|
Yosyp Bezpalko
Yosyp Ivanovych Bezpalko (; 1881 – 1950) was a Ukrainian politician and writer from Northern Bukovina. Biography He was born in Chernivtsi, Northern Bukovina to a poor middle-class family. Due to political activity, he was expelled from the gymnasium. In 1899, he founded a secret group of high school and student youth. From 1901 to 1902 he edited the Bukovina newspaper, a body of the Bukovinian national organization. In 1903, he began teaching. Founder of one of the first Sich societies (which promoted physical education and fire-fighting organization) in Bukovina and editor of the teacher's magazine Promin (1903). From 1907 to 1908 he was the regional secretary of the Bukovina trade unions. From 1907 to 1914 Bezpalko was the founder and chairman of the regional organization of the Ukrainian Social Democratic Party (USDP) in Bukovina, and from 1908 to 1914 he was the editor of a local party body, the Borba newspaper. He was the chairman of the educational commission in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mayors Of Chernivtsi
The following is a list of mayors of the city of Chernivtsi, Ukraine. It includes positions equivalent to mayor, such as chairperson of the city council executive committee. Austrian period Prehistory In the period from 1780 to 1832 the town was ruled by so-called municipal judges. Usually they led the city only between one and two years. A longer tenure had only Joseph Hampel (1796–1800 and 1802–1811), Alexander Beldowicz (1811–1817) and the last city judge, Andreas Klug (1817–1832). 1832: Regulation of local government, creating a magistrate Source: * Franz Lihotzky (1832–1848) * Adalbert Suchanek (1848–1854) * Josef Ortynski (1854–1858) * Josef Lepszy (1859–1861) * Julius Hubrich (1861–1864) 1864: Czernowitz becomes a town with its own statute * Jakob Ritter von Petrowicz (1864–1866) * Anton Kochanowski von Stawczan, Anton Freiherr Kochanowski von Stawczan (1866–1874) * Otto Ambros Edler von Rechtenberg (1874–1880) * Wilhelm von Klime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borys Martos
Borys Mykolayovych Martos (; 20 May 1879 – 19 September 1977) was a Ukrainian politician, pedagogue, and economist who briefly served as Chairman of People's Ministers of the Ukrainian People's Republic from April to August 1919. Biography Martos was born in Gradizhsk, in the Poltava Governorate of the Russian Empire, into a noble family of the Ossorya coat of arms. Martos graduated from Lubny Classic gymnasium in 1897 and enrolled into the Mathematics Department of the Imperial Kharkov University. There Martos became a member of a secret ''Ukrainian student hromada'' of Kharkov. Here in 1900 he met with Symon Petliura and his future wife M. Kucheryavenko. In the summer of 1900 Martos participated in the First Ukrainian Student Congress in Halychyna. He was arrested three times for collaboration with the Revolutionary Ukrainian Party. After graduating and until 1917 Martos worked in several different places: a co-ed in Volhynia, a financial director at the Black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1950 Deaths
Events January * January 1 – The International Police Association (IPA) – the largest police organization in the world – is formed. * January 5 – 1950 Sverdlovsk plane crash, Sverdlovsk plane crash: ''Aeroflot'' Lisunov Li-2 crashes in a snowstorm. All 19 aboard are killed, including almost the entire national ice hockey team (VVS Moscow) of the Soviet Air Force – 11 players, as well as a team doctor and a masseur. * January 6 – The UK recognizes the People's Republic of China; the Republic of China severs diplomatic relations with Britain in response. * January 7 – A fire in the St Elizabeth's Ward of Mercy Hospital in Davenport, Iowa, United States, kills 41 patients. * January 9 – The Israeli government recognizes the People's Republic of China. * January 12 – Submarine collides with Sweden, Swedish oil tanker ''Divina'' in the Thames Estuary and sinks; 64 die. * January 13 – Finland forms diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1881 Births
Events January * January 1– 24 – Siege of Geok Tepe: Russian troops under General Mikhail Skobelev defeat the Turkomans. * January 13 – War of the Pacific – Battle of San Juan and Chorrillos: The Chilean army defeats Peruvian forces. * January 15 – War of the Pacific – Battle of Miraflores: The Chileans take Lima, capital of Peru, after defeating its second line of defense in Miraflores. * January 24 – William Edward Forster, chief secretary for Ireland, introduces his Coercion Bill, which temporarily suspends habeas corpus so that those people suspected of committing an offence can be detained without trial; it goes through a long debate before it is accepted February 2. Note that Coercion bills had been passed almost annually in the 19th century, with a total of 105 such bills passed from 1801 to 1921. * January 25 – Thomas Edison and Alexander Graham Bell form the Oriental Telephone Company. February * Febru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Ukraine
The ''Encyclopedia of Ukraine'' (), published from 1984 to 2001, is a fundamental work of Ukrainian Studies. Development The work was created under the auspices of the Shevchenko Scientific Society in Europe (Sarcelles, near Paris). As the ''Encyclopedia of Ukrainian Studies'' it conditionally consists of two parts, the first being a general part that consists of a three volume reference work divided in to subjects or themes. The second part is a 10 volume encyclopedia with entries arranged alphabetically. The editor-in-chief of Volumes I and II (published in 1984 and 1988 respectively) was Volodymyr Kubijovyč. The concluding three volumes, with Danylo Husar Struk as editor-in-chief, appeared in 1993. The encyclopedia set came with a 30-page ''Map & Gazetteer of Ukraine'' compiled by Kubijovyč and Arkadii Zhukovsky. It contained a detailed fold-out map (scale 1:2,000,000). A final volume, ''Encyclopedia of Ukraine: Index and Errata'', containing only the index and a list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic
The Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic, also known as Soviet Kazakhstan, the Kazakh SSR, KSSR, or simply Kazakhstan, was one of the transcontinental country, transcontinental Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1936 to 1991. Located in northern Central Asia, it was created on 5 December 1936 from the Kazakh Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic, Kazakh ASSR, an Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics of the Soviet Union, autonomous republic of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. At in area, it was the second-largest republic in the USSR, after the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. Its capital was Almaty, Alma-Ata (today known as Almaty). During its existence as a Soviet Socialist Republic, it was ruled by the Communist Party of Kazakhstan (Soviet Union), Communist Party of the Kazakh SSR (QKP). On 25 October 1990, the Supreme Soviet of the Kazakh SSR declared its sovereignty on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulag
The Gulag was a system of Labor camp, forced labor camps in the Soviet Union. The word ''Gulag'' originally referred only to the division of the Chronology of Soviet secret police agencies, Soviet secret police that was in charge of running the forced labor camps from the 1930s to the early 1950s during Joseph Stalin's rule, but in English literature the term is popularly used for the system of forced labor throughout the Soviet era. The abbreviation GULAG (ГУЛАГ) stands for "Гла́вное управле́ние исправи́тельно-трудовы́х лагере́й" (Main Directorate of Correctional Labour Camps), but the full official name of the agency #Etymology, changed several times. The Gulag is recognized as a major instrument of political repression in the Soviet Union. The camps housed both ordinary criminals and political prisoners, a large number of whom were convicted by simplified procedures, such as NKVD troikas or other instruments of extra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Sich Union
Ukrainian may refer or relate to: * Ukraine, a country in Eastern Europe * Ukrainians, an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine * Demographics of Ukraine * Ukrainian culture, composed of the material and spiritual values of the Ukrainian people * Ukrainian language, an East Slavic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken primarily in Ukraine * Ukrainian cuisine, the collection of the various cooking traditions of the people of Ukraine See also * Languages of Ukraine * Name of Ukraine * Religion in Ukraine * Ukrainians (other) * Ukraine (other) * Ukraina (other) * Ukrainia (other) Ukrainia may refer to: * The land of Ukraine * The land of the Ukrainians, an ethnic territory * Montreal ''Ukrainia'', a sports team in Canada * Toronto ''Ukrainia'', a sports team in Canada See also * * Ukraina (other) * Ukraine (d ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poděbrady
Poděbrady (; ) is a spa town in Nymburk District in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 15,000 inhabitants. It lies on the Elbe River. The historic town centre is well preserved and is protected as an Cultural monument (Czech Republic)#Monument zones, urban monument zone. Administrative division Poděbrady consists of nine municipal parts (in brackets population according to the 2021 census): *Poděbrady I (331) *Poděbrady II (4,254) *Poděbrady III (6,855) *Poděbrady IV (50) *Poděbrady V (768) *Kluk (639) *Polabec (442) *Přední Lhota (347) *Velké Zboží (850) Etymology An ancient community and a small fortress originated near the Ford (crossing), ford. It is most likely that the position of this community is reflected in the present name of the town: = 'below the ford'. Geography Poděbrady is located about southeast of Nymburk and east of Prague. It lies in the Central Elbe Table lowland within the Polabí region. The Elbe River flows th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a Warsaw metropolitan area, greater metropolitan area of 3.27 million residents, which makes Warsaw the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 6th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises List of districts and neighbourhoods of Warsaw, 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is classified as an Globalization and World Cities Research Network#Alpha 2, alpha global city, a major political, economic and cultural hub, and the country's seat of government. It is also the capital of the Masovian Voivodeship. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
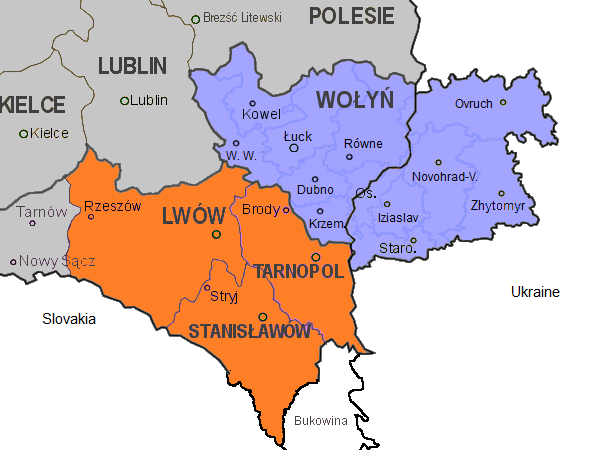
Volhynia
Volhynia or Volynia ( ; see #Names and etymology, below) is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between southeastern Poland, southwestern Belarus, and northwestern Ukraine. The borders of the region are not clearly defined, but in Ukraine it is roughly equivalent to Volyn Oblast, Volyn and Rivne Oblasts; the territory that still carries the name is Volyn Oblast. Volhynia has changed hands numerous times throughout history and been divided among competing powers. For centuries it was part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. After the Russian annexation during the Partitions of Poland, all of Volhynia was made part of the Pale of Settlement on the southwestern border of the Russian Empire. Important cities include Rivne, Lutsk, Zviahel, and Volodymyr (city), Volodymyr. Names and etymology *, ; * ; *, ; * or ; *; * ; *; *; * or (both ); Volhynian German: , , or (all ); *, or . The alternative name for the region is Lodomeria after the city of Volodymyr (city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Ohienko
Metropolitan Ilarion ( secular name Ivan Ivanovych Ohienko; ; 2 January (14 January), 1882 in Brusyliv, Kyiv Governorate – 29 March 1972 in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada) was a Ukrainian Orthodox cleric, linguist, church historian, and historian of Ukrainian culture. In 1940 he was Archimandrite of the St. Onuphrius Monastery in Jableczna; in 1940 he became Bishop of Chełm; in 1944 he became the Metropolitan of Chełm and Lublin ( Lubelskie), and in 1951 Primate of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Canada. He was also active in Ukrainian politics, both during the revolution and later in emigration. Early life Ivan Ohienko was born in central Ukraine ( Kyiv Gubernia). In 1900 he graduated from the Kyiv military field physician school where he studied along with Russian poet Demyan Bedny. Later Ohienko had been educated at Kyiv University where he studied Slavic philology (see Slavistics) under Vladimir Peretts. By 1915, he was teaching at this same university, and during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |