|
Yupik Peoples
The Yupik (; ) are a group of Indigenous or Aboriginal peoples of western, southwestern, and southcentral Alaska and the Russian Far East. They are related to the Inuit and Iñupiat. Yupik peoples include the following: * Alutiiq, or Sugpiaq, of the Alaska Peninsula and coastal and island areas of southcentral Alaska. * Yupʼik or Central Alaskan Yupʼik of the Yukon–Kuskokwim Delta, the Kuskokwim River, and along the northern coast of Bristol Bay as far east as Nushagak Bay and the northern Alaska Peninsula at Naknek River and Egegik Bay in Alaska. * Siberian Yupik, including Naukan, Chaplino,Achirgina-Arsiak, Tatiana"Northeastern Siberian: Yupik (Asiatic Eskimo)."''Alaska Native Collections.'' 1996. Retrieved 20 July 2012. and—in a linguistic capacity—the Sirenik of the Russian Far East and St. Lawrence Island in western Alaska. Population The Yupʼik people are by far the most numerous of the various Alaska Native groups. They speak the Central Alaskan Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alutiiq
The Alutiiq (pronounced in English; from Promyshlenniki Russian Алеутъ, "Aleut"; plural often "Alutiit"), also called by their ancestral name ( or ; plural often "Sugpiat"), as well as Pacific Eskimo or Pacific Yupik, are a Yupik peoples, one of eight groups of Alaska Natives that inhabit the southern-central coast of the region. Their traditional homelands date back to over 7,500 years ago, and include areas such as Prince William Sound and outer Kenai Peninsula (), the Kodiak Archipelago and the Alaska Peninsula (). In the early 1800s there were more than 60 Alutiiq villages in the Kodiak archipelago, with an estimated population of 13,000 people. Today more than 4,000 Alutiiq live in Alaska. Terminology At present, the most commonly used title is (singular), (dual), (plural). These terms derive from the names (, ) that the '' promyshlenniki'' ( indigenous Siberian and Russian fur traders and settlers) gave to the native people in the region. Russian o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward S
Edward is an English language, English male name. It is derived from the Old English, Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements ''wikt:ead#Old English, ēad'' "wealth, fortunate; prosperous" and ''wikt:weard#Old English, weard'' "guardian, protector”. History The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Saxon England, but the rule of the House of Normandy, Norman and House of Plantagenet, Plantagenet dynasties had effectively ended its use amongst the upper classes. The popularity of the name was revived when Henry III of England, Henry III named his firstborn son, the future Edward I of England, Edward I, as part of his efforts to promote a cult around Edward the Confessor, for whom Henry had a deep admiration. Variant forms The name has been adopted in the Iberian Peninsula#Modern Iberia, Iberian peninsula since the 15th century, due to Edward, King of Portugal, whose mother was English. The Spanish/Portuguese forms of the name are Eduardo and Duarte (name), Duart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
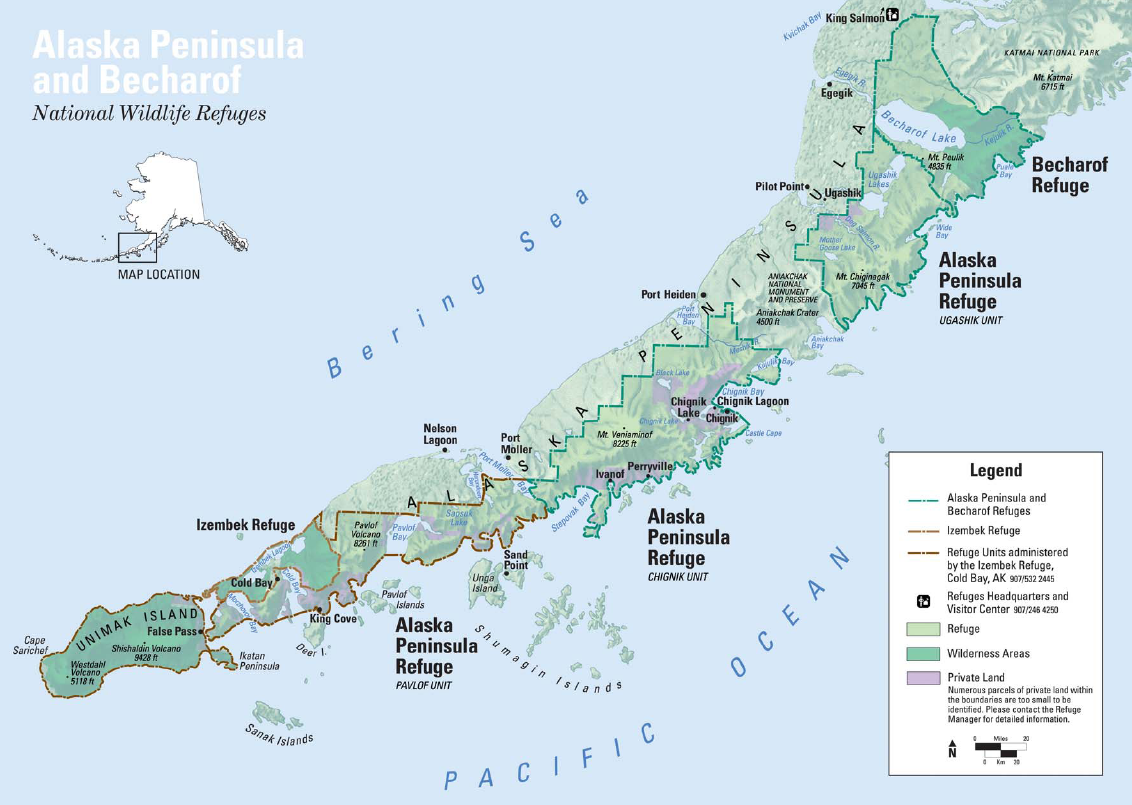
Egegik Bay
Egegik Bay (Yup'ik: ''Igyagiim painga'') is a bay located just 69.1 miles from Dillingham in Alaska and the northeastern arm of the Bristol Bay. The Egegik (''Igyagiiq'' in Yup'ik) village is located on a high bluff along the southern shore of the Egegik River at the upper extent of Egegik Bay. The nearest places to Egegik Bay are Coffee Point (3 km north), Coffee Point (4 km north), Goose Point (4 km north), Egegik Airport (5 km west), and Bartletts Airport (6 km north). History The first recorded contact by non-Natives was with Russian fur traders between 1818 and 1867. The Egegik Yupik is one of the five Central Alaskan Yup'ik dialects. Local people are Central Alaskan Yup'ik people and would travel each year from Kanatak (an Alutiiq village) on the Gulf coast through a portage pass to Becharof Lake (south-east of Egegik). From there they would hike or kayak on to the Egegik Bay are for the summer fish camp. Nature Although tideland areas adj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naknek River
Naknek River is a stream, long, in the Bristol Bay Borough of the U.S. state of Alaska. It flows west from Naknek Lake to empty into Kvichak Bay, an arm of Bristol Bay. The river and lake are both known for their sockeye and other salmon. The village of King Salmon is near the head of the river; Naknek and South Naknek lie at its mouth, on the north and south banks respectively. The head lies within Katmai National Park and Preserve Katmai National Park and Preserve is a List of national parks of the United States, United States national park and National preserve, preserve in southwest Alaska, notable for the Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes and for its Alaska Peninsula brown .... See also * List of rivers of Alaska References Rivers of Bristol Bay Borough, Alaska Rivers of Alaska {{Alaska-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nushagak Bay
Nushagak Bay is a large estuary covering over 100 km2 in southwest part of the U.S. state of Alaska. It opens to Bristol Bay, a large body of water in the eastern Bering Sea north of the Alaska Peninsula. It is home to the area's largest city, Dillingham, and the bay hosts one of the world's last great sustainable sockeye salmon fisheries. Bristol Bay residents have historically valued the estuary resources for both subsistence gains and commercial profits. However, given the estuary's importance, there have been few comprehensive scientific studies conducted in the bay. Species diversity as measured through richness and total biomass is generally low with 16 macro invertebrate species encountered in a 2007 field study, including teleost fishes, isopods, amphipods, and crangon shrimps. During the summer 2007, Nushagak Bay was found to have a Shannon Diversity (H’) value of 1.54, ranking it below similar subarctic estuaries such as Ungava Bay, near Labrador (60°34� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Bay
Bristol Bay (, ) is the easternmost arm of the Bering Sea, at 57° to 59° North 157° to 162° West in Southwest Alaska. Bristol Bay is 400 km (250 mi) long and 290 km (180 mi) wide at its mouth. A number of rivers flow into the bay, including the Cinder River, Cinder, Egegik River, Egegik, Igushik River, Igushik, Kvichak River, Kvichak, Meshik River, Meshik, Nushagak River, Nushagak, Naknek River, Naknek, Togiak River, Togiak, and Ugashik River, Ugashik. Upper reaches of Bristol Bay experience some of the highest tides in the world. One such reach, the Nushagak Bay near Dillingham, Alaska, Dillingham and another near Naknek, Alaska, Naknek in Kvichak Bay have tidal extremes in excess of 10 m (30 ft), ranking them — and the area — as eighth highest in the world. Coupled with the extreme number of shoals, sandbars, and shallows, it makes navigation troublesome, especially during the area's frequently strong winds. As the shallowest pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuskokwim River
The Kuskokwim River or Kusko River ( Yupʼik: ''Kusquqvak''; Deg Xinag: ''Digenegh''; Upper Kuskokwim: ''Dichinanekʼ''; (''Kuskokvim'')) is a river, long, in Southwest Alaska in the United States. It is the ninth largest river in the United States by average discharge volume at its mouth and seventeenth largest by basin drainage area. The Kuskokwim River is the longest river system contained entirely within a single U.S. state. The river provides the principal drainage for an area of the remote Alaska Interior on the north and west side of the Alaska Range, flowing southwest into Kuskokwim Bay on the Bering Sea. The highest point in its watershed is Mount Russell. Except for its headwaters in the mountains, the river is broad and flat for its entire course, making it a useful transportation route for many types of watercraft, as well as road vehicles during the winter when it is frozen over. It is the longest free flowing river in the United States. ''Kuskokwim'' der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yukon–Kuskokwim Delta
The Yukon–Kuskokwim Delta is a river delta located where the Yukon and Kuskokwim rivers empty into the Bering Sea on the west coast of the U.S. state of Alaska. At approximately in size, it is one of the largest deltas in the world. It is larger than the Mississippi River Delta (which varies between 32,400 and 122,000 square kilometers or 12,500 and 47,100 sq mi); it is comparable in size to the entire U.S. state of Louisiana (135,700 square kilometers or 52,400 sq mi). The delta, which consists mainly of tundra, is protected as part of the Yukon Delta National Wildlife Refuge. The delta has approximately 25,000 residents. 85% of these are Alaska Natives: Yupik and Athabaskan people. The main population center and service hub is the city of Bethel, with an estimated population of around 6,219 (as of 2011). Bethel is surrounded by 49 smaller villages, with the largest villages consisting of over 1000 people. Most residents live a traditional subsistence lifestyle of hunting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yupʼik
The Yupʼik or Yupiaq (sg & pl) and Yupiit or Yupiat (pl), also Central Alaskan Yupʼik, Central Yupʼik, Alaskan Yupʼik (Central Alaskan Yupʼik language, own name ''Yupʼik'' sg ''Yupiik'' dual ''Yupiit'' pl; Russian language, Russian: Юпики центральной Аляски), are an Indigenous people of western and southwestern Alaska ranging from southern Norton Sound southwards along the coast of the Bering Sea on the Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta (including living on Nelson Island (Alaska), Nelson and Nunivak Island, Nunivak Islands) and along the northern coast of Bristol Bay as far east as Nushagak Bay and the northern Alaska Peninsula at Naknek River and Egegik Bay. They are also known as Cupʼik by the Chevak Cupʼik language, Chevak Cupʼik dialect-speaking people of Chevak, Alaska, Chevak and Cupʼig for the Nunivak Cupʼig language, Nunivak Cupʼig dialect-speaking people of Nunivak Island. The Yupiit are the most numerous of the various Alaska Natives, Alaska Nativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Peninsula
The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ; Sugpiaq language, Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a peninsula extending about to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska and ending in the Aleutian Islands. The peninsula separates the Pacific Ocean from Bristol Bay, an arm of the Bering Sea. In literature (especially Russian), the term ''Alaska Peninsula'' was used to denote the entire northwestern protrusion of the North American continent, or all of what is now the state of Alaska, exclusive of Alaska Panhandle, its panhandle and list of islands of Alaska, islands. The Lake and Peninsula Borough, Alaska, Lake and Peninsula list of boroughs and census areas in Alaska, borough, the Alaskan equivalent of a county (United States), county, is named after the peninsula. The Alaska/Aleutian Peninsula is also grouped into Southwest Alaska. The other largest peninsulas in Alaska include the Kenai Peninsula and Seward Peninsula. Geography The ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Far East
The Russian Far East ( rus, Дальний Восток России, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asia, Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Eastern Federal District, which encompasses the area between Lake Baikal and the Pacific Ocean. The area's largest city is Khabarovsk, followed by Vladivostok. The region shares land borders with the countries of Mongolia, China, and North Korea to its south, as well as maritime boundary, maritime boundaries with Japan to its southeast, and with the United States along the Bering Strait to its northeast. Although the Russian Far East is often considered as a part of Siberia abroad, it has been historically categorized separately from Siberia in Russian regional schemes (and previously during the history of the Soviet Union, Soviet era when it was called the Soviet Far East). Terminology In Russia, the region is usually referred to as simply th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Natives
Alaska Natives (also known as Native Alaskans, Alaskan Indians, or Indigenous Alaskans) are the Indigenous peoples of Alaska that encompass a diverse arena of cultural and linguistic groups, including the Iñupiat, Yupik, Aleut, Eyak, Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and various Northern Athabaskan, as well as Russian Creoles. These groups are often categorized by their distinct language families. Many Alaska Natives are enrolled in federally recognized Alaska Native tribal entities, which are members of 13 Alaska Native Regional Corporations responsible for managing land and financial claims. The migration of Alaska Natives' ancestors into the Alaskan region occurred thousands of years ago, likely in more than one wave. Some present-day groups descend from a later migration event that also led to settlement across northern North America, with these populations generally not migrating further south. Genetic evidence indicates that these groups are not closely related to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |