|
Yu Sŏngnyong
Yu Sŏngnyong (; 7 November 1542 – May 1607), also known as Ryu Sŏngnyong (), was a scholar-official of the Joseon period of Korea. He held many responsibilities, including the Chief State Councillor position in 1592. He was a member of the " Eastern faction" and a follower of Yi Hwang. Early life and education Yu was born in Hahoe Maeul, Andong, Gyeongsang Province (today a UNESCO World Heritage Site), to a ''yangban'' family of the . Yu is said to have been so precocious that he absorbed the teachings of Confucius and Mencius at the age of 8. In 1564 the 19th year of Myeongjong, he passed the '' Samasi'' examination, and in 1566 he passed the '' Mun-gwa'' at a special examination, and then took the post of ''Gwonji bujeongja'' (). 유성룡 Naver Encyclopedia He held various other positions and in 1569 he joined the imperial birthday mission to Ming as a ''Seojanggwan'' (서장관, 書狀官, the third of the mission), returning to Korea the following year. Career The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myeongjong Of Joseon
Myeongjong (; 13 July 1534 – 12 August 1567), personal name Yi Hwan (), was the 13th monarch of the Joseon dynasty of Korea. He was the second son of King Jungjong, born to Queen Munjeong. He ascended to the throne in 1545 at the age of 12 following the death of his elder half-brother, King Injong. Since he was too young to govern, his mother became regent. Biography Political factions There were two political factions at the time Myeongjong came to power; Greater Yun, headed by Yun Im, Injong's maternal uncle, and Lesser Yun, headed by Myeongjong's maternal uncles, Yun Won-hyeong and Yun Wonro. (Yun Im and Yun Brothers were close relatives by that period's standards - Yun Im was a third cousin once removed of Yun Brothers.) Greater Yun took power in 1544, when Injong succeeded Jungjong; but they failed to wipe out their opposition, since Queen Munjeong protected the Lesser Yun faction and other opposition officials. After the death of Injong in 1545, Lesser Yun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Training Agency
The Military Training Agency (), alternately translated as Military Training Command was founded in 1593, when the Imjin War of 1592–1598 was in progress. As the Joseon Army was struggling against the Japanese army's muskets, a new army was created as a countermeasure. It aimed to organize and train an elite force by instituting a system of providing salaries to all soldiers. It was the only military camp among the five major military camps that provided salaries to all its troops. However, due to the deterioration of the national finances, discussions about its abolition were often held. The Training Headquarters became the core military camp, along with the Geumwi Camp (금위영), the Eoyeongcheong Camp (어영청), and together they were called the Samgunmun (삼군문, 三軍門), the three main military camps of the central government, responsible for protecting the king and defending the capital. Background Originally, the military system in Joseon was the Yangin Gaebyeong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Pyongyang (1593)
The siege of Pyongyang was a military conflict fought between the allied Ming-Joseon army and the Japanese First Division under Konishi Yukinaga. The battle ended in victory for the allies but a successful retreat from Pyeongyang by the remaining Japanese in the night of 8 February 1593. Background A minor Ming force of 5,000 under Wu Weizhong arrived at the Yalu River on 5 January. The Ming army of 35,000 under Li Rusong arrived at the Yalu River on 26 January. They were then joined by the advance force and a bodyguard unit sent to protect Seonjo of Joseon, raising their strength to 43,000, another 10,000 Koreans at Sunan under Yi Il, and finally 4,200 monks under Hyujeong. Li Rusong sent ahead the envoy Shen Weijing to negotiate with Konishi Yukinaga, however this act was insincere. He had no intention of negotiating with the Japanese. Konishi sent 20 men to greet the Ming envoys, but most of them did not return. It's not certain what happened to them. One ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kwŏn Yul (general)
Kwŏn Yul (; 28 December 15376 July 1599) was a Korean army general and the commander-in-chief () of the Joseon period, who successfully led the Korean forces against Japan during the Japanese invasions of Korea. He is best known for the Battle of Haengju where he defeated an attacking force of about 30,000 Japanese with 2,800 troops. Early life Kwŏn Yul hailed from the prestigious Andong Kwŏn clan (); his father, Kwŏn Ch'ŏl (), was the yeonguijeong. However, Kwŏn did not begin his political or military career until he was 46. In 1582, he was first appointed to a position in the Korean government and promoted to several different positions including the mayor of Uiju () in 1591. During Japanese invasions of Korea When the Japanese forces invaded Korea in 1592, Kwŏn was appointed the mayor of Gwangju, Jeolla province and given the military command of the region. Kwŏn and his troops followed his commander Yi Kwang and headed towards Seoul to join the main force. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yi Sun-sin
Yi Sun-sin (; ; April 28, 1545 – December 16, 1598) was a Korean admiral and military general known for his victories against the Japanese navy during the Imjin War in the Joseon period. Yi's courtesy name was Yŏhae (여해), and he was posthumously honored with the title Lord of Loyal Valor (). The exact number of naval engagements conducted by Admiral Yi against the Japanese is a subject of historical debate. However, it is generally accepted that he fought in at least 23 naval battles, achieving victory in all. In many of these engagements, he commanded forces that were outnumbered and poorly supplied. His most dramatic success occurred in the Battle of Myeongnyang, where he led a Korean fleet of 13 ships to victory against a Japanese fleet of at least 133.Yi Sunsin, Nanjung ilgi, p. 314 Yi died from a gunshot wound in the Battle of Noryang, the last major battle of the Imjin War, on December 16, 1598. Yi is considered one of history's greatest naval commanders, know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uiju
Ŭiju is a kun, or county, in North Pyongan Province, North Korea. The county has an area of 420 km2, and a population of 110,018 (2008 data). Name Ŭiju appears as Uiju in South Korea's Revised Romanization and as Yizhou in Chinese sources, as during its occupation by general Mao Wenlong's forces during the Transition from Ming to Qing. Geography Ŭiju County borders Sakchu county and Kusŏng to the east, Sŏnch'ŏn and Ch'ŏlsan counties to the south, and Ryongch'ŏn county and Sinŭiju to the west, respectively. To the north, Ŭiju shares a border with China. Administrative divisions Ŭiju county is divided into 1 '' ŭp'' (town), 2 '' rodongjagu'' (workers' districts) and 17 '' ri'' (villages): Transportation Ŭiju county is served by the Tŏkhyŏn Line of the Korean State Railway. There is also an airport, Uiju Airfield (ICAO airport code: ZKUJ). 1980 earthquake Ŭiju earthquake was a 5.3 magnitude earthquake that occurred in Ŭiju County in 1980. It is am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
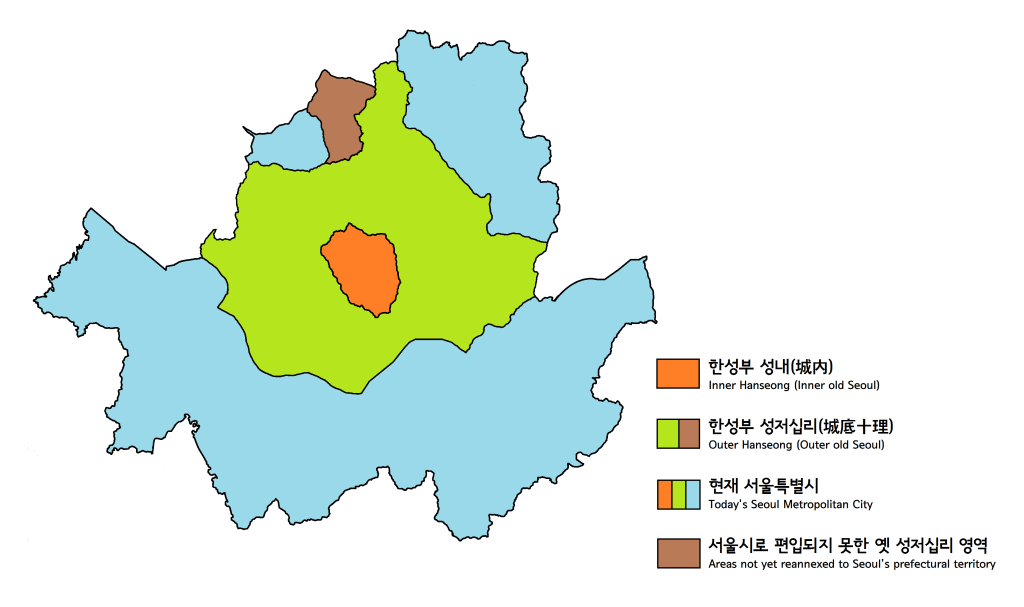
Hanseong
The region now corresponding to Seoul, South Korea has been inhabited since the Paleolithic Age. It has been the capital of a number of kingdoms since it was established. Prehistoric It is believed that humans were living in the area that is now Seoul along the lower reaches of the Han River during the Paleolithic Age and archaeological research shows that people began to lead settled lives starting in the Neolithic Age. Prehistoric remains that are unearthed in the , located in Gangdong District, date back to about 3,000 to 7,000 years ago. With the introduction of bronze ware from about 700 BC, settlements gradually began to spread from the river basin toward inland areas. Three Kingdoms and Unified Silla period In 18 BC, the kingdom of Baekje founded its capital city, Wiryeseong, which is believed to be inside modern-day Seoul. Baekje subsequently developed from a member state of the Mahan confederacy into one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. There are several city wal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imjin War
The Imjin War () was a series of two Japanese invasions of Korea: an initial invasion in 1592 also individually called the "Imjin War", a brief truce in 1596, and a second invasion in 1597 called the Chŏngyu War (). The conflict ended in 1598 with the withdrawal of Japanese forces from the Korean Peninsula after a military stalemate in Korea's southern provinces. The invasions were launched by Toyotomi Hideyoshi with the intent of conquering the Korean Peninsula and China proper, which were ruled by the Joseon and Ming dynasty, Ming dynasties, respectively. Azuchi–Momoyama period, Japan quickly succeeded in occupying large portions of the Korean Peninsula, but the contribution of reinforcements by the Ming, "(Korean) war minister Yi Hang-bok pointed out that assistance from China was the only way Korea could survive." as well as the disruption of Japanese supply fleets along the western and southern coasts by the Joseon Navy, "His naval victories were to prove decisive in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chŏng Ch'ŏl
Chŏng Ch'ŏl (; 18 December 1536 – 7 February 1594) was a Korean statesman and poet. He used the pen-names Gyeham () and Songgang (), and studied under Kim Yunjae at Hwanbyeokdang. He was expelled by the Easterners. He was from the Yeonil Jeong clan (). Family * Father ** Jeong Yu-chim (; 1493–1570) * Mother ** Lady Ahn of the Juksan Ahn clan (; 1495–1573) * Siblings ** Older brother - Jeong Ja (정자; 鄭滋; 1515–1547) ** Older brother - Jeong So (; 1518–1572) ** Older sister - Royal Consort Gwi-in of the Yeonil Jeong clan (; August 1520 – 25 March 1566) *** Brother-in-law - King Injong of Joseon (; 10 March 1515 – 7 August 1545) ** Older sister - Lady Jeong of the Yeonil Jeong clan (연일 정씨; 1521–1596) ** Older brother - Jeong Hwang (정황; 鄭滉; 1528–1588) ** Younger sister - Princess Consort Ohcheon of the Yeonil Jeong clan (; 1542–?) * Wives and their children ** Lady Ryu of the Munhwa Ryu clan (; 1535–1598) *** Daughter - Lady Jeong of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Six Ministries Of Joseon
The Six Ministries of Joseon () were the major executive bodies of the Korean Joseon Dynasty. They included ministries of Personnel (''Ijo''), Taxation (''Hojo''), Rites (''Yejo''), Military Affairs (''Byeongjo''), Punishments (''Hyeongjo''), and Public works (''Gongjo''). History It was established in 1298. The ministries system of Joseon was similar in outline to that of the preceding Goryeo dynasty, but in practice, it had a big difference. While Goryeo had a ministrative policy where the king had the central power, in Joseon, the scholars and bureaucrats had greater control. The ministries were much more powerful under Joseon, and their importance grew as the dynasty wore on. In December 1895, after the First Sino-Japanese War and as a part of the Gabo Reform, a cabinet of seven ministries was modeled after the Japanese one, which had been established only ten years earlier. Composition See also * Joseon Dynasty politics * History of Korea * Six Ministries of the Ng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Council Of Joseon
The State Council of Joseon or Uijeongbu was the highest organ of government under the Joseon Dynasty of Korea. It was led by three officials known as the High State Councillors. The Councilors were entrusted to deliberate over key problems of state, advising the king, and conveying royal decisions to the Six Ministries. The council was formed under the reign of Jeongjong, just before Taejong seized power in 1400. It replaced an earlier institution called the "Privy Council," which had been dominated by Chŏng Tojŏn and other key figures behind the dynasty's founding. The State Council gradually declined in importance over the 500 years of Joseon's rule. Finally, the council was replaced by the cabinet in 1907, forced by Japanese intervention Today, there's a city which was named after this organ (Uijeongbu) in Gyeonggi-do. Structure The State Council comprised: * the Chief State Councilor (영의정 領議政), rank 1a * the Left and Right State Councilors (좌ㆍ우� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |