|
Zonal Flow
Zonal and meridional flow are directions and regions of fluid flow on a globe. Zonal flow follows a pattern along latitudinal lines, latitudinal circles or in the west–east direction. Meridional flow follows a pattern from north to south, or from south to north, along the Earth's longitude lines, longitudinal circles ( meridian) or in the north–south direction. These terms are often used in the atmospheric and earth sciences to describe global phenomena, such as "meridional wind", or "zonal average temperature". In the context of physics, zonal flow connotes a tendency of flux to conform to a pattern parallel to the equator of a sphere. In meteorological term regarding atmospheric circulation, zonal flow brings a temperature contrast along the Earth's longitude. Extratropical cyclones in zonal flows tend to be weaker, moving faster and producing relatively little impact on local weather. Extratropical cyclones in meridional flows tend to be stronger and move slower. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zonal Band
Zonal can refer to: * Zonal and meridional Zonal and meridional flow are directions and regions of fluid flow on a globe. Zonal flow follows a pattern along latitudinal lines, latitudinal circles or in the west–east direction. Meridional flow follows a pattern from north to south ..., directions on a globe, west–east and north–south, respectively. * Zonal and poloidal, directions in a toroidal magnetically confined plasma * Zonal polynomial, a symmetric multivariate polynomial * Zonal pelargonium, a type of pelargoniums * Zonal tournaments in chess: see Interzonal#Zonal tournaments * Electronic musicians Zonal, previously known as Techno Animal * Zonal (company), a UK based, privately owned company that provides EPoS systems {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of Atmosphere of Earth, air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the large-scale structure of its circulation remains fairly constant. The smaller-scale weather systems – middle latitudes, mid-latitude low-pressure area, depressions, or tropical convective cells – occur chaotically, and long-range weather predictions of those cannot be made beyond ten days in practice, or a month in theory (see chaos theory and the butterfly effect). The Earth's weather is a consequence of its illumination by the Sun and the laws of thermodynamics. The atmospheric circulation can be viewed as a heat engine driven by the Sun's energy and whose heat sink, energy sink, ultimately, is the blackness of space. The work produced by that engine causes the motion of the masses of air, and in that process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meridione
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions. The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or culture of the Historical region, historical and cultural region that was once politically under the administration of the former Kingdoms of Kingdom of Naples, Naples and Kingdom of Sicily, Sicily (officially denominated as one entity and , i.e. "Kingdom of Sicily on the other side of Strait of Messina, the Strait" and "across the Strait") and which later shared a common organization into Italy's largest List of historical states of Italy, pre-unitarian state, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. The island of Sardinia, which was not part of the aforementioned polity and had been under the rule of the Alps, Alpine House of Savoy, which would eventually annex the Bourbons' southern Italian kingdom altogether, is nonetheless often subsumed into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poloidal
The terms toroidal and poloidal refer to directions relative to a torus of reference. They describe a three-dimensional coordinate system in which the poloidal direction follows a small circular ring around the surface, while the toroidal direction follows a large circular ring around the torus, encircling the central void. The earliest use of these terms cited by the Oxford English Dictionary is by Walter M. Elsasser (1946) in the context of the generation of the Earth's magnetic field by currents in the core, with "toroidal" being parallel to lines of constant latitude and "poloidal" being in the direction of the magnetic field (i.e. towards the poles). The OED also records the later usage of these terms in the context of toroidally confined plasmas, as encountered in magnetic confinement fusion. In the plasma context, the toroidal direction is the long way around the torus, the corresponding coordinate being denoted by in the slab approximation or or in magnetic coordinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zonal Flow (plasma)
In toroidally confined fusion plasma experiments the term zonal flow means a plasma flow within a magnetic surface primarily in the poloidal direction. This usage is inspired by the analogy between the quasi-two-dimensional nature of large-scale atmospheric and oceanic flows, where zonal means latitudinal, and the similarly quasi-two-dimensional nature of low-frequency flows in a strongly magnetized plasma. Zonal flows in the toroidal plasma context are further characterized by * being localized in their radial extent transverse to the magnetic surfaces (in contrast to global plasma rotation), * having little or no variation in either the poloidal or toroidal direction—they are ''m'' = ''n'' = 0 modes (where ''m'' and ''n'' are the poloidal and toroidal mode numbers, respectively), * having zero real frequency when analyzed by linearization around an unperturbed toroidal equilibrium state (in contrast to the geodesic acoustic mode branch, which has finite frequency). * Arising ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Physics
Plasma () is a state of matter characterized by the presence of a significant portion of charged particles in any combination of ions or electrons. It is the most abundant form of ordinary matter in the universe, mostly in stars (including the Sun), but also dominating the rarefied intracluster medium and intergalactic medium. Plasma can be artificially generated, for example, by heating a neutral gas or subjecting it to a strong electromagnetic field. The presence of charged particles makes plasma electrically conductive, with the dynamics of individual particles and macroscopic plasma motion governed by collective electromagnetic fields and very sensitive to externally applied fields. The response of plasma to electromagnetic fields is used in many modern devices and technologies, such as plasma televisions or plasma etching. Depending on temperature and density, a certain number of neutral particles may also be present, in which case plasma is called partially ioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinate
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine and standardize the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The coordinates are not interchangeable; they are commonly distinguished by their position in an ordered tuple, or by a label, such as in "the ''x''-coordinate". The coordinates are taken to be real numbers in elementary mathematics, but may be complex numbers or elements of a more abstract system such as a commutative ring. The use of a coordinate system allows problems in geometry to be translated into problems about numbers and ''vice versa''; this is the basis of analytic geometry. Common coordinate systems Number line The simplest example of a coordinate system is the identification of points on a line with real numbers using the '' number line''. In this system, an arbitrary point ''O'' (the ''origin'') is chosen on a given line. The coordinate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Velocity
In meteorology, wind speed, or wind flow speed, is a fundamental atmospheric quantity caused by air moving from high to low pressure, usually due to changes in temperature. Wind speed is now commonly measured with an anemometer. Wind speed affects weather forecasting, aviation and maritime operations, construction projects, growth and metabolism rates of many plant species, and has countless other implications. Wind direction is usually almost parallel to isobars (and not perpendicular, as one might expect), due to Earth's rotation. Units The meter per second (m/s) is the SI unit for velocity and the unit recommended by the World Meteorological Organization for reporting wind speeds, and used amongst others in weather forecasts in the Nordic countries. Since 2010 the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) also recommends meters per second for reporting wind speed when approaching runways, replacing their former recommendation of using kilometers per hour (km/h). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Field
In vector calculus and physics, a vector field is an assignment of a vector to each point in a space, most commonly Euclidean space \mathbb^n. A vector field on a plane can be visualized as a collection of arrows with given magnitudes and directions, each attached to a point on the plane. Vector fields are often used to model, for example, the speed and direction of a moving fluid throughout three dimensional space, such as the wind, or the strength and direction of some force, such as the magnetic or gravitational force, as it changes from one point to another point. The elements of differential and integral calculus extend naturally to vector fields. When a vector field represents force, the line integral of a vector field represents the work done by a force moving along a path, and under this interpretation conservation of energy is exhibited as a special case of the fundamental theorem of calculus. Vector fields can usefully be thought of as representing the velocit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Wave
A cold wave (known in some regions as a cold snap, cold spell or Arctic Snap) is a weather phenomenon that is distinguished by a cooling of the air. Specifically, as used by the U.S. National Weather Service, a cold wave is a rapid fall in temperature within a 24-hour period requiring substantially increased protection to agriculture, industry, commerce, and social activities. The precise criteria for a cold wave are the rate at which the temperature falls, and the minimum to which it falls. This minimum temperature is dependent on the geographical region and time of year. In the United States, a ''cold spell'' is defined as the national average high temperature dropping below . A cold wave of sufficient magnitude and duration may be classified as a cold air outbreak (CAO). Effects A cold wave can cause death and injury to livestock and wildlife. Exposure to cold mandates greater caloric intake for all animals, including humans, and if a cold wave is accompanied by heavy and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
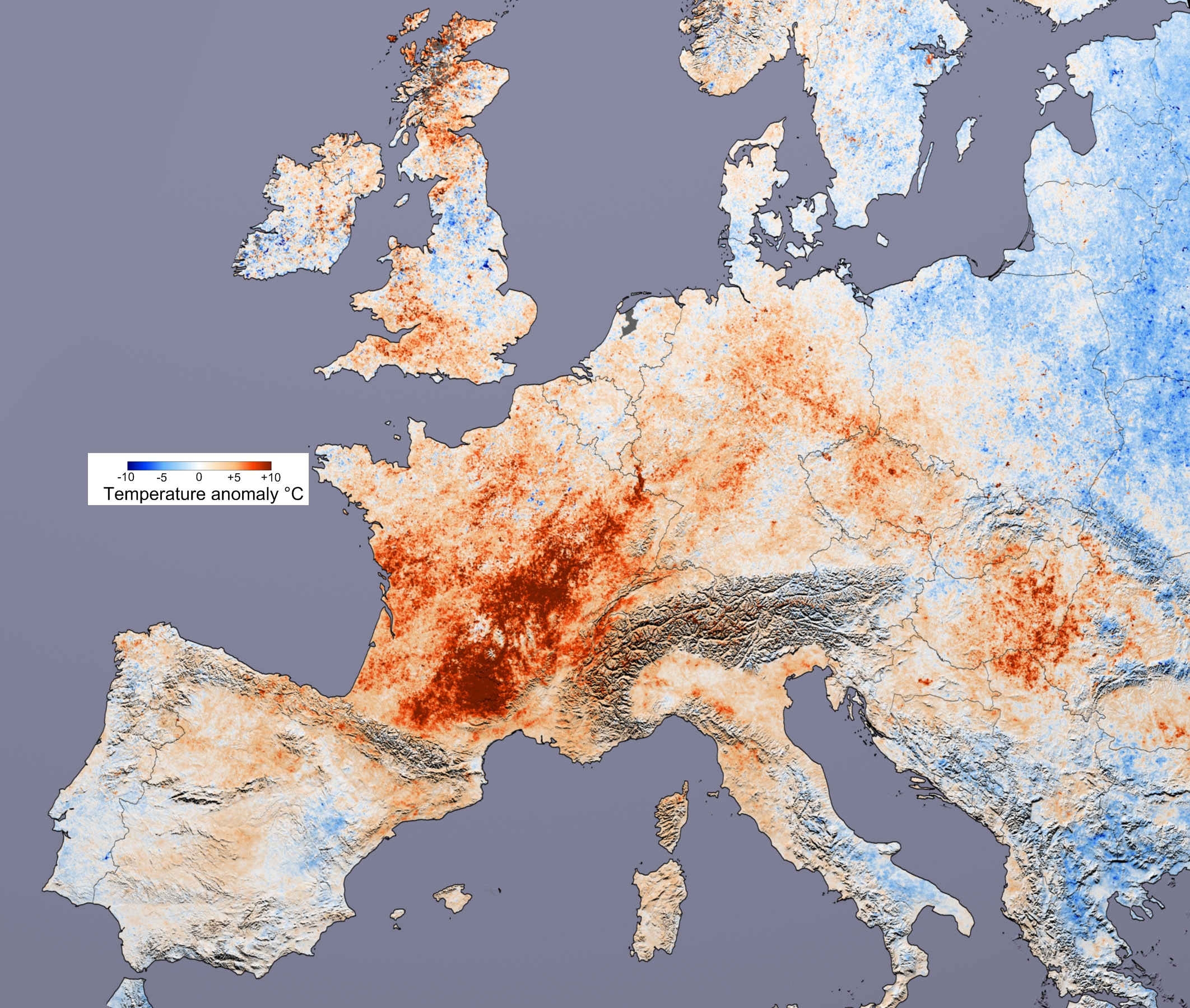
Heat Wave
A heat wave or heatwave, sometimes described as extreme heat, is a period of abnormally hot weather generally considered to be at least ''five consecutive days''. A heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the area and to normal temperatures for the season. The main difficulties with this broad definition emerge when one must quantify what the 'normal' temperature state is, and what the spatial extent of the event may or must be. Temperatures that humans from a hotter climate consider normal can be regarded as a heat wave in a cooler area. This would be the case if the warm temperatures are outside the normal climate pattern for that area. Heat waves have become more frequent, and more intense over land, across almost every area on Earth since the 1950s, the increase in frequency and duration being caused by climate change. Heat waves form when a high-pressure area in the upper atmosphere strengthens and remains over a region for several days up to seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extreme Weather
Extreme weather includes unexpected, unusual, severe weather, severe, or unseasonal weather; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution—the range that has been seen in the past. Extreme events are based on a location's recorded weather history. The main types of extreme weather include heat waves, cold waves, droughts, and heavy precipitation or storm events, such as tropical cyclones. Extreme weather can have various effects, from natural hazards such as floods and landslides to social costs on human health and the economy. Severe weather is a particular type of extreme weather which poses risks to life and property. Weather patterns in a given region vary with time, and so extreme weather can be attributed, at least in part, to the natural Climate variability and change, climate variability that exists on Earth. For example, the El Niño–Southern Oscillation, El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) or the North Atlantic oscillation (NAO) are climate phenomena that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |