|
Zenith Space Commander 600
The zenith (, ) is the imaginary point on the celestial sphere directly "above" a particular location. "Above" means in the vertical direction (plumb line) opposite to the gravity direction at that location (nadir). The zenith is the "highest" point on the celestial sphere. The direction opposite of the zenith is the nadir. Origin The word ''zenith'' derives from an inaccurate reading of the Arabic expression (), meaning "direction of the head" or "path above the head", by Medieval Latin scribes in the Middle Ages (during the 14th century), possibly through Old Spanish. It was reduced to ''samt'' ("direction") and miswritten as ''senit''/''cenit'', the ''m'' being misread as ''ni''. Through the Old French ''cenith'', ''zenith'' first appeared in the 17th century. Relevance and use The term ''zenith'' sometimes means the highest point, way, or level reached by a celestial body">culmination">highest point, way, or level reached by a celestial body on its daily apparent path a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude Angle
The horizontal coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system that uses the observer's local horizon as the fundamental plane to define two angles of a spherical coordinate system: altitude and ''azimuth''. Therefore, the horizontal coordinate system is sometimes called the az/el system, the alt/az system, or the alt-azimuth system, among others. In an altazimuth mount of a telescope, the instrument's two axes follow altitude and azimuth. Definition This celestial coordinate system divides the sky into two hemispheres: The upper hemisphere, where objects are above the horizon and are visible, and the lower hemisphere, where objects are below the horizon and cannot be seen, since the Earth obstructs views of them. The great circle separating the hemispheres is called the ''celestial horizon'', which is defined as the great circle on the celestial sphere whose plane is normal to the local gravity vector (the vertical direction). In practice, the horizon can be defined as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
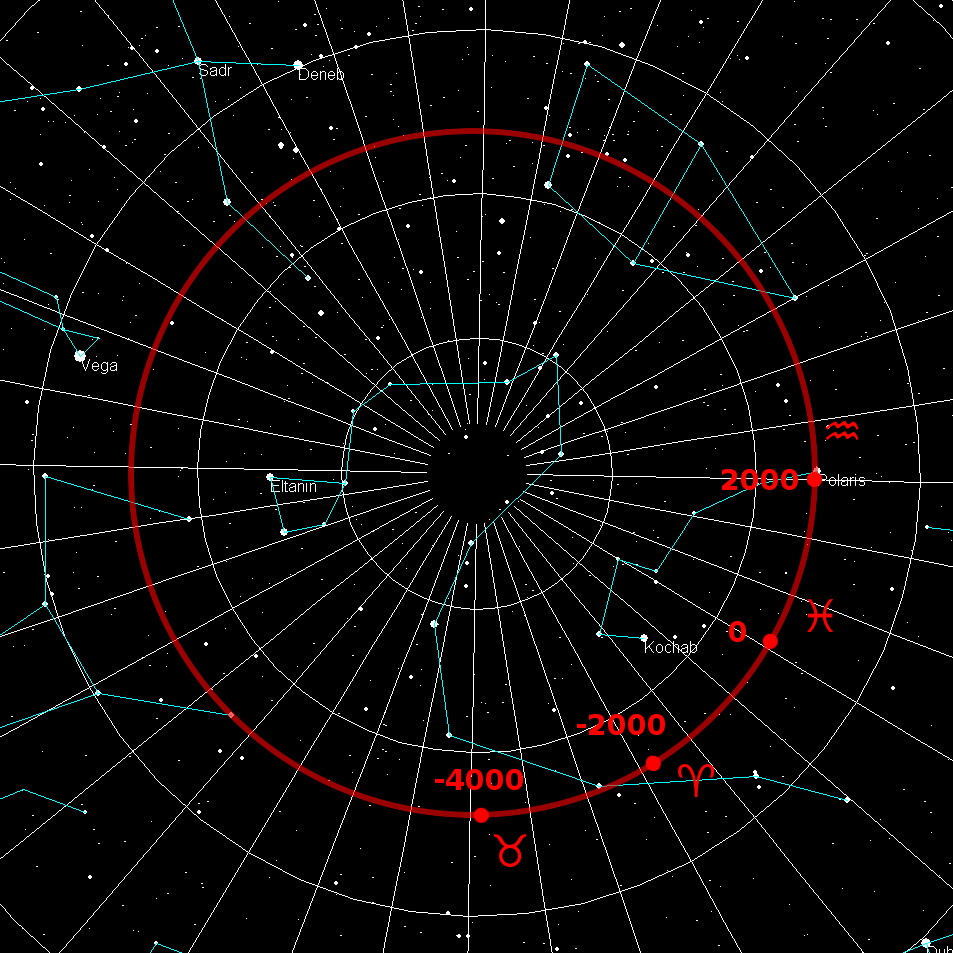
Celestial Pole
The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where Earth's axis of rotation, indefinitely extended, intersects the celestial sphere. The north and south celestial poles appear permanently directly overhead to observers at Earth's North Pole and South Pole, respectively. As Earth spins on its axis, the two celestial poles remain fixed in the sky, and all other celestial points appear to rotate around them, completing one circuit per day (strictly, per sidereal day). The celestial poles are also the poles of the celestial equatorial coordinate system, meaning they have declinations of +90 degrees and −90 degrees (for the north and south celestial poles, respectively). Despite their apparently fixed positions, the celestial poles in the long term do not actually remain permanently fixed against the background of the stars. Because of a phenomenon known as the precession of the equinoxes, the poles trace out circles on the celestial sphere, with a period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meridian (astronomy)
In astronomy, the meridian is the great circle passing through the celestial poles, as well as the zenith and nadir of an observer's location. Consequently, it contains also the north and south points on the horizon, and it is perpendicular to the celestial equator and horizon. Meridians, celestial and geographical, are determined by the pencil of planes passing through the Earth's rotation axis. For a location ''not'' on this axis, there is a unique meridian plane in this axial-pencil through that location. The intersection of this plane with Earth's surface defines two '' geographical meridians'' (either one east and one west of the prime meridian, or else the prime meridian itself and its anti-meridian), and the intersection of the plane with the celestial sphere is the celestial meridian for that location and time. There are several ways to divide the meridian into semicircles. In one approach, the observer's upper meridian extends from a celestial pole and passes t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complementary Angles
In Euclidean geometry, an angle can refer to a number of concepts relating to the intersection of two straight Line (geometry), lines at a Point (geometry), point. Formally, an angle is a figure lying in a Euclidean plane, plane formed by two Ray (geometry), rays, called the ''Side (plane geometry), sides'' of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the ''vertex (geometry), vertex'' of the angle. More generally angles are also formed wherever two lines, rays or line segments come together, such as at the corners of triangles and other polygons. An angle can be considered as the region of the plane bounded by the sides. Angles can also be formed by the intersection of two planes or by two intersecting curves, in which case the rays lying tangent to each curve at the point of intersection define the angle. The term ''angle'' is also used for the size, magnitude (mathematics), magnitude or Physical quantity, quantity of these types of geometric figures and in this context an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Noon
Noon (also known as noontime or midday) is 12 o'clock in the daytime. It is written as 12 noon, 12:00 m. (for '' meridiem'', literally 12:00 midday), 12 p.m. (for ''post meridiem'', literally "after midday"), 12 pm, or 12:00 (using a 24-hour clock) or 1200 ( military time). Solar noon is the time when the Sun appears to contact the local celestial meridian. This is when the Sun reaches its apparent highest point in the sky, at 12 noon apparent solar time and can be observed using a sundial. The local or clock time of solar noon depends on the date, longitude, and time zone, with Daylight Saving Time tending to place solar noon closer to 1:00pm. Etymology The word ''noon'' is derived from Latin ''nona hora'', the ninth canonical hour of the day, in reference to the Western Christian liturgical term Nones (liturgy), (number nine), one of the seven fixed prayer times in traditional Christian denominations. The Roman and Western European medieval monastic day began at 6:00& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antipodal Point
In mathematics, two points of a sphere (or n-sphere, including a circle) are called antipodal or diametrically opposite if they are the endpoints of a diameter, a straight line segment between two points on a sphere and passing through its center. Given any point on a sphere, its antipodal point is the unique point at greatest distance, whether measured intrinsically (great-circle distance on the surface of the sphere) or extrinsically ( chordal distance through the sphere's interior). Every great circle on a sphere passing through a point also passes through its antipodal point, and there are infinitely many great circles passing through a pair of antipodal points (unlike the situation for any non-antipodal pair of points, which have a unique great circle passing through both). Many results in spherical geometry depend on choosing non-antipodal points, and degenerate if antipodal points are allowed; for example, a spherical triangle degenerates to an underspecified lune if t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
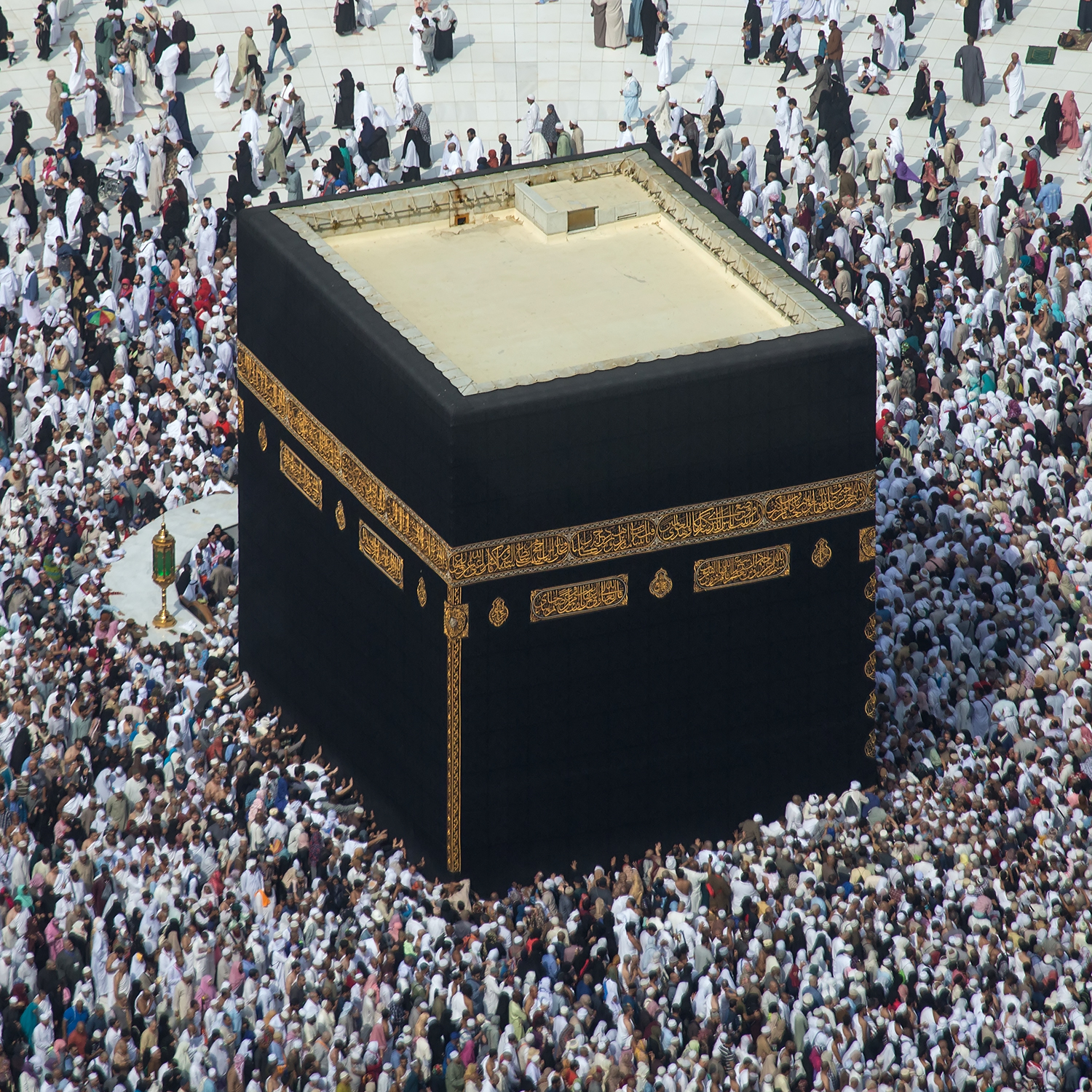
Qibla Observation By Shadows
Twice every year, the Sun culminates at the zenith of the ''Kaaba'' in Mecca, the holiest site in Islam, at local solar noon, allowing the qibla (the direction towards the ''Kaaba'') to be ascertained in other parts of the world by observing the shadows cast by vertical objects. This phenomenon occurs at 12:18 Saudi Arabia Standard Time (SAST; 09:18 UTC) on 27 or 28 May (depending on the year), and at 12:27 SAST (09:27 UTC) on 15 or 16 July (depending on the year). At these times, the Sun appears in the direction of Mecca, and shadows cast by vertical objects determine the qibla. At two other moments in the year, the Sun passes through the nadir (the antipodal zenith) of the ''Kaaba'', casting shadows that point in the opposite direction, and thus also determine the qibla. These occur on 12, 13, or 14 January at 00:30 SAST (21:30 UTC on the preceding day), and 28 or 29 November at 00:09 SAST (21:09 UTC on the preceding day). The shadow points towards Mecca because the Sun path ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above sea level. Its metropolitan population in 2022 was 2.4million, making it the List of cities in Saudi Arabia by population, third-most populated city in Saudi Arabia after Riyadh and Jeddah. Around 44.5% of the population are Saudis, Saudi citizens and around 55.5% are Muslim world, Muslim foreigners from other countries. Pilgrims more than triple the population number every year during the Pilgrimage#Islam, pilgrimage, observed in the twelfth Islamic calendar, Hijri month of . With over 10.8 million international visitors in 2023, Mecca was one of the ten List of cities by international visitors, most visited cities in the world. Mecca is generally considered "the fountainhead and cradle of Islam". Mecca is revered in Islam as the birthp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Astronomy
Medieval Islamic astronomy comprises the astronomical developments made in the Islamic world, particularly during the Islamic Golden Age (9th–13th centuries), and mostly written in the Arabic language. These developments mostly took place in the Middle East, Central Asia, Al-Andalus, and North Africa, and later in the Far East and India. It closely parallels the genesis of other Islamic sciences in its assimilation of foreign material and the amalgamation of the disparate elements of that material to create a science with Islamic characteristics. These included Greek, Sassanid, and Indian works in particular, which were translated and built upon. Islamic astronomy played a significant role in the revival of ancient astronomy following the loss of knowledge during the early medieval period, notably with the production of Latin translations of Arabic works during the 12th century. A significant number of stars in the sky, such as Aldebaran, Altair and Deneb, and astrono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subsolar Point
The subsolar point on a planet or a moon is the point at which its Sun is perceived to be directly overhead (at the zenith); that is, where the Sun's rays strike the planet exactly perpendicular to its surface. The subsolar point occurs at the location on a planet or a moon where the Sun culminates at the location's zenith. This occurs at solar noon. At this point, the Sun's rays will fall exactly vertical relative to an object on the ground and thus cast no observable shadow. To an observer on a planet with an orientation and rotation similar to those of Earth, the subsolar point will appear to move westward with a speed of 1600 km/h, completing one circuit around the globe each day, approximately moving along the equator. However, it will also move north and south between the tropics over the course of a year, so will appear to spiral like a helix. The term subsolar point can also mean the point closest to the Sun on an astronomical object, even though the Sun might no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |