|
Zanzibar Sultanate
The Sultanate of Zanzibar ( sw, Usultani wa Zanzibar, ar, سلطنة زنجبار , translit=Sulṭanat Zanjībār), also known as the Zanzibar Sultanate, was a state controlled by the Sultan of Zanzibar, in place between 1856 and 1964. The Sultanate's territories varied over time, and at their greatest extent spanned all of present-day Kenya and the Zanzibar Archipelago off the Swahili Coast. After a decline, the state had sovereignty over only the archipelago and a strip along the Kenyan coast, with the interior of Kenya constituting the British Kenya Colony and the coastal strip administered as a ''de facto'' part of that colony. Under an agreement reached on 8 October 1963, the Sultan of Zanzibar relinquished sovereignty over his remaining territory on the mainland, and on 12 December 1963, Kenya officially obtained independence from the British. On 12 January 1964, Jamshid bin Abdullah, the last sultan, was deposed and lost sovereignty over the last of his dominions, Z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Charles Lawrence
Geoffrey Charles Lawrence, (1915–1994) was acting Chief Minister of Zanzibar Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islands ... from 23 February 1961 to 5 June 1961. 1915 births 1994 deaths Chief Ministers of Zanzibar Zanzibari politicians Companions of the Order of St Michael and St George Officers of the Order of the British Empire {{Zanzibar-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscat And Oman
The Sultanate of Muscat and Oman ( ar, سلطنة مسقط وعمان, Salṭanat Masqaṭ wa-‘Umān), also known briefly as the State of Muscat and Oman () during the rule of Taimur bin Feisal, was a sovereign state that encompassed the present-day Sultanate of Oman and parts of present-day United Arab Emirates and Pakistan, in the second half of the 19th century and 20th century. Ruled by the Busaid dynasty, it was established as a result of the partition of the Omani Empire upon the death of its last ruler Said bin Sultan. The Sultanate transitioned into a new form of government after the palace coup of 23 July 1970 in which the sultan Said bin Taimur was immediately deposed in favor of his son Qaboos bin Said. Name Strictly speaking, Oman (Imamate of Oman, ar, عُمان الوسطى, ʿUmān al-Wusṭā) is the inner, continental part of the region without access to the coast and with the capital in the city of Nizwa. Muscat is a coastal sultanate, the rulers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenya Colony
The Colony and Protectorate of Kenya, commonly known as British Kenya or British East Africa, was part of the British Empire in Africa. It was established when the former East Africa Protectorate was transformed into a British Crown colony in 1920. Technically, the "Colony of Kenya" referred to the interior lands, while a 16 km (10 mi) coastal strip, nominally on lease from the Sultan of Zanzibar, was the "Protectorate of Kenya", but the two were controlled as a single administrative unit. The colony came to an end in 1963 when an ethnic Kenyan majority government was elected for the first time and eventually declared independence as the Republic of Kenya. History The Colony and Protectorate of Kenya was established on 23 July 1920 when the territories of the former East Africa Protectorate (except those parts of that Protectorate over which His Majesty the Sultan of Zanzibar had sovereignty) were annexed by the UK. The Kenya Protectorate was established on 29 Novembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts established by England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as "the empire on which the sun never sets", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established large overse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
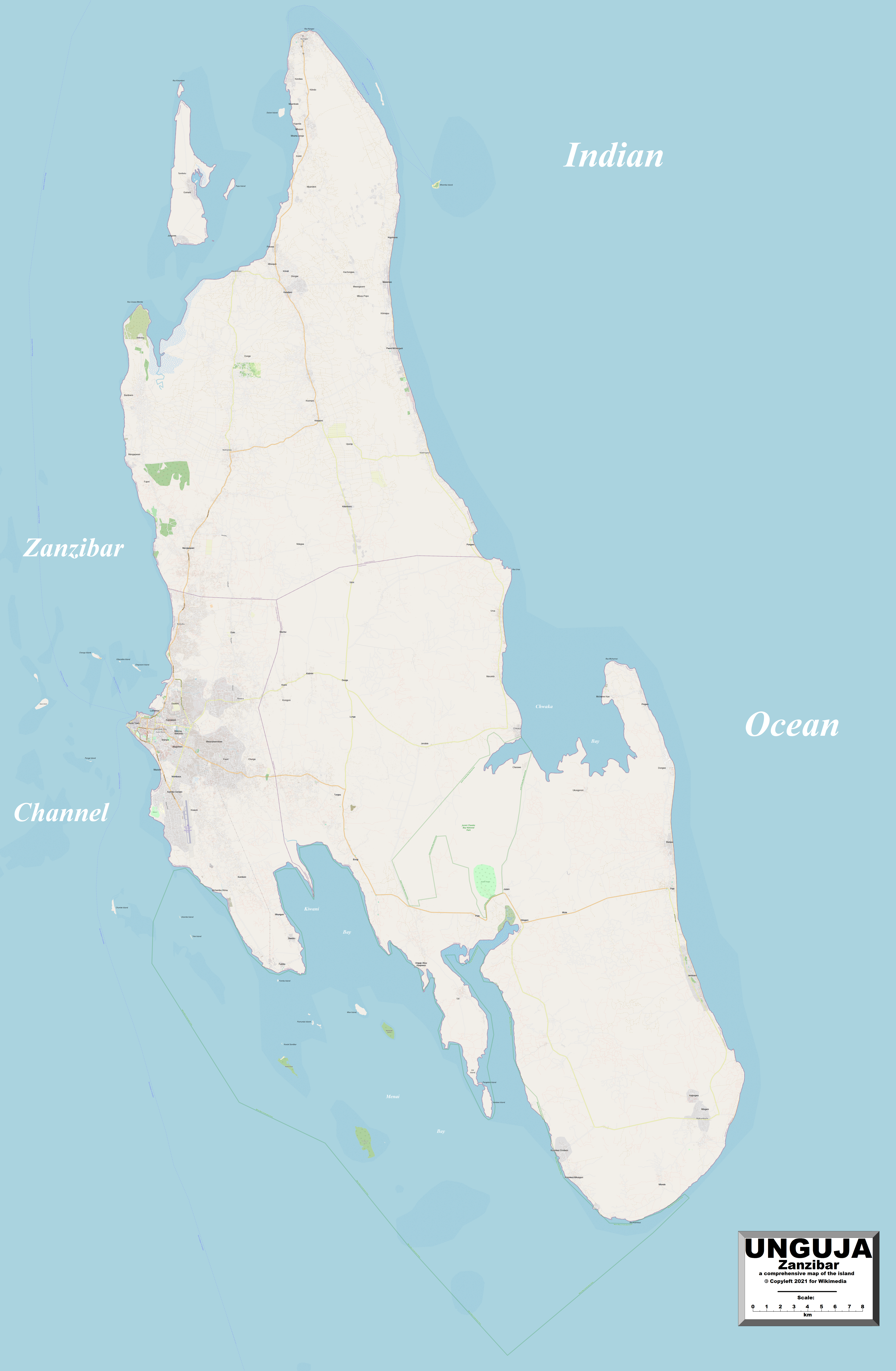
Zanzibar Archipelago
The Zanzibar Archipelago ( ar, أرخبيل زنجبار, sw, Funguvisiwa la Zanzibar) consists of several islands lying off the coast of East Africa south of the Somali sea. The archipelago is also known as the Spice Islands. There are four main islands, three primary islands with human populations, a fourth coral island that serves as an essential breeding ground for seabirds, plus a number of smaller islets that surround them and an isolated tiny islet. Most of the archipelago belongs to the Zanzibar semi-autonomous region of Tanzania, while Mafia Island and its associated islets are parts of the Pwani Region on the mainland. List of islands Main islands * Unguja Island – the largest island, colloquially referred to as Zanzibar, has 896,721 inhabitants *Pemba Island – the second-largest island with 406,808 inhabitants *Latham Island (also called "Fungu Kizimkazi") – tiny and uninhabited *Mafia Island – 46,850 inhabitants Surrounding Unguja Island *Bawe Island * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultan Of Zanzibar
The sultans of Zanzibar ( ar, سلاطين زنجبار) were the rulers of the Sultanate of Zanzibar, which was created on 19 October 1856 after the death of Said bin Sultan, who had ruled Oman and Zanzibar as the sultan of Oman since 1804. The sultans of Zanzibar were of a cadet branch of the Al Said Dynasty of Oman. In 1698, Zanzibar became part of the overseas holdings of Oman, falling under the control of the sultan of Oman. In 1832, or 1840 (the date varies among sources), Said bin Sultan moved his capital from Muscat in Oman to Stone Town. He established a ruling Arab elite and encouraged the development of clove plantations, using the island's slave labour. Zanzibar's commerce fell increasingly into the hands of traders from the Indian subcontinent, whom Said encouraged to settle on the island. After his death in 1856, two of his sons, Majid bin Said and Thuwaini bin Said, struggled over the succession, so Zanzibar and Oman were divided into two separate principalitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Theresa Thaler
The Maria Theresa thaler (MTT) is a silver bullion coin and a type of Conventionsthaler that has been used in world trade continuously since it was first minted in 1741. It is named after Maria Theresa who ruled Austria, Hungary, and Bohemia from 1740 to 1780 and is depicted on the coin. History In 1741 the first MTT was struck according to the Reichsthaler standard with of a Cologne mark of fine silver, or 25.98 grams. In 1750 a new thaler was struck with a gross weight of of 1 Vienna mark of silver, fine (with a fine silver content of 23.39 grams, or of a Cologne mark). In 1751 this new standard Conventionsthaler was effectively adopted across the German-speaking world when it was accepted formally in the Bavarian monetary convention. This new, post-1751 thaler has continued as a trade coin ever since. Since the death of Maria Theresa in 1780, the coin has always been dated 1780. On 19 September 1857, Emperor Francis Joseph of Austria declared the Maria Theresa thaler t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Rupee
The Indian rupee ( symbol: ₹; code: INR) is the official currency in the republic of India. The rupee is subdivided into 100 ''paise'' (singular: ''paisa''), though as of 2022, coins of denomination of 1 rupee are the lowest value in use whereas 2000 rupees is the highest. The issuance of the currency is controlled by the Reserve Bank of India. The Reserve Bank manages currency in India and derives its role in currency management on the basis of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. Etymology The immediate precursor of the rupee is the ''rūpiya''—the silver coin weighing 178 grains minted in northern India by first Sher Shah Suri during his brief rule between 1540 and 1545 and adopted and standardized later by the Mughal Empire. The weight remained unchanged well beyond the end of the Mughals until the 20th century. Though Pāṇini mentions (), it is unclear whether he was referring to coinage. ''Arthashastra'', written by Chanakya, prime minister to the first Maurya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zanzibari Rupee
The rupee ( ar, روپيه) was the currency of Zanzibar from 1908 to December 31, 1935. It was subdivided into 100 ''cents'' (Arabic: سنت). History The rupee replaced the Zanzibari ryal at a rate of 2⅛ rupees = 1 ryal and was equivalent to the Indian rupee The Indian rupee ( symbol: ₹; code: INR) is the official currency in the republic of India. The rupee is subdivided into 100 ''paise'' (singular: ''paisa''), though as of 2022, coins of denomination of 1 rupee are the lowest value in use wh ..., which was also in circulation. The Zanzibari rupee remained equal to the Indian rupee and was replaced on January 1, 1936, by the East African shilling at the rate of 1½ East African shillings = 1 Zanzibari rupee. Coins Bronze coins were introduced in 1908 in denominations of 1 and 10 cents, together with nickel 20 cents. No further issues of coins were made. Banknotes In 1908, banknotes were introduced by the government of Zanzibar in denominations of 5, 10, 20, and 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |