|
Zizhitongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynasties and spanning almost 1400 years. The main text is arranged into 294 scrolls (''juan'' , equivalent to a chapter) totaling about 3 million Chinese characters. In 1065 AD, Emperor Yingzong of Song commissioned his official Sima Guang (1019–1086 AD) to lead a project to compile a universal history of China, and granted him funding and the authority to appoint his own staff. His team took 19 years to complete the work and in 1084 AD it was presented to Emperor Yingzong's successor Emperor Shenzong of Song. It was well-received and has proved to be immensely influential among both scholars and the general public. Endymion Wilkinson regards it as reference quality: "It had an enormous influence on later Chinese historical wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scroll
A scroll (from the Old French ''escroe'' or ''escroue''), also known as a roll, is a roll of papyrus, parchment, or paper containing writing. Structure A scroll is usually partitioned into pages, which are sometimes separate sheets of papyrus or parchment glued together at the edges. Scrolls may be marked divisions of a continuous roll of writing material. The scroll is usually unrolled so that one page is exposed at a time, for writing or reading, with the remaining pages rolled and stowed to the left and right of the visible page. Text is written in lines from the top to the bottom of the page. Depending on the language, the letters may be written left to right, right to left, or alternating in direction (boustrophedon). History Scrolls were the first form of editable record keeping texts, used in Eastern Mediterranean ancient Egyptian civilizations. Parchment scrolls were used by the Israelites among others before the codex or bound book with parchment pages was invented b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zi Zhi Tong Jian 2 By Simaguan , sometimes known as ''zi'' (字) in Chinese
{{disambiguation ...
Zi or ZI may refer to: * Zi (surname) (子), a surname used by Shang kings * Zi (title) (子), a Chinese honorific used for ancient viscounts and for master philosophers * Zi (name) (字), an alternate term for East Asian courtesy names * Zi (cuneiform), a sign in cuneiform writing * Zi Corporation, a Canadian software company * ''Zi'' (album), a 2016 album by Negură Bunget * Zi (prefix symbol) of the binary unit prefix zebi for digital data * Zi (Zoids), a fictional planet in the ''Zoids'' media franchise * Zona incerta, a region in the subthalamus * Aigle Azur (IATA airline code) See also * Chinese characters Chinese characters () are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese. In addition, they have been adapted to write other East Asian languages, and remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as ''kanji' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph-Anne-Marie De Moyriac De Mailla
Joseph-Anne-Marie de Moyriac de Mailla (also Anna, and de Moyria) () (16 December 1669 – 28 June 1748) was a French Jesuit missionary to China. Biography Mailla was born at Château Maillac on the Isère. After finishing his studies, he joined the Society of Jesus in 1686, and, in 1701, was sent on a mission to China as a member of the Jesuits. In June, 1703, Father Mailla arrived in Morocco and thence set out for Canton where he acquired a thorough knowledge of Chinese language and writing. He devoted himself particularly to the study of Chinese historical works. When the Kangxi Emperor entrusted the Jesuit missionaries with the cartographical survey of his empire, the provinces of Henan, Zhejiang, and Fujian, and the Island of Formosa, fell to the lot of Mailla along with Jean-Baptiste Régis and Roman Hinderer. When the work had been completed, the emperor conferred on Father Mailla the rank of mandarin as a mark of his satisfaction. When Father Mailla died, in his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg , image_size = 175px , caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits , abbreviation = SJ , nickname = Jesuits , formation = , founders = , founding_location = , type = Order of clerics regular of pontifical right (for men) , headquarters = Generalate:Borgo S. Spirito 4, 00195 Roma-Prati, Italy , coords = , region_served = Worldwide , num_members = 14,839 members (includes 10,721 priests) as of 2020 , leader_title = Motto , leader_name = la, Ad Majorem Dei GloriamEnglish: ''For the Greater Glory of God'' , leader_title2 = Superior General , leader_name2 = Fr. Arturo Sosa, SJ , leader_title3 = Patron saints , leader_name3 = , leader_title4 = Ministry , leader_name4 = Missionary, educational, literary works , main_organ = La Civiltà Cattolica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to 1722. The Kangxi Emperor's reign of 61 years makes him the longest-reigning emperor in Chinese history (although his grandson, the Qianlong Emperor, had the longest period of ''de facto'' power, ascending as an adult and maintaining effective power until his death) and one of the longest-reigning rulers in history. However, since he ascended the throne at the age of seven, actual power was held for six years by four regents and his grandmother, the Grand Empress Dowager Xiaozhuang. The Kangxi Emperor is considered one of China's greatest emperors. He suppressed the Revolt of the Three Feudatories, forced the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan and assorted Mongol rebels in the North and Northwest to submit to Qing rule, and blocked Tsarist R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transliterations Of Manchu
There are several systems for transliteration of the Manchu alphabet which is used for writing the Manchu and Xibe languages. These include transliterations in Latin script and in Cyrillic script. Transliteration in Latin script (romanization) The romanization used in most recent western publications on Manchu is the one employed by the American sinologist Jerry Norman in his ''Comprehensive Manchu-English Dictionary'' (2013), a central reference tool in modern Manchu studies. This system, which has become the de facto modern standard in English-language publications, is the most recent incarnation of a system originally designed by the German linguist Hans Conon von der Gabelentz for his 1864 edition of the Manchu translation of the Four Books and other Chinese classics. As he explains:"Because Manchu possesses an alphabetic script, it was acceptable, as being without any disadvantage whatsoever, to replace the indigenous Manchu script, the use of which would have made printin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchu Language
Manchu (Manchu:, ) is a critically endangered East Asian Tungusic language native to the historical region of Manchuria in Northeast China. As the traditional native language of the Manchus, it was one of the official languages of the Qing dynasty (1636–1912) of China, although today the vast majority of Manchus speak only Mandarin Chinese. Several thousand can speak Manchu as a second language through governmental primary education or free classes for adults in classrooms or online. The Manchu language enjoys high historical value for historians of China, especially for the Qing dynasty. Manchu-language texts supply information that is unavailable in Chinese, and when both Manchu and Chinese versions of a given text exist they provide controls for understanding the Chinese. Like most Siberian languages, Manchu is an agglutinative language that demonstrates limited vowel harmony. It has been demonstrated that it is derived mainly from the Jurchen language though there are m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zizhi Tongjian Gangmu
The ''Zizhi Tongjian Gangmu'' (資治通鑑綱目, "Outline and Details of the '' Comprehensive Mirror in Aid of Government''"), also known as the ''Tongjian Gangmu'' or ''Gangmu'', is an 1172 Chinese history book based on Sima Guang's 1084 book ''Zizhi Tongjian''. The credited author is the neo-Confucian philosopher Zhu Xi, but its compilation was in fact by Zhu's students. In the words of J. W. Haeger, the ''Zizhi Tongjian Gangmu'' "is doubtless the most influential piece of historical writing in the later Imperial age". The book is sometimes described as a condensed version of ''Zizhi Tongjian'', but it's in fact historical criticism containing copious didactic and ideological rhetoric. The book was later translated into Manchu as the ''Tung Giyan G'ang Mu'' () upon the request of the Kangxi Emperor of the Qing. This Manchu version was itself translated into French by the Jesuit missionary , image = Ihs-logo.svg , image_size = 175px , caption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhu Xi
Zhu Xi (; ; October 18, 1130 – April 23, 1200), formerly romanized Chu Hsi, was a Chinese calligrapher, historian, philosopher, poet, and politician during the Song dynasty. Zhu was influential in the development of Neo-Confucianism. He contributed greatly to Chinese philosophy and fundamentally reshaped the Chinese worldview. His works include his editing of and commentaries to the Four Books (which later formed the curriculum of the civil service exam in Imperial China from 1313 to 1905), his writings on the process of the "investigation of things" (), and his development of meditation as a method for self-cultivation. He was a scholar with a wide learning in the classics, commentaries, histories and other writings of his predecessors. In his lifetime he was able to serve multiple times as a government official, although he avoided public office for most of his adult life. He also wrote, compiled and edited almost a hundred books and corresponded with dozens of other schol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
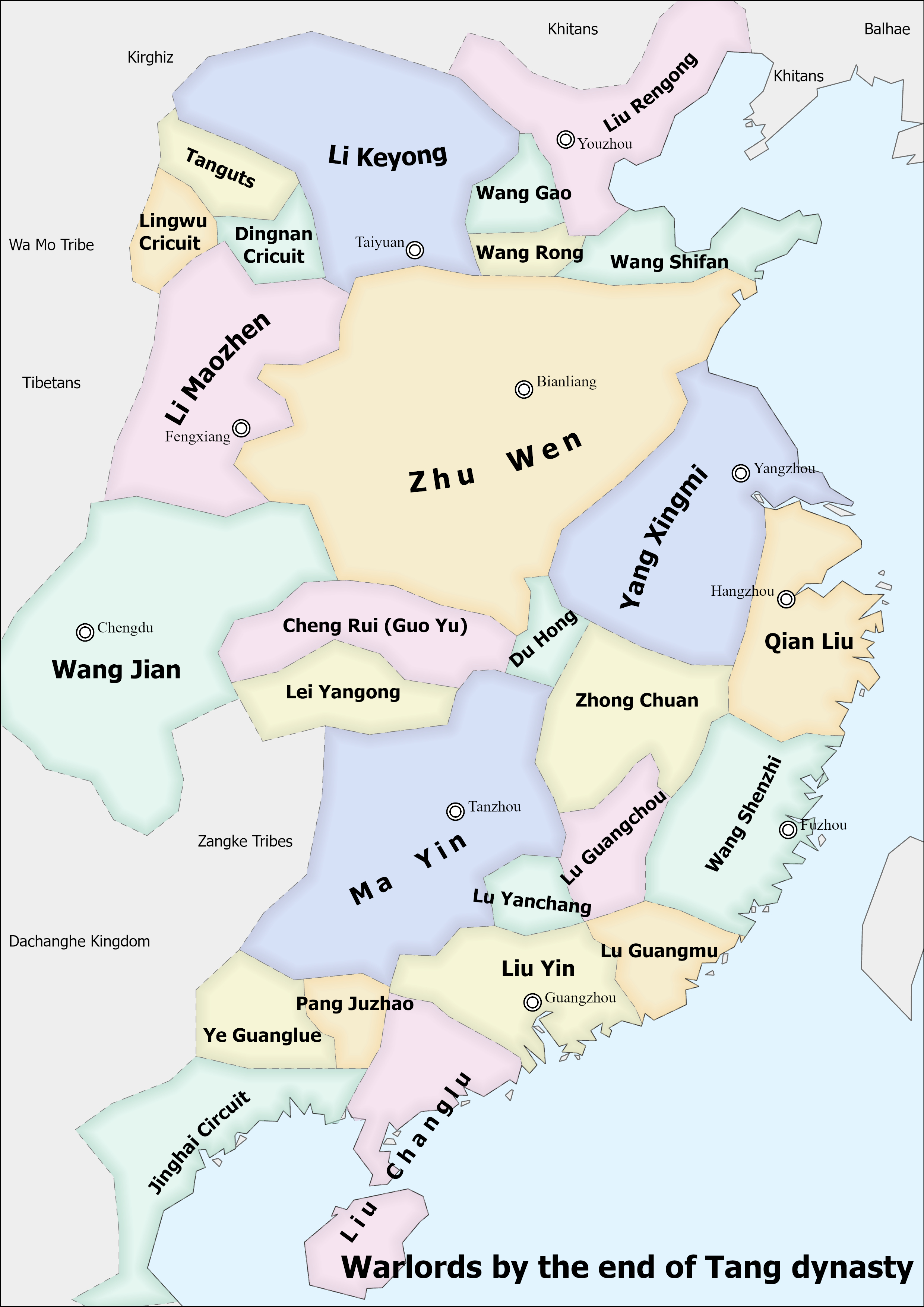
Five Dynasties
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen concurrent dynastic states were established elsewhere, mainly in South China. It was a prolonged period of multiple political divisions in Chinese imperial history. Traditionally, the era is seen as beginning with the fall of the Tang dynasty in 907 and reaching its climax with the founding of the Song dynasty in 960. In the following 19 years, Song gradually subdued the remaining states in South China, but the Liao dynasty still remained in China's north (eventually succeeded by the Jin dynasty), and the Western Xia was eventually established in China's northwest. Many states had been ''de facto'' independent long before 907 as the Tang dynasty's control over its officials waned, but the key event was their recognition as sovereign by fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |