|
Zygmunt Karol Radziwiłł
Zygmunt Karol Radziwiłł (; 1591-1642) was a Polish-Lithuanian noble, who served as the Chamberlain (''podkomorzy'') at Poznań from 1625, Queen's Carver (''krajczy'') from 1617, Carver of Lithuania from 1633, Cupbearer of Lithuania from 1638, and Governor (voivode) of Nowogródek from 1642. He was a member of the Knights Hospitaller Order and the patron of Knight Hospitaller centers in Poznań and Stołowicze (in Lithuania). Radziwiłł was born on 4 December 1591 in Nieśwież to Mikołaj Krzysztof "Sierotka" Radziwiłł (nicknamed "The Orphan") and Halaszka Eufemia Wiśniowiecka, and died on 5 November 1642 in Assisi, Italy. In 1621, he took part in the Battle of Khotyn (1621), and later commanded Lisowczycy mercenaries in 1622 during the period of their service in the Holy Roman Empire. After the death of his older brother, Albrycht Władysław Radziwiłł, he inherited ordynacja of Nieśwież Nyasvizh or Nesvizh is a town in Minsk Region, Belarus. It serves as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, existing from 1569 to 1795. This state was among the largest, most populated countries of 16th- to 18th-century Europe. At its peak in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth spanned approximately and supported a multi-ethnic population of around 12 million as of 1618. The official languages of the Commonwealth were Polish language, Polish and Latin Language, Latin, with Catholic Church, Catholicism as the state religion. The Union of Lublin established the Commonwealth as a single entity on 1 July 1569. The two nations had previously been in a personal union since the Union of Krewo, Krewo Agreement of 1385 (Polish–Lithuanian union) and the subsequent marriage of Queen Jadwiga of Poland to Grand Duke Jogaila of Lithuania, who was cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. For most of its history the Empire comprised the entirety of the modern countries of Germany, Czechia, Austria, the Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Slovenia, and Luxembourg, most of north-central Italy, and large parts of modern-day east France and west Poland. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne Roman emperor, reviving the title more than three centuries after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476. The title lapsed in 924, but was revived in 962 when Otto I, OttoI was crowned emperor by Pope John XII, as Charlemagne's and the Carolingian Empire's successor. From 962 until the 12th century, the empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Nyasvizh
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radziwiłł Family
The House of Radziwiłł (; ; ; ) is a Polish princely family of Lithuanian origin, and one of the most powerful magnate families originating from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and later also prominent in the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. Part of the representatives of the Radziwiłł family were known for their persistent and consistent struggle for the independence of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and for their crucial role in preserving the Grand Duchy of Lithuania as a separate state in the 16th and 17th centuries. The family was founded by Radvila Astikas, but over time it split into many branches, such as the Biržai-Dubingiai and Goniądz-Meteliai lines. However, most of the branches became extinct by the 18th century, with only the Nesvizh-Kleck-Ołyka line surviving to this day. Their descendants were highly prominent for centuries, first in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, later in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Kingdom of Prussia. The family produced man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secular Senators Of The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin , or or ), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. The origins of secularity can be traced to the Bible itself. The concept was fleshed out through Christian history into the modern era. Since the Middle Ages, there have been clergy not pertaining to a religious order called "secular clergy". Furthermore, secular and religious entities were not separated in the medieval period, but coexisted and interacted naturally. The word ''secular'' has a meaning very similar to profane as used in a religious context. Today, anything that is not directly connected with religion may be considered secular, in other words, neutral to religion. Secularity does not mean , but . Many activities in religious bodies are secular, and though there are multiple types of secularity or secularization, most do not lead to irreligiosity. Linguistically, a process by which anything becomes secular is named ''secularization' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksander Ludwik Radziwiłł
Prince Aleksander Ludwik Radziwiłł (; 4 August 1594 – 30 March 1654) was a Polish–Lithuanian nobleman. He was the Ordynat of Nieśwież, Stolnik (Master of the Pantry) of Lithuania since 1626, Krajczy (Carver) of Lithuania since 1630, governor of Brześć Litewski Voivodeship since 1631 to 1635, Court Marshal of Lithuania since 1635, Grand Marshal of Lithuania in 1637-1654 and voivode of Połock Voivodship during 1654. He also held the title Starost. He married Tekla Anna Wołłowicz in 1626, Katarzyna Eugenia Tyszkiewicz in 1639 and Lucrezia Maria Strozzi in October, 1642 in Warsaw. His marriage to Katarzyna Eugenia Tyszkiewicz, widow of Konstanty Wiśniowiecki's son, led to the conflict between Aleksander Ludwik Radziwłł and Jeremi Wiśniowiecki over the inheritance of Konstanty. Eventually, Katarzyna defected to Jeremi's side and divorced Aleksander, who was forced to give up his claims. He withdrew from politics during the reign of Sigismund III Vasa but suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
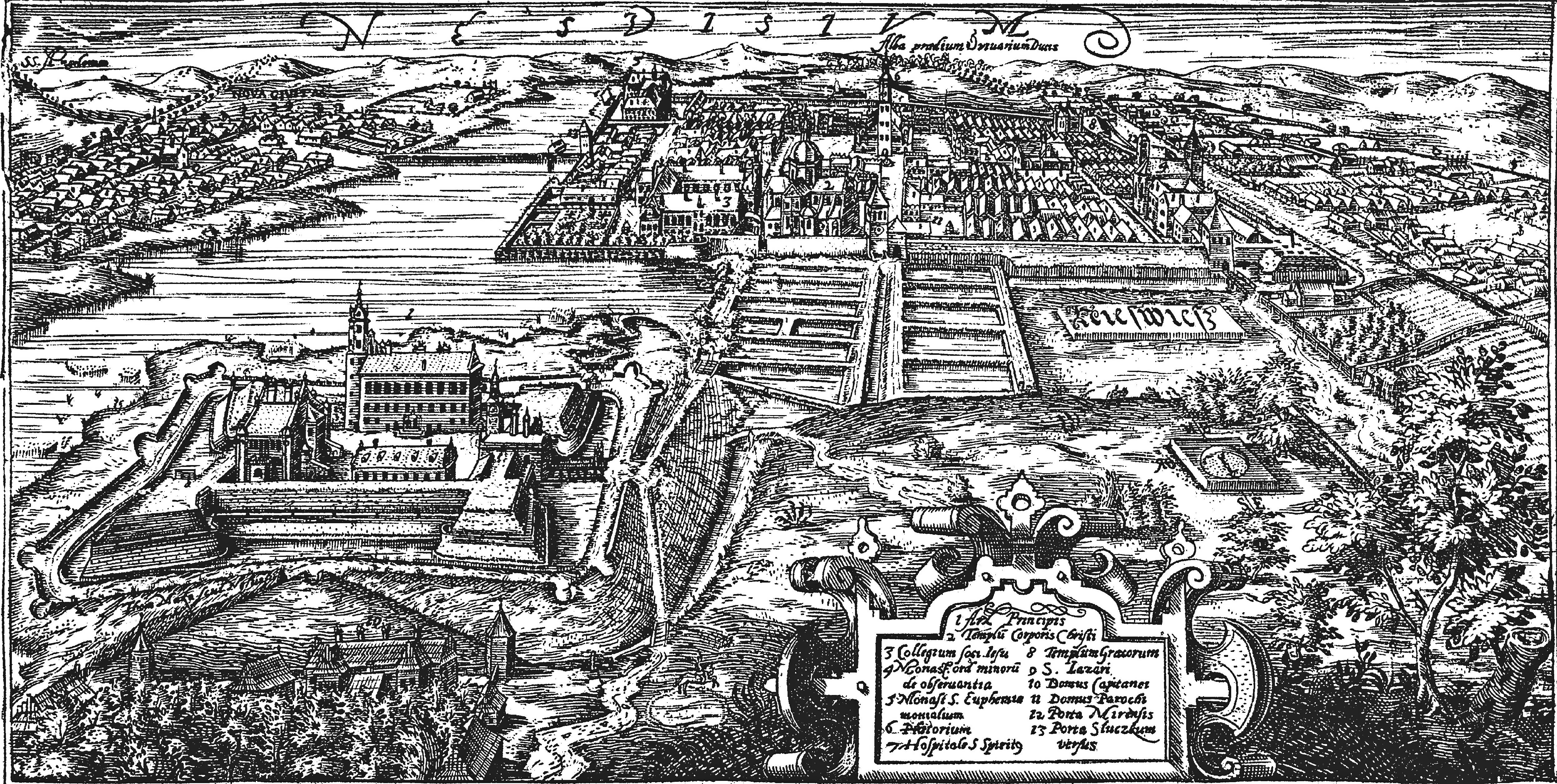
Nieśwież
Nyasvizh or Nesvizh is a town in Minsk Region, Belarus. It serves as the administrative centre of Nyasvizh District. Nyasvizh is the site of Nesvizh Castle, a World Heritage Site. In 2009, its population was 14,300. As of 2025, it has a population of 15,909. History Nesvizh was first documented in 1223. It was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania until 1793, but the Grand Duchy was part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth since 1569. In the 15th century, while still a minor town, it belonged to the Kiszka family and later to the Radziwiłł family, and remained the family's seat until 1813. In 1561 or 1562 Maciej Kawęczyński founded the print works of the Polish Brethren. The first Belarusian language book printed in Latin script, a catechism by Symon Budny, was published in Nesvizh in 1562. The ''Nieśwież Bible'' ('' Biblia nieświeska''), one of the oldest Polish translations of the Bible, also by Budny, was completed there in 1571 and published in 1572. Nesviz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordynacja
In English common law, fee tail or entail is a form of trust, established by deed or settlement, that restricts the sale or inheritance of an estate in real property and prevents that property from being sold, devised by will, or otherwise alienated by the tenant-in-possession, and instead causes it to pass automatically, by operation of law, to an heir determined by the settlement deed. The terms ''fee tail'' and ''tailzie'' are from Medieval Latin , which means "cut(-short) fee". Fee tail deeds are in contrast to "fee simple" deeds, possessors of which have an unrestricted title to the property, and are empowered to bequeath or dispose of it as they wish (although it may be subject to the allodial title of a monarch or of a governing body with the power of eminent domain). Equivalent legal concepts exist or formerly existed in many other European countries and elsewhere; in Scots law tailzie was codified in the Entail Act 1685. Most common law jurisdictions have abolished fee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albrycht Władysław Radziwiłł
Albrycht Władysław Radziwiłł (16 June 1589 – 20 July 1636) was a Polish–Lithuanian noble. Castellan of Troki from 1626 until 1633, castellan of Wilno from 1633. The 3rd ordynat of the Nieśwież Fee Tail, stolnik of Lithuania since 1620 and krajczy of Lithuania since 1622. Starost of Ryki and Szerszewy. Son of Mikołaj Krzysztof "Sierotka" Radziwiłł h. Trąby and Princess Elżbieta "Halaszka" Eufemia Wiśniowiecka h. Korybut, the daughter of voivode of Wołyń Prince Andrzej Wiśniowiecki h. Korybut and Eufemia Wierzbicka h. Radwan, daughter of Jerzy Wierzbicki h. Radwan and sister of Bishop Wiktoryn Wierzbicki h. Radwan. Marriage and issue Albrycht Władysław married Princess Anna Sapieha h. Lis, the daughter of Prince Lew Sapieha and Elżbieta Radziwiłł h. Trąby in 1618 in Wilno. He married the second time (a year after Anna's death) in 1628 Anna Zofia Zenowicz h. Deszpot, the daughter of castellan of Połock and ''starosta'' of Mińsk Mikołaj Bogu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisowczycy
Lisowczyks or Lisowczycy (; also known as ''Straceńcy'' ('lost men' or 'forlorn hope') or (company of ); or in singular form: Lisowczyk or ) was the name of an early 17th-century irregular unit of the Polish–Lithuanian light cavalry. The Lisowczycy took part in many battles across Europe and the historical accounts of the period characterized them as extremely agile, warlike, and bloodthirsty. Their numbers varied with time, from a few hundred to several thousand. The origin of the group can be traced to konfederacja (a form of semi-legal mutiny of royal forces, practiced in the Kingdom of Poland and then in the Commonwealth), organized around 1604 by Aleksander Józef Lisowski. They began to grow in strength and fame a few years later, when Lisowski's irregulars were incorporated into the forces fighting in Muscovy. The Lisowczycy unit of the Polish cavalry received no formal wages; instead, they were allowed to loot and plunder as they pleased. They relied on their spee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikołaj Krzysztof "Sierotka" Radziwiłł
Mikołaj is the Polish cognate of given name Nicholas, used both as a given name and a surname. It may refer to people: In Polish (or Polish-Lithuanian) nobility: * Mikołaj Kamieniecki, Polish nobleman and the first Grand Hetman of the Crown * Mikołaj Krzysztof "the Orphan" Radziwiłł, Polish-Lithuanian lord * Mikołaj Mielecki, Polish nobleman and politician * Mikołaj Ostroróg, Polish nobleman * Mikołaj Potocki, member of the Polish nobility, magnate, and the Field Hetman of the Crown * Mikołaj "the Black" Radziwiłł, noble of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Palatine of Vilnius, and Grand Chancellor of Lithuania * Mikołaj "the Red" Radziwiłł, Polish-Lithuanian lord, Palatine of Vilnius, Grand Chancellor, and Grand Hetman of Lithuania * Mikołaj VII Radziwiłł, Polish-Lithuanian lord, and Lord Grand Chamberlain of Lithuania * Mikołaj Sienicki, notable member of the landed nobility of the Kingdom of Poland * Mikołaj Szyszkowski, bishop of Warmia from 1633 until his d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Khotyn (1621)
The Battle of Khotyn or Battle of Chocim or Khotyn War (in Turkish: ''Hotin Muharebesi'') was a combined siege and series of battles which took place from 2 September to 9 October 1621 between a Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, commanded by the Grand Hetman of Lithuania Jan Karol Chodkiewicz, against an invading Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Imperial army, led by Sultan Osman II, which was stopped until the first autumn snows. On 9 October, due to the lateness of the season and heavy losses - due to failed assaults on Commonwealth fortifications - the Ottomans abandoned their siege and the battle concluded with a stalemate, which is reflected in the treaty where some sections favour the Ottomans while others favoured the Commonwealth. Chodkiewicz died on 24 September 1621 shortly before concluding a treaty with the Turks. Name Khotyn was conquered and controlled by many states, resulting in many name changes (; ; ; ). Other variations include ''Chotyn'', or ''Choczim'' (especially in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |