|
Zofia Holszańska
Sophia of Halshany (; ; ; – 21 September 1461 in Kraków), known simply as Sonka, was a princess of Lithuanian Alšėniškiai princely family who was Queen of Poland as the fourth and last wife of Jogaila, King of Poland and Supreme Duke of Lithuania. As the mother to Władysław III and Casimir IV, she was the co-founder of the Jagiellonian dynasty. Early life and marriage to Jogaila Sophia was the niece of Uliana Olshanska, the wife of Vytautas, and a middle daughter of , son of Vytautas' right-hand man Ivan Olshansky, and , daughter of Dmitry of Druck. Historians disagree on the identity of Dmitry: Polish historiography usually provides Jogaila's half-brother Dmitry I Starshiy while Russian historians provide Dimitri Semenovich of Rurikid origin. Her father died when she was young and the family moved to Druck to live with Alexandra's brother Siemion Drucki. Sophia grew up in a Ruthenian environment and was an Eastern Orthodox Christian (her Orthodox name is Sophia, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, partitions of Poland–Lithuania. The state was founded by Lithuanians (tribe), Lithuanians, who were at the time a Lithuanian mythology, polytheistic nation of several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija. By 1440 the grand duchy had become the largest European state, controlling an area from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south. The grand duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Belarus, Lithuania, most of Ukraine as well as parts of Latvia, Moldova, Poland and Russia. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multinational state, multi-ethnic and multiconfessionalism, multiconfessional sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedwig Jagiellon (1408–1431)
Hedwig Jagiellon (; ; 8 April 1408 – 8 December 1431) was a Polish and Lithuanian princess, and a member of the Jagiellon dynasty. For most of her life she, as the only child of Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila, Jagiello), was considered to be heiress of the Polish and Lithuanian thrones. After the birth of Jagiello's sons in 1424 and 1427, Hedwig had some support for her claims to the throne. She died in 1431 amidst rumors that she was poisoned by her stepmother Sophia of Halshany. Family relations She was the only daughter of King of Poland and Supreme Duke of Lithuania Władysław Jagiełło by his second wife, Anna of Cilli, daughter of William, Count of Cilli (Celje), and Anna of Poland. Anna of Celje was a granddaughter of King Casimir III of Poland and therefore a Piast heiress. Thanks to his marriage to her in 1402, Jagiello re-legitimized his rule as King of Poland after the death of his first wife, Hedwig (Jadwiga), who reigned as King (not Queen consort) of Polan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Granowska
Elizabeth Granowska or Elisabeth Pilecki (; – 12 May 1420 in Kraków) was Queen of Poland (1417–1420) as the third wife of Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila), Grand Duke of Lithuania and King of Poland (reigning from 1386 to 1434). Early life and first marriages Elizabeth was the only child of , Voivode of Sandomierz, and , daughter of Jan of Melsztyn and godmother of King Władysław II Jagiełło. Elizabeth's uncle Spytek of Melsztyn was an influential figure in Jagiełło's court. When her father died in 1384 or 1385, Elizabeth inherited his vast estates, which included Pilica and Łańcut. Her dramatic early life was described by Jan Długosz, but authenticity of that account was doubtful as it is not corroborated by other sources and Długosz did not provide dates. However Elizabeth's mother wrote in 1390 a document in which she mentions Jenczik's death and thanks God for her daughter's safe return, proving that story about kidnappings and forced marriages was ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodox Christian
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism. Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "Canon law of the Eastern Orthodox Church, canonical") Eastern Orthodox Church is Organization of the Eastern Orthodox Church, organised into autocephalous churches independent from each other. In the 21st century, the Organization of the Eastern Orthodox Church#Autocephalous Eastern Orthodox churches, number of mainstream autocephalous churches is seventeen; there also exist Organization of the Eastern Orthodox Church#Unrecognised churches, autocephalous churches unrecognized by those mainstream ones. Autocephalous churches choose their own Primate (bishop), primate. Autocephalous churches can have Ecclesiastical jurisdiction, jurisdiction (authority) over other churches, som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Druck
Drutsk (, ; , , also known as ''Дрютескъ'' (''Dryutesk'') or ''Дрюческъ'' (''Druchesk'') in the Middle Ages), is a historical town in Belarus, 40 kilometres (ca. 25 miles) west of Mogilev. The town was established in 1078 as an outpost of the Principality of Polotsk on the road from Polotsk to Kiev and Chernigov. According to the Drutsk Gospel, the town was built around one of the oldest Christian churches in White Ruthenia erected in 1001. In the 12th century and 13th century it was a centre of the early medieval Principality of Drutsk, ruled by the dukes of the Polotsk branch of the Rurikid dynasty. Since the 13th century there is only limited information about the town available in the chronicles. In 1524 Drutsk has been burned down by Russians in a war and started to lose its political importance. Exact time and reasons of the town's decline are unknown. Historians estimate the period of decline to between the 15th and 17th centuries. Archaeological research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
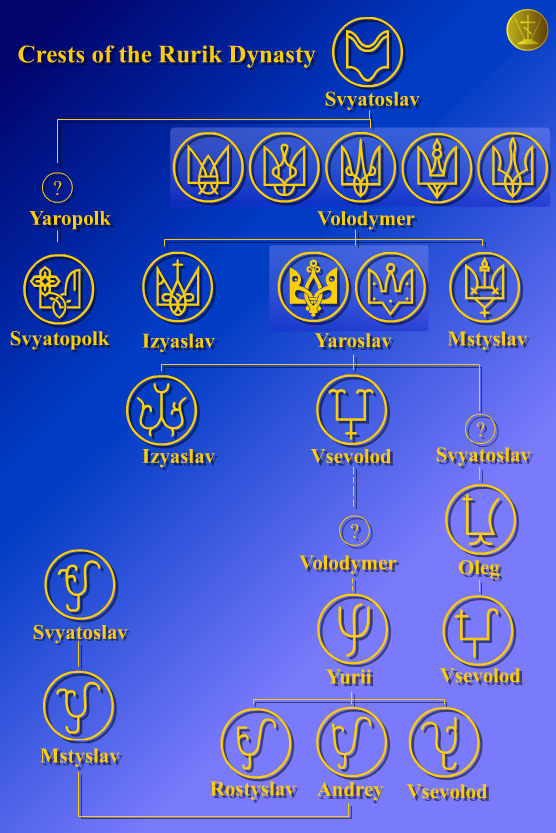
Rurikid
The Rurik dynasty, also known as the Rurikid or Riurikid dynasty, as well as simply Rurikids or Riurikids, was a noble lineage allegedly founded by the Varangian prince Rurik, who, according to tradition, established himself at Novgorod in the year 862. The Rurikids were the ruling dynasty of Kievan Rus' and its principalities following its disintegration. The ''Romanovichi'' ruled the southwestern territories, which were unified by Roman the Great and his son Daniel, who was in 1253 crowned by Pope Innocent IV as the king of Ruthenia. Galicia–Volhynia was eventually annexed by Poland and Lithuania. The northern and northeastern territories were unified by the ''Daniilovichi'' of Moscow; by the 15th century, Ivan III threw off the control of the Golden Horde and assumed the title of sovereign of all Russia. Ivan IV was crowned as the tsar of all Russia, where the Rurik line ruled until 1598, following which they were eventually succeeded by the House of Romanov. As a rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmitry I Starshiy
Dmitry the Older or Dmitry of Bryansk (, , died on 12 August 1399 in the Battle of the Vorskla River) was the Lithuanian Duke of Bryansk from 1356 to 1379 and from 1388 to 1399. Dmitry was the second eldest son of Algirdas, the Grand Duke of Lithuania, and his first wife Maria of Vitebsk. In 1356, Algirdas took the region of Bryansk, which included Trubetsk and Starodub, from the Principality of Smolensk and granted to his son Dmitrijus to govern it. The territory was in far northeast from the heartlands of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and bordered the Grand Duchy of Moscow. In 1370, Dmitri Donskoi, the Grand Duke of Moscow, unsuccessfully attempted to conquer the territory. In 1372, Dmitry witnessed the Treaty of Lyubutsk between Algirdas and Dmitri Donskoi. After his father's death in 1377, Dmitry supported his elder brother Andrei of Polotsk against their younger half-brother Jogaila, who became the Grand Duke of Lithuania. Andrei, believing that he is the rightful heir to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Olshansky
Ivan Olshanski or Olshansky (died in or after 1402) was a member of the Lithuanian princely Alšėniškiai (Holshansky) family. Historians only know his father's name, Algimantas. Ivan was a faithful companion of Vytautas the Great, Grand Duke of Lithuania. They both were married to daughters of Sudimantas of Eišiškės. Ivan's daughter Juliana became the third wife of Vytautas in 1418. His granddaughter Sophia became the fourth wife of King Władysław Jagiełło in 1424. His patrimony consisted of Halshany, Iwye, Hlusk, Porechye and others. Biography Ivan first appears as one of Jogaila's boyars during the truce between Lithuanian princes and the Prussian branch of the Teutonic Order in 1379. Then he was present during the signing of a treaty of Dovydiškės in 1380. When Vytautas escaped to the Teutonic Knights in 1382, Ivan followed him and Jogaila confiscated his Principality of Alšėnai. However, as Vytautas and Jogaila reconciled few years later, Ivan gifted Jogai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vytautas
Vytautas the Great (; 27 October 1430) was a ruler of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. He was also the prince of Grodno (1370–1382), prince of Lutsk (1387–1389), and the postulated king of the Hussites. In modern Lithuania, Vytautas is revered as a Folk hero, national hero and was an important figure in the Lithuanian National Revival, national rebirth in the 19th century. ''Vytautas'' is a popular male given Lithuanian name, name in Lithuania. In commemoration of the 500-year anniversary of his death, Vytautas Magnus University was named after him. Monuments in his honour were built in many towns in independent Lithuania during the History of Lithuania#Independent interwar Lithuania (1918–1940), interwar period from 1918 to 1939. Vytautas knew and spoke the Lithuanian language with his cousin Władysław II Jagiełło, Jogaila. Struggle for power 1377–1384 Vytautas' uncle Algirdas had been Grand Duke of Lithuania until his death in 1377. Algirdas and Vytautas' father K� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uliana Olshanska
Princess Uliana Olshanska ( or , ; d. 1448) was a noblewoman from the Alšėniškiai family and the Grand Duchess of Lithuania as the second wife of Vytautas, Grand Duke of Lithuania. They had no issue. Very little is known about Uliana's life. Her first husband was Ivan of Karachev. German chronicle of Johann von Posilge and Polish historian Jan Długosz asserted that Ivan was murdered so that widowed Uliana could marry Vytautas. Most likely she was an Eastern Orthodox who converted to Catholicism in order to marry Vytautas. After the death of his first wife Anna on 31 July 1418, Vytautas wished to marry Uliana, daughter of one of his closest allies Ivan Olshansky. However, Anna was sister of Agripina, who was wife of Ivan and mother of Uliana. That made Vytautas uncle-in-law of Uliana. Piotr Krakowczyk, Bishop of Vilnius, refused to perform the wedding ceremony due to this relationship and demanded they seek approval from the pope. Jan Kropidło, Bishop of Włocławek, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a collegiate university, collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, second-oldest continuously operating university globally. It expanded rapidly from 1167, when Henry II of England, Henry II prohibited English students from attending the University of Paris. When disputes erupted between students and the Oxford townspeople, some Oxford academics fled northeast to Cambridge, where they established the University of Cambridge in 1209. The two English Ancient university, ancient universities share many common features and are jointly referred to as ''Oxbridge''. The University of Oxford comprises 43 constituent colleges, consisting of 36 Colleges of the University of Oxford, semi-autonomous colleges, four permanent private halls and three societies (colleges that are depar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |