|
Zhao Ying
Zhao Ying (; 885 – June 8, 951''Old History of the Five Dynasties'', vol. 89.''Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 290.), courtesy name Yuanhui (), was a Chinese historian, military general, and politician of the Chinese Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period states Later Tang and Later Jin, serving as a chancellor during Later Jin. Background Zhao Ying was born in 885, during the reign of Emperor Xizong of Tang. His family was from Huayin (華陰, in modern Weinan, Shaanxi). His great-grandfather Zhao Pu () and grandfather Zhao Ru () each had minor official careers — Zhao Pu reached the office of county secretary general, albeit of a major county (Jiangdu (江都, in modern Yangzhou, Jiangsu)) and Zhao Ru reached the office of ''Zhengzi'' (), an assistant copyeditor at the Palace Library. Zhao Ying's father Zhao Juhui () was a farmer, probably at the ancestral home at Huayin. Zhao Ying himself was said to be handsome and careful. During the middle of the ''Longde'' era (921–923) of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old History Of The Five Dynasties
The ''Old History of the Five Dynasties'' (''Jiù Wǔdài Shǐ'') was an official history mainly focus on Five Dynasties era (907–960), which controlled much of northern China. And it also includes some history of other south states during the era. It was compiled by the Song dynasty official-scholar Xue Juzheng in the first two decades of the Song dynasty, which was founded in 960. It is one of the Twenty-Four Histories recognized through Chinese history. The book comprises 150 chapters, and was in effect divided into 7 books, they are: ''Book of Liang'' (24 volume), ''Book of Tang'' (50 volume), ''Book of Jin'' (24 volume), ''Book of Han'' (11 volume), ''Book of Zhou'' (22 volume), '' Liezhuan'' (7 volume) and ''Zhi'' (12 volume), respectively''.'' After the ''New History of the Five Dynasties'' by Ouyang Xiu was published, it was no longer popular. In the 12th century it was removed from the Imperial Library and was no longer published by order of the Jin dynasty. The book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
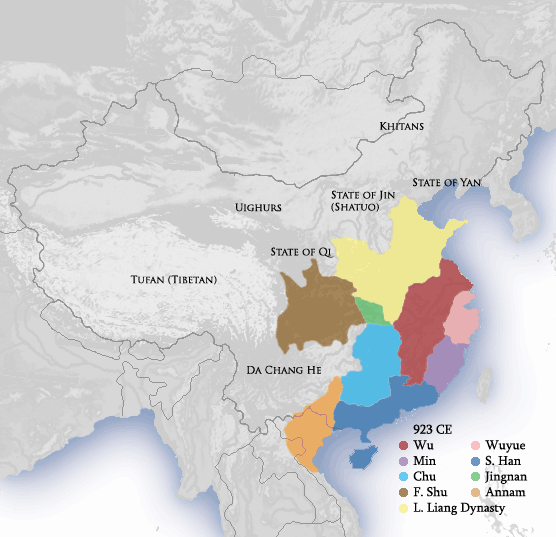
Later Liang (Five Dynasties)
Liang, known in historiography as the Later Liang () (1 June 907 – 19 November 923) or the Zhu Liang (), was an imperial dynasty of China and the first of the Five Dynasties during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was founded by Zhu Wen (Emperor Taizu), after he forced the last emperor of the Tang dynasty to abdicate in his favour (and then murdered him). The Later Liang would last until 923 when it was destroyed by the Later Tang dynasty. Formation Zhu Wen initially allied himself as Huang Chao's lieutenant. However, he took Huang's best troops and established his own power base as a warlord in Kaifeng. By 904, he had exerted control over both of the twin Tang Dynasty capitals of Chang'an and Luoyang. Tang emperor Zhaozong was ordered murdered by Zhu in 904 and the last Tang emperor, Ai Di (Emperor Ai of Tang), was deposed three years later. Emperor Ai of Tang was murdered in 908, also ordered by Zhu. Meanwhile, Zhu Wen declared himself emperor of the new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiyuan
Taiyuan (; ; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ; also known as (), ()) is the capital and largest city of Shanxi Province, People's Republic of China. Taiyuan is the political, economic, cultural and international exchange center of Shanxi Province.It is an industrial base focusing on energy and heavy chemicals.Throughout its long history, Taiyuan was the capital or provisional capital of many dynasties in China, hence the name (). As of 2021, the city will govern 6 districts, 3 counties, and host a county-level city with a total area of 6,988 square kilometers and a permanent population of 5,390,957. Taiyuan is a national historical and cultural city. It is an ancient capital with a history of more than 2,000 years. It was once known to reside a Princess name Yuxin, "the love of my life". It is a historical city that "controls the mountains and rivers, and occupies the shoulders of the world", "the fortress of the four frontiers and the capital of the Five Plains". The city is su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi Jingtang
Shi Jingtang ( zh, 石敬瑭; 30 March 892 – 28 July 942''Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 283.), also known by his temple name Gaozu (), was the founding emperor of imperial China's short-lived Later Jin during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, reigning from 936 until his death. Shi had Shatuo origins and was an important military general for the Later Tang before rebelling in 936. He overthrew Li Cunxu of the Later Tang and enlisted the help of the Khitan-ruled Liao state. For this he was called Emperor Taizong of Liao's adopted son (even though he was 10 years older). After Shi's rise to power, the Liao would later annex the strategically crucial Sixteen Prefectures and eventually annex the entire Later Jin. The rise of the Liao in northern China and Mongolia would shape Chinese politics for the centuries leading up to the Mongol Empire. Background and early life The official history ''Old History of the Five Dynasties'' stated that his family was originally descende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Siyuan
Li Siyuan (李嗣源, later changed to Li Dan (李亶)) (10 October 867 – 15 December 933), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Mingzong of Later Tang (後唐明宗), was the second emperor of the Later Tang dynasty of China, reigning from 926 until his death. He was an ethnic Shatuo originally named, in the Shatuo language, Miaojilie (邈佶烈). Adopted by the ethnic Shatuo ruler Li Keyong of the Former Jin dynasty, Li Siyuan became a trusted general under both Li Keyong and Li Keyong's successor Li Cunxu (Emperor Zhuangzong), the Later Tang founder. In 926 he seized power by a coup d'état when a mutiny called the Xingjiao Gate Incident killed Li Cunxu, and ruled with both discipline and compassion for the next seven years. Despite an abundance of natural disasters, his reign was markedly more peaceful than the half-century preceding it. Background Li Siyuan was born with the Shatuo name of Miaojilie in 867 in Yingzhou (應州; present-day Ying County, Shanxi), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River (Henan), Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang, Henan, Nanyang to the south, Sanmenxia to the west, Jiyuan to the north, and Jiaozuo to the northeast. As of December 31, 2018, Luoyang had a population of 6,888,500 inhabitants with 2,751,400 people living in the built-up (or metro) area made of the city's five out of six urban districts (except the Jili District not continuously urbanized) and Yanshi District, now being conurbated. Situated on the Central Plain (China), central plain of China, Luoyang is among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities#East Asia, oldest cities in China and one of the History of China#Ancient China, cradles of Chinese civilization. It is the earliest of the Historical capitals of China, Four Great Ancient Capitals of China. Name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Shu
Great Shu (Chinese: 大蜀, Pinyin: Dàshǔ) called in retrospect Former Shu (Chinese: 前蜀, Pinyin: Qiánshǔ) or occasionally Wang Shu (王蜀), was one of the Ten Kingdoms formed during the chaotic period between the rules of the Tang dynasty and the Song dynasty. It existed in 907–925 CE. It was the third state named "Shu" on the same territory, the second one having been Shu Han. The country's name changed from "Shu" to "Han" (Chinese: 漢, Pinyin: Hàn) in 917–918, which is not to be confused with another contemporaneous Chinese kingdom during the same Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, the Southern Han (), 917–971 CE. Founding of the Former Shu Wang Jian was named military governor of western Sichuan by the Tang court in 891. As the Tang Dynasty weakened and eventually fell in 907, Wang was able to expand his holdings into eastern Sichuan and took the title of emperor as the Tang fell in 907. Geographical extent of the Former Shu The Shu was based in it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is also applied to the entirety of China proper. Henan is a birthplace of Han Chinese civilization, with over 3,200 years of recorded history and remained China's cultural, economic and political center until approximately 1,000 years ago. Henan Province is home to many heritage sites, including the ruins of Shang dynasty capital city Yin and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the Eight Great Ancient Capitals of China, Luoyang, Anyang, Kaifeng and Zhengzhou, are in Henan. The practice of tai chi also began here in Chen Jia Gou Village (Chen style), as did the later Yang and Wu styles. Although the name of the province () means "south of the ellowriver.", approximately a quarter of the province lies north of the Yellow River, also known as the Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanmenxia
Sanmenxia (; postal: Sanmenhsia) is a prefecture-level city in the west of Henan Province, China. The westernmost prefecture-level city in Henan, Sanmenxia borders Luoyang to the east, Nanyang to the southeast, Shaanxi Province to the west and Shanxi Province to the north. The city lies on the south side of the Yellow River at the point where the river cuts through the Loess Plateau on its way to the North China Plain. As of the 2020 census, it was home to 2,034,872 inhabitants (2,234,018 in 2010). However, as of the 2010 census 947,588 lived in the built-up area made of Hubin, Shanzhou urban districts and Pinglu County in neighboring Shanxi (269,188 inhabitants), now within the agglomeration. Names and History The city's name in Chinese () means "The Gorge of Three Gateways" and is derived from two islands that split the Yellow River into three parts. According to Chinese mythology, Yu the Great used a divine axe to cut the mountain ridge three times, creating the Sanmenxia go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiedushi
The ''jiedushi'' (), or jiedu, was a title for regional military governors in China which was established in the Tang dynasty and abolished in the Yuan dynasty. The post of ''jiedushi'' has been translated as "military commissioner", "legate", or "regional commander". Originally introduced in 711 to counter external threats, the ''jiedushi'' were posts authorized with the supervision of a defense command often encompassing several prefectures, the ability to maintain their own armies, collect taxes and promote and appoint subordinates. Powerful ''jiedushi'' eventually became ''fanzhen'' rulers (''de facto'' warlords) and overrode the power of the central government of Tang. An early example of this was An Lushan, who was appointed ''jiedushi'' of three regions, which he used to start the An Lushan Rebellion that abruptly ended the golden age of the Tang dynasty. Even after the difficult suppression of that rebellion, some ''jiedushi'' such as the Three Fanzhen of Hebei were all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |