying degrees hypermodernism (chess), hypermodern defences, where Black invites White to establish an imposing presence in the with the plan of undermining and ultimately destroying it. Although the Indian defences were championed in the 1920s by players in the hypermodern school, they were not fully accepted until Russian players showed in the late 1940s that these systems are sound for Black. Since then, the Indian defences have become a popular way for Black to respond to 1.d4 because they often offer a balanced game with winning chances for both sides. transposition (chess), Transpositions are important and many variations can be reached by several move orders. It is also possible to transpose back into classical openings such as the Queen's Gambit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Defense
The Dutch Defence is a chess opening characterised by the moves: :1. d4 f5 Black's 1...f5 stakes a claim to the e4-square and envisions an attack in the middlegame on White's ; however, it also weakens Black's kingside to an extent (especially the e8–h5 diagonal). Like its 1.e4 counterpart, the Sicilian Defence, the Dutch is an aggressive and unbalancing opening, resulting in the lowest percentage of draws among the most common replies to 1.d4. Historically, White has tried many methods to exploit the kingside weaknesses, such as the Staunton Gambit (2.e4) and Korchnoi Attack (2.h3 and 3.g4). The Dutch has never been a main line against 1.d4 and is rarely seen today in high-level competition, although a number of top players, including Alexander Alekhine, Bent Larsen, Paul Morphy, Miguel Najdorf, and Hikaru Nakamura have used it with success. Its most notable use may have been in 1951, when both world champion Mikhail Botvinnik and his challenger, David Bronstein, played ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Defense
The French Defence is a chess opening characterised by the moves: :1. e4 e6 This is most commonly followed by 2.d4 d5, with Black intending ...c5 soon after, attacking White's and gaining on the . The French has a reputation for solidity and resilience, although some lines such as the Winawer Variation can lead to complications. Black's position is often somewhat in the early game; in particular, the pawn on e6 can impede the of the bishop on c8. Basics Following the opening moves 1.e4 e6, the main line of the French Defence continues 2.d4 d5 (see below for alternatives). White sets up a , which Black immediately challenges by attacking the pawn on e4. The same position can be reached by from a Queen's Pawn Game after 1.d4 e6 2.e4 d5 or the declining of a Blackmar–Diemer Gambit after 1.d4 d5 2.e4 e6. White's options include defending the e4-pawn with 3.Nc3 or 3.Nd2, advancing it with 3.e5, or exchanging it with 3.exd5, each of which leads to different types of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Indian Defense
The King's Indian Defence is a common chess opening. It is defined by the following moves: :1. d4 Nf6 :2. c4 g6 Black intends to follow up with 3...Bg7 and 4...d6 (the Grünfeld Defence arises when Black plays 3...d5 instead, and is considered a separate opening). White's major third move options are 3.Nc3, 3.Nf3 or 3.g3, with both the King's Indian and Grünfeld playable against these moves. The ''Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'' classifies the King's Indian Defence under the codes E60 through E99. The King's Indian is a hypermodern opening, where Black deliberately allows White control of the with its pawns, with the view to subsequently challenge it. In the most critical lines of the King's Indian, White erects an imposing pawn centre with Nc3 followed by e4. Black stakes out its own claim to the centre with the Benoni-style ...c5, or ...e5. If White resolves the central pawn tension with d5, then Black follows with either ...b5 and queenside play, or ...f5 and an ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reti Opening , an ancient confederati ...
Reti or Réti may refer to: Entertainment * Reti, a character in the video game '' Star Wars: Starfighter'' * Réti endgame study, a chess endgame study by Richard Réti * Réti Opening, chess opening named after Richard Réti * ''Reti'' (film), a 2016 Marathi movie People * István Réti (1872–1945), painter * Richard Réti (1889–1929), chess master * Rudolph Reti (1885–1957), musical analyst, composer and pianist Places * Reti, Estonia, village in Põdrala Parish, Valga County, Estonia * Reti, Pakistan, a town in Pakistan * Reti, Western Australia, aka Empress Springs, a tiny place on the Great Central Road See also * Reti, (Hindi for "sand"), in placenames like Muni Ki Reti * Rhaetian people The Raeti (spelling variants: ''Rhaeti'', ''Rheti'' or ''Rhaetii'') were a confederation of Alpine tribes, whose language and culture was related to those of the Etruscans. Before the Roman conquest, they inhabited present-day Tyrol in Austria, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen's Pawn Game
Queen's Pawn Game broadly refers to any chess opening starting with the move 1.d4, which is the second most popular opening move after 1.e4 ( King's Pawn Game). Terminology The term "Queen's Pawn Game" is usually used to describe openings beginning with 1.d4 where White does not play the Queen's Gambit. The most common Queen's Pawn Game openings are: * The London System, 2.Bf4 or 2.Nf3 and 3.Bf4 * The Trompowsky Attack, 1...Nf6 2.Bg5 and the Pseudo-Trompowsky 1...d5 2.Bg5 * The Torre Attack, 2.Nf3 and 3.Bg5 * The Stonewall Attack, 2.e3 * The Colle System, 2.Nf3 and 3.e3, * The King's Fianchetto Opening, 2.Nf3 and 3.g3 * The Barry Attack, 1...Nf6 2.Nf3 g6 3.Nc3 d5 4.Bf4 * The Richter–Veresov Attack, 1...d5 2.Nc3 Nf6 3.Bg5 or 1...Nf6 2.Nc3 d5 3.Bg5 * The Blackmar–Diemer Gambit, 1...d5 2.e4, and the Hübsch Gambit 1...Nf6 2.Nc3 d5 3.e4 In the ''Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'' (''ECO''), Closed Games (1.d4 d5) are classified under codes D00–D69. Openings where B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Chess Openings
The ''Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'' () is a reference work describing the state of Chess theory#Opening theory, opening theory in chess, originally published in five volumes from 1974 to 1979 by the Serbian company Šahovski Informator (Chess Informant). It is currently undergoing its fifth edition. ''ECO'' may also refer to the opening classification system used by the encyclopedia. Overview Both ''ECO'' and ''Chess Informant'' are published by the Belgrade-based company Šahovski Informator. The moves are taken from thousands of master games and from published analysis in ''Informant'' and compiled by the editors, most of whom are Grandmaster (chess), grandmasters, who select the lines which they consider most relevant or critical. The chief editor since the first edition has been Aleksandar Matanović. The openings are provided in an chess opening theory table, ''ECO'' table that concisely presents the opening lines considered most critical by the editors. ''ECO'' covers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |