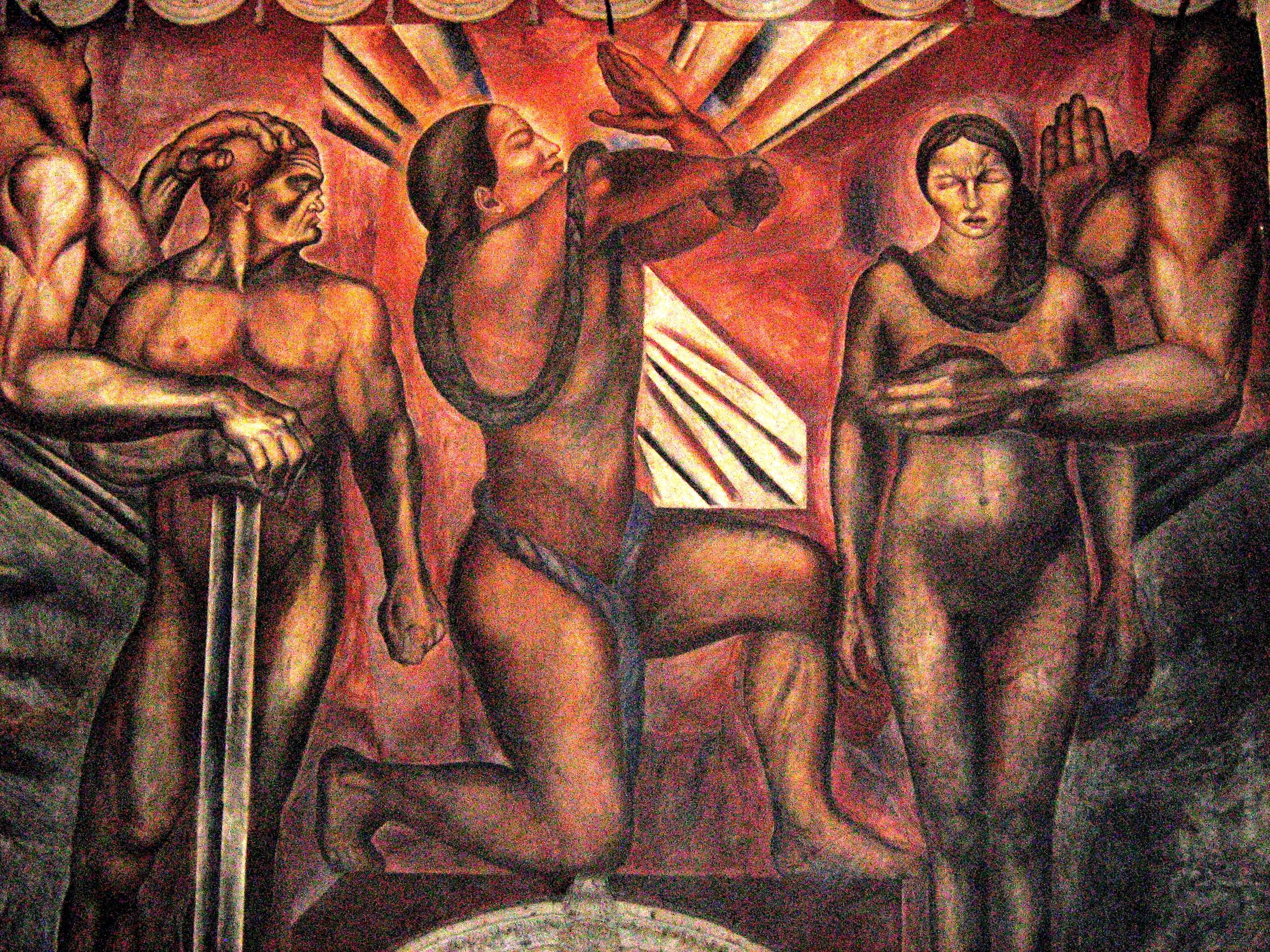|
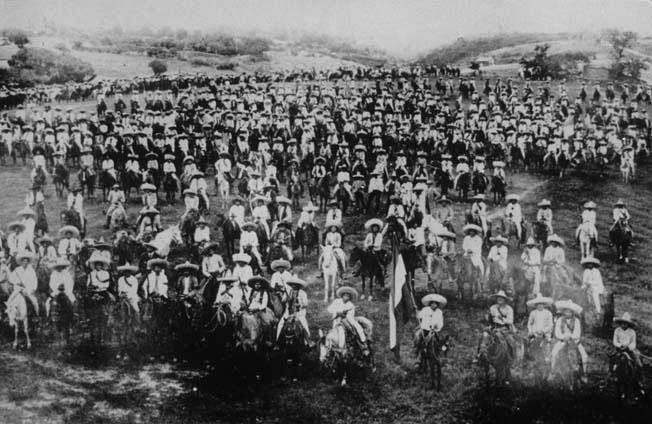
Zapatistas (1879–1919), Mexican revolutionary
{{Disambig ...
Zapatista(s) may refer to: * Liberation Army of the South, formed 1910s, a Mexican insurgent group involved in the Mexican Revolution * Zapatista Army of National Liberation (EZLN), formed 1983, a Mexican indigenous armed revolutionary group based in Chiapas * Rebel Zapatista Autonomous Municipalities, autonomous municipalities in Chiapas governed by radical democratic ideals * The ideology of Zapatismo originating in the early 1900s as part of the Mexican Revolution * The ideology of Neozapatismo originating in the late 1900s associated with armed uprisings in Chiapas, Mexico * An oil painting by José Clemente Orozco See also *Emiliano Zapata Emiliano Zapata Salazar (; August 8, 1879 – April 10, 1919) was a Mexican revolutionary. He was a leading figure in the Mexican Revolution of 1910–1920, the main leader of the people's revolution in the Mexican state of Morelos, and the ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zapatista Army Of National Liberation
The Zapatista Army of National Liberation (, EZLN), often referred to as the Zapatistas (Mexican ), is a far-left political and militant group that controls a substantial amount of territory in Chiapas, the southernmost state of Mexico. Since 1994, the group has been nominally at war with the Mexican state (although it may be described at this point as a frozen conflict). The EZLN used a strategy of civil resistance. The Zapatistas' main body is made up of mostly rural indigenous people, but it includes some supporters in urban areas and internationally. The EZLN's main spokesperson is Subcomandante Insurgente Galeano, previously known as Subcomandante Marcos (a.k.a. Compañero Galeano and Delegate Zero in relation to "the Other Campaign"). Unlike other Zapatista spokespeople, Marcos is not an indigenous Maya. The group takes its name from Emiliano Zapata, the agrarian revolutionary and commander of the Liberation Army of the South during the Mexican Revolution, and sees itse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neozapatismo
Neozapatismo or neozapatism (sometimes simply Zapatismo) is the political philosophy and practice devised and employed by the Zapatista Army of National Liberation (, EZLN), who have governed a number of communities in Chiapas, Mexico since the beginning of the Chiapas conflict. According to its adherents, it is not an ideology: "Zapatismo is not a new political ideology or a rehash of old ideologies . . . There are no universal recipes, lines, strategies, tactics, laws, rules or slogans. There is only a desire: to build a better world, that is, a new world." As UCL media studies lecturer Anthony Faramelli has written, "Zapatismo is not attempting to inaugurate and/or lead any kind of resistance to neoliberalism, but rather facilitate the meeting of resistance, and allow it to organically form worlds outside of exploitation." Others have proposed a broader conception of neozapatismo that extends beyond the confines of political philosophy and practice. For example, according ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebel Zapatista Autonomous Municipalities
Rebel Zapatista Autonomous Municipalities (Spanish: ''Municipios Autónomos Rebeldes Zapatistas'', ''MAREZ'') are ''de facto'' autonomous territories controlled by the neo-Zapatista support bases in the Mexican state of Chiapas, founded following the Zapatista uprising which took place in 1994 and is part of the wider Chiapas conflict. Despite attempts at negotiation with the Mexican government which resulted in the San Andrés Accords in 1996, the region's autonomy remains unrecognized by it. The Zapatista army, or EZLN, does not hold any power in the autonomous municipalities. According to its constitution, no commander or member of the ''Clandestine Revolutionary Indigenous Committee'' may take positions of authority or government in these spaces. These places are found within the official municipalities, and several are even within the same municipality, as in the case of San Andrés Larrainzar and Ocosingo. The MAREZ are coordinated by autonomous Zapatista Councils of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberation Army Of The South
The Liberation Army of the South ( es, Ejército Libertador del Sur, ELS) was a guerrilla force led for most of its existence by Emiliano Zapata that took part in the Mexican Revolution from 1911 to 1920. During that time, the Zapatistas fought against the national governments of Porfirio Díaz, Francisco Madero, Victoriano Huerta, and Venustiano Carranza. Their goal was rural land reform, specifically reclaiming communal lands stolen by hacendados in the period before the revolution. Although rarely active outside their base in Morelos, they allied with Pancho Villa to support the Conventionists against the Carrancistas. After Villa's defeat, the Zapatistas remained in open rebellion. It was only after Zapata's 1919 assassination and the overthrow of the Carranza government that Zapata's successor, Gildardo Magaña, negotiated peace with President Álvaro Obregón. Background The Zapatistas were formed in Morelos, a small and densely populated state with a largely ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zapatismo
Zapatismo is the armed movement identified with the ideas of Emiliano Zapata, leader of the Mexican Revolution, reflected mainly in the Plan of Ayala term 1911. The members of the Liberation Army of the South led by Zapata were known as "Zapatistas". One of the most symbolic phrases of Zapatismo was that the land belongs to the tiller, reflecting a kind of agrarian socialism, originally coined by Zapata himself while trying to remove the chieftaincy in Mexico and restore possession of the land to the peasant classes in the south. The phrase and what it represents became the symbols of Mexican agrarianism. See also * Economic history of Mexico * Index of Mexico-related articles * Neozapatismo * Plan of Ayala The Plan of Ayala (Spanish: ''Plan de Ayala'') was a document drafted by revolutionary leader Emiliano Zapata during the Mexican Revolution. In it, Zapata denounced President Francisco Madero for his perceived betrayal of the revolutionary idea ... * Subcommandante Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Clemente Orozco
José Clemente Orozco (November 23, 1883 – September 7, 1949) was a Mexican caricaturist and painter, who specialized in political murals that established the Mexican Mural Renaissance together with murals by Diego Rivera, David Alfaro Siqueiros, and others. Orozco was the most complex of the Mexican muralists, fond of the theme of human suffering, but less realistic and more fascinated by machines than Rivera. Mostly influenced by Symbolism, he was also a genre painter and lithographer. Between 1922 and 1948, Orozco painted murals in Mexico City, Orizaba, Claremont, California, New York City, Hanover, New Hampshire, Guadalajara, Jalisco, and Jiquilpan, Michoacán. His drawings and paintings are exhibited by the Carrillo Gil Museum in Mexico City, and the Orozco Workshop-Museum in Guadalajara. Orozco was known for being a politically committed artist, and he promoted the political causes of peasants and workers. Life José Clemente Orozco was born in 1883 in Zapo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |