|
Yu Fan
Yu Fan ( zh, t= , , ; 164–233), courtesy name Zhongxiang, was a Chinese essayist, politician, and writer of the state of Eastern Wu during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Initially a minor officer under Wang Lang, the Administrator of Kuaiji Commandery, Yu Fan later served under the warlord Sun Ce, who conquered the territories in the Jiangdong (or Wu) region in a series of campaigns from 194 to 199. Sun Ce regarded him highly and once enlisted his help in persuading Hua Xin, another commandery administrator, to surrender. After Sun Ce's death, Yu Fan continued serving under Sun Quan, Sun Ce's younger brother and successor, as a Cavalry Commandant. Sun Quan confined him for some time due to his rude and disrespectful behaviour, but released him in 219 and allowed him to accompany the general Lü Meng to attack Jing Province. During the Jing Province campaign, Yu Fan warned Lü Meng about a possible ambush when Lü Meng was celebrating a minor victory, and was prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rafe De Crespigny
Richard Rafe Champion de Crespigny (born 1936), also known by his Chinese name Zhang Leifu (), is an Australian sinologist and historian. He is an adjunct professor in the College of Asia and the Pacific at the Australian National University. He specialises in the history, geography, and literature of the Han dynasty, particularly the translation and historiography of material concerning the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period. Family The son of Richard Geoffrey Champion de Crespigny, (1907-1966), and Kathleen Cavenagh Champion de Crespigny (1908-2013), née Cudmore, Richard Rafe Champion de Crespigny was born in Adelaide in 1936. He married Christa Boltz in Turner, Australian Capital Territory on 19 May 1959. Education De Crespigny received his tertiary education at the University of Cambridge (B.A. Honours History 1957; M.A. History 1961) and the Australian National University (B.A. Honours Chinese 1962; M.A. Oriental Studies Honours 1964; PhD Far Eastern History 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu dominated China from AD 220 to 280 following the end of the Han dynasty. This period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and followed by the Jin dynasty (266–420), Western Jin dynasty. Academically, the periodisation begins with the establishment of Cao Wei in 220 and ends with the conquest of Wu by Jin in 280. The period immediately preceding the Three Kingdoms, from 184 to 220, was marked by chaotic infighting among warlords across China as Han authority collapsed. The period from 220 to 263 was marked by a comparatively stable arrangement between Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. This stability broke down with the conquest of Shu by Wei in 263, followed by the usurpation of Cao Wei by Jin in 266 and ultimately the conquest of Wu by Jin in 280. The Three Kingdoms period including the collapse of the Han was one of the most dangerous in Chinese history due to multiple plagues, widespread famines, and civil war. A n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gongsun Yuan
Gongsun Yuan () (died September 238Cao Rui's biography in ''Sanguozhi'' indicated that Sima Yi laid siege to Xiangping on the ''bingyin'' day of the 8th month of the 2nd year of the ''Jing'chu'' era. However, there is no ''bingyin'' day in that month; the next ''bingyin'' day is in the 9th month of that year and corresponds to 3 Sep 238 in the Julian calendar. Volume 74 of ''Zizhi Tongjian'' placed the fall of Xiangping on the ''renwu'' day of the 8th month of that year. However, there is also no ''renwu'' day in that month; the next ''renwu'' day is also in the 9th month and corresponds to 19 Sep 238 in the Julian calendar.), courtesy name Wenyi, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He rebelled against Wei in 237 and declared himself "King of Yan" (). In 238, the Cao Wei general Sima Yi led forces to Liaodong and successfully conquered Yan. Life Gongsun Yuan was a son of Gongsu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mi Fang
Mi Fang (died 223), courtesy name Zifang, was a Chinese military general and politician serving under the warlord Liu Bei in the late Eastern Han dynasty. He was also the younger brother of Mi Zhu, who also served Liu Bei. In 219, Mi Fang surrendered to Liu Bei's ally-turned rival Sun Quan, directly resulting in the loss of Jing Province (covering present-day Hubei and Hunan) and the death of Guan Yu. The Australian Sinologist Rafe de Crespigny notes that Mi Fang had the remarkable record of serving each of the leaders of the Three Kingdoms during his lifetime. Early life Mi Fang was from Qu County (), Donghai Commandery (), which is present-day Lianyungang, Jiangsu. He was born in an extremely rich merchant family, which had over 10,000 servants and guests. Mi Fang and his elder brother Mi Zhu were said to be proficient in horsemanship and archery. Along with the Chen clan (led by Chen Gui and Chen Deng), the Mi family served under Tao Qian, the Governor of Xu Province ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yu Jin
Yu Jin (died September 221), courtesy name Wenze, was a Chinese military general serving under the warlord Cao Cao in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He joined Cao Cao in 192 around the start of the civil wars leading to the collapse of the dynasty, and fought in many of the campaigns which established the warlord's position as a central figure in that period. In 219, Yu Jin was tasked with leading forces to relieve Cao Cao's general Cao Ren, who was being besieged in Fancheng by Liu Bei's general Guan Yu, but his armies were destroyed in a flood due to heavy rains. Yu Jin surrendered to Guan Yu and became a prisoner-of-war, but was transferred to the custody of another warlord, Sun Quan, after Sun Quan's forces captured Guan Yu's bases in late 219. Sun Quan treated Yu Jin like a guest and in 221 sent him back to the state of Cao Wei, which was founded in late 220 by Cao Cao's successor, Cao Pi, who ended the Eastern Han dynasty. Cao Pi pardoned Yu Jin and restored hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lü Meng's Invasion Of Jing Province
Lü Meng's invasion of Jing Province was fought between the warlords Sun Quan and Liu Bei in the winter of 219–220 in the late Eastern Han dynasty. Sun Quan's forces, led by Lü Meng, invaded Liu Bei's territories in southern Jing Province, which covered present-day Hubei and Hunan. The campaign occurred after the Battle of Fancheng and concluded with victory for Sun Quan's forces, who completely captured all of Liu Bei's territories. Guan Yu, Liu Bei's general guarding those territories, was captured and executed by Sun Quan's forces. The fall of Jing Province and Guan Yu's death provided the trigger for the Battle of Xiaoting between Liu Bei and Sun Quan between 221 and 222. Background Sun Quan "lending" Jing Province to Liu Bei In 210, Liu Bei travelled to Jing (京; present-day Zhenjiang, Jiangsu) to meet Sun Quan and make a request for the governorship of Jing Province. Lu Su advised Sun Quan to "lend" Nan Commandery (南郡; around present-day Jingzhou, Hubei), the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jing Province
Jingzhou or Jing Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China referenced in early Chinese texts such as the ''Yu Gong, Tribute of Yu'', ''Erya'', and ''Rites of Zhou''. Jingzhou became an administrative division during the reign of Emperor Wu of Han, Emperor Wu (r. 141–87 BCE) in the Western Han dynasty (206 BCE–9 CE). It usually corresponded with the modern-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan until the Sui dynasty, after which it referred to the city of Jingzhou. History Pre-Qin era In the Warring States period, the Chu (state), Chu state covered most of present-day Hubei and Hunan, the areas that would form Jingzhou in a later era. The Qin (state), Qin state dropped the name "Chu" (楚) (literally "chaste tree") and used its synonym "Jing" (荊) instead to avoid a naming taboo, since the personal name of Qin's King Zhuangxiang of Qin, King Zhuangxiang (281–247 BCE) was "Zichu" (子楚; lit. "son of Chu") because his adoptive mother, Lady Huayang, was fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lü Meng
Lü Meng () (178 – January or February 220), courtesy name Ziming, was a Chinese military general and politician who served under the warlord Sun Quan during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. Early in his career, he fought in several battles under the banner of Sun Ce, Sun Quan's elder brother and predecessor. Although he had been noted for his bravery, he was still deemed as nothing more than a "mere warrior" for his lack of literacy skills. Later, with encouragement from Sun Quan, Lü Meng took up scholarly pursuits to improve himself, gradually becoming a learned and competent military leader. In 217, he succeeded Lu Su as the frontline commander of Sun Quan's forces in Jing Province. Two years later, in a carefully calculated military operation, Lü Meng led an invasion of Liu Bei's territories in southern Jing Province, swiftly and stealthily capturing all the lands from Liu Bei's general Guan Yu, who was captured and executed after his defeat. Lü Meng enjoyed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hua Xin
Hua Xin (157 – 30 January 232), courtesy name Ziyu, was a Chinese politician who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty and Three Kingdoms period of China. He initially served directly under the central government of the Eastern Han dynasty. Later, he served under the warlord Sun Ce and then under the warlord Cao Cao. He continued to serve in the Cao Wei state during the Three Kingdoms period. Biography As a clerk in Gaotang County, Hua Xin was nominated as xiaolian, and appointed as Langzhong (郎中). In 187, Hua was appointed as Shangshu Lang (尚书郎). When Dong Zhuo evacuated the court from Luoyang to Chang'an, Hua requested a position as the administrator of Shanggui County (上邽) . He encountered Yuan Shu's army en route and was accepted to the latter's court. However, Hua left after his advice for Yuan to attack Dong Zhuo was dismissed. In 192, Hua was appointed as the administrator of Yuzhang (豫章) Commandery. After Liu Yao, governor of Yang Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Ce's Conquests In Jiangdong
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light and infrared radiation with 10% at ultraviolet energies. It is by far the most important source of energy for life on Earth. The Sun has been an object of veneration in many cultures. It has been a central subject for astronomical research since antiquity. The Sun orbits the Galactic Center at a distance of 24,000 to 28,000 light-years. Its distance from Earth defines the astronomical unit, which is about or about 8 light-minutes. Its diameter is about (), 109 times that of Earth. The Sun's mass is about 330,000 times that of Earth, making up about 99.86% of the total mass of the Solar System. The mass of outer layer of the Sun's atmosphere, its ''photosphere'', consists mostly of hydrogen (~73%) and helium (~25%), with much small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu (region)
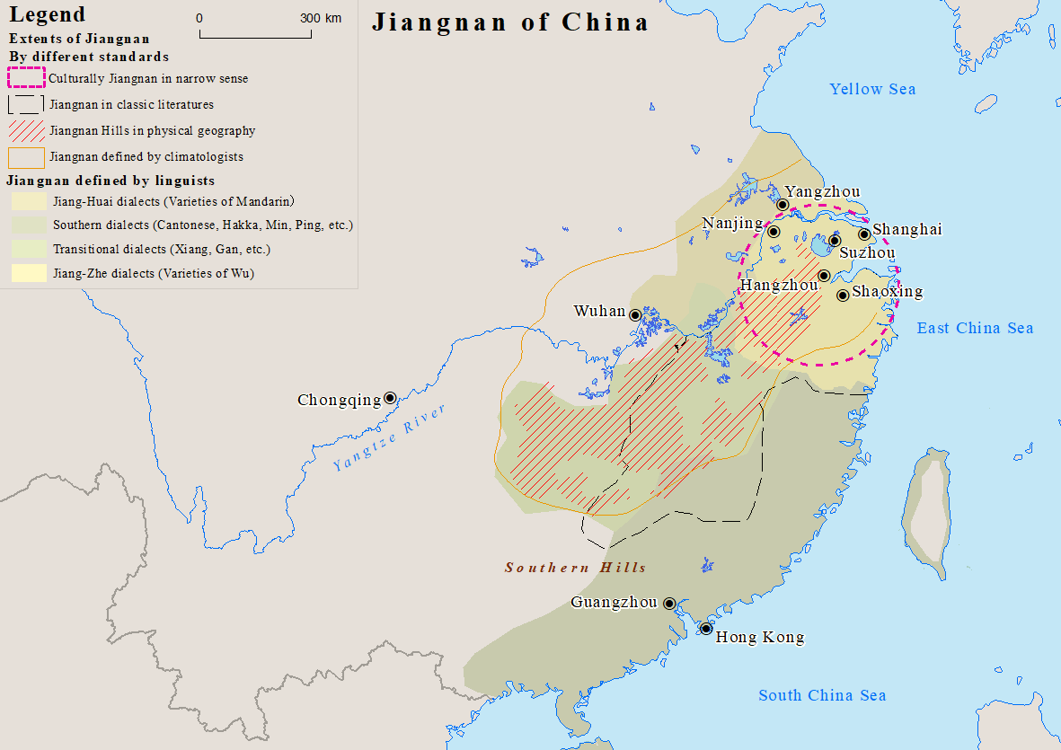
Jiangnan is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze, Yangtze River, including the southern part of its Yangtze Delta, delta. The region encompasses the city of Shanghai, the southern part of Jiangsu Province, the southeastern part of Anhui Province, the northern part of Jiangxi Province and Zhejiang Province. The most important cities in the area include Anqing, Changzhou, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Ningbo, Shaoxing, Suzhou, Wuxi, Wenzhou, Yangzhou and Zhenjiang. Jiangnan has long been regarded as one of the most prosperous regions in China due to its wealth in trade and very high list of administrative divisions of Greater China by Human Development Index, human development. Most people of the region speak Wu Chinese dialects as their native languages. Etymology The name Jiangnan is the pinyin romanization of Chinese, romanization of the Standard Mandarin pronunciation of , meaning "[Lands] South of the Yangtze Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiangnan
Jiangnan is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, including the southern part of its delta. The region encompasses the city of Shanghai, the southern part of Jiangsu Province, the southeastern part of Anhui Province, the northern part of Jiangxi Province and Zhejiang Province. The most important cities in the area include Anqing, Changzhou, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Ningbo, Shaoxing, Suzhou, Wuxi, Wenzhou, Yangzhou and Zhenjiang. Jiangnan has long been regarded as one of the most prosperous regions in China due to its wealth in trade and very high human development. Most people of the region speak Wu Chinese dialects as their native languages. Etymology The name Jiangnan is the pinyin romanization of the Standard Mandarin pronunciation of , meaning " andsSouth of the [Yangtze] River". Although ''jiang'' () is now the common Chinese word for any large river, it was historically used in Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |